11 Oct 2018 | Artistic Freedom, News, Risks, Rights and Reputations
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”97076″ img_size=”full” add_caption=”yes”][vc_column_text]Agnieszka Kolek is curator and co-founder of Passion for Freedom, an annual competition exhibition of by artists facing censorship worldwide. In February 2015, Kolek survived the terrorist attack in Copenhagen, targeting the panel discussion she appeared in alongside Swedish artist Lars Vilks. Later that year in London, the Passion for Freedom 2015 exhibition at Mall Galleries, London, hit the headlines when a work Isis Threaten Sylvania by Mimsy was removed by the curators on the advice of the police. They had no choice because they couldn’t pay the £36,000 demanded by the police to guarantee security of the exhibition.
JF: How does your experience of the Danish police compare to the British police?
AK: The panel discussion — Art, Blasphemy and Freedom of Speech — was organised by the Lars Vilks Committee with the full support of the police. This was only a month after the Charlie Hebdo attack, but there was no question that the discussion should go ahead. There were two plain-clothed police officers, two uniformed police and then two special service officers responsible for Lars, who has 24-hour police protection. Police checked bags as the audience came in. When the attack happened — the Danish filmmaker Finn Nørgaard, one of the guests, was shot outside the venue and died on the pavement — the two special service officers took Lars to safety. We know that after an attack on freedom of speech the next target is Jews – it happened with Charlie Hebdo and it happened in Copenhagen when the same gunman attacked a bat mitzvah party in the evening, killing the security guard. Danes feel very bad that they didn’t anticipate this pattern and there was a lot of blaming of the police for this, but they did their best considering the circumstances. I think there has to be more legal power give to the police to extinguish the sources of the extremism, and its results. When you already have flames it is harder to put it, instead you have to prevent the fire from starting.
In London in 2015 it was very different. The police wanted to determine what artworks could go on show, and even the artistic value of exhibited works, showing an indirect form of censorship claiming it was “for your own good – security”. Police intelligence identified “serious concerns” regarding the “potentially inflammatory content” of Mimsy’s work and for this reason “advised” us to remove the work or pay protection money at £6,000 a day. We were completely shocked. Out of all the works in the exhibition, we would never have thought that they would pick this one out. We asked for more information about the “serious concerns”, especially because we wanted to know if there was a threat to Mimsy herself. They didn’t give us any more information. They wanted to place blame on the festival or its artists for causing problems, rather than protecting the space for art to show the suffering of people around the world and the lack of freedom to openly discuss it. While we tried to fundraise for our own protection, we were threatened with more works being withdrawn. Art cannot be controlled by the police – not in London, which for hundreds of years is a symbol of democracy and freedom. Not in the creative capital of Europe where artists flock from all over the world.
JF: But in Copenhagen two people lost their lives – you could have lost yours. How do you reconcile the loss of life with the pursuit of freedom?
AK: It is not easy to answer as I am not treating others’ and my own life lightly. Behind each individual there is a unique person, unique life story and to cut it short for the supposedly abstract ideal of free speech and expression might seem reckless. It is not. Again and again we learn how giving concessions to those who want to restrict freedoms of speech allows the darkness not only to enter our home but also our hearts. Not resisting it at early stages causes our societies to change beyond recognition.
I was invited to the Copenhagen event way ahead, so after the Charlie Hebdo attack, the chair got in touch with me to say she would understand in view of the heightened security risk, if I chose not to come. So I thought long and hard about it and said I will have to die someday, and I know I will look back at that this moment and I will remember the choice I made and it will be important.
Passion for Freedom is a very effective tool for assessing how much freedom there is in society. Artists cannot be easily controlled. In their inner core they are idealists. We stand with them giving them space and time to express themselves. Freedom will prevail despite political and corporate pressure to censor and restrict open debate. We are its guardians.
JF: How have the experiences of 2015 impacted on how you approach this year’s exhibition?
