31 May 16 | Events, Middle East and North Africa

The New Arab news network invites you to a panel discussion to discuss the challenges faced by the media and journalists in the post-Arab Spring era. The Arab Spring of 2011 presented hope for a region free from dictatorial rule and media constraints, but since the people’s uprising, much the opposite has happened. The Arab world is still plagued by media censorship, and independent journalism and objective coverage can be a life-threatening exercise.
The Arab Spring of 2011 presented hope for a region free from dictatorial rule and media constraints, but since the people’s uprising, much the opposite has happened. The Arab world is still plagued by media censorship, and independent journalism and objective coverage can be a life-threatening exercise.This discussion will explore the current state of the media in the region and the future of press freedom in the wider Arab world.
This discussion will explore the current state of the media in the region and the future of press freedom in the wider Arab world.
Hosted and Chaired by SNP MP Tommy Sheppard.
Speakers Include:
– Faitma El-Issawi, research fellow, LSE Middle East Centre
– Melody Patry, advocacy officer at Index on Censorship
– Abdu Elshayyal, CEO of The New Arab
When: Wednesday, 15 June 2016 from 5.30-7pm
Where: Conference Room 15, House of Commons, London, SW1A 0AA (view map)
Tickets: Free, but registration is required.
27 May 16 | About Index, Azerbaijan, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News and features
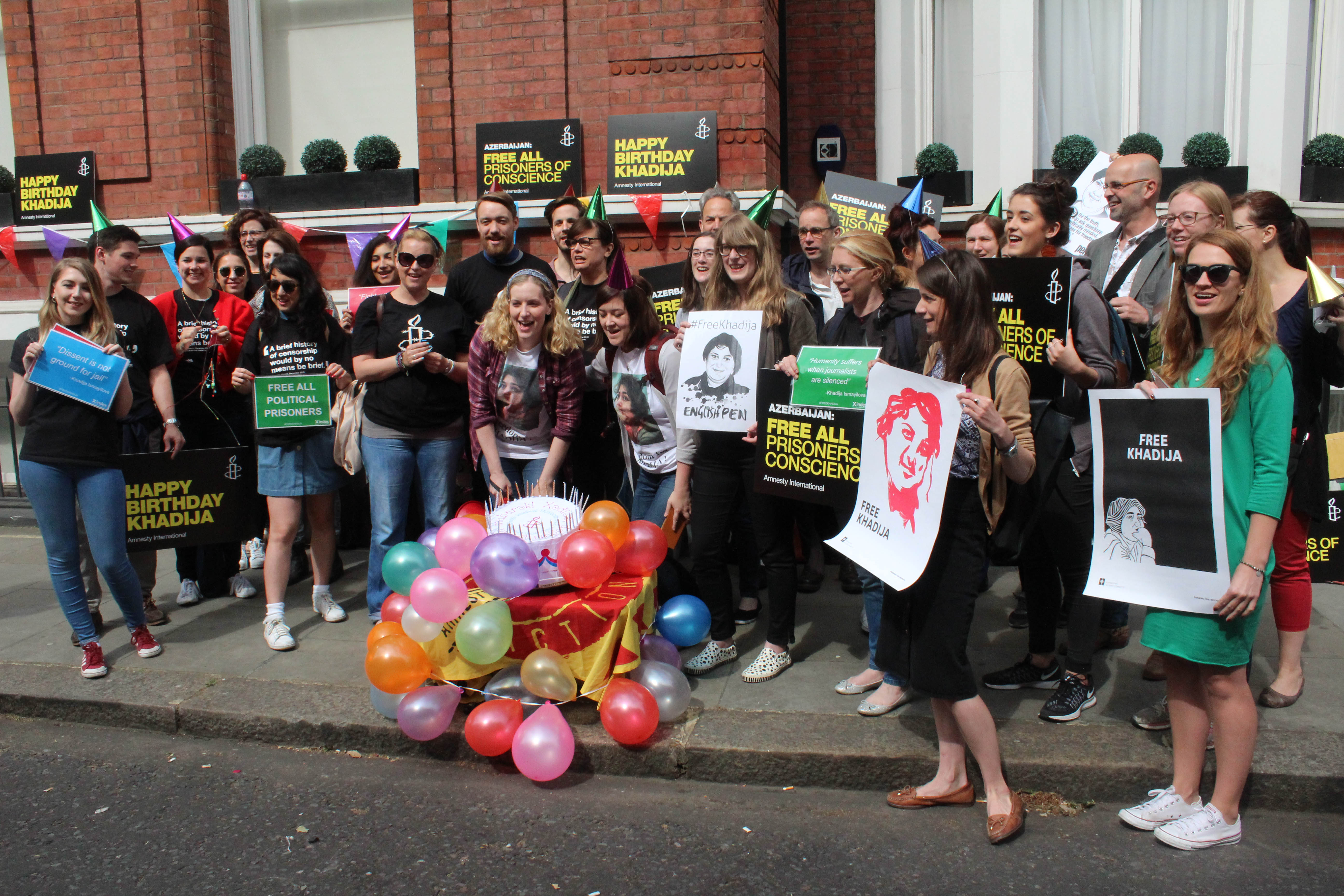
Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
Azerbaijani investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova may have been released from prison on Wednesday, but two trumped-up charges against her — illegal entrepreneurship and tax evasion –remain. Her seven-and-a-half-year jail sentence has only been reduced to a three-and-a-half-year suspended term and she isn’t free to leave the country.
Today is Ismayilova’s 40th birthday and to mark the occasion, protesters gathered at 40 different demonstrations from around the world, not just to celebrate, but to call for all charges against her to be quashed. Index joined other members of the Sports for Rights coalition at the Azerbaijani embassy in London (see above).
“Let’s take a moment to celebrate the work that’s been done by this remarkable woman,” Rebecca Vincent, the co-ordinator of the Sport for Rights campaign, told demonstrators.
Currently, around 70 political prisoners — including journalists, bloggers, activists and religious followers — sit in Azerbaijani jails, and Vincent called on protesters to sustain their focus on all of them. “That’s what Khadija has asked for for her birthday,” she said.
Seymur Hezi is an Azerbaijani journalist serving a five-year prison sentence on charges of “aggravated hooliganism”. Hezi, who contributed to the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award-winning newspaper Azadliq, was sentenced on 29 January 2015. He was arrested on 29 August 2014 following an altercation in which the journalist was defending himself from a physical assault and harassment, according to his lawyers. “His case doesn’t get enough international attention, possibly because he is not an English speaker and not well networked,” Vincent said.
