29 Jul 15 | mobile, Morocco, News and features

Ali Lmrabet was on hunger strike outside the UN building in Geneva (Photo: alisinpapeles.blogspot.com.es)
Moroccan officials said on Tuesday 28 July that satirist Ali Lmrabet’s passport would be renewed immediately. Lmrabet had been holding a hunger strike in front of the UN’s Geneva offices since 24 June because of refusals to renew his identity documents.
“The Moroccan authorities have publicly committed to renew his passport immediately, and not put obstacles to do the same with their identity. We hope that the authorities keep their word,” Lmrabet’s partner Laura Feliu wrote in an email to Index on Censorship.
Lmrabet called off his hunger strike and was admitted to hospital in Geneva for a checkup, according to Feliu.
In a period spanning over a decade, Lmrabet, who was the editor of two satirical publications, was continuously targeted by Moroccan authorities. In 2003, he was jailed for reporting on personal and financial affairs of Morocco’s King Mohammed VI. His magazine Demain was banned. Though initially handed down a three-year sentence, Lmrabet was released after six months. But his troubles were far from from over: in 2005, he was banned from practising journalism in his home country for ten years, over comments made about the dispute in Western Sahara between Morocco and the Algerian-backed Polisario Front.
As his ban expired in April this year, he returned to Morocco with the aim of relaunching Demain. But there he was denied a residency permit, without which he is unable to set up the magazine. In a further complication, he also needs the residence permit to renew his passport. When this expired on 24 June, Lmrabet, who was in Geneva to participate in a session of the UN Human Rights Council, decided to start a hunger strike.
Related:
• “He is denied his right to an identity”: why a Moroccan satirist is on hunger strike
• Open letter to the King of Morocco in support of Ali Lmrabet
This article was posted on 29 July 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
28 Jul 15 | Magazine, mobile

Index on Censorship magazine cover, November/December 1977
Novelist, playwright and short story writer Milan Kundera is one of the many Czech authors who, though they represent the best in their country’s contemporary literature, cannot publish their work in Prague. Acclaimed in France, where in 1973 he won a major literary prize for his last but one novel, and published in English, German, Dutch, Swedish, Finnish, Hebrew, Japanese and many other languages, he remains one of the 400 or more writers who are “on the index” in post-invasion, “normalised” Czechoslovakia.
Born in Brno forty-eight years ago, Kundera was until 1969 a professor at the Prague Film Faculty, his students including all the young film makers who were to bring fame to the Czechoslovak cinema in the sixties with such movies as The Firemen’s Ball, A Blonde in Love and Closely Observed Trains. In 1960 he published a highly influential essay, The Art of the Novel. Two years later the National Theatre put on his first play, The Owners of the Keys. Produced by Otomar Krejca, the play was an immediate success and was awarded the State Prize in 1963.
His first novel, The Joke, came out in 1967, being reprinted twice in a matter of months and reaching a total of 116,000 copies. This book, whose appearance was delayed by a long, determined struggle with the censor, opened the way to publication abroad, where Aragon called it one of the greatest novels of the century.
After the Soviet invasion Kundera was forced to leave the faculty, his work was no longer published in Czechoslovakia, all his books being removed from the public libraries. Since then, his works have only come out in translation. Life Is Elsewhere (see Index 4/1974, ppJ3-62) first appeared in Paris in 1973, where it won the Prix Medicis for the best foreign novel of the year. The French version of his latest novel, The Farewell Party, way published last year.
In 1975 Kundera was offered a professorship by the University of Rennes and obtained permission from the Czechoslovak authorities to go to France, which is now his second home. All his prose works now exist in English translation. (For an appraisal of his work, see Robert C. Porter’s article in Index 4/1975, pp.41-6). Unfortunately, The Joke – published by Macdonald in London and Coward McCann in New York in 1969 – was drastically cut without the author’s consent, forcing Kundera to write an indignant letter to the Times Literary Supplement, disclaiming all responsibility – an interesting case of a non-political, commercial censorship. The irony of the situation was certainly not lost on the author, who is a master of the genre. His collection of short stories, Laughable Loves (with a foreword by Philip Roth) and his other two novels have since been published by Knopf, and The Farewell Party has just been brought out by John Murray in London.
This selection of Kundera’s stimulating and often provocative views on such topics as the writer in exile, committed literature, the death of the novel, the nature of comedy, and so on, has been compiled by George Theiner.
Writing for translator
I am certainly in a rather odd situation. I write my novels in Czech. But since 1970 I have not been allowed to publish in my own country, and so no one reads me in that language. My books are first translated into French and published in France, then in other countries, but the original text remains in the drawer of my desk as a kind of matrix.
In the autumn of 1968 in Vienna I met a fellow-countryman, a writer, who had decided to leave Czechoslovakia for good. He knew that this meant his books would no longer be published there. I thought he was committing a form of suicide, and I asked him if he was reconciled to writing only for translators in future, if the beauty of his mother tongue had ceased to have any meaning for him. When I returned to Prague, I had two surprises in store for me: even though I didn’t emigrate, I too was forced from then on to write for translators only. And, paradoxical as it may seem, I feel it has done my mother tongue a lot of good.
Conciseness and clarity are, for me, what makes a language beautiful. Czech is a vivid, suggestive, sensuous language, sometimes at the expense of a firm order, logical sequence and exactitude. It contains a strong poetic element, but it is difficult to convey all its meanings to a foreign reader. I am very concerned that I should be translated faithfully. Writing my last two novels, I particularly had my French translator in mind. I made myself-at first unknowingly-write sentences that were more sober, more comprehensible. A cleansing of the language. I have a great affection for the eighteenth century. So much the better then if my Czech sentences have to peer carefully into the clear mirror of Diderot’s tongue.
Goethe once said to Eckermann that they were witnessing the end of national literature and the birth of a world literature. I am convinced that a literature aimed solely at a national readership has, since Goethe’s time, been an anachronism and fails to fulfil its basic function. To depict human situations in a way which makes it impossible for them to be understood beyond the frontiers of any single country is a disservice to the readers of that country too. By so doing we prevent them from looking further than their own backyard, we force them into a straitjacket of parochialism. Not to have one’s work published in one’s own country is a cruel lesson, but I think a useful one. In our times we must consider a book that is unable to become part of the world’s literature to be non-existent.
 Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Ahead of our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Ahead of our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
14 July: The power of satirical comedy in Zimbabwe by Samm Farai Monro | 17 July: How to Win Friends and Influence an Election by Rowan Atkinson | 21 July: Comfort Zones by Scott Capurro | 24 July: They shoot comedians by Jamie Garzon | 28 July: Comedy is everywhere by Milan Kundera | Student reading lists: Comedy and censorship

Central Europe
As a Czech writer I don’t like being pigeon-holed in the literature of Eastern Europe. Eastern Europe is a purely political term barely thirty years old. As far as cultural tradition is concerned, Eastern Europe is Russia, whereas Prague belongs to Central Europe. Unfortunately, West Europeans don’t know their geography. This ignorance could be fatal, as indeed it has proved to be in the past. Remember Chamberlain in 1938 and his words about “a small country we know little about”.
The nations of Central Europe are small and far too well concealed behind a barrier of languages which no one knows and few study. And yet it is this very part of Europe which, over the past fifty years, has become a kind of crucible in which history has carried out incredible experiments, both with individuals and with nations. And the fact that those living in Western Europe have only very simplified notions, have never taken the trouble properly to study what is going on a few hundred kilometres from their own tranquil homes can, I repeat, be fatal to them.
From this Central Europe have come several major cultural impulses, without which our century would be unthinkable: Freud’s psychoanalysis; Schonberg’s dodecaphony; the novels of Kafka and Hasek, which have discovered a grotesque new literary world and the new poetry of the non-psychological novel; and finally structuralism, born and developed in Prague in the twenties, to become a fashion in West Europe thirty years later. I grew up with these traditions and have little in common with Eastern Europe. Forgive me if I seem to dwell on these ridiculous geographical details.
Small nations
Large nations are obsessed with the idea of unification. They see progress in unity. Even President Carter’s message to the inhabitants of outer space contains a passage expressing regret that the world is as yet divided into nations and the hope that it will soon come together in a single civilisation. As if unity were a cure for all ills. A small nation, in its efforts to maintain its very existence, fights for its right to be different. If unification is progress, then small nations are anti-progressive to the core, in the finest sense of the word. Big nations make history, small ones receive its blessings. Big nations consider themselves the masters of history and thus cannot but take history, and themselves, seriously. A small nation does not see history as its property and has a right not to take it seriously.
Franz Kafka was a Jew, Jaroslav Hasek a Czech – both members of a minority. When the First World War broke out, Europe was seized by a paroxysm of warlike nationalism, which did not spare even Thomas Mann or Apollinaire. In Franz Kafka’s diary we can read: “Germany has declared war on Russia. Went swimming in the afternoon“. And when, in 1914, Hasek’s Schweik learns that Ferdinand has been killed, he asks which one – the barber’s apprentice who once drank some hair oil, or was it the Ferdinand who collects dogshit on the pavement?
