21 Apr 17 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan Statements, Campaigns -- Featured, Statements
We, representatives of international and national non-governmental organisations, issue this appeal prior to a discussion of the investigation into allegations of corruption at the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) in connection with its work on Azerbaijan, at the Assembly’s April 2017 session and a meeting of the Bureau of the Assembly before the session. We call upon you to support a full, thorough and independent investigation into the corruption allegations, with full civil society oversight.
We are extremely concerned about credible allegations presented in a December 2016 report by the European Stability Initiative (ESI), “The European Swamp: Prosecutions, corruption and the Council of Europe” building on previous findings by ESI and others published in 2012-16, detailing improper influencing of Assembly members by representatives of the Azerbaijani government. In particular, the reports include credible allegations that PACE members from various countries and political groups received payments and other gifts with a view to influencing the appointment of Assembly rapporteurs on Azerbaijan, as well as reports and resolutions of the Assembly on Azerbaijan, most notably the PACE vote on the draft resolution on political prisoners in Azerbaijan in January 2013.
The allegations regarding improper conduct of PACE members are serious, credible, and risk gravely undermining the credibility of the Assembly, as well as the Council of Europe as a whole. It is essential that these allegations are investigated thoroughly and impartially. Calls and recommendations for independent investigation into these allegations put forward by ESI have been echoed by many civil society actors, including Amnesty International, Transparency International, and a group of 60 members of Azerbaijani civil society actors and 20 international NGOs.
We welcome the decision of the PACE Bureau on 27 January 2017 to set up an independent investigation body to shed light on hidden practices that favour corruption. The Bureau has also committed to revising the Assembly’s Code of Conduct and invited GRECO (the Council of Europe’s Group of States against Corruption) to provide advice to the Rules Committee, charged with the investigation.
On 3 March, Wojciech Sawicki, PACE Secretary General, presented the Assembly Bureau with a draft terms of reference for the external and independent investigation at the Bureau meeting in Madrid. The proposal is credible, defining a wide mandate and competences and including strong guarantees for the independence of the investigation and safeguards against non-compliance with its work.
Unfortunately, the proposal was met with resistance at the meeting, and no agreement was made on its substance. The proposal was further discussed at a meeting of the heads of the PACE Parliamentary groups on 28 March in St Petersburg: again, no consensus was reached on its content, and whether it should be adopted.
A thorough investigation is essential to restore PACE’s credibility and allow it to effectively address human rights violations across the Council of Europe, including in Azerbaijan. The chairman of Azerbaijani NGO the Institute for Reporters Freedom and Safety, Mehman Huseynov is already facing reprisals for raising the corruption allegations during the January PACE session. A day after his NGO sent a letter about the corruption allegations to PACE members in January, he was abducted and tortured by police and later sentenced for 2 years on defamation charges for allegedly making false allegations about torture. For PACE to be in a position to respond to such violations, it must be seen as independent and not under the influence of states wishing to influence their conduct.
We call upon members of the PACE Bureau to commit to the Sawicki proposal and to call for a full plenary debate on the proposal at the April session of PACE. We also call on the PACE Bureau to include a mechanism of civil society oversight of the investigation to ensure its full independence and impartiality.
We call upon all Members of the Assembly to support in the strongest possible terms an independent, external and thorough investigation. This can be done by signing a written Declaration on the Parliamentary Assembly Integrity introduced on 25 January 2017 by PACE members Pieter Omtzigt (The Netherlands, Christian Democrat), and Frank Schwabe (Germany, Social Democrat) urging the PACE President Pedro Agramunt (Spain, EPP) to launch a “deep, thorough investigation by an independent panel” that makes its findings public. More than one fifth of the Assembly members have joined the declaration. More voices in support of the Assembly integrity are needed. Moreover, PACE members must insist on their right to discuss the Sawicki proposal at the April session of the Assembly, to ensure that PACE has the mechanisms in place to adequately deal with corruption allegations.
We call on the Secretary General of the Council of Europe Thorbjorn Jagland to make a very strong statement to affirm that there will be no tolerance of any corruption, including bribery, trading in influence or taking up of roles that imply a conflict of interest, in the Parliamentary Assembly and the Council of Europe in general.
Commitment to the rule of law, integrity, transparency, and public accountability should be effectively enforced as the key principles of the work of the Parliamentary Assembly. If such a decision is not made now, reputational damage to PACE may become irreparable, preventing PACE from fulfilling its role as a guardian of human rights across the Council of Europe region.