AK: The commitment and the conviction are still there. But we are not clear where we stand, because there is no clear definition of what is appropriate or what is inflammatory. It is a shifting ground. In the past, we created the space to fully exhibit work that had been censored elsewhere by a curator or a gallery owner. Now we are in the situation where the state, through the arm of the police, imposes this pre-emptive self-censorship on you. Since the censorship incident, we cannot guarantee artists that they will be able to exhibit/perform during a festival talking about freedom. Over the years there has been a number of artists who requested to be exhibited under pseudonyms (as often their lives are threatened in the UK or back in their home countries). Can we guarantee that the police will not arrest them? Until now, we could guarantee it to them. Since 2015 we are not sure that is the case. My approach is not to have any preconceived idea of how it will go with the police this time. We will still try to be open and have a dialogue in the belief that the police are still there to protect us and it is still a democratic country. I will be honest – we are also treating it as a kind of testing ground. Let’s see if this is still a democratic country or is it just on paper?
The artistic community in the United States and Australia is shocked by the police’s censorious attitude to arts in London. There are groups of people who decided to open Passion for Freedom branch offices in New York and Sydney to ensure that British censorship is being exposed. And in case freedom is completely extinguished in the UK they can continue the important work to give artists the platform to exhibit their works and debate important issues in our societies. And if we discover that there is even less freedom than in 2015, we are considering moving this exhibition to Poland because there is more freedom there. This is on the cards, we are already discussing it.
JF: Do you think Passion for Freedom exhibition represents a security risk?
AK: The way it is being framed in the media it looks like we are troublemakers and we are asking for it. I see it another way – we are representing the majority of society that wants to ask questions, to solve problems and to move forward together. Instead of giving in to a minority that wants to use violence and threats as a way to push forward their own agenda. I think it is in the interests of any society to make sure there is the space for difficult conversations because it moves away from creating the situation where the only way to solve problems is violence. You need to allow people to have this space and art is a wonderful tool to do that, without falling for propaganda, or just favouring one way of looking at things over another. Here you can have different voices, at different volumes, and different issues at play.
JF: The 2015 terror attack in Copenhagen targeted Swedish artist Lars Vilks and those who support him. Why do you think it is important for an artist to be free to deliberately insult and offend people’s religious beliefs?
AK: The world is a much more complex place than the newspaper headlines would like us to believe. Lars Vilks was invited to participate in an art exhibition on the theme “The Dog in Art” that was to be held in the small town of Tällerud in Värmland. Vilks submitted three pen and ink drawings on A4 paper depicting Muhammad as a roundabout dog. At this time, Vilks was already participating with drawings of Muhammad in another exhibition in Vestfossen, Norway, on the theme “Oh, My God”. Vilks has stated that his original intention with the drawings was to “examine the political correctness within the boundaries of the art community”. It is not a secret that Sweden is known for vehemently criticising the United States and Israel, whereas political Islam and its influence on non-Muslim communities are rarely questioned.
Artists practising various forms of art, whether poetry, drama, drawing or film, have been challenging those who hold power for millennia.
Few kings, warlords or dictators allowed criticism or satire of themselves. The blasphemy laws were in place not to protect God but those who claimed to be his only representatives on earth. Nowadays, the same seems to be disguised in the cloak of hurt feelings and delicate egos. Artists are idealistic visionaries. They cannot hold themselves back pretending that they are blind to what is in front of their eyes. Lack of open discussion stifles our development as societies. Fear of reprisal and death cripples the human spirit. Those who cower under the whip hoping to appease and remove the threat are actually risking the fate of a slave and subordinating to dehumanised serfdom their true nature – that of a free man.
JF: Why do you have this passion for freedom?