They say the greatness of life is to be found only where life transcends itself. But what if all transcendent life is history – which does not belong to us anyway? Is there only Kafka’s absurd
office? Only the daftness of Hasek’s army? Where then is the greatness, the gravity, the meaning of
it all? The genius of the minorities has discovered a world without gravity and greatness. Discovered its grotesqueness. Hegel’s concept of history -wise and ascending, like assiduous schoolgirls, ever higher on the staircase of progress – has been inconspicuously buried by Hasek and Kafka. In this sense we are their heirs.
Our Prague humour is often difficult to understand. The critics took Miloš Forman to task because in one of his films he made the audience laugh where they shouldn’t. Where it was out of place. But isn’t that just what it is all about? Comedy isn’t here simply to stay docilely in the drawer allotted to comedies, farces and entertainments, where “serious spirits” would confine it. Comedy is everywhere, in each one of us, it goes with us like our shadow, it is even in our misfortune, lying in wait for us like a precipice. Joseph K. is comic because of his disciplined obedience, and his story is all the more tragic for it. Hasek laughs in the midst of terrible massacres, and these become all the more un- bearable as a result. You see, there is consolation in tragedy. Tragedy gives us an illusion of greatness and meaning. People who have led tragic lives can speak of this with pride. Those who lack the tragic dimension, who have known only the comedies of life, can have no illusions about themselves.
When I came to France, the thing that astonished me most was the difference in national humour. The French are immensely humorous, witty, gay. But they take themselves and the world seriously. We are far more sad, but we take nothing seriously.
Committed literature
All my life in Czechoslovakia I fought against literature being reduced to a mere instrument
of propaganda. Then I found myself in the West only to discover that here people write about the literature of the so-called East European countries as if it were indeed nothing more than a propaganda instrument, be it pro- or-anti- Communist. I must confess I don’t like the word “dissident”, particularly when applied to art. It is part and parcel of that same politicising, ideological distortion which cripples a work of art. The novels of Tibor Dery, Miloš Forman’s films – are they dissident or aren’t they? They cannot be fitted into such a category. If you cannot view the art that comes to you from Prague or Budapest in any other way than by means of this idiotic political code, you murder it no less brutally than the worst of the Stalinist dogmatists. And you are quite unable to hear its true voice. The importance of this art does not lie in the fact that it accuses this or that political regime, but in the fact that, on the strength of social and human experience of a kind people over here cannot even imagine, it offers new testimony about the human conditions.
If by “committed” you mean literature in the service of a certain political creed, then let me tell you straight that such a literature is mere, conformity of the worst kind.
A writer always envies a boxer or a revolutionary. He longs for action and, wishing to take a direct part in real life, makes his work serve immediate political aims. The nonconformity of the novel, however, does not lie in its identification with a radical, opposition political line, but in presenting a different, independent, unique view of the world. Thus, and only thus, can the novel attack conventional opinions and attitudes.
There are commentators who are obsessed with the demon of simplification. They murder books by reducing them to a mere political interpretation. Such people are only interested in so-called “Eastern” writers as long as their books are banned. As far as they’re concerned, there are official writers and opposition writers – and that is all. They forget that any genuine literature eludes this sort of evaluation, that it eludes the Manichaeism of propaganda.
There are historical situations which open people’s souls the way you open a tin of sardines. Without the key offered to me by my country’s recent history, I would not, for instance, have been able to discover in Jaromil’s soul the incredible coexistence of the Poet and the Informer.
We have got into the habit of putting the blame for everything on “regimes”. This enables us not to see that a regime only sets in motion mechanisms which already exist in ourselves. A novel’s mission is not to pillory evident political realities but to expose anthropological scandals.
The death of the novel
Since the twenties, everyone seems to have been writing the obituary of the novel – the Surrealists, the Russian avant-garde, Malraux, who claims the novel has been dead since the time Malraux stopped writing novels, and so on and so forth. Isn’t it strange? No one talks about the death of poetry. And yet, since the great generation of Surrealists, I know of no truly great and innovatory work of poetry. No one talks about the death of the theatre. No one talks about the death of painting. No one talks about the death of music. Yet, since Schonberg, music has abandoned a thousand-year-old tradition based on tonality and on musical instruments. Varese, Xenakis . . . I am very fond of them, but is this still music? In any case, Varese himself preferred to speak about the organisation of sound rather than music. So, music may have been dead for several decades, yet no one talks about its demise. They talk about the death of the novel, though this is possibly the least dead of all art forms.
To speak of the end of the novel is a local preoccupation of West European writers, notably the French. It’s absurd to talk about it to a writer from my part of Europe, or from Latin America. How can one possibly mumble something about the death of the novel and have on one’s bookshelf A Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel Garcia Marquez? As long as there is human experience which cannot be depicted except in a novel, all conjectures about its having expired are mere expressions of snobbery. It is, of course, possibly true to say that the novel in Western Europe no longer provides many new insights and that for those we have to look to the other part of Europe and to Latin America.
I expect that all this talk of the death of the novel is due to the eschatological thinking of the avant-garde. Spurred on by revolutionary illusions, the avant-garde dreamed of installing a completely new art, a new era. If you like, in the spirit of Marx’s well-known saying about the prehistory and the history of mankind. From this point of view, the novel would belong to prehistory, while history would be ruled by poetry, in which all earlier genres would dissolve and vanish. It’s quite remarkable how this eschatological concept, utterly irrational though it is, has gained general acceptance, becoming one of the commonest clichis of the contemporary snob. He despises the novel, preferring to speak of’ a text’. According to him, the novel is a thing of the past (the prehistory of letters), and this in spite of the fact that the greatest strength of literature over the past 50 years has been in that very sphere-just take Robert Musii, Thomas Mann, Faulkner, Celine, Pasternak, Gombrowicz, Giinter Grass, Boll, or my dear friends, Philip Roth and Garcia Marquez.
The novel is a game with invented characters. You see the world through their eyes, and thus you
see it from various angles. The more differentiated the characters, the more the author and the reader have to step outside themselves and try to understand. Ideology wants to convince you that its truth is absolute. A novel shows you that everything is relative. Ideology is a school of intolerance. A novel teaches you tolerance and understanding. The more ideological our century becomes, the more anachronistic is the novel. But the more anachronistic it gets, the more we need it. Today, when politics have become a religion, I see the novel as one of the last forms of atheism.
When I was a boy I used to idealise the people who returned from political imprisonment. Then I discovered that most of the oppressors were former victims. The dialectics of the executioner and his victim is very complicated. To be a victim is often the best training for an executioner. The desire to punish injustice is not only a desire for justice, pure and simple, but also a subconscious desire for new evil…
Jacob knows all this when he thinks about others. He does not know it in relation to himself. So that all it needs is a single unguarded moment, when his reason takes a nap, and his subconscious dislike of people, his suppressed hatred, take over and an innocent girl dies. The more noble a person is, the darker the shadow of suppressed evil within.
A true novel always stands beyond hope and despair. Hope is not a value, merely an unproven supposition that things will get better. A novel gives you something far better than hope. A novel gives you joy. The joy of imagination, of narration, the joy provided by a game. That is how I see a novel – as a game. One of the characters in The Farewell Party occasionally has a halo round his head. The spa gynaecologist cures his patients by injecting his own semen and becomes the father of many children. Am I being serious, or is it just a joke? It is a game . . .
Of course, if the game is to be worthwhile, it must be played and must be about something serious. It must be a game with fire and demons. The game of the novel combines the lightest and the hardest, the most serious with the most light-hearted.
Milan Kundera is a Czech-born writer who has been living in exile in France since 1975.
 This article is from the November/December 1977 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives. Subscribe here, or buy a single issue. Every purchase helps fund Index on Censorship’s work around the world. For reproduction rights, please contact Index on Censorship directly, via vicky@indexoncensorship.org
This article is from the November/December 1977 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives. Subscribe here, or buy a single issue. Every purchase helps fund Index on Censorship’s work around the world. For reproduction rights, please contact Index on Censorship directly, via vicky@indexoncensorship.org
27 Jul 15 | Academic Freedom, Magazine, mobile, Student Reading Lists
Index on Censorship has had a longstanding interest in the issue of freedom of expression relating to satire. Drawing on Index on Censorship magazine’s more than 40-year-archive, this reading list compiles articles looking at the relationship between comedy and censorship, including a recent piece by Samm Farai Monro aka Comrade Fatso, founder of Zambezi News, Zimbabwe’s leading satirical news programme.
Students and academics can browse the Index magazine archive in thousands of university libraries via Sage Journals.
Comedy and censorship articles
Comedy of Terrors: Zimbabwean satirists challenge power by Samm Farai Monro
Samm Farai Monro, June 2015; vol. 44, 2: pp. 78-82.
Samm Farai Monro, aka Comrade Fatso, talks about founding Zimbabwe’s leading satirical show, and how the nation’s comedians challenge politicians and take on longstanding taboos
Out in Africa by Scott Capurro
Scott Capurro, March 2001; vol. 30, 2: pp. 190-194.
Stand up comedian Scott Capurro explores the limits of stand-up comedy in South Africa
Laughter Lines by Arthur Matthews
Arthur Matthews, March 2015; vol. 44, 1: pp. 86-88.