Signatures:
1. The Netherlands Helsinki Committee
2. International Partnership for Human Rights (Belgium)
3. Centre for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights (Russia)
4. Freedom Files (Russia/Poland)
5. Norwegian Helsinki Committee
6. Ukrainian Helsinki Human Rights Union
7. Analytical Center for Interethnic Cooperation and Consultations (Georgia)
8. Article 19 (UK)
9. The Barys Zvozskau Belarusian Human Rights House (Belarus/Lithuania)
10. Index on Censorship (UK)
11. Human Rights House Foundation (Norway)
12. Human Rights Movement “Bir Duino-Kyrgyzstan”
13. PEN International (UK)
14. Crude Accountability (USA)
15. Legal Transformation Center (Belarus)
16. Bulgarian Helsinki Committee
17. World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT) (Switzerland)
18. The Kazakhstan International Bureau for Human Rights and the Rule of Law
19. Belarusian Helsinki Committee
20. Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
21. Promo LEX (Moldova)
22. Libereco – Partnership for Human Rights (Germany/Switzerland)
23. Public Association “Dignity” (Kazakhstan)
24. Human Rights Monitoring Institute (Lithuania)
25. Swiss Helsinki Committee
26. Human Rights Information Center (Ukraine)
27. Public Verdict Foundation (Russia)
28. Albanian Helsinki Committee
29. Kharkiv Regional Foundation “Public Alternative” (Ukraine)
30. Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights (Poland)
31. Women of Don (Russia)
32. DRA – German-Russian Exchange (Germany)
33. Association UMDPL (Ukraine)
34. European Stability Initiative (Germany)
35. International Media Support (IMS) (Denmark)
36. Civil Rights Defenders (Sweden)
37. International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH) (France)
38. Sova Center for Information and Analysis (Russia)
39. Kosova Centre for Rehabilitation of Torture Victims (Kosovo)
40. Truth Hounds (Ukraine)
41. People in Need Foundation (Czech Republic)
42. Eastern Partnership Civil Society Forum (Belgium)
43. Macedonian Helsinki Committee
44. International Youth Human Rights Movement
45. Human Rights First (USA)
46. Regional Center for Strategic Studies (Georgia/Azerbaijan)
47. Human Rights Club (Azerbaijan)
48. Institute for Reporters Freedom and Safety (IRFS) (Azerbaijan)
49. Media Rights Institute (Azerbaijan)
50. Public Association for Assistance to Free Economy (Azerbaijan)
51. Institute for Peace and Democracy (Netherlands/Azerbaijan)
52. Turan News Agency (Azerbaijan)
53. Democracy and NGO development Resource Center (Azerbaijan)
54. Youth Atlantic Treaty Association (Azerbaijan)
55. Monitoring Centre for Political Prisoners (Azerbaijan)
56. Azerbaijan without Political Prisoners (Azerbaijan)
28 Mar 17 | Belarus, Campaigns -- Featured, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]We, the undersigned members of the Civic Solidarity Platform (CSP), a coalition of human rights NGOs from Europe, the former Soviet Union region and North America, and other non-governmental organisations decry the mass detentions of peaceful demonstrators, journalists and human rights defenders, as well as the use of violence and abusive treatment targeting them in Belarus on 25-26 March 2017. These events were the culmination of a series of repressive measures taken by the authorities of the country since the beginning of March to stifle the public expression of grievances. Given the severity of this human rights crisis of unprecedented scale since December 2010, it is crucial that the international community takes resolute action to push for an end to the crackdown in Belarus and justice for those targeted by it.
We condemn the gross violations of the right to peaceful assembly, freedom of expression, freedom from arbitrary detention, and the right to fair trial in Belarus in connection with the recent peaceful protests, and call on the international community to use all available means to put pressure on the Belarusian authorities to immediately end these violations.
Such measures by the authorities should include:
- immediately releasing those currently behind bars because of their involvement in the peaceful protests or their efforts to monitor them;
- dropping charges against all those prosecuted on these grounds;
- carrying out prompt, thorough and impartial investigations into all allegations of arbitrary detention, ill-treatment and other violations of the rights of protesters, passers-by, journalists, human rights defenders and political activists in connection with the protests; and
- bringing those responsible for violations to justice.