AK: Behind the Iron Curtain we naively believed that not only was the West this Land of Milk and Honey of material goods, we were also certain that there was freedom here, that people would value and protect it. So moving here, first you discover that everything is not so perfect materially, but then the bigger eye-opener is that there is always someone who wants to take freedom away and if you don’t stand up tall in society this threat is always present. I don’t think you can continue just exercising freedom of speech without appreciating what it has brought to us over the long years when previous generations were fighting for it, and though it is not ideal, the state we are in is much better than it used to be.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”103159″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”3/4″][vc_column_text]
Passion for Freedom Art Festival
10th-anniversary edition, 1 – 12 October 2018, London
The Royal Opera Arcade Gallery & La Galleria Pall Mall
Royal Opera Arcade, 5b Pall Mall, London SW1Y 4UY
The 10th-anniversary edition of internationally renowned Passion for Freedom Art Festival will open in London on 1 – 12 October 2018 at its new location – the Royal Opera Arcade Gallery & La Galleria Pall Mall. The exhibition showcases uncensored art from around the world, promoting human rights, highlighting injustice and celebrating artistic freedom.
Passion for Freedom was founded in 2008 and over the past ten years grew into an international network of artists, journalists, filmmakers and activists striving to celebrate and protect freedom of expression. We have displayed more than 600 artworks from 55 countries, including China, Iran and Venezuela.
The competition attracts much worldwide attention. This year, we received more than 200 submissions out of which we will exhibit over 50 shortlisted artists. From Venezuela to Turkey to the United Kingdom, those artists ceaselessly expose the restraints on freedom of speech, expression, and information in their countries. Altogether, we will display 100 such artworks during the festival. Passion for Freedom covers painting, photography, sculpture, performance, video, as well as authors, filmmakers and journalists.
Competitors will be judged by a prestigious selection panel. Winners will be announced on the 6th of October at the Gala Award Night.
This year’s judges are:
Andrew Stahl (United Kingdom)
Francisco Laranjo (Portugal)
Gary Hill (USA)
Lee Weinberg, PhD (Israel)
Mehdi-Georges Lahlou (Belgium)
Miriam Elia (United Kingdom)
Mychael Barratt PRE (Canada/United Kingdom)
This year we are thrilled to announce a Special Theo Van Gogh Award awarded in honour of his courage and contributions to freedom of expression.
Furthermore, we have invited a select group of special guest artists to display their latest works.
Passion for Freedom 2018 Guest Artists are:
Agata Strzalka (Poland)
Andreea Medar (Romania)
Emma Elliott (United Kingdom)
Jana Zimova (Czech Republic/Germany)
Mimsy (United Kingdom)
Öncü Hrant Gültekin (Turkey/Germany)
Oscar Olivares (Venezuela)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1539249597657-189331c4-e1af-0″ taxonomies=”15471, 8884″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
29 Aug 2018 | Bahrain, Bahrain Statements, Campaigns -- Featured, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”95198″ img_size=”full” add_caption=”yes”][vc_column_text]For the second time since 2013, the United Nations (UN) Working Group on Arbitrary Detention (WGAD) has issued an Opinion regarding the legality of the detention of Mr. Nabeel Rajab under international human rights law.
In its second opinion, the WGAD held that the detention was not only arbitrary but also discriminatory. The 127 signatory human rights groups welcome this landmark opinion, made public on 13 August 2018, recognising the role played by human rights defenders in society and the need to protect them. We call upon the Bahraini Government to immediately release Nabeel Rajab in accordance with this latest request.
In its Opinion (A/HRC/WGAD/2018/13), the WGAD considered that the detention of Mr. Nabeel Rajabcontravenes Articles 2, 3, 7, 9, 10, 11, 18 and 19 of the Universal Declaration on Human Rights and Articles 2, 9, 10, 14, 18, 19 and 26 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, ratified by Bahrain in 2006. The WGAD requested the Government of Bahrain to “release Mr. Rajab immediately and accord him an enforceable right to compensation and other reparations, in accordance with international law.”