Co-writer of comedy sitcom, Arthur Matthews discusses censorship in comedy and satire in Ireland
Opiate of the Masses by Saeed Okasha
Saeed Okasha, November 2000; vol. 29, 6: pp. 106-111.
“No matter what form it takes, comedy is a political act in the first degree. It serves as an outlet for frustrations and is a way of putting impossible and incomprehensible situations into perspective. Egyptian society today is urgently in need of such therapy”
Comfort Zones by Scott Capurro
Scott Capurro, November 2000; vol. 29, 6: pp. 134-138.
Stand-up Comedian Capurro provides commentary on how political correctness stifles comedy
South Korea: A Serious Business by Andrew H. Malcolm
Andrew H. Malcolm, July 1978; vol. 7, 4: pp. 62.
A brief look at how comedy was strictly censored in South Korea, as the “serious government has cracked down on humour.”
Side road, dark corner by Edgar Langeveldt
Edgar Langeveldt, November 2000; vol. 29, 6: pp. 86-89.
A stand-up comedian in Zimbabwe describes the dangers comedians face for covering controversial topics, including an account of his own violent attack in 1999.
They shoot comedians by Jamie Garzon
Jamie Garzon, January 2000; vol. 29, 1: pp. 132-133.
Transcripts of television satires by journalist and humourist Jaime Garzon. In August of 1999, Garzon was executed on his way to the Radionet studio.
How to Win Friends and Influence an Election by Rowan Atkinson
Rowan Atkinson, May 2005; vol. 34, 2: pp. 117-120.
Atkinson, a foremost British comedian, opposes the government’s proposed law of Incitement of Religious Hatred in a speech given at the House of Lords, as he considers its dire effects on his profession.
Dark Magic by Martin Rowson
Martin Rowson, February 2009; vol. 38, 1: pp. 140-164
Author and cartoonist Martin Rowson expounds on satire, discussing how breaking cultural taboos often stimulates the best political satire
Confronting fear with laughter by Martin Smith
Martin Smith, January 1992; vol. 21, 1: pp. 8-10.
Smith writes about the terror that Burma’s army has inflicted, specifically mentioning the comedian Zargana, who was punished for his bold, pointed jokes.
Comedy is everywhere by Milan Kundera
Milan Kundera , November 1977; vol. 6, 6: pp. 3-7
Banned novelist, playwright, and short story writer Kundera writes on committed literature, the death of the novel, the nature of comedy, and more topics.
“Comedy isn’t here simply to stay docilely in the drawer allotted to comedies, farces and entertainments, where ‘ serious spirits’ would confine it.”
Egypt: Shame on the censor by Karim Alrawi
Karim Alrawi, December 1983; vol. 12, 6: pp. 40..
Discusses the charges filed against the comic actor Said Saleh
“We can only assume that Said Saleh has been made an example of for the shameful act of making people laugh.”
The reading list for comedy and censorship can also be found at the Sage website.
 Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Prior to our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Prior to our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
14 July: The power of satirical comedy in Zimbabwe by Samm Farai Monro | 17 July: How to Win Friends and Influence an Election by Rowan Atkinson | 21 July: Comfort Zones by Scott Capurro | 24 July: They shoot comedians by Jamie Garzon | 28 July: Comedy is everywhere by Milan Kundera

27 Jul 15 | Campaigns, mobile, Morocco, Statements
To Your Majesty Mohammed VI,
At a time when Morocco is advocating openness, democratisation and full respect for human rights as instruments for confronting the future, we receive the news of the hunger strike begun by the journalist Ali Lmrabet. For this reason, we wish to pass on to you our deep concern for the situation of this journalist, who has received dozens of international awards and who is deprived of his national identity documents coinciding with the end of a 10-year ban on exercising the profession of journalist in Morocco and also with his announcement that he wishes to return to professional activity.
Freedom of expression and criticism are fundamental elements for the consolidation of a democratic state that is active against regression and intolerance. Any attempt to restrict freedom of expression degrades the image of Morocco and the credibility of its commitment to the rule of law.
Precisely because, from here, we wish to lend our full support to any effort to transform Morocco developed at different levels of the political world and civil society in the country, we are writing to you to express our serious concern at the current situation of Ali Lmrabet, whose life is in danger.
For all these reasons, we would ask you to reflect on this to give instructions to the administration in your country, and its diplomatic staff in Switzerland in particular, to renew all Ali Lmrabet’s Moroccan citizenship documents.
Without a residence certificate, passport and other documents related to journalistic work, Ali Lmrabet would become the first Moroccan deprived of his civil and political rights.
We do not need to give you, Your Majesty, lessons in the fact that the deprivation of these rights is contrary to all liberties, including fundamental freedoms, freedom of expression and, in the case of Ali, the internationally recognised and acclaimed right to freely exercise the profession of journalist. The only thing we would ask you, Your Majesty, in your capacity as Head of State, is to strictly apply the provisions of the Moroccan Constitution, giving the right to all citizens to fully and freely exercise their profession, in this case as journalist and editor of publications in Morocco.
We look forward to your considered response.
Yours sincerely,
Letter signed by the following:
Míriam Acebillo Baqué, President of Lafede.cat, Organisations for Global Justice
Mariano Aguirre, Director of Norwegian Peacebuilding Resource Centre (Norway)
Cinta Arasa, Coordinator of the Persecuted Writers Committee
Carmen Arenas, President of Catalan PEN
Homero Aridjis, Emeritus President of International PEN
Jordi Armadans, Director of FundiPau (Peace Foundation)
Sion Assidon, former Secretary General of Transparency-Morocco
Margaret Atwood, Vice-President of Canada International PEN, Prince of Asturias Award
Danielle Auroi, MP of the National Assembly of France
Juan Tomás Ávila Laurel, Writer, HM Award International Odón Betanzos Palacios of the New York Circle of Ibero-American writers and poets (Equatorial Guinea)
Malén Aznárez, President of Reporters without Borders (RSF- Spanish section)
Elisabeth Badinter, Philosopher
Ekbal Baraka, Chair of PEN International Women Writers Committee, former president of Egyptian PEN
Isaías Barreñada Bajo, University Professor and Human Rights activist
Ana Barrero Tiscar, Peace Culture Foundation
Mark Barwick, Policy Adviser at Human Rights Without Frontiers International (Switzerland)
David Bassa i Cabanas, Journalist, president of the Barnils Group of Journalists
Lluís Bassets, Deputy director of El Pais (Spain)
Anouar Bassi, Transparency 25 President (Tunisia)
Abdejelil Bedoui, Economist and member of the FTDES Steering committee
Sélim Ben Abdesselem, Former member of the Tunisian National Constituent Assembly
Abdelkader Benali, Writer and journalist, Libris Prize (Netherlands)
Thijs Berman, Former Dutch MP of the European Parliament
Mylène Botbol–Baum, Writer, University professor of philosophy and bioethics
Marian Botsford Fraser, Writer and journalist, Chair of Writers in Prison Committee, PEN International Canada
Jean-Marcel Bouguereau, Journalist Le Nouvel Observateur and former chief editor of Libération
Sfia Bouarfa, Belgian honorary MP and former senator
Jim Boumelha, President of the International Federation of Journalists (IFJ)
François Burgat, Political scientist, Research Director of CNRS
Teresa Cadete, Portuguese writer, board member of PEN International
Lindsay Callaghan, President of PEN South Africa
Maria Cañadas, President of Catalonia Amnesty International (AIC)
Gemma Calvet, MP of Parliament of Catalonia (Spain)
Carles Campuzano, MP of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Marius Carol, Editor of La Vanguardia
Ignacio Cembrero, Journalist, former correspondent of El País in Maghreb
Nadia Chaabane, Former deputy of Tunisian National Constituent Assembly
Alain Chabod, International Consultant, former journalist of France Television
Luc Chartrand, Journalist, Radio-Canada
Larbi Chouikha, University professor; Institut de Presse et des Sciences de l’Information (IPSI) (Tunisia)
John Maxwell Coetzee, Writer, Nobel Prize in Literature 2003, Vicepresident of PEN International
Robert Coover, Writer, William Faulkner Foundation Award, American Academy of Arts and Letters, and National Endowment of the Arts (USA)
Olivier Corten, Professor; Centre of international law of ULB; Brussels
Joan Coscubiela, Deputy of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Olivier Da Lage, Journalist, Vice-president of IFJ, RFI and SNJ
Luc Dardenne, Filmmaker
Eric David, Emeritus professor of International Law; Chairman of The International Law Centre of the ULB
Ascensión de las Heras, MP of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Antonio Della Rocca, President of the Trieste PEN Center, Member of the Board of PEN International (Italy)
Christophe Deloire, Secretary General of Reporters Without Borders
Nicolas Dot Pouillard, Resercher of MAEE
Christos Doulkeridis, President of ECOLO group in the Parliament of the Wallonie-Bruxelles Federation (Belgium)
André du Bus, Deputy of Wallonie-Bruxelles Federation