We call in particular for the following concrete actions by international community in response to the current crackdown in Belarus:
To the OSCE:
- The OSCE participating States should initiate and support the renewal of the Moscow Mechanism in relation to Belarus and the appointment of a new rapporteur for this process, in view of the fact that the current developments mirror those on the grounds of which this mechanism was invoked in 2011;
- The OSCE Chairmanship should appoint a Special Representative on Belarus, whose mandate should include investigating the recent violations;
- The Office of Democratic Institutions and Human Rights should monitor the trials of those facing charges because of their participation in the recent peaceful protests, or their efforts to monitor and report on them;
- The OSCE Parliamentary Assembly should reconsider holding its annual session in Minsk in July 2017 and identify another host country and city for this event.
To the Council of Europe:
- The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe should replace its current rapporteur on the situation in Belarus, ensuring that the individual holding this position forcefully speaks out against human rights violations in the country.
To the UN:
- Members of the Human Rights Council should extend the mandate of the Special Rapporteur on the human rights situation in Belarus, continue urging the Belarusian authorities to allow the Special Rapporteur to visit the country, and adopt a strong resolution on the human rights situation in Belarus at the next session of the Council;
- High Commissioner on Human Rights should publicly condemn the crackdown in Belarus and engage in direct contact with the Belarusian authorities on this matter.
To international financial institutions:
- International financial institutions should apply strong human rights conditionality in the implementation of their programs in Belarus and refrain from allocating funding to government projects until the human rights situation in the country has substantially improved. Specifically, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development should reinstate its calibrated strategy on Belarus.
To the EU:
- The EU member states and institutions should apply stronger and more consistent human rights conditionality to the development of its relations with Belarus and consider the prospects of reinstating sanctions similar to those applied in 2011-12 for widespread human rights violations.
To the USA:
- The US government should consider reinstating the sanctions against Belarus that it suspended in 2015-16.
Background information, based on reports from the ground:
In the afternoon of 25 March 2017, people took to the streets in the Belarusian capital of Minsk for planned peaceful protests on the occasion of the Day of Freedom, which commemorates the Belarusian declaration of independence in 1918. There was as a heavy police and security presence in the city, the downtown area where protests were due to be held was cordoned off, and traffic was blocked on the main Independence Avenue. Local and international human rights monitors representing the CSP member organisations documented the use of heavy-handed tactics by the law enforcement and security authorities to prevent the peaceful protests, for which authorities had not given advance permission as required by Belarusian law and in violation of international standards. At least 700 people were detained on 25 March, including elderly and passers-by. As can be seen on available photos and footage, police forcefully rounded up and beat protesters with batons, although these made no resistance. More than 30 journalists and photographers from both Belarusian and international media outlets were detained; cameras and other equipment of some of them were damaged by police. Toward the evening, police started releasing detainees from the detention facilities, in many cases without charge. However, others remain in detention, and dozens of individuals are expected to stand trial starting Monday 27 March on charges relating to their participation in the peaceful protests.
The following episode requires particular attention: At 12.45 pm local time on 25 March, about an hour before the start of the planned peaceful protest, anti-riot police raided the offices of the Human Rights Center Viasna and detained a total of 57 Belarusian and foreign human rights defenders and volunteers as well as journalists. Human rights defenders and volunteers had gathered there for a training on monitoring the protests and were planning to go to the streets of Minsk for observation of the assemblies. Among them were representatives of Viasna, the Belarusian Helsinki Committee, the Belarusian Documentation Center, Frontline Defenders, International Partnership for Human Rights and other organisations. The police shouted at all present, intimidated them, and ordered to lie down on the floor face down. 57 people were detained without any charges, packed in the buses and brought to the Pervomaisky district police station, where their belongings were searched and their personal information recorded. The detainees were held there for two and a half hours and were released afterwards without charges. One of the detained needed medical treatment because of injuries sustained when being beaten by police. The raid of the offices of Viasna and the detention of the monitors were clearly aimed at intimidating and preventing them from observing the peaceful assembly and documenting possible violations.
The crackdown continued on 26 March, with dozens of people being detained by police as they gathered at October Square in Minsk at noon to express solidarity with those detained the day before. Among the detained on 26 March were at least one human rights defender, one civil society activist and one journalist. Representatives of national and international human rights NGOs, including members of the CSP, continue to document violations perpetrated in connection with the events of the last few days.
