Ever since environmental activist Deanna “Violet” Coco was handed down a 15-month sentence earlier in December, protesters in New South Wales (NSW), Australia, have rallied in solidarity and to voice their dismay. On Tuesday this week, Coco walked free from prison. The temporary reprieve came as her bail appeal was approved, while she awaits an appeal on her sentence.
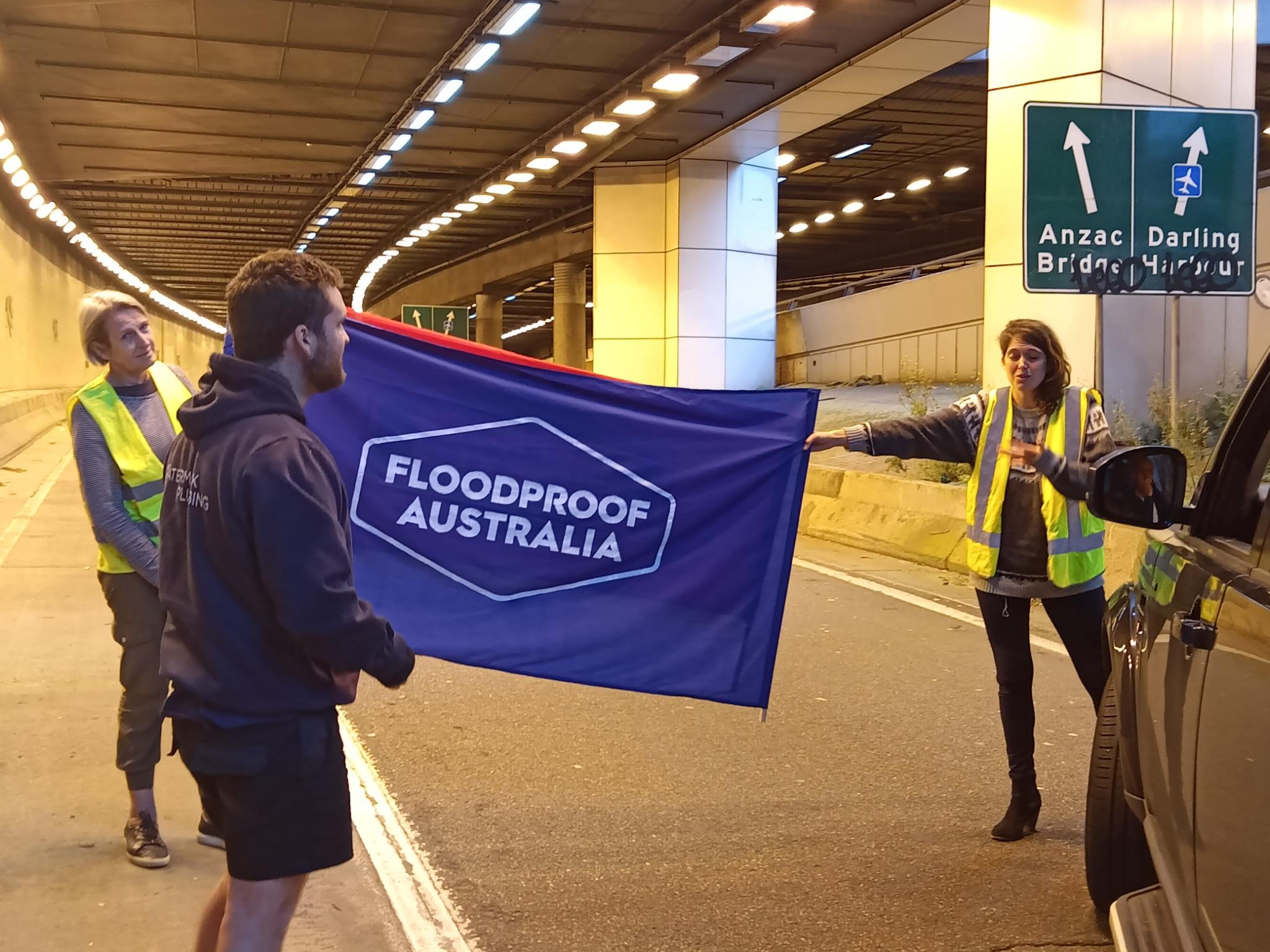
In April, Coco and a handful of other protesters from Fireproof/|Floodproof Australia blocked one lane of traffic on Sydney Harbour Bridge, holding aloft a flare to signal the climate emergency. Her sentence is the first of its kind under new laws in New South Wales.
For Suelette Dreyfus, executive director at Australia-based organisation Blueprint for Free Speech, Coco’s recent release must not divert attention from the serious penalties being given to environmental protesters, and the impact on freedom of expression.
“New South Wales has been targeting environmental protesters in the past year especially,” Dreyfus said. “That includes a Conservative state government and a streak in the media that is quite anti-environmentalist.”
She describes the penalties environmental activists typically faced in the past compared to today. What could once have been a fine for a few hundred Australian dollars, has become the threat of a lengthy prison sentence. This comes after NSW introduced the Roads and Crimes Legislation Amendment Act 2022 in April, meaning protesters could be fined up to AU$22,000 or be imprisoned for up to two years for trespassing on a major road and causing damage or disruption, or for damaging or disrupting a major facility.
Alongside this, a new police unit was created to disrupt environmental protest, called Strike Force Guard.
Dreyfus called this “an extreme power that’s been given to both police and the judiciary, to silence environmental protesters”.
When Coco’s sentence was handed down, NSW premier Dominic Perrottet described it as “pleasing to see”.
“It seems to be a strange thing to want to put a peaceful young woman exercising her right to freedom of expression in prison for two years, and feel self-satisfied about it,” Dreyfus told Index.
Coco is not alone in facing the sharp end of NSW’s new laws. In April, fellow Fireproof Australia activist Andrew George interrupted a National Rugby League match by running onto the pitch with a flare, and was handed down a three-month jail sentence, which he later appealed and won. In September, Blockade Australia activist Mali Cooper was cleared of charges against them, after they blocked the Sydney Harbour Tunnel in an attempt to force systemic change after witnessing the Lismore floods. They had faced the threat of two years in prison and $22,000 in fines.
Dreyfus referred to this landscape for environmental protest as a New South Wales phenomenon, but she said there is evidence that it’s leaching to other states. Victoria and Tasmania introduced similar laws this year.
“I think that the New South Wales government is actually weaponising the law against environmental protest in that state by going for the most serious charges they think they can, rather than charges that are commensurate with the very often very minor disruption that the protesters may cause,” Dreyfus said.
“We’re not talking about people who have burned down the Sydney Opera House here. We’re talking about people who have marched peacefully, and may have marched some bit of time in the road,” she said. “It’s really a minor offence, and it’s being treated like a major offence. So, it’s definitely chilling freedom of expression. It’s not a spring chill. It’s a full-on disturbing kind of winter hail.”
She said people are not attending ordinary protests in the same way as before, referring to demonstrations of around 100 people marching along a road, where some might step off the pavement and disrupt traffic. Coco’s sentencing, she said, has dampened participation.
However, she does not believe people will be silenced in this harsh landscape: “Most protesters of that nature are resourceful. So they will find another way to express what they think is important.”
The unintended consequence of the way NSW is dealing with this issue, she said, is that they are ultimately giving a bigger microphone to the protesters. Where before, disruptive protests were encouraging people to talk about environmental issues, now people are talking about environmental issues, freedom of expression and law reform. She calls that a killer combination for positive change.
“It will be up to the civil society community to make the most of that,” she said. “That’s something that they have to decide how they’re going to embrace.”