This constitutes a landmark opinion as it recognises that the detention of Mr. Nabeel Rajab – President of the Bahrain Center for Human Rights (BCHR), Founding Director of the Gulf Centre for Human Rights (GCHR), Deputy Secretary General of FIDH and a member of the Human Rights Watch Middle East and North Africa Advisory Committee – is arbitrary and in violation of international law, as it results from his exercise of the right to freedom of opinion and expression as well as freedom of thought and conscience, and furthermore constitutes “discrimination based on political or other opinion, as well as on his status as a human rights defender.” Mr. Nabeel Rajab’s detention has therefore been found arbitrary under both categories II and V as defined by the WGAD.
Mr. Nabeel Rajab was arrested on 13 June 2016 and has been detained since then by the Bahraini authorities on several freedom of expression-related charges that inherently violate his basic human rights. On 15 January 2018, the Court of Cassation upheld his two-year prison sentence, convicting him of “spreading false news and rumors about the internal situation in the Kingdom, which undermines state prestige and status” – in reference to television interviews he gave in 2015 and 2016. Most recently on 5 June 2018, the Manama Appeals Court upheld his five years’ imprisonment sentence for “disseminating false rumors in time of war”; “offending a foreign country” – in this case Saudi Arabia; and for “insulting a statutory body”, in reference to comments made on Twitter in March 2015 regarding alleged torture in Jaw prison and criticising the killing of civilians in the Yemen conflict by the Saudi Arabia-led coalition. The Twitter case will next be heard by the Court of Cassation, the final opportunity for the authorities to acquit him.
The WGAD underlined that “the penalisation of a media outlet, publishers or journalists solely for being critical of the government or the political social system espoused by the government can never be considered to be a necessary restriction of freedom of expression,” and emphasised that “no such trial of Mr. Rajab should have taken place or take place in the future.” It added that the WGAD “cannot help but notice that Mr. Rajab’s political views and convictions are clearly at the centre of the present case and that the authorities have displayed an attitude towards him that can only be characterised as discriminatory.” The WGAD added that several cases concerning Bahrain had already been brought before it in the past five years, in which WGAD “has found the Government to be in violation of its human rights obligations.” WGAD added that “under certain circumstances, widespread or systematic imprisonment or other severe deprivation of liberty in violation of the rules of international law may constitute crimes against humanity.”
Indeed, the list of those detained for exercising their right to freedom of expression and opinion in Bahrain is long and includes several prominent human rights defenders, notably Mr. Abdulhadi Al-Khawaja, Dr.Abduljalil Al-Singace and Mr. Naji Fateel – whom the WGAD previously mentioned in communications to the Bahraini authorities.
Our organisations recall that this is the second time the WGAD has issued an Opinion regarding Mr. Nabeel Rajab. In its Opinion A/HRC/WGAD/2013/12adopted in December 2013, the WGAD already classified Mr. Nabeel Rajab’s detention as arbitrary as it resulted from his exercise of his universally recognised human rights and because his right to a fair trial had not been guaranteed (arbitrary detention under categories II and III as defined by the WGAD).The fact that over four years have passed since that opinion was issued, with no remedial action and while Bahrain has continued to open new prosecutions against him and others, punishing expression of critical views, demonstrates the government’s pattern of disdain for international human rights bodies.
To conclude, our organisations urge the Bahrain authorities to follow up on the WGAD’s request to conduct a country visit to Bahrain and to respect the WGAD’s opinion, by immediately and unconditionally releasing Mr. Nabeel Rajab, and dropping all charges against him. In addition, we urge the authorities to release all other human rights defenders arbitrarily detained in Bahrain and to guarantee in all circumstances their physical and psychological health.