The detentions on 25-26 March followed the earlier detention of about 300 people, including opposition members, journalists and human rights defenders in the last few weeks. These detentions have taken place against the background of a wave of peaceful demonstrations that were carried out across Belarus since mid-February 2017 to protest against so-called “social parasites” law which imposes a special tax on those who have worked for less than six months during the year without registering as unemployed. The legislation, which has affected hundreds of thousands of people in the economically struggling country, has caused widespread dismay. On 9 March, President Lukashenko suspended the implementation of the law but refused to withdraw it, resulting in further protests. Many of those detained have been fined or arrested for up to 15 days on administrative charges related to their participation in the peaceful protests. Over two dozen people are facing criminal charges on trumped-up charges of preparation to mass riots.
Signed by the following CSP members:
- Analytical Center for Inter-Ethnic Cooperation and Consultations (Georgia)
- Article 19 (United Kingdom)
- Association UMDPL (Ukraine)
- Bir Duino (Kyrgyzstan)
- Bulgarian Helsinki Committee
- Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
- Centre for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights (Russia)
- Committee against Torture (Russia)
- Crude Accountability (USA)
- Freedom Files (Russia/Poland)
- German-Russian Exchange – DRA (Germany)
- Helsinki Association of Armenia
- Helsinki Citizens’ Assembly – Vanadzor (Armenia)
- Helsinki Committee of Armenia
- Helsinki Committee for Human Rights in Serbia
- Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights (Poland)
- Human Rights Center of Azerbaijan
- Human Rights First (USA)
- Human Rights House Foundation (Norway)
- Human Rights Information Center (Ukraine)
- Human Rights Monitoring Institute (Lithuania)
- The institute for Reporters’ Freedom and Safety (Azerbaijan/Georgia/Switzerland)
- Index on Censorship (United Kingdom)
- Institute Respublica (Ukraine)
- International Partnership for Human Rights (Belgium)
- Kazakhstan International Bureau for Human Rights and Rule of Law
- The Kosova Rehabilitation Center for Torture Victims
- Macedonian Helsinki Committee
- Moscow Helsinki Group (Russia)
- The Netherlands Helsinki Committee
- Norwegian Helsinki Committee
- Office of Civil Freedoms (Tajikistan)
- Promo-LEX (Moldova)
- Protection of Rights without Borders (Armenia)
- Public Association “Dignity” (Kazakhstan)
- Public Alternative Foundation (Ukraine)
- Public Foundation Golos Svobody (Kyrgyzstan)
- Public Verdict Foundation (Russia)
- Regional Center for Strategic Studies (Azerbaijan/ Georgia)
- Serbian Helsinki Committee for Human Rights
- SOLIDARUS e.V. (Germany)
- The Swiss Helsinki Committee
- Ukrainian Helsinki Human Rights Union
- Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom
- World Organisation against Torture (OMCT)
Other organisations who have joined the statement:
- Belarus Free Theatre
- Libereco – Partnership for Human Rights (Switzerland)
- PEN International
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1490686433484-ad7cf42c-cf25-10″ taxonomies=”172″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
23 Mar 17 | Belarus, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, Statements
Dear Mr. President
We, 48 undersigned organizations from 24 countries, strongly condemn the continuing wave of detentions and harassment of peaceful protesters, journalists, human rights defenders, civil society activists, anarchists and opposition party members in Belarus.
Most of the detentions and harassment are linked to participation in peaceful protests demanding the cancellation of Presidential Decree No. 3, the so-called “social parasite” legislation, which imposes a tax on unemployed people in Belarus. Decree No. 3 obligates citizens to work a specific number of days or pay a special duty to the State under threat of arrest. This is contrary to Art. 41 of the Belarusian Constitution and violates international human rights law.
According to reports from Belarusian and international human rights organizations, as of 22 March 2017 more than 250 people have been detained since 3 March 2017, including at least 31 journalists. At least 110 people have been sentenced to 3-15 days of administrative arrest. Many of them remain in detention, while others have been subject to different forms of harassment.
We strongly condemn the fact that several detentions of peaceful protesters at different places across Belarus have been carried out with the excessive use of force by Belarusian security officers.
Several Belarusian organizations have announced a demonstration that will take place in Minsk and in other cities in Belarus on 25 March 2017. We are deeply concerned about the physical and psychological integrity of the participants of these protest marches.