Other political prisoners include Ilgar Mammadov, the opposition politician who leads Azerbaijan Republican Alternative Movement, who has been in jail for over three years, and Ilkin Rustemzade, the activistt originally jailed following his Harlem Shake video filmed in Baku.
On the same day Ismayilova was released, two more political prisoners, a youth activist and a journalist, were arrested.

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
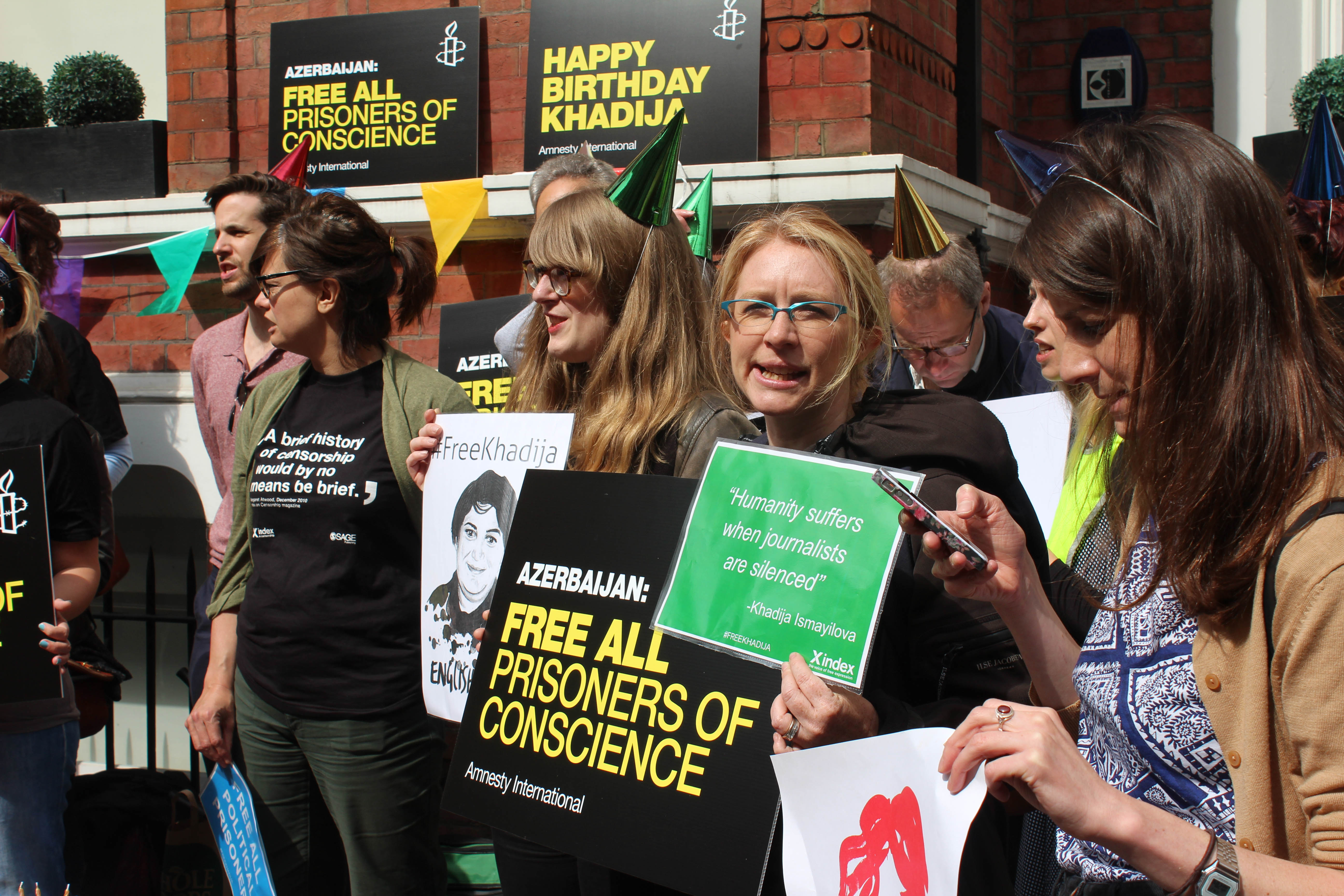

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
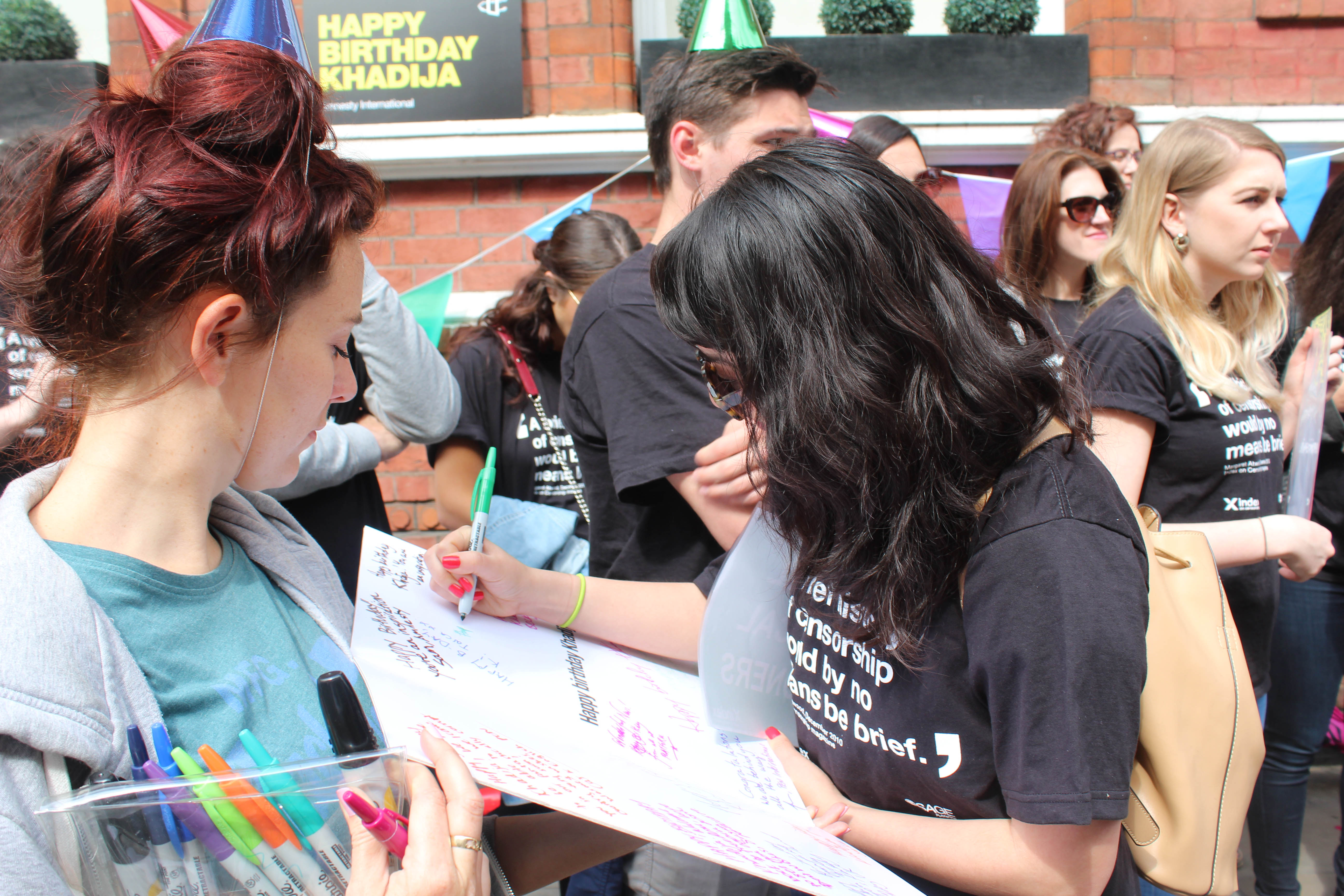

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
Many more protests took place today. Here are some of them:
Paris, France
Washington DC, USA
Brussels, Belgium
Oslo, Norway
27 May 16 | Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Spain
When Axier López, the 37-year-old reporter for the Basque-language magazine Argia, opened the mailbox at his home in Barakaldo early April, he discovered he’d become the first journalist in Spain to be punished under the Public Security Law.
He was ordered to pay €601 (£466) for photos of an arrest he published on Twitter without state permission on 7 March.
“It is a fine similar to a parking ticket,” López told Mapping Media Freedom. “Signed by a local government representative, it claims I committed a crime by putting on-duty police officers in danger.”
The photos in question were taken when López was in the city of Eibar covering the arrest of a woman who had previously refused to appear in court. In 2007 she had participated in a protest against the forced closure of a local youth organisation which the state and court linked to a Basque separatist terrorist group. The woman was accused of blocking a road.
The so-called “gag law” under which López was fined came into force on 1 June 2015. It bans coverage of on-duty police officers without prior police permission and prohibits the publication of any clue as to their identity. The Spanish centre-right government said the purpose of the law is to protect officer security.
“What is the problem if we track and inform the public about events involving police officers?” López asked. “Policemen are paid with public money, so I don’t see a problem if they appear in media content.”
“Almost every day you can see arrests of different people on TV, where police officers appear in front of the camera, but they punished only us,” he added.
Journalists in Spain have recently come under mounting legal pressures related to their work.
In April two journalists from the daily newspaper ABC, Pablo Muñoz and Cruz Morcillo, were facing two-and-a-half-year prison sentences for publishing a telephone conversation between members of the Italian mafia, who were talking about Luis Bárcenas, former treasurer of Partido Popular. After an avalanche of support for the journalists, the general attorney in Madrid dropped the charges in May.