Josy Dubié, Honorary senator (Belgium), former journalist and ONU official
François Dubuisson, Professor, International Law Centre of ULB (Brussels)
Patrick Dupriez, Co-chair of Ecolo party
Isabelle Durant, Brussels MP (Belgium)
Mohamed El Battiui, President of the Amazigh World Assembly
Najat El Hamchi, Writer, Ramon Llull Prize
Ahmed El Khannous, MP, Brussels Parliament
Mahmoud El May, MP and Member of the National Constituent Assembly (Tunisia)
Isabelle Emmery, Brussels Member of Parliament
Mathias Enard, Writer, Gouncourt Prize 2012
Charles Enderlin, Journalist, former France2 correspondent in Israel
Moris Farhi, MBE Vice-President, PEN International
Halim Feddal, Secretary General of the National Association for the Fights against corruption (Algeria)
Soledad Gallego-Díaz, Journalist of El País
Vicent Garcés, Former Member of the European Parliament
María Caridad García Álvarez, MP of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Lise Garon, Professor, Laval University
Zoé Genot, Ecolo MP, Brussels Regional Parliament
François Gèze, President and chief editor of Éditions La Découverte (France)
Jodie Ginsberg, Chief Executive Officer of Index on Censorship
Henri Goldman, Editor of Politique, revue de débats and MICmag (Belgium)
Eric Goldstein, human rights activist (United States)
Elsa González, FAPE President (Spanish Press Associations Federation)
Juan Goytisolo, Writer, National Prize of Spanish Letters and Miguel de Cervantes Prize
Rafael Grasa Hernández, President of Institut Català Internacional per a la Pau
Ricardo Gutiérrez, Secretary general of European Federation of Journalists (EFJ)
Maher Hanin, Member of steering committee of FTDES
Abderrahmane Hedhili, President of Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights (FTDES)
Seymour M. Hersh, American journalist
Francis Hickel, Coordinator Pâquis Solidarity Space, Geneva
Jesús Iglesias Fernández, Senator (Spain)
Jon Iñárritu García, MP of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Véronique Jamoulle, MP, Brussels Parliament
Jean-Jacques Jespers, University Professor, Université libre de Bruxelles
Oriol Junqueres i Vies, Chairman of the party “Esquerra Republicana de Catalunya” (ERC) and opposition leader in Parliament of Catalonia
Lucina Kathmann, Writer, Vice-president of PEN International (United States)
Salam Kawakibi, Arab Reform Initiative, president of the Initiative for a New Syria
Melek Kefif, Doctor and member of the Steering committee of FTDES
Charefeddine Kellil, Lawyer for the families of martyrs and wounded (Tunisia)
Zakia Khattabi, Co-chair of Ecolo Party (Green Belgian)
Kamel Labidi, Tunisian journalist, former director of Amnesty International in Tunisia and former president of the National Authority to Reform Information and Communication (INRIC)
Luis Las Heras, Editor (Spain)
Gilwon Lee, Poète, Poet, Sang-Byeong Cheon Prize and Dong-Ju Yoon Literary Prize, Board Member, PEN International South Korea
Joanne Leedom-Ackerman, vice-president of PEN International (USA)
Jean-Claude Lefort, Former MP at the French Parliament
Emmanuel Lemieux, Essayist, and investigation journalist (France)
Stefano Liberti, journalist and writer, Luchetta Award to the best journalist and Anello Debole Prize
Jonathan Littell, Writer, Goncourt Award and Grand Prix du Roman of the French Academy
Robert Littell, Writer and journalist, Los Angeles Times Book Prize (USA)
Juan López de Uralde, Executive Commission Equo party, former Greenpeace-Spain Director
Bernabé López García, Professor, former member of Averroes Committee Spain-Morocco
Mehdi Mabrouk, Former Culture Minister (Tunisia)
Noël Mamère, MP of the National Assembly and Mayor of Bègles (France)
Sherif Mansour, MENA Program Coordinator, Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ)
Christophe Marchand, Lawyer, Brussels (Belgium)
Jean-Paul Marthoz, journalist, correspondent of the Committe to Protect Journalists (CPJ) in the European Union
Sandrine Martins Espinoza, Lawyer and international consultant for elections (Argentine)
Daniel Patrick Maunier, University Professor, New York University
Fernando Maura Barandarián, Spanish MP, European Parliament
Federico Mayor Zaragoza, President of Foundation for a culture of peace, former Director of UNESCO
Daniel Menschaert, Diplomatic, Honorary Officer of the Federation Wallonia-Brussels in Morocco
Manuela Mesa Peinado, CEIPAZ Director, Peace Culture Foundation
Rosa Montero, Writer and journalist, Grinzane Cavour award and National Journalism Award (Spain)
Quim Monzó, Writer, National Literature award (Catalonia)
Alexandre Niyungeko, President of the Burundi Journalists Union (UBJ)
Elisabeth Nordgren, Chair of the Search Committee, PEN International (Finland)
Vida Ognjenovic, Vicepresident, PEN International (Serbia)
Margie Orford, Board Member, PEN International (South Africa)
Mario Orrù, Observer Coordinator at Democracy International
Bechir Ouarda, Journalist, Former Coordinator of the civil coalition in defence of freedom of expression in Tunisia
Rémy Pagani, Administrative Councillor for the city of Geneva
Andrés Perelló, Former Member of the European Parliament, Spain
Rosana Pérez Fernández, MP of the Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Tone Peršak, Chair of Writers for Peace Committee, Pen International (Slovenia)
Thomas Pierret, University professor, University of Edinburgh
John Ralston Saul, Writer, president of PEN International
Pedro J. Ramírez, Editor of El Español, former editor of El Mundo
Raul Rivero, Cuban writer, UNESCO / Guillermo Cano Press Freedom Prize
Raül Romeva Rueda, Former Spanish MP, European Parliament
Jean Louis Roumegas, MP of the French Parliament
Elena Ruiz Ruiz, University professor (Spain)
Hélène Ryckmans, Member of the Walloon Parliament and the Parliament of the Federation Wallonia-Brussels, Senator
Messaoud Romdhani, Member of the Executive Committee of the Euro-Mediterranean Network of Human Rights (EMHRN), and vice president of the Tunisian League of Human Rights (LTDH)
Amor Safraoui, Chairman of the Independent National Coordination for Transitional Justice (Tunisia)
Mohamed Salah Kherigi, Trade unionist, Vice-president of the Tunisian League of Human Rights (LTDH)
Raffaella Salierno, General Secretary of PEN Català, Director of the GuestWriter programme
Victoria Salvy, Artist and writer (France)
Gervasio Sánchez Fernández, Journalist, National Photography Award, and Ortega y Gasset Journalism Award (Spain)
Mhamed Seghier, Journalist of Liberté (Algeria)
Màrius Serra, Writer, Ramon Llul and Sant Jordi Awards (Catalonia)
Amira Aleya Sghaier, Tunisian historian and university professor
Mohamed Sheriff, President of PEN Sierra Leona
Ricardo Sixto Iglesias, MP at Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Simona Skrabec, Chair of Translation and Linguistic Rights Committee, PEN International
Mohamed Smaïn, Activist in charge of human rights, Algerian League for the Defence of Human Rights (LADDH)
Carles Solà, Journalist, TV3 program Director (Catalonia, Spain)
Carlo Sommaruga, Lawyer, MP of the Swiss parliament
Karima Souid, Former MP of the Tunisians from abroad, member of National Constituent Assembly of Tunisis
Simone Susskind, MP of Brussels – Capital Region
Abdellah Taïa, Moroccan Writer, Flore Award
Alaa Talbi, President of Alternatives, Tunisian Section
Joan Tardà, MP of Congreso de los Diputados (Spain)
Sami Tlili, Tunisian Filmmaker, Cinema and Human Rights Award of Amnesty International and Best documentary of the Arab world Award
Jarkko Tontti, Treasurer of PEN International (Finland)
Manuel Tornare, Swiss MP, former Mayor of Geneva
Carles Torner, Executive Director of PEN International
Estefania Torres, Spanish MP of the European Parliament
Mathew Tree, Writer, Octubre – Andròmina Award
Jane Unrue, Director of the Harvard Scholars at Risk (SAR) Program and Freedom to Write Committee board for PEN, New England (United States)
Miguel Urban, Spanish MP of the European Parliament)
Dominique Vidal, Journalist
Santiago Vidal i Marsal, Judge of Provincial Audience Chamber of Barcelona, Judges for Democracy
Per Wästberg, Writer, President of Nobel Committee for Literature, former President of PEN International
Lawrence Weschler, écrivain, George Polk et Lannan Literary Award (United States)
24 Jul 15 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Campaigns, mobile

Khadija Ismayilova
Investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova declared her innocence at a pre-trial hearing, calling the charges against her poltically motivated.
Ismayilova, who has reported on corruption allegations involving the family of President Ilham Aliyev, is accused of embezzlement, tax evasion and abuse of power. Detained since December 2014, Ismayilova was originally charged with “incitement to suicide”, though that charge was later dropped.
The court barred members of the public, journalists, political figures and foreign diplomats, who had come to observe the proceedings, from entering the courtroom, Contact.az and Radio Free Europe reported.
Ismayilova’s trial was set to begin on 7 August.
“The decision to bar access to the public on the first day of Khadija’s trial underscores the capricious manner in which the government of President Ilham Aliyev is ruling Azerbaijan. Her’s is not the first spurious case aimed squarely at stifling critical voices in civil society. It’s vital that court officials hold the trial in a transparent manner”, Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index on Censorship said.
