The most apt description of the impact of the death of George Floyd, the 46-year-old African American man who died on 25 May when a police officer leant on his neck and back for eight minutes and 46 seconds, came from a child. Floyd’s six-year-old daughter Ginna simply said: “Daddy changed the world!”
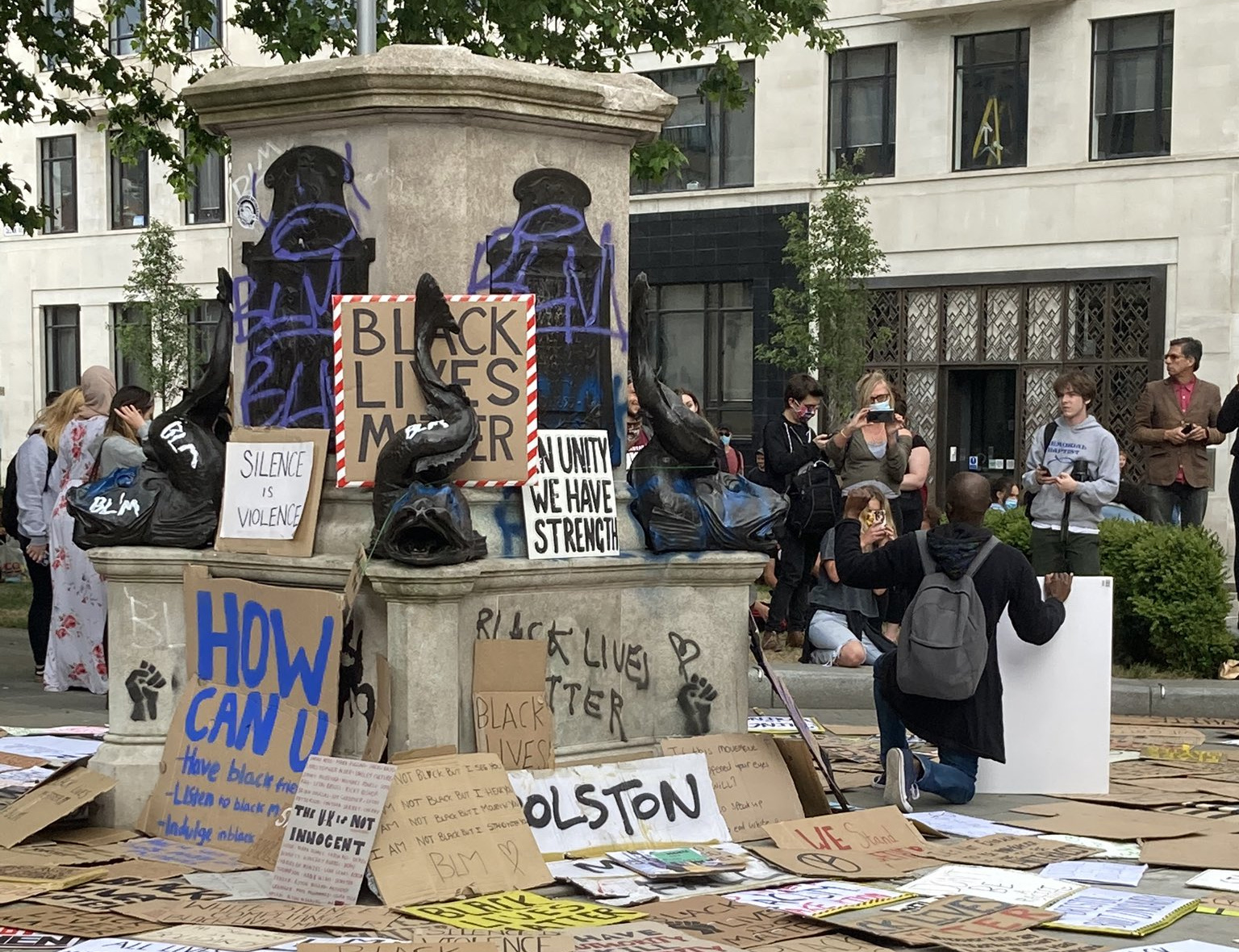
She’s right. Floyd’s death has sparked large-scale, public Black Lives Matter protests around the world, including in the UK. And it was in the UK that Black Lives Matter protesters in Bristol pulled down the statue of slave trader Edward Colston last weekend. It was then rolled through the city centre and dumped in Bristol Harbour.
Colston was a member of the Royal Africa Company, which had a monopoly on the slave trade at the time and is believed to be responsible for an estimated 30,000 African deaths.
The toppling of the statue has been both celebrated and criticised. Bristol Mayor Marvin Rees, for example, condemned the manner of the statue’s removal, though he admitted that the statue’s presence was an “affront” to black people in the city.
Some have attacked the action as one that is silencing and could set a bad precedent. But was it?
Removing a statue is symbolic and as the national debate about history, slavery and empire shows, it also very significant. The prime minister and other officials have stressed that it is important to follow process in these matters. But the people of Bristol had tried. For years, there had been an ongoing discussion about removing or adding a plaque to contextualise the statue. All efforts had reached a stalemate and frustration grew as suggested language for a plaque was watered down in efforts, some felt, to minimise his crimes. In the end, the whole thing came down and those who tried to stymy efforts to tell a fuller version of history found themselves swept aside as history was made.
It is perhaps in an effort to forestall similar actions that local Labour councils across England and Wales have indicated that they intend to set up commissions to look at other monuments and explore which ones ought to be taken down. This is not a bad thing, but if the public is not engaged in the process then a valuable moment for public education and civic participation could be lost. The act of tearing down of Edward Colston’s statue arguably did more to further a public discussion of slavery, history and racism than the statue ever did standing serenely in place all these years.
It’s an important discussion because putting up a statue is also a political act. Those who decry the removal of statues as erasing history might consider that in the many cases where statues represent editing or curating the past, that is itself a form of erasure. Colston’s statue was erected long after his death and is not even his true likeness. The honouring of the man has less to do with the facts of his life and career than the fact that he had given a lot of money to his home town, for which he was described in no less glowing terms than as one “of the most virtuous and wise” sons of Bristol.
Statues are also about who we wish to hold up for admiration and that is where history is dialogue with the present. It makes sense to discuss to whom we want to draw our eye upwards, to stand head and shoulders above the rest of us? There is potential for a rich discussion on which statues could be added, moved to museums, contextualised or quietly brought down to earth.
Parliament Square is now home to a statue of Nelson Mandela, who was once considered a terrorist by the Conservative government, and Millicent Fawcett, who as a suffragette endured much opposition and criticism of the group’s methods of direct action. With the passage of time, views on these historical figures have changed. The graffiti artist Banksy has suggested putting Colston back on his plinth as part of a new sculpture depicting Black Lives Matter protesters pulling him down. We may yet see public art memorialising these protesters in years to come.
Where will it end? Some ask. The answer is it never ends. Humans are dynamic and creative creatures, always making history and looking back over it. The prevailing view on Colston’s removal is one of broad agreement with the result but not the methods, the familiar “Yes – but not like that.” But if it was comfortable, it wouldn’t be a protest. Nobody advocates violence, but there is another familiar saying: “Power concedes nothing without a demand.”
The issue of statues is by no means the most important thing at this moment. But it’s not without significance, otherwise he wouldn’t have been there in the first place. We need more discussion about statues, their symbolism and the history around them, not less. Colston’s removal has done that.
Kiri Kankhwende is a freelance journalist who writes about politics, race and human rights