The journalists had published their article in July 2014, a year after police investigators intercepted the phone conversation between two mafioso. The general attorney had claimed they revealed details of a secret police investigation.
“Charges, in this case, were really severe,” said Elsa González, president of the Spanish Federation of Journalist Associations (FAPE), the main journalist body in the country. “A journalist has to publish information if it’s in the public interest.”
González added that according to a poll by Madrid’s Association of Journalist (APM), last year only 23.2% of reporters with permanent contracts and 22.2% of freelancers said they never received pressure to modify information in their reports. APM said the pressure could come from multiple angles, including political and corporate powers, public institutions and advertisers.
A group of Spanish media companies has also recently been threatened with legal action after online newspapers El Confidencial and Eldiario.es, along with private TV channel La Sexta reported that Juan Luís Cebrián, president of the Prisa media group, publisher of the national newspaper El País and sports daily AS, appeared in the Panama Papers.
On 26 April Prisa issued a statement on its website stating that its president had taken legal action against the outlets for “clear defamatory intent” by linking Cebrián to the Panama Papers “in which he categorically does not appear”.
The centre-right daily newspaper El Mundo, a competitor of Prisa’s left-leaning daily El País, then reported that journalists who work for Prisa publishing house were prohibited from engaging with the three media outlets.
Nacho Cardero, director of El Confidencial, told Mapping Media Freedom that Cebrián has yet to take any formal action.
“At the moment there are no actions against any of the three media sources and furthermore, the intention to expel contributors of El Confidencial, La Sexta or Eldiario.es from his group, hasn’t occurred,” said Cardero. “However, Prisa has closed the door to Ignacio Escolar, director of Eldiario.es.”
López believes all these cases serve to spread fear among journalists. Meanwhile, his appeal against his fine has been refused. It could have been reduced to €300 (£232) if he had paid in 15 days. “However, we are not going to pay because we were doing our job,” he said.
“I don’t know where we can go in the legal process,” López added. “But it is important that the debate on this law is open and that we resist in order to prevent possible fear in other journalists.”
Mapping Media Freedom approached Cebrián for comment but received no response.
26 May 16 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan Statements, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, Statements
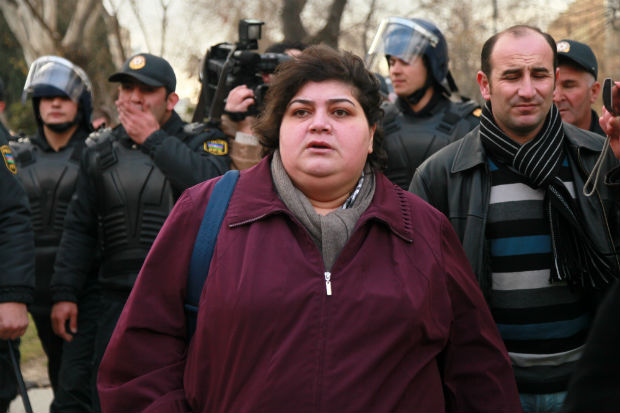

Khadija Ismayilova is one of the government critics jailed ahead of the 2015 Baku European Games.