In the past year major figures in Azerbaijan’s civil society have been silenced through pre-trial detentions and multi-year prison sentences.
An earlier version of this article incorrectly stated that the pre-trial hearing was part of the trial.
Recent coverage:
• Married political prisoners kept apart for 11 months, reunited in court
• Lawyers call for the release of Intigam Aliyev
• Azerbaijan: Silencing human rights
This article was posted on 24 July 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
24 Jul 15 | Events, mobile, Pakistan

Mahenaz Mahmud spoke of her daughter Sabeen’s dedication to Pakistan. (Click for video on Vimeo)
“Tonight, please don’t forget to laugh and dream out loud, that would be the best tribute you could pay to Sabeen”, said Mahenaz Mahmud via video at Unsilencing Pakistan, an event co-hosted by Index on Censorship at London’s Conway Hall on Thursday 23 July.
Three months earlier, Mahenaz’s daughter Sabeen Mahmud was killed by gunmen. On 24 April 2015, travelling home from hosting a panel discussion about the missing people of Balochistan two men on motorbikes surrounded the car and opened fire. Mother survived, daughter didn’t.
Sabeen Mahmud had been a prominent ‘social activist’ and human rights advocate including founding The Second Floor, a cafe dedicated to being a safe space for community discussion. Three months on from her murder, the London event was a tribute to a woman described by so many as an inspiration, a fantastic listener and a champion of free speech and freedom of expression.
Hosted by comedian Aatif Nawaz, the evening was a celebration of Mahmud’s life and Pakistani culture. Multiple speakers, many of whom knew Mahmud well, shared their thoughts on her work and the issues she confronted as she worked to encourage greater openness in Pakistan.
The event began with the trailer from forthcoming documentary Silencing Sabeen, a look back on the life and tragic death of a woman loved by so many. All of those who were close to Mahmud showered praise upon her and told anecdotes of a woman dedicated to the cause of free expression. BBC journalist Ziad Zafar, founder of Pakistan for All and a member of the newly launched Sabeen Mahmud Foundation’s board, said: “She was at the forefront of every progressive movement that has taken precedence in Pakistan in the last decade”. Dr Ayesha Siddiqa from the University of Oxford, who had met Sabeen on a number of occasions, said: “Conversation doesn’t weaken Pakistan. Sabeen knew that to free Pakistan, you need to unsilence it.”
Ali Dayan Hasan, a Pakistani human rights activist, knew Mahmud as a child and watched her grow into a beautiful woman. Of Karachi, her beloved birthplace, he said: “Her life, her achievement, her death is all quintessentially about the city that she came from”.
Childhood friend and Index on Censorship magazine contributor Kamila Shamsie described their blossoming friendship from the moment they met at Kindergarten. She had recently asked friends and colleagues of Sabeen to send her written praise of their late friend. One said: “Her passion was contagious,” while another said: “Sabeen would never have kept the spoils of victory, even if she had fought alone.”
The evening’s speakers also explored the state of Pakistan’s democracy and numerous attacks on free speech in recent times. Tehmina Kazi from British Muslims for Secular Democracy warned that “universal human rights have been tossed aside and been replaced by cultural relativism. The very people who need to have their eyes wide open have their eyes wide shut”.
Shaan Taseer of Pakistan For All, whose father Salmaan was murdered for his opposition to Pakistan’s blasphemy law, spoke forcefully about standing up to nationalist and religious figures like Abdul Aziz.
The New York Times Pakistan Bureau Chief Declan Walsh, who now operates from London after having his visa cancelled by Pakistani authorities, spoke of how, on first arriving in Pakistan in 2004, he was struck by the vibrancy and free speech of the press even though at the time it was under military rule. He called Mahmud’s murder a “very dark watershed in the decline of free speech in Pakistan in the last ten years.”
Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index on Censorship, said: “It takes bravery to be a dissenter at any time but it takes a special kind of courage to stick your head above the parapet in times of danger.”
Other speakers on the night included Annie Zaman from Bytes For All and Suniya Qureshi of the Qismat Foundation.
Paying tribute to Mahmud’s passion for the Art, and T2F’s ongoing role as a gallery and performance space, Pakistani singers and dancers including Kali Chandrasegaram, Hyder Cheema and Ustad Roshan Abbas Khan were also on the programme. In a fitting nod to Mahmud’s well known support for young people and future generations, three students from City and Islington Sixth Form College were also invited, bringing diversity to the bill.
Co-organisers of the event, Yasmin Whittaker-Khan and Anneqa Malik thanked the audience and Index on Censorship, encouraging action to prevent more tragedies like Mahmud’s.
Malik, a personal friend of Mahmud’s, implored people to take personal responsibility for drawing people’s attention to the plights of those in Pakistan themselves rather than shouldering it on to others. She said: “Please don’t let them silence us. Please don’t let them silence Sabeen.”
This article was posted on 24 July 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
24 Jul 15 | mobile, News and features, Sri Lanka
 The Colombo Telegraph, Sri Lanka’s most iconoclastic investigative news website, is gearing up for this year’s second national election. And once again they face the threat of censorship — despite a presidential promise to bring it to an end.
The Colombo Telegraph, Sri Lanka’s most iconoclastic investigative news website, is gearing up for this year’s second national election. And once again they face the threat of censorship — despite a presidential promise to bring it to an end.
January’s polls saw the website blocked to domestic voters by order of authoritarian incumbent president Mahinda Rajapaksa. Unseated by shock winner Maithripala Sirisena, one of the victor’s first acts after the vote was to lift the official banning order.
Unfortunately his officials didn’t get the memo and simply resorted to more subtle and illegal censorship. Their covert interference was exposed by the Colombo Telegraph just a month later, drawing a personal apology from the minister responsible, Mangala Samaraweera, and a promise of a full investigation.
That promised investigation has so far come to nothing, while the later announcement of a general election for August 18 has raised political tensions. This week eight international freedom of expression groups, including Index on Censorship, wrote to Samaraweera reminding him of his promise.
“The media must be free to cover the upcoming campaigns without fear of interference, covert or overt, online or off,” said the groups. Censorship, legal or illegal, may fall hard on independent voices like the Colombo Telegraph unless the state’s secret censors are found and stopped.
Colombo Telegraph editor Uvindu Kurukulasuriya is calling on the government to complete the inquiry as soon as possible and guarantee that the media will be free to report the campaign.
But the Colombo Telegraph has few friends among the current government, led by United National Party prime minister Ranil Wickremesinghe.
The government has been embarrassed by the site’s publication of parts of a leaked 19-page draft parliamentary committee report into an alleged government bond scam linked to Central Bank Governor Arjuna Mahendran and his son-in-law. The dissolution of parliament would have buried its detailed allegations had it not been leaked.
Wickremesinghe said the draft report was ‘false and perverted’ and has no official status. This did not stop him threatening media that cite it with prosecution under an act prohibiting sharing details of committee proceedings before they are presented to parliament itself. The use of the act – much criticised by independent media who have called for its repeal – is designed to deter other journalists following up the story during the election campaign.
Media rights are suddenly looking shaky across the country. Despite pledging to introduce a Right to Information Act as a key part of the Sirisena-Wickremesinghe government’s first 100 days in power, they failed to deliver. And the ruling party set the tone for the election campaign by reportedly pressing state media to downplay coverage of the start of Rajapakse’s bid to return to power as prime minister.
Meanwhile the threat of more illegal online censorship remains as long as the original crime remains un-investigated. It took a careful study by the site’s technical advisers in Denmark to discover that what appeared to be poor connections to some of the site’s more controversial news pages, was in fact targeted interference.
The source of the interference was traced to a server in the central office of Sri Lanka Telecom at the OTS Building in Lotus Road in Colombo.
Websites can be “prohibited or be subject to supervision and control” under section 69 of the Sri Lanka Telecommunications Act 1991 – but only under ministerial authority, and under a publicly announced order. No such order was made to replace the one lifted by Sirisena.
Kurukulasuriya’s online news site, run by volunteers for four years, has developed a strong record of controversial scoops backed with an impressive array of documentation.
“We’ve never supported any particular political party, organisation or individual over another, and have proven it over the years. We just want our site to continue as an independent media organisation without unnecessary legal interference or illegal censorship.”
24 Jul 15 | About Index, Campaigns, mobile, Press Releases
• Fear of prosecution over free speech can force arts practitioners to self-censor
• “Art and the Law” packs offer guidance for controversial exhibitions
• Issues exposed by “Exhibit B” and “The City” shut down last year show need for guidance
Index on Censorship and advocacy group Vivarta, supported by law firms Bindmans, Clifford Chance and others, have launched a new set of guidelines to help UK artists, curators and exhibitors navigate the legal framework underpinning artistic freedom of expression.
“Art and the Law” information packs covering Child Protection, Counter Terrorism, Obscene Publications, Public Order and Race and Religion will be available to galleries and practitioners across the country.
“Free expression is crucial to the arts,” said Julia Farrington, who spearheaded the project. “But we have found that too often, artists and exhibitors are unsure of their rights under the law. Our Art and the Law guides will help them approach controversy with more confidence.”
