What did Russia block this autumn?

This autumn the Russian authorities have made it clear that they are intent on extending the blocking of websites. In September, two prominent State Duma members of the ruling United Russia party, Robert Shlegel and Maria Maksakova, submitted amendments to an anti-piracy law, prohibiting illegal distribution of movie. These entered into force on 1 August. The deputies propose to supplement the law with measures that protect the copyright of musicians, writers and computer program developers.
In November, Andrei Lugovoi, a MP from the rightwing nationalist Liberal Democratic Party, submitted a bill proposing the extrajudicial blocking of sites containing calls for riots or extremist activities, including calls to take part in public events held deemed to be in violation of the established order. Hitherto, such sites have been subject to blocking by a court order. This initiative was met with general approval by members of the State Duma.
Extremism
Chechen prosecutor seeks to block anti-Putin article
On 23 September the Chechen Republic prosecutor announced the filing of writs against internet service providers (ISPs), demanding restrictions on access to a website publishing the anti-Putin polemic “Putin’s plan is Russia’s misfortune”. The article is on the Federal List of Extremist Materials.
Chechen prosecutor moves against ISPs over Islamist material
On 11 September the Chechen Republic prosecutor announced the filing of writs to restrict access to a website featuring the Islamist piece “Zaiavlenie komandovaniia mudzhakhidov Vilaiata Galgaiche” (Statement of the Mujahideen commanders of Vilayata Galgaiche), which is on the Federal List of Extremist Materials. The defendants were not identified in the report.
Smolensk prosecutor starts proceedings against ISP for video
On 11 September it was reported the Leninsky district prosecutor had issued a writ to the ISP MAN Set for allowing public access to videos included on the Federal List of Extremist Materials. The ISP complied with the writ and those responsible for allowing access faced disciplinary charges.
MTS receives a order to block video in Altai Republic
On 10 September the Gorno-Altaysk city court granted the Altai Republic prosecutor’s motion demanding that the ISP Mobilnye Telesystemy restrict access “to an extremist video clip posted on 16 websites”. The clip in question was not specified. The decision was made in the absence of the defendant.
Moscow court orders ISPs to block sites
On 25 September the Moscow city prosecutor reported that the Kuzminsky district court had accepted the demand of the Kuzminskaia interdistrict prosecutor that the ISPs Click and Obiedinennye Lokalnye Seti limit access to five websites that made available Hitler’s Mein Kampf. The prosecutor also demanded a block on a website containing citizens’ personal data.
Krasnodar moves against extremist posts on social network
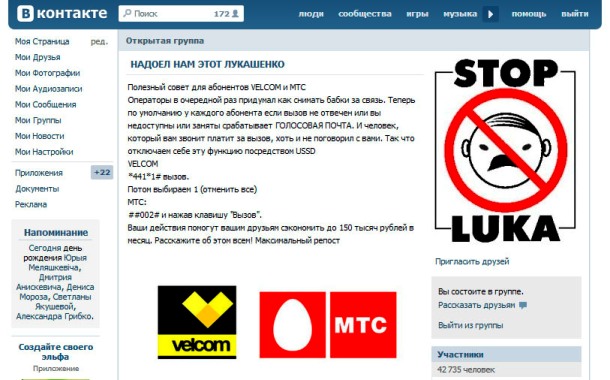
On 25 September the Krasnodar regional prosecutor reported that the Adlersky district court in Sochi had accepted the demand of the district prosecutor that it define two Islamist texts published on the VKontakte social network as extremist.
Prosecutors move against website in Chechnya
On 11 September the Urus-Martanovsky district prosecutor filed a lawsuit demanding that ISPs limit access to a website for publishing the video Videovestnik Russkoi Molodezhi (the Youth Messenger), included on the Federal List of Extremist Materials. The case is pending.
Blogs targeted in Ulyanovsk
On 25 September the Ulyanovsk regional prosecutor reported that the Zavolzhsky district prosecutor had issued writs demanding the ISPs ER-Telecom Holding and Rostelecom cease offering access to the websites kcblog.info and t-kungurova.livejournal.com. Both are legally recognised as extremist [for being aliases] for the Chechen militants’ website Kavkazcenter.
Education and schools
Kamchatka schools told to shield students
On 13 September it was reported that the Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky city prosecutor had issued demands that several schools install content filters to prevent access to websites containing extremist propaganda.
Lipetsk schools allowed access to banned sites
On 27 September it was reported that the Dankovskaia interdistrict prosecutor in Lipetsk region had demanded the director of Dankov Secondary School No 1 eliminate violations of the child protection law. An inspection had revealed that the internet filtering system installed on school computers was not blocking access to websites about drugs, pornography and suicide. It also allowed access to the texts of songs included in the Federal List of Extremist Materials.
Blind students ‘could read Mein Kampf’ in Omsk school
On 17 September it was reported that the Omsk city prosecutor had identified a number of violations at Boarding School No 14 for visually impaired children. In particular, the school computers allowed access to Hitler’s Mein Kampf, included on the Federal List of Extremist Materials, as well as to websites containing pornographic images, violence and drug propaganda.