Index on Censorship calls for all Khadija Ismayilova’s convictions to be quashed following the reduction in her jail sentence to a three-and-a-half-year suspended term.
Ismayilova, an award-winning journalist, was imprisoned since December 2014 and sentenced in September 2015 to seven-and-a-half years in prison on trumped-up charges.
“Khadija is a courageous journalist who speaks truth to power despite relentless harassment and pressure,” said Index on Censorship’s senior advocacy officer Melody Patry. She added: “Her imprisonment was unjust and the Supreme Court should have gone further and overturned the conviction rather than merely reducing the sentence.”
Officially charged with large-scale misappropriation and embezzlement, illegal entrepreneurship, tax evasion and abuse of official duties, the real reason for Ismayilova’s imprisonment is her investigative journalism and advocacy.
Although Ismayilova is out of jail, her conviction still stands and carries many restrictions on her freedoms. She will have to report herself to the police every month and won’t be able to leave the country for five years without a permission from state institutions, Azadliq Radiosu reports.
“The struggle is not over for Khadija Ismayilova, and it is certainly not over for the remaining political prisoners in Azerbaijan,” Index’s CEO Jodie Ginsberg said. “Substantial change and reform are needed so that the authorities cannot jail and free their critics as they please.”
Index on Censorship will take part in the Sport for Rights global action to mark Ismayilova’s 40th birthday on Friday 27 May. Gatherings across the globe will go ahead, and participants will celebrate Ismayilova’s release and call for the release of the country’s dozens of remaining political prisoners.
Azerbaijan: Journalist Khadija Ismayilova released from prison
Who is investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova?
25 May 16 | Azerbaijan, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News and features

Khadija Ismayilova
Azerbaijan’s Supreme Court has ordered the release of investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova after an international campaign to free her and just two days before international protests against her detention were due to take place.
Khadija, who turns 40 on Friday, had previously been sentenced to seven-and-a-half years in prison on trumped-up financial charges in September 2015, having been detained since December 2014. The supreme court has just announced that her sentence has been reduced to a suspended three-year sentence. She will be subject to a travel ban and other restrictions.
“We are delighted that Khadija Ismayilova has been released from prison,” said Index’s senior advocacy officer Melody Patry. “She shouldn’t have spent a day in jail. The charges against her were spurious and we call for her full acquittal. We also reiterate our calls for Azerbaijan to release all political prisoners.”
Ismayilova was jailed in December 2014 on a range of politically motivated charges – initially inciting someone to attempt suicide, and later the charges of which she was eventually convicted: illegal entrepreneurship, tax evasion, and abuse of office. The real reason she was targeted, however, was her investigative reporting exposing corruption among Azerbaijan’s ruling elite.
Eastern Europe, Caucasus and Central Asia (ECCA) International Media Support team leader Gulnara Akhundova said today: “We are beyond relieved that Khadija Ismayilova has finally been released, but emphasise that she should never have spent a single day in jail. We call for all restrictions on her to be immediately dropped and for her conviction to be overturned.”
Rebecca Vincent of Sports for Rights, which has been campaigning for Ismayilova’s release, said: “We are delighted that Khadija is finally free, after spending 537 days unjustly jailed. On the occasion of her release, we echo Khadija’s call that we should not focus only on her case, but call for the releases of all political prisoners and concrete steps to address the rampant corruption and human rights abuses in Azerbaijan that Khadija has sacrificed so much to expose.”
Sport for Rights has organised a global action to mark Ismayilova’s 40th birthday on Friday 27 May in 40 cities around the world. Gatherings will still go ahead, and participants will celebrate Ismayilova’s release, call for her full acquittal and call for the release of the country’s dozens of remaining political prisoners.
Index on Censorship senior advocacy officer Melody Patry is available for comment at +44 (0)207 963 7290 / melody@indexoncensorship.org.
Sport for Rights coordinator Rebecca Vincent is available for comment at +44 (0)7583 137751 / rebecca.jane.vincent@gmail.com.
25 May 16 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News and features
 Azerbaijan’s Supreme Court has ordered the release of investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova. But who is Ismayilova and why was she in prison?
Azerbaijan’s Supreme Court has ordered the release of investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova. But who is Ismayilova and why was she in prison?
One of Azerbaijan’s most celebrated journalists, Ismayilova investigated, among other things, Azerbaijan’s human rights abuses and the corruption involving the family of president Ilham Aliyev. The recent Panama Papers have followed up on her work, exposing links between the president’s family and a network of offshore tax havens and hidden wealth.
Ismayilova was arbitrarily imprisoned in December 2014 and was sentenced in September 2015 to seven-and-a-half years in prison. Although she is officially charged with large-scale misappropriation and embezzlement, illegal entrepreneurship, tax evasion and abuse of official duties, it is widely believed that the real reason for Ismayilova’s imprisonment is her investigative journalism.
Before her arrest, Ismayilova had been subjected to a relentless campaign of intimidation and persecution, possibly orchestrated by the Azerbaijani authorities to discredit her investigative reporting on corruption amongst the highest levels of society.
“Khadija Ismayilova has suffered a serious invasion of her personal privacy through the installation of hidden cameras and wires in her flat and publication of secretly filmed videos among other incidents. Azerbaijan has a positive obligation to carry out an effective investigation into these violations,” said Camila Graham-Wood, legal officer at Privacy International.
Human rights lawyer Amal Clooney has been representing Ismayilova during her case at the European Court of Human Rights.
Her work was recognised by the United Nations which awarded her the prestigious Unesco/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize. When Ismayilova was in prison, her mother, Elmira Ismayilova, accepted the award on her daughter’s behalf. She read a statement Ismayilova wrote from prison: “As you gather here tonight, I ask you not to laud my work or my courage, but to dedicate yourself to the work each one of you can do on behalf of press freedom and justice.”
She read a statement Ismayilova wrote from prison: “As you gather here tonight, I ask you not to laud my work or my courage, but to dedicate yourself to the work each one of you can do on behalf of press freedom and justice.” Ljiljana Zurovac, president of the Unesco/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize 2016 jury, said: “Khadija Ismayilova highly deserves the prize and I am happy to see that her courage and professionalism are recognised.”
Azerbaijan is one of the lowest ranked countries for press freedom, being placed 163 out of 180 countries on the 2016 Reporters Without Border’s World Press Freedom Index.