“The police, prosecutors and courts have a duty to defend free speech, said Jodie Ginsberg, Index on Censorship Chief Executive. “But, as we have seen with cases such as Exhibit B and Behzti, police will go along with a ‘heckler’s veto’ and advise that artistic productions shut down when threatened with protest.”
The Barbican’s “Exhibit B”, a show replicating slavery-era “Human Zoo” exhibitions of African people featuring live actors, was shut down in September 2014 in the face of protesters who saw the piece as racist and exploitative.
“The Exhibit B closure demonstrates clearly the power the police have over decisions about art that offends,” said Farrington. “These packs set out to explain the powers of the police and the rights and responsibilities of arts organisations in this area.”
The Art and the Law Guides will be published on 24 July. PDFs of the law packs are available at indexoncensorship.org/artandoffence
For more info, contact Julia Farrington; julia@indexoncensorship.org /
+44 (0) 790288365
23 Jul 15 | Magazine, mobile
Garzon is dressed as the kitchen maid of Government Palace. There is a party attended by ‘Tirifijo'[FARC commander], who is playing cards. President Andres Pastrana is talking to US ambassador Myles Frechette. He taunts Frechette with a riddle:
It is white, Colombia makes it and gringos eat it.”
Frechette answers: “It must be salt.”
Pastrana: “No, it is not salt.”
Frechette: “Ifit is not salt, then it must be the coco [nut].”
The maid says: “Yes, yes, it’s the coco, that little magic powder we
are always talking about.”
An advert for ELN guerrillas directed at the small investor. Voiceover:
Worried about your money? Relax, you no longer have to worry about money. Invest your savings in official certificates. ELNs are the only market instruments that can convert a heap of oil into a mountain of money. Remember that nefarious liquid emissions are not taxable or subject to deductions at source. There’s no time to waste, invest now in nefarious liquid emissions. Your future will be like oil: black.
 Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Ahead of our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
Index on Censorship has been publishing articles on satire by writers across the globe throughout its 43-year history. Ahead of our event, Stand Up for Satire, we published a series of archival posts from the magazine on satire and its connection with freedom of expression.
14 July: The power of satirical comedy in Zimbabwe by Samm Farai Monro | 17 July: How to Win Friends and Influence an Election by Rowan Atkinson | 21 July: Comfort Zones by Scott Capurro | 24 July: They shoot comedians by Jamie Garzon | 28 July: Comedy is everywhere by Milan Kundera | Student reading lists: Comedy and censorship

A woman looking out her window sees the Rodriguez family [drug cartel] leaving their apartment block. The family is wanted by the police. She calls the police. The captain regretfully informs her that the Rodriguez family does not exist, he has checked the phonebook and there is no Rodriguez family listed. The woman perseveres:
I’ve spent the last 25 minutes trying to hand you these bad men. Now they are leaving. They’re getting into a car with some politicians. God! These politicians are like Pontius Pilate, some denied him and others wash their hands of him. But captain, if you come quickly you’ll understand what is happening in this country. Too late, they’re gone. I’ll call you again next week.
Edited transripts of television satires by journalist and humourist Jaime Garzon (1995). At Gam on 13 August 1999, Garzon was executed on his way to the Radionet studio by two men riding on a motorcycle. Garzon, known for his intervention in the stalled peace process, had reportedly been threatened by Carlos Castano, head of the paramilitary United Self-Defence Force of Colombia (AUC), in the preceding days. According to colleagues, Garzon planned to meet Castano on 14 August 1999. The AUC denied any responsibility in the assassination. Translated by Paulo Drinot.
 This article is from the January/February 2000 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives. Subscribe here, or buy a single issue. Every purchase helps fund Index on Censorship’s work around the world. For reproduction rights, please contact Index on Censorship directly, via vicky@indexoncensorship.org
This article is from the January/February 2000 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives. Subscribe here, or buy a single issue. Every purchase helps fund Index on Censorship’s work around the world. For reproduction rights, please contact Index on Censorship directly, via vicky@indexoncensorship.org
22 Jul 15 | Middle East and North Africa, mobile, Morocco, News and features
Outside the United Nations building in Geneva, Switzerland, Ali Lmrabet is in his 28th day of a hunger strike. The journalist and satirist is protesting what he sees as the latest bid from his country Morocco to stop him from doing his job.
In a period spanning over a decade, Lmrabet, who was the editor of two satirical publications, has continuously been targeted by Moroccan authorities. In 2003, he was jailed for reporting on personal and financial affairs of Morocco’s King Mohammed VI. His magazine Demain was banned. Though initially handed down a three-year sentence, Lmrabet was released after six months. But his troubles were far from from over: in 2005, he was banned from practising journalism in his home country for ten years, over comments made about the dispute in Western Sahara between Morocco and the Algerian-backed Polisario Front.
Now authorities are seemingly using bureaucracy as a tool to try and silence Lmrabet again. As his ban expired in April this year, he returned to Morocco with the aim of relaunching Demain. But there he was denied a residency permit, without which he is unable to set up the magazine. In a further complication, he also needs the residence permit to renew his passport. When this expired on 24 June, Lmrabet, who was in Geneva to participate in a session of the UN Human Rights Council, decided to start a hunger strike.
“He is very tired,” his partner Laura Feliu told Index on Censorship in a phone interview. She explained how the heat in Geneva has played a part in leaving Lmrabet drained of energy, and while he hasn’t had any serious health problems, he is experiencing sensations of seasickness.
Lmrabet’s protest takes place outside the UN offices, though a heatwave forced him to move inside on Sunday. He sleeps in a Protestant church near the centre of the city. Subsisting on water and some sugar and salt, he has lost at least seven kilograms since the start of the strike.
“He started a hunger strike to protest because he has been denied the right to work as a journalist,” Feliu explained. But in addition to having his free expression and press freedom curtailed, he also has another problem, she adds: “He is denied his right to an identity.”
Lmrabet has support in his country. Some 100 well-known Moroccans from the worlds of media, human rights and academia have signed a petition to the government calling on him to be allowed to renew his documents and continue his work in journalism. Independent and prominent human rights organisations in Morocco are also backing him, according to Feliu.
The response from Moroccan authorities, meanwhile, has so far been unsympathetic. The country’s UN ambassador Mohamed Aujjar has urged Lmrabet to contest what he labelled an “administrative decision” in Morocco, telling AFP that “you don’t get your papers by staging a hunger strike”. Lmrabet, on his part, is unwilling to risk being stranded in Morocco without papers and the ability to work or leave the country. “No one trusts the judical system in Morocco,” he said.
Feliu says it’s difficult to know what the outcome will be, but that Lmrabet is convinced this is the only way to protest. And he remains hopeful.
“He is very convinced of his fight. He is very convinced of his cause. He says that he has the moral to do it.”
Join us 30 July at Stand Up for Satire, a fundraiser in support of Index on Censorship.
This article was posted on 21 July 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
21 Jul 15 | Art and the Law Case Studies, Artistic Freedom Case Studies
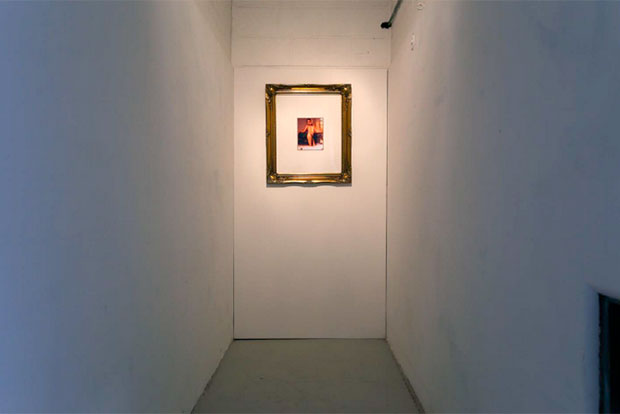

Installation image of Spiritual America 2014 at Goldsmiths College. With Permission Xenofon Kavvadias
Spiritual America 2014
Xenofon Kavvadias
As part of Index on Censorship’s programme looking into art, law and offence in the UK, this case study looks at Xenofon Kavvadias’s mission to exhibit Spiritual America by Richard Prince in public, effectively reversing the censorship of the image by Tate Modern who removed it from the gallery and the catalogue of their exhibition Pop Life, Art in a Material World 2009-10. Kavvadias called his exhibit Spiritual America 2014 and it formed part of his MA degree show at Goldsmiths College.
The work illustrates many of the issues raised in Index’s Art and the Law pack on Child Protection, giving useful insights into what happens when a work is contested in this area of legislation, the negotiations with the police and how far the law is open to interpretation.
Introduction
Spiritual America by Richard Prince was exhibited as part of The Tate Modern exhibition Pop Life Art: in a Material World, October 1 2009–January 17 2010. The piece is a reproduction of an original 1976 photograph depicting Brooke Shields, aged 10, naked in a bath. The Tate took the work down apparently on the advice by the Obscene Publications Unit of the Metropolitan Police Service that the image might be in breach of the Child Protection Act 1978. Under pressure from the police, the image of the work was also redacted from the catalogue of the show.