This statement is endorsed by the following organisations:
1- ACAT Germany – Action by Christians for the Abolition of Torture
2- ACAT Luxembourg
3- Access Now
4- Acción Ecológica (Ecuador)
5- Americans for Human Rights and Democracy in Bahrain – ADHRB
6- Amman Center for Human Rights Studies – ACHRS (Jordania)
7- Amnesty International
8- Anti-Discrimination Center « Memorial » (Russia)
9- Arabic Network for Human Rights Information – ANHRI (Egypt)
10- Arab Penal Reform Organisation (Egypt)
11- Armanshahr / OPEN Asia (Afghanistan)
12- ARTICLE 19
13- Asociación Pro Derechos Humanos – APRODEH (Peru)
14- Association for Defense of Human Rights – ADHR
15- Association for Freedom of Thought and Expression – AFTE (Egypt)
16- Association marocaine des droits humains – AMDH
17- Bahrain Center for Human Rights
18- Bahrain Forum for Human Rights
19- Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy – BIRD
20- Bahrain Interfaith
21- Cairo Institute for Human Rights – CIHRS
22- CARAM Asia (Malaysia)
23- Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
24- Center for Constitutional Rights (USA)
25- Center for Prisoners’ Rights (Japan)
26- Centre libanais pour les droits humains – CLDH
27- Centro de Capacitación Social de Panama
28- Centro de Derechos y Desarrollo – CEDAL (Peru)
29- Centro de Estudios Legales y Sociales – CELS (Argentina)
30- Centro de Políticas Públicas y Derechos Humanos – Perú EQUIDAD
31- Centro Nicaragüense de Derechos Humanos – CENIDH (Nicaragua)
32- Centro para la Acción Legal en Derechos Humanos – CALDH (Guatemala)
33- Citizen Watch (Russia)
34- CIVICUS : World Alliance for Citizen Participation
35- Civil Society Institute – CSI (Armenia)
36- Colectivo de Abogados « José Alvear Restrepo » (Colombia)
37- Collectif des familles de disparu(e)s en Algérie – CFDA
38- Comisión de Derechos Humanos de El Salvador – CDHES
39- Comisión Ecuménica de Derechos Humanos – CEDHU (Ecuador)
40- Comisión Nacional de los Derechos Humanos (Costa Rica)
41- Comité de Acción Jurídica – CAJ (Argentina)
42- Comité Permanente por la Defensa de los Derechos Humanos – CPDH (Colombia)
43- Committee for the Respect of Liberties and Human Rights in Tunisia – CRLDHT
44- Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative – CHRI (India)
45- Corporación de Defensa y Promoción de los Derechos del Pueblo – CODEPU (Chile)
46- Dutch League for Human Rights – LvRM
47- European Center for Democracy and Human Rights – ECDHR (Bahrain)
48- FEMED – Fédération euro-méditerranéenne contre les disparitions forcées
49- FIDH, in the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
50- Finnish League for Human Rights
51- Foundation for Human Rights Initiative – FHRI (Uganda)
52- Front Line Defenders
53- Fundación Regional de Asesoría en Derechos Humanos – INREDH (Ecuador)
54- Groupe LOTUS (DRC)
55- Gulf Center for Human Rights
56- Human Rights Association – IHD (Turkey)
57- Human Rights Association for the Assistance of Prisoners (Egypt)
58- Human Rights Center – HRIDC (Georgia)
59- Human Rights Center « Memorial » (Russia)
60- Human Rights Center « Viasna » (Belarus)
61- Human Rights Commission of Pakistan
62- Human Rights Foundation of Turkey
63- Human Rights in China
64- Human Rights Mouvement « Bir Duino Kyrgyzstan »
65- Human Rights Sentinel (Ireland)
66- Human Rights Watch
67- I’lam – Arab Center for Media Freedom, Development and Research
68- IFEX
69- IFoX Turkey – Initiative for Freedom of Expression
70- Index on Censorship
71- International Human Rights Organisation « Club des coeurs ardents » (Uzbekistan)
72- International Legal Initiative – ILI (Kazakhstan)
73- Internet Law Reform Dialogue – iLaw (Thaïland)
74- Institut Alternatives et Initiatives Citoyennes pour la Gouvernance Démocratique – I-AICGD (RDC)
75- Instituto Latinoamericano para una Sociedad y Derecho Alternativos – ILSA (Colombia)
76- Internationale Liga für Menschenrechte (Allemagne)
77- International Service for Human Rights – ISHR
78- Iraqi Al-Amal Association
79- Jousor Yemen Foundation for Development and Humanitarian Response
80- Justice for Iran
81- Justiça Global (Brasil)