Protests due to take place this Friday to mark Ismayilova spending her 40th birthday in prison will still go ahead to celebrate her release, call for her full acquittal and for the release of the country’s political prisoners, including Ilgar Mammadov, Seymur Hezi and Ilkin Rustemzade.
24 May 16 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia, Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, France, Germany, Greece, Index Reports, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Poland, Serbia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine
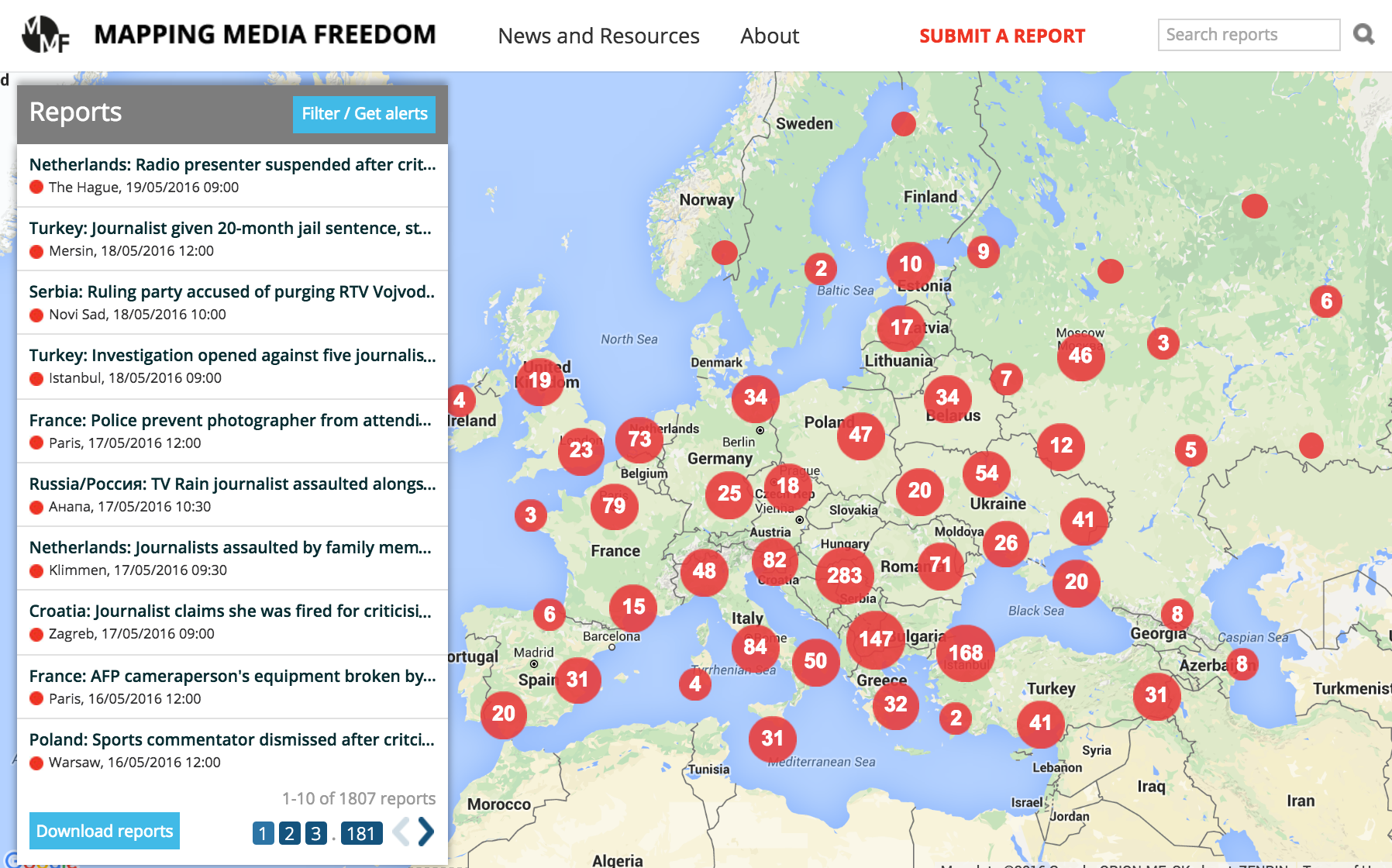
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
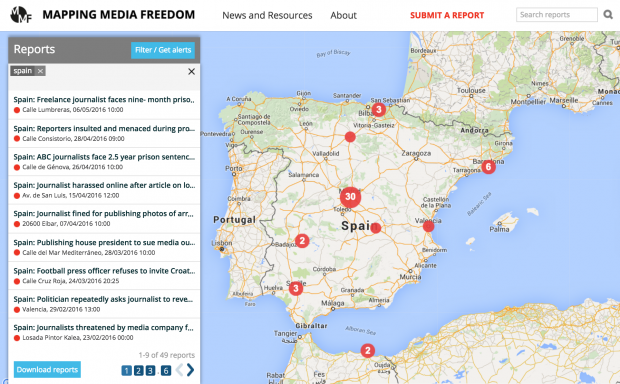
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar
24 May 16 | About Index, Azerbaijan News, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile
Journalists have been murdered and burned in effigy. Reporters have been publicly discredited by government officials, prosecuted for under anti-terrorism laws and excluded from public meetings on the refugee crisis. We’ve even recorded journalists being menaced with mechanical diggers.
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 incidents, ranging from insults and cyberbullying to physical assaults and assassination.
“The original impetus behind the project was to uncover everyday attacks on press freedom in Europe. The database has given Index, its partners and policy makers a highly unnerving look at the ways journalists are barred, attacked or even murdered simply for doing their jobs,” Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom, said.
The project has been granted renewed funding by the European Commission.
“The strength of Mapping Media Freedom is that it provides an ongoing narrative about the state of press freedom in the European region. It is gratifying that the European Commission values its contribution to the project by renewing its funding for a third year,” Melody Patry, senior advocacy officer, Index on Censorship said.
Over the period of coverage, Mapping Media Freedom has released periodic reports on the verified incidents. In the first quarter of 2016, the project received a total of 301 violations of press freedom to the database, a 30% rise over the fourth quarter of 2015. Earlier reports documented similar trends: February 2016, October 2015, May 2015 and December 2014.
The platform — a joint undertaking with the European Federation of Journalists and Reporters Without Borders and partially funded by the European Commission — covers 40 countries, including all EU member states, plus Albania, Belarus, Bosnia, Iceland, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Norway, Russia, Serbia, Turkey, Ukraine and Azerbaijan. In September 2015 the platform expanded to monitor Russia, Ukraine and Belarus and in February 2016 into Azerbaijan. Since launching in May 2014, the map has recorded over 1,800 violations of media freedom, as 17 May 2016. Each report is fact checked with local sources before becoming publicly available on the interactive map.