As the president of Belarus we urge you:
- to respect the right to peaceful assembly and expression
- to ensure that there are no obstructions to the exercising of these rights in Belarus, including in relation to the planned demonstration on 25 March 2017 in Minsk and in other cities across the country
- to guarantee in all circumstances the physical and psychological integrity of all peaceful protesters at the demonstration on 25 March 2017 in Minsk as well as at all other peaceful demonstrations across Belarus
- to refrain from the use of excessive force by security officers on 25 March 2017 in Minsk as well as at all other peaceful demonstrations across Belarus
- to ensure that journalists are able to fully exercise their professional duties, including during peaceful demonstrations
- to immediately and unconditionally release all protesters, journalists, human rights defenders, civil society activists and opposition members who have been detained in connection with the current wave of demonstrations solely for peacefully exercising their right to freedom of assembly and expression
- to refrain from preventively detaining journalists, human rights defenders, civil society activists, anarchists and opposition activists
- to immediately stop the persecution, harassment and intimidation of those who exercise their right to freedom of assembly, expression and association and ensure these rights to all Belarusian citizens
- to abolish Presidential Decree No. 3 since it violates international human rights law
Signatories:
Albanian Helsinki Committee
Analytical Center for Interethnic Cooperation and Consultations (Georgia)
Article 19 (UK)
Association UMDPL (Ukraine)
Bir Duino (Kyrgyzstan)
Bulgarian Helsinki Committee
Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights (Russia)
Charity foundation “East-SOS” (Ukraine)
Civic Belarus (Czech Republic)
CIVICUS: World Alliance for Citizen Participation, Johannesburg
Committee to Protect Journalists (USA)
Crude Accountability (USA)
FIDH, Paris
Freedom Files (Russia/Poland)
German-Russian Exchange (Germany)
Helsinki Committee for Human Rights in Serbia
Helsinki Committee of Armenia
Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights (Poland)
Human Rights Center “Postup” (Ukraine)
Human Rights Center (Azerbaijan)
Human Rights Information Center (Ukraine)
Human Rights Monitoring Institute (Lithuania)
Humanrights.ch (Switzerland)
Index on Censorship (UK)
Institute Respublica (Ukraine)
International Partnership for Human Rights (Belgium)
IRFS (Azerbaijan)
JEF Europe: Young European Federalists, Brussels
Kazakhstan Interantional Bureau for Human Rights and the Rule of Law
Kharkiv Human Rights Protection Group (Ukraine)
KRF Public Alternative (Ukraine)
Libereco – Partnership for Human Rights (Switzerland/Germany)
Macedonian Helsinki Committee
Memorial International, Moscow
Menschenrechte in Belarus e.V. (Germany)
Moscow Helsinki Group (Russia)
NESEHNUTI – Independent Social Ecological Movement (Czech Republic)
Norwegian Helsinki Committee
Ostgruppen – Swedish Initiative for Democracy and Human Rights
Promo LEX (Moldova)
Protection of Rights without Borders NGO (Armenia)
Public Verdict Foundation Russia)
Reporters Without Borders International, Paris
The Netherlands Helsinki Committee
The Swiss Helsinki Committee
Ukrainian Helsinki Human Rights Union
World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT), Geneva
02 Jun 16 | Magazine, mobile, Volume 45.01 Spring 2016
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

American academic Alexa Huang explores how Shakespeare’s plays were edited to make them more acceptable to Victorians.
Shakespeare has been used to divert around censorship, “sanitised” and redacted for children, young adults and school use, and even used as a form of protest all over the world. While censors have reacted differently to Shakespeare (sometimes with a blind eye), self-censorship (by directors and audiences) is part of the picture as well.
Not all censors work in the capacity of a public official. Many censors are in fact editors, writers and educators who are gatekeepers of specific forms of knowledge. Julius Caesar, for example, is often deemed one of the more appropriate plays to teach and perform in American school systems, because the themes of honor, free will and principles of the republic (as opposed to more sexually charged themes in other plays) are considered inspiring and suitable in the educational context.
The themes in such plays as Romeo and Juliet (teen exuberance and sex), The Merchant of Venice (anti-Semitism), Othello (racism and domestic violence), and Taming of the Shrew (sexism) make modern audiences uncomfortable, but they compel us to ask harder questions of our world.