82- Kazakhstan International Bureau for Human Rights and the Rule of Law
83- Latvian Human Rights Committee
84- Lawyers’ Rights Watch Canada
85- League for the Defense of Human Rights in Iran
86- League for the Defense of Human Rights – LADO Romania
87- Legal Clinic « Adilet » (Kyrgyzstan)
88- Liga lidských práv (Czech Republic)
89- Ligue burundaise des droits de l’Homme – ITEKA (Burundi)
90- Ligue des droits de l’Homme (Belgique)
91- Ligue ivoirienne des droits de l’Homme
92- Ligue sénégalaise des droits humains – LSDH
93- Ligue tchadienne des droits de l’Homme – LTDH
94- Ligue tunisienne des droits de l’Homme – LTDH
95- MADA – Palestinian Center for Development and Media Freedom
96- Maharat Foundation (Lebanon)
97- Maison des droits de l’Homme du Cameroun – MDHC
98- Maldivian Democracy Network
99- MARCH Lebanon
100- Media Association for Peace – MAP (Lebanon)
101- MENA Monitoring Group
102- Metro Center for Defending Journalists’ Rights (Iraqi Kurdistan)
103- Monitoring Committee on Attacks on Lawyers – International Association of People’s Lawyers
104- Movimento Nacional de Direitos Humanos – MNDH (Brasil)
105- Mwatana Organisation for Human Rights (Yemen)
106- Norwegian PEN
107- Odhikar (Bangladesh)
108- Pakistan Press Foundation
109- PEN America
110- PEN Canada
111- PEN International
112- Promo-LEX (Moldova)
113- Public Foundation – Human Rights Center « Kylym Shamy » (Kyrgyzstan)
114- RAFTO Foundation for Human Rights
115- Réseau Doustourna (Tunisia)
116- SALAM for Democracy and Human Rights
117- Scholars at Risk
118- Sisters’ Arab Forum for Human Rights – SAF (Yemen)
119- Suara Rakyat Malaysia – SUARAM
120- Taïwan Association for Human Rights – TAHR
121- Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights – FTDES
122- Vietnam Committee for Human Rights
123- Vigilance for Democracy and the Civic State
124- World Association of Newspapers and News Publishers – WAN-IFRA
125- World Organisation Against Torture – OMCT, in the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
126- Yemen Organisation for Defending Rights and Democratic Freedoms
127- Zambia Council for Social Development – ZCSD[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1535551119543-359a0849-e6f7-3″ taxonomies=”716″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
28 Aug 2018 | Campaigns -- Featured, Statements, Turkey, Turkey Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]We the undersigned organizations call on Turkey’s government to follow through on its promise to end the state of emergency by withdrawing recently passed legislation that replicates many of the state of emergency’s special provisions.
The adoption of rights-restricting laws that closely mirror those in force during the state of emergency makes a mockery of the government’s claim to have ended the state of emergency; if anything, it seems to be making the state of emergency more permanent.
Many of the new provisions continue to violate universally recognized human rights, including those to freedoms of thought, expression, peaceful demonstration and assembly.
Amongst the new legislation we believe violate fundamental rights and must be repealed, we would highlight:
-
- The extension of detention without charge to up to 12 days via amendment of Turkey’s Anti-Terrorism law;
- The granting of the authority to ban individuals from passage between and within provinces to provincial governors, and to forbid public assemblies at their discretion;
- The renewal of arbitrary authority to dismiss individuals from academic, public and judicial service, and authority to confiscate the passports of those dismissed;
- The relaxation of judicial review of the cases of individuals in pre-trial detention, from requiring in-person or video presentation of the detainee in court every 30 days, to requiring visual review only every 90 days.
These provisions harm and restrict the rights of individuals who are not genuine security threats to Turkey’s government or citizens, but who are critical of government policies or defending human rights- at a time when reconciliation would help to restore prosperity.