Mapping Media Freedom works in conjunction with the Council of Europe’s platform about the safety and protection of journalists, provides resources for researchers and information for journalists. It is also affiliated with European Youth Press, Media Legal Defence Initiative, Human Rights House Kiev, Ossigeno per L’Informazione, Osservatorio Balconi e Caucaso and the European Centre for Press and Media Freedom.
24 May 16 | About Index, mobile, Music in Exile, News and features

Jodie Ginsberg, CEO Index on Censorship. Credit: Eric Hobson
Thanks to generous support from fans at a gig for Malian rock band Songhoy Blues at The Roundhouse in London, Index on Censorship raised more than £1,800 on Saturday to support its new fund for persecuted musicians.
Reflecting on the music ban imposed by extremists in northern Mali in 2012, Index chief executive Jodie Ginsberg reminded a capacity crowd of the threats faced by musicians worldwide. “If we don’t support these musicians, the next act would not be Songhoy Blues but an empty stage,” she said.
The money raised will go towards supporting the Music in Exile Fellowship — part of Index’s Freedom of Expression Awards programme — to support a group or individual facing persecution for their work.
Over £200 was also raised at a special screening of the film They Will Have to Kill Us First, whose producers came up with the idea for the fund, at the Everyman in Belsize Park on Saturday afternoon.
“The response of the audiences at Saturday’s events was amazing — we’re delighted,” Ginsberg said. “Few people can imagine a world without music, and the support for the fund shows just how important it is to so many people to make sure we don’t end up with such a world.”
The first Music in Exile Fellow — Serge Bambara, aka Smockey — will be performing in London in July.
If you would like to support the fund, please text BAND61 £10 to 70070 to donate £10 or visit our Justgiving page.
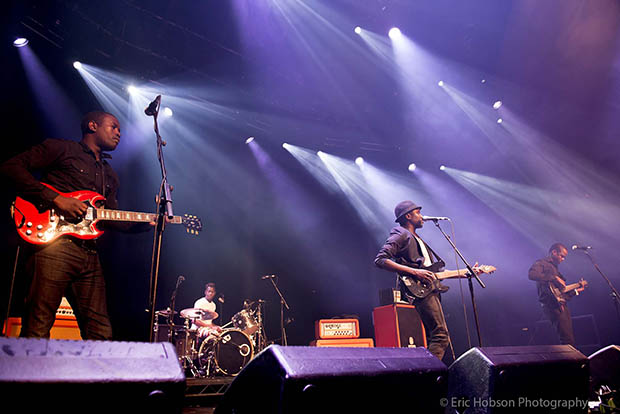

Songhoy Blues at The Roundhouse, May 2016. Credit: Eric Hobson
23 May 16 | Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, mobile, Statements
The Global Network Initiative welcomes the announcement that Google is appealing a French data protection authority ruling requiring the global take down of links to search information banned in France under Europe’s “right to be forgotten”.
We are concerned that the ruling, made by Commission Nationale de L’Informatique et des Libertes (CNIL) in March, sets a disturbing precedent for the cause of an open and free Internet, and sends the message to other countries that they can force the banning of search results not just inside their own jurisdictions, but assert that jurisdiction across the globe.
Google began delisting search content in response to the Costeja ruling in July of 2014. Search links that are delisted in response to French citizens’ requests are removed from the local French domain (google.fr) as well as all of Europe. In early 2016 the company announced that it would further restrict access to links delisted in Europe by using geolocation technology to restrict access to the content on any Google Search domain when an individual searches from France. Despite this, the French authorities continue to demand global removal of these links from all Google search domains – regardless of from where in the world they are accessed.
“We are concerned about the impact of the CNIL order, which effectively allows the government of one country to dictate what the rest of the world is allowed to access online,” said GNI Board Chair Mark Stephens, CBE. “Enshrined in international law is the principle that one country cannot infringe upon the rights of citizens of another country,” he said.
Online search engines and intermediaries are vital tools to inform public discourse, hold the powerful to account, and highlight injustice.
“The right of academics, journalists, historians and all citizens to access complete and uncensored information is the bedrock of civic participation and a free society,” said GNI Executive Director, Judith Lichtenberg.
“This ruling could set the stage for a global internet where the most censored and repressive societies will effectively dictate the standard for all humanity,” Mr Stephens said.
It is highly problematic that the authorities in one country should be able to force the global removal of search information that even if deemed inadequate, inaccurate or irrelevant under the criteria of the Costeja ruling, is arguably still lawful, and is publicly available in other countries. That same information could also be the subject of legal protections in other countries. This includes laws that criminalize the criticism of leaders and governments and laws that ban content pertaining to religious or ethnic minorities, LGBT people, or relating to women’s health.
Previous statements from GNI about the implications of the global enforcement of the ‘right to be forgotten’, can be found on website.
19 May 16 | Hungary, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features
In early April 2016, major Hungarian news website vs.hu began publishing less than normal. On 25 April a dozen journalists, including editor-in-chief Olivér Lebhardt, resigned. While the newsroom is still functioning, its future is yet to be decided by its owners, according to daily newspaper Népszabadság.
The mass resignation was prompted by revelations that the site, owned by New Wave Media (NWM), had received funding from foundations established by the Hungarian National Bank, the country’s central bank. The financing totaled more than 500 million HUF ($1.8 million).
NWM is owned by Czech company Bawaco Invest, which, Hungarian news site 444.hu reported, can be linked to Tamás Szemerey, a cousin of the central bank’s governor, György Matolcsy. The company issued a statement denying Szemerey’s ownership, according to the Financial Times.
The educational foundations were established in 2014 by Matolcsy, a politician allied to Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán. The foundations were endowed with over 314 billion forints ($1.1 billion) of central bank funding that was then invested in government bonds, Reuters reported.
The finances of these foundations were kept secret, but after a ruling from the country’s constitutional court in March, their contracts were published on 22 April 2016. Since then, the press has delighted in revelations of the foundations’ profligacy, The Economist wrote. The bank’s foundations spent money on real estate and artworks, as well as funding web projects covering social and economic issues.