A 14 October 2009 BBC report carried a statement from the gallery that said: “In consultation with the artist, Richard Prince, Tate has replaced Spiritual America 1983 with a later version of the work made by him in collaboration with Brooke Shields, Spiritual America IV 2005. Tate is in ongoing discussions with legal advisors about the catalogue.”
Charlotte Higgins and Vikram Dodd writing in The Guardian on 30 September 2009 reported:
The decision by officers to visit Tate Modern is understood to have been made after police chiefs saw coverage of the exhibition in today’s newspapers, rather than as a result of complaints.
Officers met gallery bosses and are also understood to have consulted the Crown Prosecution Service as to whether the image broke obscenity laws.
A Scotland Yard source said the actions of its officers were ‘common sense’ and were taken to pre-empt any breach of the law. The source said the image of Shields was of potential concern because it was of a 10-year-old, and could be viewed as sexually provocative.”
The Tate chose not to include the original picture in Pop Life: Art In A Material World, after seeking legal advice.
Research leading to the presentation of Spiritual America 2014
Kavvadias undertook to display Richard Prince’s Spiritual America in his MA show at Goldsmiths, which he called Spiritual America 2014. As well as displaying a framed replica of the artwork, a record of all his research was available to the viewer to place the image in context. Gaining as full an understanding as possible of the legal and policing positions regarding the removal of the image from the Tate in 2009 was his point of departure.
Freedom of Information Requests
Kavvadias issued FoI requests to the Tate, the Police and the CPS. All FoI correspondence was included in the exhibition.
Key findings:
1 October 2009: The police wrote an email to the Tate regarding their visit:

2 October 2009: The police continued to put pressure on the Tate about their plans for the catalogue, writing a follow up email to the one above the next day.
6 October 2009: The Head of Director’s Office, Tate wrote to the trustees:
[Formalities]…we felt that given the important issues at stake (acting within the law while defending artistic freedom of expression) and the level of public interest in the case that we should keep each of you as individual trustees informed.
At the request of the owner and as provided for under our loan agreement with him, we have returned the work to him. In light of this, we have also consulted with the artist and are considering the option of substituting the work with another worked titled Spiritual America IV.
The Tate Enterprises Ltd board will meet…to discuss their position and options with regard to the distribution of the catalogue. Legal advice has been sought to inform their decision from leading counsel and specialist solicitors. …In the meantime the catalogue will continue to be withdrawn”
The Metropolitan Police Obscene Publications Unit wrote regarding their position as requested by the Tate:

- 12 October 2009: The catalogue was removed from sale while the Tate was taking legal advice.
- 13 October 2009: Metropolitan Police Service Directorate of Public Affairs Central Operations Press Desk, writing to head of communications at the Tate: “I’d just like to raise how categorical you interpret the police advice as having been. We did not state that we definitely considered the image to be indecent but explained that it may be, and that if it was then an offence would be committed if it was displayed. Police can never say when someone will be prosecuted, as that is a decision for the CPS, but did inform yourselves we would consult with the CPS. This is the MPS position as we have been and will continue to, explain to reporters.”
- 13 October 2009: The plan to obscure the image was in place.
- 13 October 2009: Tate asked Richard Prince for approval to obscure the image on the catalogue.
- 16 October 2009: In an email written to the police in support of including the image in the catalogue, Nicholas Serota compiled a list of freely available books featuring “Spiritual America”. Serota, who was Deputy Director of the Tate at the time, wrote: “As outlined already, we presented the work in the exhibition and catalogue because of its art historical significance in the study of 20th century art, as well as its intrinsic artistic merit”.
- 28 October 2009: The decision was made for the director of the Tate to write to the director of Public Prosecutions seeking clarification on the legal position concerning the work, and guidance on whether a prosecution would follow should the catalogues be distributed again. There is no written reply to this request. However, in 2013, Index spoke to the former DPP, Sir Keir Starmer who had been in post at the time of the controversy, and he said that he received many letters from arts organisations with similar requests but he cannot give advice as to whether a prosecution would follow. This is the work of the courts. However he felt there was a strong case for drawing up guidelines on how CPS reached a decision when considering whether or not to prosecute where artwork is involved.
- The legal advice was redacted from the FoI though the explanation of the offences and possible sentencing was made available. See below:

Additional Research
Availability of the image
Kavvadias carried out his own research into the availability of the image in books mentioned in Serota’s list, one of which was written by a professor at Goldsmiths. He researched the libraries of four leading art colleges in London and the British Library, where he easily located the books. He sent an FoI request to the British Library for their position regarding the advice Metropolitan Police gave to Tate. The British Library replied after two months, with a full and considered response robustly defending the books.
Ethics approval from Goldsmiths
The fact that one of the books containing the image was written by a Goldsmiths’ professor reinforced the view held by all of the committee that the Richard Prince picture is an accepted artwork. However, given that this defence failed to convince the legal team working with the Tate, it was not enough itself. They wanted reassurance on three additional concerns:
- the possibility of harm, including damage to reputation of the minor in the original
- that displaying the image might be in breach of copyright
- that the image was not presented in a sensational way that could bring the college into disrepute; they retained the right to withdraw until Kavvadias’ work was in situ in his exhibition
Issue of harm
Kavvadias addressed the issue of harm by presenting the history of the image:
- The original image, by Gary Gross, was commissioned by the Playboy publication Sugar ‘n’ Spice in 1976. Consent was given by Brooke Shield’s mother. She was paid $450 for the rights to the image.
- In 1983 Brooke Shields sought an injunction from the New York State Court of Appeals to bar further publishing of the image. Her motion was denied. According to the court’s ruling, “It should be noted that plaintiff did not contend that the photographs were obscene or pornographic. Her only complaint was that she was embarrassed because ‘they [the photographs] are not me now.'” While the judges found that the photographs were not pornographic, the court left in place an earlier decision that barred the sale of the photo to pornographic magazines.(Shields v. Gross, 58N.Y.2d338,448 N.E.2d108,461 N.Y.S.2d 254,9 Media l Rep. 1466 (N.Y.1983).
- Richard Prince purchased the rights to the image after the court ruling.
- Prince displayed the framed image with the title Spiritual America in 1983 in a New York gallery he rented, amid considerable controversy. Prince later created an edition of 10 prints.
- The image has subsequently been displayed in galleries around the world:
- Valencia, IVAM Centre del Carme, Spiritual America, 1989 (another example exhibited).
Cologne, Museum Ludwig, Ars Pro Domo, May-August 1992, p. 238 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- Ludwig Forum für Internationale Kunst, Dirty Data, June-August 1992, p. 75 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- New York, Whitney Museum of American Art; Dusseldorf, Kunstverein; San Francisco, Museum of Modern Art; and Rotterdam, Museum Boymans-van Beuningen, Richard Prince, May 1992-November 1993, p. 86 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- Munich, Kunstverein and Hamburg, Kunsthaus, Someone Else with my Fingerprints, April-July 1998, p. 75 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- New York, Museum of Modern Art, Fame After Photograph, July-October 1999 (another example exhibited).
- New York, Whitney Museum of American Art, The American Century-Art & Culture 1950-2000, September 1999-February 2000, p. 285, no. 466 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- Minneapolis, Walker Art Center; Paris, Centre Pompidou; Mexican City, Museo Rufino Tamayo and Miami Art Museum, Let’s Entertain, February 2000-November 2001, p. 254 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- Basel, Museum für Gegenwartskunst and Kunstmuseum Wolfsburg, December 2001-July 2002, Richard Prince: Photographs, p. 115 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- New York, New Museum of Contemporary Art, East Village USA, December 2004-March 2005, pl. 113, p. 75 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- New York, Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum; Minneapolis, Walker Art Center and London, Serpentine Gallery, Richard Prince: Spiritual America, September 2007-Summer 2008, p. 46 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- New York, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, The Pictures Generation 1974-1984, April-August 2009, pl. 231 (illustrated, another example exhibited).
- London, Tate Modern; Hamburger Kunsthalle and Ottawa, The National Gallery of Canada, Pop Life: Art in a Material World, October 2009-September 2010, pp. 123 and 196.
- Source: Christies
- In 2005, Brooke Shields, 40, posed for Richard Prince, in a bikini, taken in a similar pose to the original.

- Spiritual America was auctioned for $3,973,000, Sale 3495, at If I Live I’ll See You Tuesday: Contemporary Art Auction 12 May 2014 New York, Rockefeller Plaza
Richard Prince on Spiritual America
“In 1987, after I joined up with Barbara Gladstone, I editioned it. Ten copies and two APs [artist’s proofs]. I had my lab print it on ektacolor paper at 20 x 24”. The first one I sold, was to Stephan, my plumber friend and drummer for the Glenn Branca band. I sold it to him for a hundred dollars and some plumbing work. A couple of years later, I heard he sold that copy to Jay Gorney for four grand. Ten years after that Myer Viceman sold the original 8 x 10” back to Barbara Gladstone for two hundred thousand dollars. Then the 8 x 10” sold to Per Skarsted and later he made a special room for it, (all alone… painted the walls red) and showed it at Art Basel and sold it to Michael Ringier for one million dollars. A couple of years ago Michael lent it to the Tate Modern for some POP show organized by Alison Gingeras and Jack Bankowsky and it was ‘confiscated’ by the London police. The Tate didn’t do much protesting… they caved in to the ‘authorities’ and let them cart it away. It was never re-hung at the Tate and it was eventually returned to Michael Ringier. (Last I heard, Michael lives with Spiritual America in his home outside of Zurich).” Source: ASX
Copyright Infringement
As for possible copyright infringement, because Kavvadias was making a replica of the entire work, including placing it in a frame similar to the one used by Richard Prince, he had to demonstrate clearly to the university that he had the relevant permissions. Given that Richard Prince based his career on copying images and putting them into a new context, Kavvadias did not anticipate a problem. Kavvadias was using the image under Fair Use in US Copyright law for non-commercial and/or academic purpose. However, in order to reassure Goldsmiths, he took two steps:
He tweeted Richard Prince that he had been accused of copying his work. Richard Prince retweeted his message.