We must emphasize that the concerns of neither Turkish citizens nor the international community will be addressed by simply changing the laws under which rights violations are rationalized. If Turkey’s government wishes to be recognized as a responsible state that upholds human rights, it must commit to ending the specific practices and policies that violate those rights.
Signed,
Initiative for Freedom of Expression – Turkey
ActiveWatch – Media Monitoring Agency
Adil Soz – International Foundation for Protection of Freedom of Speech
Albanian Media Institute
ARTICLE 19
Asociación Mundial de Radios Comunitarias América Latina y el Caribe (AMARC ALC)
Association of Caribbean Media Workers
Bytes for All (B4A)
Cartoonists Rights Network International (CRNI)
Foro de Periodismo Argentino
Freedom Forum
Fundamedios – Andean Foundation for Media Observation and Study
Globe International Center
Independent Journalism Center (IJC)
Index on Censorship
Instituto Prensa y Sociedad de Venezuela
International Federation of Journalists (IFJ)
International Press Centre (IPC)
Maharat Foundation
Mediacentar Sarajevo
Media, Entertainment and Arts Alliance
Media Foundation for West Africa (MFWA)
Media Institute of Southern Africa (MISA)
Media Watch
Norwegian PEN
Pacific Islands News Association (PINA)
PEN American Center
PEN Canada
PEN International
Reporters Without Borders (RSF)
South East European Network for Professionalization of Media (SEENPM)
South East Europe Media Organisation
Syrian Center for Media and Freedom of Expression (SCM)
Vigilance for Democracy and the Civic State
Articolo 21
Association of European Journalists
European Centre for Press and Media Freedom
European Federation of Journalists
Fair Trials
Frontline Defenders
German PEN
Italian Press Federation
Global Editors Network
Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights (FTDES)[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1535467423408-441388ac-b920-0″ taxonomies=”55″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
26 Jul 2018 | Campaigns -- Featured, Egypt, Middle East and North Africa, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
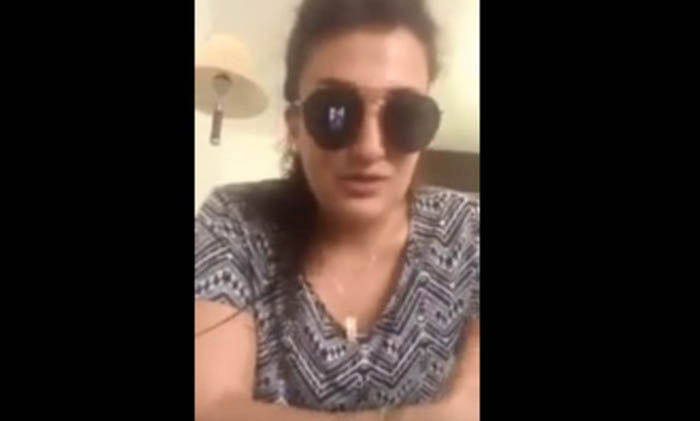
Screenshot from Mona el-Mazbouh’s apology video.
The below signatories express grave concern for the status of free speech and expression in Egypt. The authorities continue to openly silence anyone who is critical of the Egyptian government and of the state of affairs in Egypt. The arrest of Lebanese tourist Mona el-Mazbouh last month is yet another episode in President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi’s continued crackdown on rights and freedoms. We call for the immediate and unconditional release of Mona el-Mazbouh, who was sentenced to eight years in prison earlier this month.
Background
Lebanese Mona el-Mazbouh, 24, posted a 10-minute video to her Facebook account in May after she was allegedly sexually harassed, a lived reality that is experienced on a daily basis by most women in Egypt. The video included profanity against Egypt and Egyptians. Mona was stopped and arrested on 31 May at Cairo airport before leaving Egypt, after her video went viral on social media. Egyptian lawyer Amr Abdelsalam had filed a report against her with the general prosecution, accusing her of insulting the Egyptian people and the president. Abdelsalam has asked that she be added to the scores of Egyptians barred from leaving the country while her case remains open and until her sentence is completed, and to later permanently prevent her from entering the country.