“I was informed by the editor-in-chief a day before [the NWM disclosures], on Wednesday 21 April 2016,” Attila Bátorfy, one of the journalists who resigned told Index on Censorship. “That day there was a meeting, where István Száraz, the CEO of the publishing company deferred to answer the journalist’s questions. Then on Friday, he was talking about only a couple hundred of million HUF, but we knew there would be a huge scandal.”
On the evening of 23 April the first articles about the foundations’ spending were published. The next day vs.hu journalists issued a joint statement saying that while some of them knew that part of their editorial projects were sponsored by the bank’s foundations, they had no knowledge of the extent of the financing, Bátorfy recalled.
“We are also surprised and shocked by the data published by the foundations,” the journalists wrote. The editorial team said that there was no interference with the content of the articles — even in projects that were sponsored.
“On that Saturday evening, we held an emergency meeting in my apartment. About 15 colleagues were present, and we talked about the minimal requirements we, as journalists, expect from our publisher, to consider continuing our work at vs.hu. We had no opportunity to present these demands, because in his opening speech the CEO made it clear that the situation is beyond hope,” Bátorfy recalled.
“Journalists started to hand in their resignations. Those working for the politics, economy, culture and multimedia sections said the situation made their work impossible, they lost credibility, and there is no reason to continue,” he told Index.
Bátorfy, who had worked for vs.hu for three months, said that he had accepted the role after he was told that the site was financed by private and state advertising and money from the owner.
In the wake of the revelations, the Editor-in-Chief’s Forum issued a statement asking parliament to pass a law that would require the transparent disclosure of ownership and state funding of media outlets. “This would be beneficial to the market transparency, and would decrease the defenselessness of the media workers,” the group said.
Hungary’s ruling conservative Fidesz party has been making changes to the country’s media market since it came to power in 2010. Most recently the government cut funding to culture magazines. In 2015 Hungarian public media laid off scores of journalists as its funding was cut, according to reports on MMF. In the case of Hungarian private TV station RTL Klub, an ongoing conflict led to a ban of its news reporters and the dismissal of the television network’s CEO. Observers like 2014 Index award-winning Tamás Bodoky have noted that government advertising contracts have been used as a “powerful censorship instrument”.
Access to information was restricted through a series of amendments in the freedom of information law in July 2015, but the free movement of journalists in the parliament building was also strictly regulated. As a consequence, journalists trying to ask questions about the National Bank scandal were banned from the Parliament.
On Tuesday 26 April 2016, a number of media outlets received notes from House Speaker László Kövér, in which the Fidesz politician informed them that their journalists were barred from entering the building for “filming without a permit” and “consciously breaking the rules”. The ban came a day after journalists attempted to question Fidesz politicians, including Orbán and Kövér. While journalists and camera crews followed MPs, they entered into a secure area that was out of bounds to members of the press.
The editor-in-chief of Népszabadság newspaper (nol.hu), András Murányi, wrote a response to the letter: “I can assure you that Népszabadság had no intention of breaking the rules. The goal of journalists working at Népszabadság was to ask those who are elected and are paid representatives of the people questions regarding public affairs, and to publish their answers. As for answers – as we could see this time again – we seldom get any, as we are more and more prevented to act as free press in Parliament (…) lately we can only do our job in a constricted area,” Murányi said.
18 May 16 | About Index, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, Counter Terrorism, Statements, United Kingdom
The government’s planned Counter-Extremism and Safeguarding Bill must be carefully crafted to avoid damaging freedom of expression.
“The government’s move to counter extremism must not end up silencing us all,” said Jodie Ginsberg, Chief Executive of Index on Censorship. “We should resist any attempts to make it a crime for people of faith to talk publicly about their beliefs, for political parties to voice unpopular views, and for venues from universities to village halls to host anyone whose opinions challenge the status quo. We urge the government to use its consultation to ensure this does not happen.”

The government’s plans to tackle extremism through a “new civil order regime” and other measures must not undermine the very values it aims to defend, free expression organisations said on Wednesday.
Index on Censorship, English PEN, the National Secular Society, the Christian Institute, ARTICLE 19, Big Brother Watch, Manifesto Club and the Peter Tatchell Foundation welcomed plans to consult on the matter, following their demands earlier this year.
The proposals for a new law, outlined in the Queen’s Speech, are more ambiguous than earlier proposals made by this government, but nevertheless leave open broad measures to police a wide swathe of speech and should be resisted, the groups said.
The new legislation will include giving law enforcement agencies new powers to protect vulnerable people – including children – “from those who seek to brainwash them with extremism propaganda so we build a stronger society around our shared liberal values of tolerance and respect”, according to the background notes accompanying the Queen’s Speech.
More specifically, the government proposals are to legislate:
· Stronger powers to disrupt extremists and protect the public.
· Powers to intervene in intensive unregulated education settings which teach hate and drive communities apart.
· A new civil order regime to restrict extremist activity, following consultation.
· Closing loopholes so that Ofcom can continue to protect consumers who watch internet-streamed television content from outside the EU on Freeview.
The new proposals should avoid creating an environment that could make it even harder for people of all faiths and ideologies to express their beliefs and opinions, the groups said. Current legislation already prohibits incitement to violence and terrorism, and a compelling case for broadening them further through civil measures has not been made.
“The government’s move to counter extremism must not end up silencing us all,” said Jodie Ginsberg, Chief Executive of Index on Censorship. “We should resist any attempts to make it a crime for people of faith to talk publicly about their beliefs, for political parties to voice unpopular views, and for venues from universities to village halls to host anyone whose opinions challenge the status quo. We urge the government to use its consultation to ensure this does not happen.”
The groups said plans to introduce new laws in this area presented three main risks:
1. Definitions
It is still not clear how new legislation would deal with the problem of defining “extremism” in a way that would not threaten free speech.
The government has previously defined extremism broadly as “the vocal or active opposition to fundamental British values, including democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty and the mutual respect and tolerance of different faiths and beliefs”. The continued lack of a clear definition risks outlawing any political expression that does not reflect mainstream or popular views.
Britain already has a host of laws to tackle the incitement of terrorist acts, as well as racial and religious hatred. The government has previously been criticised for the broad definitions of “terrorism” in existing legislation, and the definition of ”extremism” in the Prevent Strategy. The proposed bill must not introduce new vague terminology and widen the net even further.
“The government’s approach to extremism is unfocused. Unless we can make them see sense, the range of people who could find themselves labelled ‘extremist’ by their own government is about to get a whole lot wider,” said Simon Calvert of the Christian Institute.
2. Nature of new civil orders
The government is ambiguous on whether they are still considering “extremism disruption orders” or “banning orders” within the package of civil measures. Though the promised consultation is welcome, these draconian measures are clearly not off the table.
Baroness Manningham-Buller, former head of MI5, has said previously that extremists need to be exposed, challenged and countered. The proposed measures would have the opposite effect and should not find their way into the new civil order regime.
“Extremism banning orders could mean political activists – or any other activists deemed to be ‘anti-democratic’ – such as environmental activists – could be outlawed in future, thereby undermining democracy itself,” said Jo Glanville, Director of English PEN.
Extremist disruption orders (EDO), suggested under earlier plans for the bill, could have a similar chilling effect on free expression and democracy. Under original plans for EDOs, the police would be able to apply to the high court for an order to restrict the “harmful activities” of an “extremist” individual. The definition of “harmful” could include a risk of public disorder, a risk of harassment, alarm or distress, or the ill-defined “threat to the functioning of democracy”.
Keith Porteous Wood, Executive Director of the National Secular Society, said: “The prosecution thresholds for EDOs – as originally envisaged – are worryingly low – civil, not criminal – yet the consequences of granting of such an order, even if not broken, are likely to be very serious, e.g. rendering the recipient unemployable. Few faced with such a threat are likely to have the resources to mount any defence as proceedings will be at the High Court.”
“No convincing case has been made for the necessity of new measures to restrict free speech. Existing measures are already deterring individuals and groups from engaging in open debate on important issues. The plans re-announced today, though watered down, do not sufficiently address criticism the government has received; they not only threaten to further chill legitimate speech, but may also fuel divisive ideologies and make us less safe,” said Thomas Hughes, Executive Director of ARTICLE 19.
3. International implications
Governments across the world – such as Russia, Turkey and Egypt – are increasingly using national security laws to censor free expression, including in the media. The government’s moves are likely to legitimise and embolden these efforts, setting a counter-productive example.
UN and regional human rights experts have jointly raised concerns regarding the potential impact of broadly defined initiatives to counter violent extremism on the free expression of minority and dissenting views. They have called for responses to violent extremism to be evidence based, and to respect international human rights law on freedom of expression and non-discrimination.
Conclusion
We call on the government to consult widely with all stakeholders, including civil society and minority groups, to ensure that a bill intended to tackle extremism does not undermine one of the values at the heart of democracy: that of free speech for all.
For more information or to arrange interviews, please contact:
– Melody Patry, head of advocacy, Index on Censorship.
melody@indexoncensorship.org; 0207 963 7262
– Robert Sharp, head of communications, English PEN
robert@englishpen.org; 020 7324 2535



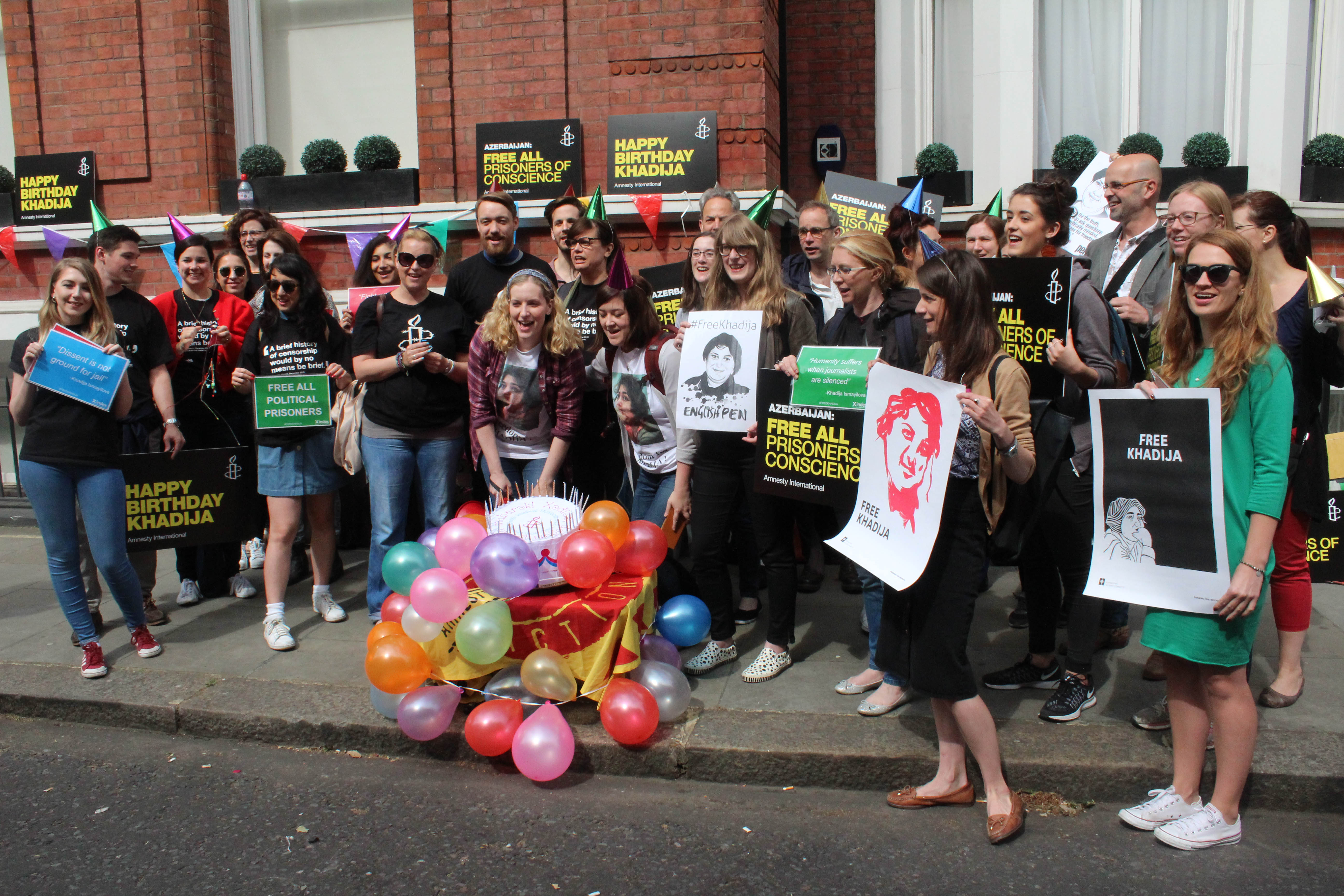






 Azerbaijan’s Supreme Court has
Azerbaijan’s Supreme Court has 