University fined for banned site breach
On 3 September it was reported that the Sverdlovsk regional arbitration court had accepted the demand of a fine for B N Yeltsin Ural Federal University, issued by the Ural regional office of the watchdog Roskomnadzor. The university had failed to submit an application for an access code to the register of banned websites. As a result, students had access to resources included on the register. The court imposed a fine of 30 thousand rubles on the university. The court’s decision has not yet entered into force.
Suicide propaganda
Penza prosecutor tries to block suicide prevention
On 11th September it became known that the local Penza’s prosecutor office asked the court to block access to the website Pobedish.ru (“You win”). The website is part of Perezhit.ru group – a suicide prevention resource that works with psychologists, psychiatrists, forensic experts and the clergy.
Kaliningrad prosecutor moves against suicide sites
On 23 September it was reported that the Moskovsky district court of Kaliningrad had received a prosecutorial request that the ISP TIS-Dialo restrict access to several websites describing methods of committing suicide.
Drugs and alcohol
Facebook almost blocked for advertising smoking blends
The Russian branch of Facebook came close to being blocked for publishing advertisements for illegal smoking blends in September, according to reports from the Itar-Tass news agency, citing Facebook’s Russian press service. Facebook said users had reported the ads for smoking blends on 16 September and the company had been unable to do so because of a technical glitch. The incident followed a warning from the Federal Antimonopoly Service (FAS) that it intended to inspect social networking sites for ads for banned substances. The media watchdog Roskomnadzor subsequently warned Facebook that it had been provisionally placed on the register of banned websites and would be shut down if it did not remove the ads. Facebook announced on 19 September that it removed the offending content.
Reports filed on ISPs in Kurgan
On 18 September it was reported that the Kurgan regional office of Roscomnadzor had compiled reports on two ISPs that were not blocking access to websites advertising illegal drugs.
Yekaterinburg complains about alcohol advertising
On 17 September it was reported that Sergei Trushin, deputy head of the Yekaterinburg administration, had sent a letter to the regional office of the interior ministry requesting action against websites advertising the sale of alcohol. The Ministry of Internal Affairs shut down the sites and the people behind them were fined.
Gambling and casinos
Yekaterinburg ISP loses appeal
On 3 September it became known that the Sverdlovsk regional court had accepted the demand of the Kirovsky district prosecutor in Yekaterinburg that the ISP VympelCom-Communications block five gambling websites based on foreign servers. The demand had been accepted by a district court but the ISP had appealed.
Eight gambling sites blocked in Tomsk
On 12 September the Tomsk regional prosecutor announced that the Strezhevoy town prosecutor had filed a lawsuit against the ISP Danzer demanding restrictions on access to eight online casinos. The ISP complied by blocking the sites.
Rostelecom blocks William Hill
On 5 September Rostelecom blocked its subscribers’ access to the largest UK betting website, williamhill.com. The ISP Qwerty in Moscow and the surrounding region also blocked access to the site.
Rostelecom subscribers could not access the website’s primary domain, online casinos or online poker sites. Instead, they saw a message announcing that the domain had been blocked by court order or that the address had been placed on the register of banned websites.
Torrents and piracy
Moscow court bans 11 torrent sites
On 5 September Moscow city court accepted the claim of NTV-Profit against 11 online torrent sites — free-torrents.org, inetkino.org, rejtinga.net, nnm-club.me, hotbase.org, x-torrents.org, goldenshara.com, rutor.org, torrnado.ru, torrent-shara.org, nntt.org – that were distributing the popular Russian-made films Vor (The Thief), Krutoi Povorot (Sharp Turn) and Interny (The Interns).
Portal avoids block for streaming
On 5 September Moscow city court accepted a request by the Central Partnership Sales House requesting to block the torrent portal Rutracker.org to prevent it distributing the American films Now You See Me and Taken 2. Rutracker removed the films and avoided being blocked.
And the rest
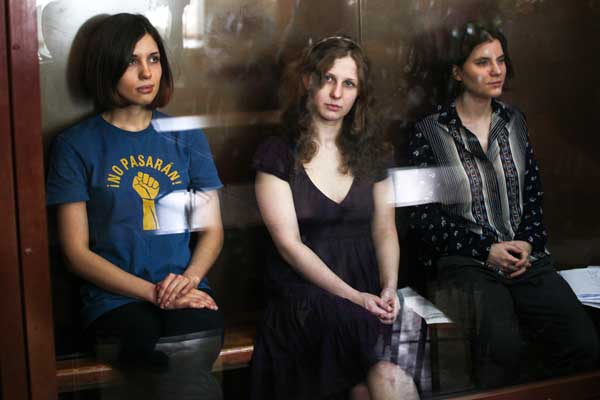
Pussy Riot icon banned
On 9 September it was announced that the Tsentralny district court had granted a request by the Zheleznodorozhny district prosecutor of Novosibirsk to declare an icon-like image of Pussy Riot, created by the artist Artyom Loskutov, banned from distribution via the internet. The image has been added to the register of banned websites.