The Egyptian attorney general ordered the immediate referral of Mona to an expedited criminal trial on 3 June for insulting the Egyptian people on social media. The prosecution accused Mona of “spreading false rumours that aim to harm society and defame religions, as well as creating inappropriate content and displaying it through her Facebook page”.
A Cairo misdemeanours court sentenced Mona to eight years in prison on 7 July for publishing a video with indecent content, defaming religion, insulting the Egyptian people and insulting the president. She was also fined EGP10,700 (around $598 USD).
Draconian laws that curtail free expression in Egypt
Accusations such as insulting the Egyptian people or the president are a serious transgression of the right to freedom of expression, which is guaranteed and protected by the Egyptian constitution and international human rights law. Over the past two years, there have been rapid and disturbing developments concerning the closure of physical and digital public spaces in Egypt, and an increased surveillance of social media and digital content.
A few weeks before Mona’s arrest, on 11 May, Egyptian activist Amal Fathy was arrested two days after she posted a video on Facebook condemning sexual harassment and disapproving of the government’s negligence on the issue. Fathy was charged with “disseminating a video on social media to publicly incite overthrowing the government”, “publishing a video that includes false news that could harm public peace”, and “misusing telecommunication tools”.
In addition, the Egyptian government continues to draft and approve laws that significantly curtail freedom of expression online, while heightening surveillance and censorship of social media users. On 5 June, Parliament approved the final draft of the new Cybercrime Law, titled “the Law on Combating Cybercrimes” that legalises broad censorship of the internet and facilitates comprehensive surveillance of communications.
Most recently, Parliament also approved a final reading a bill allowing authorities to monitor social media users and combat “fake news”, whereby individuals whose social media accounts have more than 5,000 followers could be placed under the supervision of Egypt’s Supreme Council for Media Regulations.
These developments reinforce the troubling and ongoing trend in Egypt of silencing public discourse and shrinking civic space that has now led to Mona’s arrest and detention.
Urgent action required
Before her arrest, Mona published a second video addressing the public response she received for the first. In her second video, Mona apologised for the content of the first, and clarified that she was not making a political statement and did not mention the Egyptian President at all in her initial video.
She was initially sentenced to 11 years in prison, however, her sentence was reduced to eight years after her lawyer provided the court with evidence that she “underwent a surgery in 2006 to remove a blood clot from her brain, which has impaired her ability to control anger”. Mona awaits her appeal date set for 29 July.
The below signatories believe that Mona el-Mazbouh’s arrest is a violation of her basic rights and freedoms, and connotes an even bigger threat to the general state of free expression in Egypt. We demand the immediate and unconditional release of Mona el-Mazbouh, and request that all charges be dropped allowing Mona to leave and enter Egypt freely.
Signed,
Association for Freedom of Thought and Expression (AFTE)
7amleh – Arab Center for the Advancement of Social Media
Adil Soz – International Foundation for Protection of Freedom of Speech
Africa Freedom of Information Centre (AFIC)
Article 19
Association of Caribbean Media Workers
Bahrain Center for Human Rights
Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies (CIHRS)
Cartoonists Rights Network International (CRNI)
Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF)
Freedom Forum
Human Rights Network for Journalists – Uganda (HRNJ-Uganda)
I’lam Arab Center for Media Freedom Development and Research
Independent Journalism Center (IJC)
Index on Censorship
Maharat Foundation
March
Mediacentar Sarajevo
Media Institute of Southern Africa (MISA)
Pacific Islands News Association (PINA)
Pen American Center
Pen Canada
Social Media Exchange (SMEX)
South East Europe Media Organisation
Vigilance for Democracy and the Civic State
Visualizing Impact (VI)[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1532684122469-2df2f596-084e-2″ taxonomies=”147″][/vc_column][/vc_row]