While Shakespeare has been a large part of American cultural life, the “Shakespeare” that is taught and enacted in schools has often been redacted and even censored. But this is not a new phenomenon. The history of bowdlerized Shakespeare goes back to the nineteenth century. To bowdlerize a classic means to expurgate or abridge the narrative by omitting or modifying sections that are considered vulgar.
In fact, the term “bowdlerized” comes from Henrietta “Harriet” Bowdler who edited the popular, “family-friendly” anthology The Family Shakespeare (1807) which contains 24 edited plays. The anthology sanitised Shakespeare’s texts and rid them of undesirable elements such as references to Roman Catholicism, sex and more. The anthology was intended for young women readers.
Multiple ambiguities in Shakespeare are replaced by a more definitive interpretation. Ophelia no longer commits suicide in Hamlet. It is an accidental drowning. Lady Macbeth no longer curses “out, damned spot” but instead she says “Out, crimson spot!” Prostitutes are omitted, such as Doll Tearsheet in Henry IV Part 2. The “bawdy hand of the dial” (Mercutio) in Romeo and Juliet is revised as “the hand of the dial.”
Contrary to popular imagination, censorship is not a top-down operation. Instead, it is often a communal phenomenon involving both the censors and the receivers who willingly accept the Shakespeare that has been improved upon. Family Shakespeare was itself a family project. Thomas Bowdler (1754-1825) worked with his sister Henrietta Bowdler to bowdlerize or clean up the classics. The subtitle of the volume states that “nothing is added to the original text; but those words and expressions are omitted which cannot with propriety be read aloud in a family.” Shakespeare is credited as the author, though Bowdler made clear the Bard needed quite some heavy-handed editing.
Ironically, Henrietta Bowdler was herself censored. Thomas Bowdler’s name appears on the cover. It took two centuries for Henrietta to be credited for the anthology, for obviously there is no way she could have admitted that she recognised the bawdy puns in Shakespeare, much less editing them out of Shakespeare. The Bowdlers are among the better-known “censors” in the nineteenth century who editorialised the classics including Shakespeare.
When laying out her editorial principles in the preface, Bowdler does not hesitate to criticise the “bad taste of the age in which [Shakespeare] lived” and Shakespeare’s “unbridled fancy”:
The language is not always faultless. Many words and expressions occur which are of so indecent Nature as to render it highly desirable that they should be erased. But neither the vicious taste of the age nor the most brilliant effusions of wit can afford an excuse for profaneness or obscenity; and if these can be obliterated the transcendent genius of the poet would undoubtedly shine with more unclouded lustre.
She further explains her motive in The Times in 1819, emphasising that the “defects” in Shakespeare have to be corrected:
My great objects in the undertaking are to remove from the writings of Shakespeare some defects which diminish their value, and at the same time to present to the public an edition of his plays which the parent, the guardian and the instructor of youth may place without fear in the hands of his pupils, and from which the pupil may derive instruction as well as pleasure: and without incurring the danger of being hurt with any indelicacy of expression, may learn in the fate of Macbeth, that even a kingdom is dearly purchased, if virtue be the price of acquisition
While censorship carries a negative connotation in our times, The Family Shakespeare did broaden Shakespeare’s audience and readership. While American schools continue to redact Shakespeare, they also infuse Shakespeare into the American cultural life in various forms.
Alexa Huang will be participating in the Index on Censorship magazine panel at the Hay Festival.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91322″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064229008534812″][vc_custom_heading text=”Bowdler revisited: Shakespeare
” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064229008534812|||”][vc_column_text]March 1990
Artist Jane Zweig discovers books burned in Boston and looks at how Romeo and Juliet has been censored in America.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”94784″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064227508532458″][vc_custom_heading text=”Censoring Shakespeare” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064227508532458|||”][vc_column_text]September 1975
A Lithuanian stage producer was dismissed from his post after sending an ‘open letter’ to Soviet authorities protesting censorship in theatre.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”93836″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228508533832″][vc_custom_heading text=”Clampdown on drama” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228508533832|||”][vc_column_text]November 2007
Livingstone Njomo Waidhura reports on drama taught in schools and whether Shakespeare is a suitable hero for Kenya. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”The unnamed” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fnewsite02may%2F2017%2F09%2Ffree-to-air%2F|||”][vc_column_text]The spring 2016 Index on Censorship magazine celebrates the 400th anniversary of William Shakespeare’s death, looking at how his plays have been used around the world to sneak past censors or take on the authorities – often without them realising. Our special report explores how different countries use different plays to tackle difficult themes.