Block on inaccessible site demanded
On 24 September it was announced that the Yegoryevsk city court had granted the city prosecutor’s motion against Yegoryevskaia Telekommunikatsionnaia Kompaniia (Yegoryevsk Telecommunications Company) to limit access to an online casino website. Earlier, the same court had ruled in favour of the provider, but the prosecutors challenged the decision, and the Moscow regional court sent the case back for retrial. The Yegoryevsk city court ordered the provider to restrict access to the site, but the access to the website was found to already be blocked – perhaps, by the online casino’s owner or another operator. However, the court insists that Yegoryevskaia Telekommunikatsionnaia Kompaniia should be the one to implement access restrictions. The court provided no advice on how to block an already inaccessible site.
Stavropol prosecutor seeks block on e-library for one book
On 25 September the Stavropol regional prosecutor reported that the Novoaleksandrovsky district prosecutor had filed a claim in Leninsky district court against the Stavropol regional branch of Rostelecom, demanding restrictions on access to the website royallib.ru. The site provides public access to the book Skiny: Rus probuzhdaetsya (Skinheads: Rus Is Awakening) by Dimitri Nesterov, which is on the Federal List of Extremist Materials
Roscomnadzor blocks porn site
On 13 September it was reported that Roscomnadzor had included the porn site redtube.com on the register of banned websites. The reason for placing the site on the register was not specified, but it might have been because it published a cartoon entitled “Hentai school girls fucking for better grades”.
TV channel targeted in Moscow
On 6 September it was announced that the central investigations directorate of the ministry of internal affairs in the Moscow Region had demanded that the website of Dozhd (Rain) TV channel be blocked for violation of Part 2 of the Criminal Code Article 282 (“incitement to hatred or hostility and humiliation of human dignity”). TV Dozhd is the country’s most popular online TV news channel and is relatively independent. The exact nature of the material deemed objectionable was not reported. The Ru-Center domain registrar confirmed the existence of the police request, but, since the request was filled out incorrectly, the TV channel website was not blocked. Interior ministry representatives subsequently denied the reports. The administration of Dozhd also stated that they had received no such orders from the ministry of internal affairs.
Saratov ISP ordered to ban ads for bankrupt company
On 6 September it was reported that the Kirovsky district prosecutor in Saratov had filed a lawsuit against the ISP Saratovskaia Sistema Sotovoi Sviazi (SSSS) demanding that it restrict access to an internet portal advertising a bankrupt company. The ISP refused to block the relevant IP address because it was also used by three unrelated sites. In addition, the provider stated that it had no control over IP address changes, while an advertiser could always change it. However, the court granted the prosecutor’s claim and ordered the ISP to restrict access to the site.
ISPs fined in Moscow and Saratov
On 3 September it was announced that the Moscow arbitration court had fined the ISP KMC Telecom and that the Saratov regional arbitration court had fined the ISP Hemikomp for ignoring the requirement to sign up to the register of banned websites. In both cases, the decisions were made based on evidence from the media watchdog Roskomnadzor. It said the ISPs’ reluctance to register and block access to websites listed on the register was in violation of Part 3.14 of the Administrative Code (entrepreneurial activity without state registration).
Amur ISPs reported for non-compliance
On 14 September it was reported that the Amur office of Roscomnadzor had filed administrative responsibility reports against the following ISPs: Amurtelekom, A- Link, Transsvyaztelekom, Inter.kom, KRUG, GudNet, Moia Komputernaia Set, Gorodok, and Edinaia Gorodskaia Set. Roscomnadzor demanded penalties for their failure to comply with the register of banned websites. If the violation is not addressed, each provider faces a fine of up to 40,000 rubles.
Consumer protection site temporarily blocked
On 26 September it was reported that www.i-zpp.ru, a consumers’ rights website, had been added to the register of banned websites. The addition was triggered by the decision of the Salekhard city court of 18 April 2013 to block access to websites containing extremist materials. The consumer protection website had been blocked because it had the same the IP- address as extremist websites. In late September the site was, once again, accessible from Moscow.
Owner loses appeal against ban
On 20 September it became known that Vladimir Kharitonov, the owner and administrator of the website Novosti elektronnogo knigoizdaniia (News of electronic book publishing, digital-books.ru), had filed an appeal with the Moscow city court against Roskomnadzor’s decision to include it on the register of banned websites. Kharitonov had previously attempted to appeal the decision, but the Tagansky district court dismissed his appeal in March. The Moscow city court did the same in September. The owner of the website intends to appeal to the European Court of Human Rights.
Prosecutor blocks 15 Omsk sites
On 17 September it became known that the Omsk city prosecutor had succeeded in blocking 15 websites. Previously, the Tsentralny district court had dismissed the claim of the Omsk city prosecutor demanding that the local branch of Rostelecom restrict access to 15 sites selling certificates and diplomas. The prosecutor appealed the decision and the Omsk regional court overturned the lower court’s decision and ordered the internet provider to block the websites.
This article was originally posted on 22 Nov 2013 at indexoncensorship.org