Kavvadias wrote to Prince’s London gallery informing them that he was attempting to legitimise the artist’s work that had been criminalised in the UK. They wished him luck.
Legal Advice — Second Opinion
Kavvadias interviewed lawyer Mark Stephens of Finers Stephens Innocent on 4 February 2013, regarding the legal advice given to the Tate to redact the image. Stephens made it clear he didn’t think there was any possibility that the CPS would have recommended a prosecution. Taking the CPS three stage test of whether to prosecute: the first, which asks is there sufficient evidence, is covered, because the image is the evidence. But he claimed it would have failed the other two:
- “that there has to be better than 50% chance of a successful prosecution: ‘Although I could see several charges that could be laid, [they] would be very difficult to succeed.'”
- “that it has to be in the public interest. Stephens stated that, in his opinion, it was not in the public interest to ‘bring the prosecution against Britain’s foremost cultural institution when the image has been around since the seventies, the culture across the planet have shown it and exhibited it without complaint. Even if you prosecute successfully this particular institution, which was displaying just one copy of this image, this was not going to eradicate the image, this was not going to eradicate any harm. If there was any harm, that occurred when this image went viral, effectively when it went on the internet…'”
The Police
Kavvadias wrote to the police informing them that he intended to display this work as part of his Masters thesis at Goldsmiths and gave them the dates. He didn’t ask them for advice or permission. He kept the email trail as evidence of his transparency. They didn’t respond.
21 Jul 15 | Art and the Law Case Studies, Artistic Freedom Case Studies

A scene from The Freedom Theatre’s UK tour of The Siege. Image courtesy of The Freedom Theatre
Throughout Index on Censorship’s Art and the Law information packs, the lawyers who wrote them stress that the packs offer guidance only and are not a substitute for legal advice. Knowing about the law helps an artist or an organisation identify when there could be a legal issue arising from an artwork. But each artwork is case specific so the advice is to contact a lawyer, if you are in doubt about whether or not you may be in breach of the law.
This short case study of the Palestinian Theatre Company’s first UK tour illustrates how the legality of The Siege was challenged in the media and how the touring venues responded to meet the challenge.
Background
The Freedom Theatre’s first UK tour, 13 May-20 June 2015, took the premiere production of The Siege to 10 UK venues: The Lowry, Manchester; Lakeside Theatre, Colchester; Battersea Arts Centre, London; The Hub, Leeds; St Mary in the Castle, Hastings; The Merlin, Frome; Birmingham Rep, Birmingham; The Cut, Halesworth; The Tron, Glasgow.
The show tells the story of the 2002 siege of the Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem, which was an international news story. The production illustrated the siege from the perspective of the Palestinian fighters who spent 39 days inside the church. The company researched the show by interviewing some of the fighters who are now living in exile in different countries.
In programming The Siege, Battersea Arts Centre (BAC) had anticipated that it and other participating venues might receive some critical feedback connected with the tour. Indeed, the 3 May 2015 Mail on Sunday contained an article with the headline: UK taxpayers fund ‘pro-terrorist’ play – £15,000 of public money given to show based on the words of Hamas killers. The Times of Israel also reported on the production with the strapline – “2002’s hostage standoff at Bethlehem’s Church of the Nativity gets historically questionable treatment in play set to tour England”
The BAC responded to the media reports. This is an excerpt from the briefing document:
- Battersea Arts Centre has agreed to help the Freedom Theatre in their liaison with the press in the UK and to act as a go-between between the company and the other 9 venues on the tour
- We are seeking legal advice from freedom of speech lawyers to reassure ourselves that nothing in the show is in contravention of UK counter-terrorism legislation
- We are looking carefully at the curation of discussions alongside the show which give the opportunity for points of view opposed to the Freedom Theatre point of view to be aired
- We are talking to our Board, funders and others to brief them on the current situation, to share information and to take their advice
- In the light of recent articles we are updating an internal document of Q&As to help us answer any questions likely to be levelled at us or other venues from the press/others. The key principle espoused in these answers is that Battersea Arts Centre (as is true of most if not all of the other venues on the tour we imagine) are providing a platform to this theatre company in the interests of freedom of expression, but BAC is not subscribing to any one particular point of view. We have previously given a platform to a theatre company that presented a piece from an Israeli perspective on the conflict in Israel/Palestine”
This last point, by referring to freedom of expression, cites the venues’ right to freedom of expression as laid out in Article 10 of the European Convention on Human Rights.
Seeking legal advice
In the Q&A mentioned above, one question raised a legal issue: Does this play glorify terrorism? It was also echoed in the media that alleged the play was “pro terrorist”.
Glorification of terrorism is a crime with serious consequences if convicted. While the guidance in our pack goes into some detail of defences for artists and arts organisation, it also stresses that the pack is not a substitute for legal advice. If you are unsure about your responsibilities under the law at any time, you must obtain independent specialist legal advice.
In order to be as confident as possible of the content in The Siege, BAC sought independent legal advice from three different sources: a Trustee contact; an Arts Council contact; Liberty. The Lowry also sought independent legal advice.
This was a sensible belt and braces approach because lawyers’ advice often varies according to interpretations of the law. Lawyers can only advise after all, so it was sensible to go three ways. All three gave advice pro-bono.
BAC created a summary statement from this advice and shared it with the other nine venues. They included a disclaimer that other venues used it at their own risk. It was advice, rather than a watertight guarantee that there couldn’t be other interpretations placed on the script. But it succeeded in its main purpose, which was to reassure the touring venues of their legal position, and enabled them to stand up to hostile press if necessary.
The statement helpfully demonstrates how freedom of expression is qualified by other considerations. In other words, once the lawyers were satisfied that the play didn’t breach legislation, then the right to freedom of expression can be upheld. Here is the summary:
The Siege does not infringe Section 1 of the Terrorism Act 2006, which prohibits the encouragement or glorification of terrorism. The play focuses on the personal struggles of the Palestinian fighters on a human level in attempting to survive the siege. It does not encourage audience members to emulate their conduct. Although the play is likely to be interpreted as sympathetic to the fighters, the sympathy is based on their struggle to survive as people and not on any violent acts or participation in terrorist groups. Violence is at no point encouraged in the play.
The presentation of The Siege, which depicts real-life events expressly from the point of view of the Palestinian fighters, is covered by Article 10 of the Human Rights Act: the right to freedom of expression, including artistic expression. Since The Siege does not commit an offence under the Terrorism Act 2006, and therefore poses no reason for this freedom of expression to be curtailed, prohibiting the play would likely be a breach of Article 10.”
David Jubb, artistic director of Battersea Arts Centre, reflected on the tour:
It was interesting to see the way that language was used in some of the reporting of The Siege. As well as raising the general temperature around the tour and adding to a sense of controversy, the use of legalistic language also introduced questions about the legal status of the show.
We felt that seeking legal advice would be useful to us in a number of ways: to inform our Q&As so that we could confidently answer any question that posed a direct legal challenge to the work; and to settle any anxiety that any staff or Trustees might understandably feel, to demonstrate that the artists and the organisation were on a solid legal footing.
This latter point was especially useful for Trustees who are one-step removed from the day-to-day and for good governance in these matters must be reassured that all risks have been assessed. Perhaps the most productive decision was made by all participating venues together: that we would support each other in the run-up to and during the tour, and work closely with the company at all times.
I know that we at Battersea Arts Centre learnt a lot from the great work of the Lowry and others. Providing each other with a support network ensured that we felt less isolated during stressful moments.”
A short survey was sent around to the venues on the tour asking if there were protests and about their contact with the police. The feedback was that the police were supportive and responsive and acted as useful liaisons between the venue and the protesters. Most venues informed the police of the forthcoming production about one week in advance. One venue approached the police a month in advance, but it seemed to “get lost in the system”. There were protests at many of the venues, but all were peaceful and took place without incident.










 The Colombo Telegraph, Sri Lanka’s most iconoclastic investigative news website, is gearing up for this year’s second national election. And once again they face the threat of censorship — despite a presidential promise to bring it to an end.
The Colombo Telegraph, Sri Lanka’s most iconoclastic investigative news website, is gearing up for this year’s second national election. And once again they face the threat of censorship — despite a presidential promise to bring it to an end.
 This article is from the January/February 2000 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives.
This article is from the January/February 2000 issue of Index on Censorship magazine and is part of a series of articles on satire from the Index on Censorship archives. 