With: Jan Fox, György Spiró, Martin Rowson[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”86201″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/newsite02may/2016/02/staging-shakespearean-dissent/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fnewsite02may%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
24 May 16 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia, Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, France, Germany, Greece, Index Reports, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Poland, Serbia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine
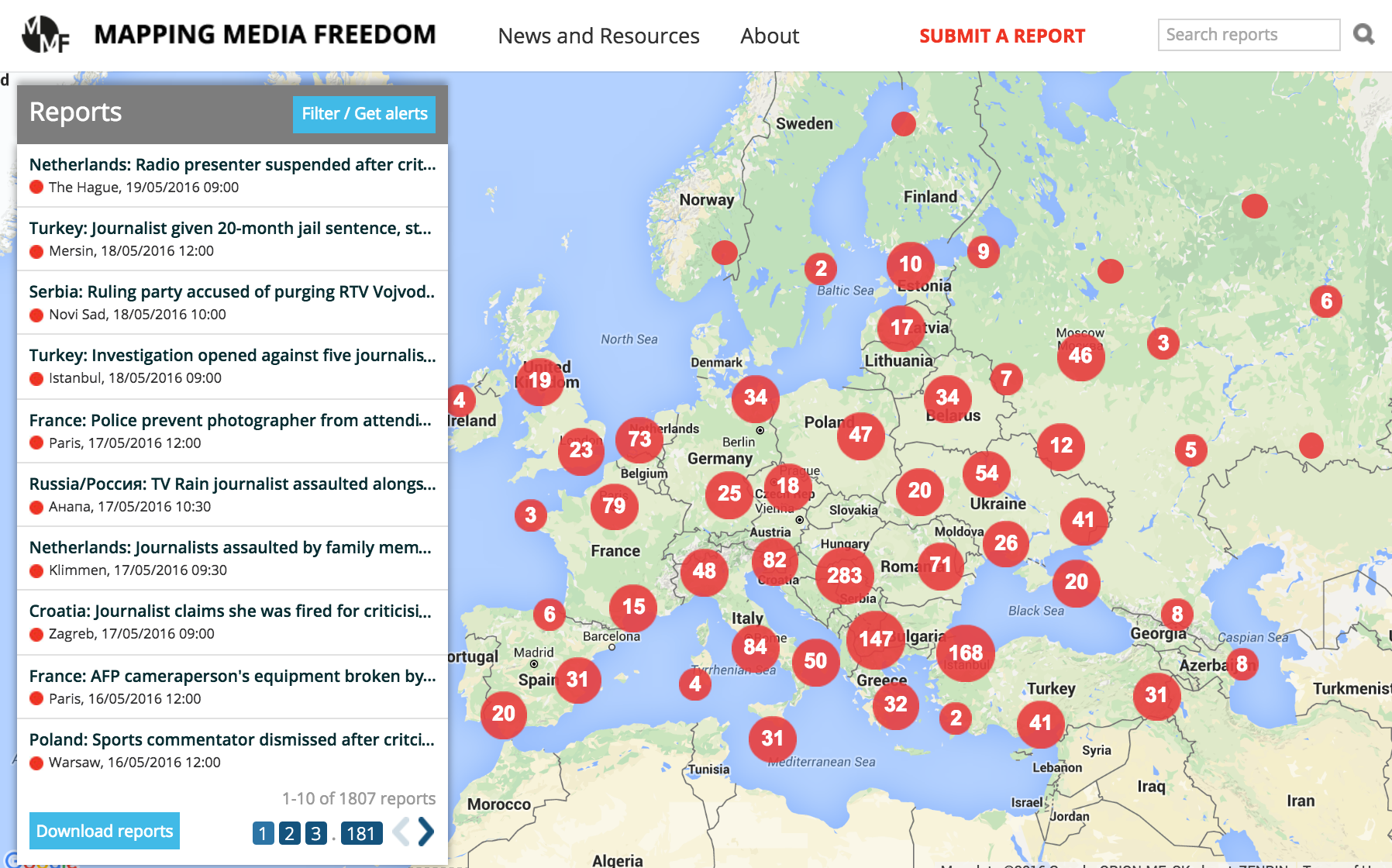
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar



