14 Jan 2014 | News, Russia
Fielding calls in the back of a London black cab, American journalist David Satter is a busy man.
Satter, who has reported on Soviet and Russian affairs for nearly four decades, was appointed an adviser to US government-funded Radio Liberty in May 2013. In September, he moved to Moscow. But at Christmas, he was informed he was no longer welcome in the country — the first time this has happened to an American reporter since the cold war.
Since Monday night, when the news of his expulsion from Russia broke, he’s been talking pretty much non stop, attempting to explain the manoeuvres which led to him being exiled from his Moscow home.
A statement issued by the Russian foreign ministry claims that Satter had violated Russian law by entering the country on 21 November, but not applying for a visa until 26 November.
Satter dismisses this as “nonsense”, saying he had been assured that a visa that had expired on 21 November would be renewed the following day, with no gap. As it happened, the visa was not renewed on time, “in order to create a pretext”, he tells Index.
To cut a short cut through a labyrinthine tale of bureaucracy: Satter says he left Russia in order to gain a new entry visa, which he could then exchange for a residency visa as an accredited correspondent for Radio Liberty.
He was repeatedly told this visa had been secured. Eventually, on 25 December, he was told that he had a number for a visa, but not the necessary invitation to accompany it. “Kafkaesque”, he calls it. The embassy official had never heard of this happening before. And, as Satter points out, he would not have been issued a number for a new visa in December if it had not been approved.
Eventually, he was told to speak to an official named as Alexei Gruby, who told him that “the competent organs” (code, Satter says, for the FSB) had decided that his presence in Russia was not desirable, language normally reserved for spies. “And now we see I have been barred for five years.”
“The point is, I urge you not to get caught up in their bureaucratic intrigues…the real reason was given to me, in Kiev, on 25 December.”
Is this just another example of FSB muscle flexing?
“Possibly. I’ve known them for a number of years, and I can’t always understand what they’re doing. Usually what they do is not very good…”
This is not Satter’s first brush with the Russian secret services. In a long career with the Financial Times, Radio Liberty and other outlets, he has experience of the KGB and its sucessor. “In 1979, they tried to expel me, accusing me of hooliganism. They once organised a provocation in one of the Baltic republics in which they posed as dissidents. I spent a couple of days with them, thinking I was with dissidents – I was really with the KGB. It’s a long history. It’s in my movie. We showed it in the Maidan [December’s anti-government protests in Ukraine]. Maybe they didn’t like that.”
Satter’s film, the Age of Delirium, is an account of the fall of the Soviet Union.
Is this expulsion a personal thing? Or a move against Radio Liberty? “It’s hard to say whether it’s me, or Radio Liberty, or both.”
Satter is concerned at leaving behind research materials and belongings in Moscow, saying it is likely his son, a London-based journalist, will have to go to Russia to collect them “unless they reverse their decision, which I hope they do”.
In spite of the recent amnesty that saw Pussy Riot’s Nadezhda Tolokonnikova and Maria Alyokhina released from prison, as well as opposition figure Mikhail Khodorkovsky, the diagnosis for free speech in Russia is not good. Alyokhina dismissed her release as a “hoax”, designed to prove Putin’s power. Meanwhile, state broadcaster RIA Novosti has been dissolved and reimagined as “Rossia Segodnya” (“Russia Today” – no coincidence it bears the same name as the notorious English language propaganda station), with many fearing closer Kremlin control.
One Russian journalist I spoke to felt that, ahead of the Sochi games, the expulsion of Satter is a message to all journalists: no matter how experienced, well-known, and well-supported you are, you are still at the mercy of the authorities.
This article was posted on 14 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
14 Jan 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, France, News

What happened last Friday was unprecedented. Four days before the third major press conference of François Hollande’s presidency, the French version of celebrity magazine Closer published seven pages alleging that the president was having an affair with Julie Gayet, a 41-year old actress. Speaking to the AFP in a personal – and non presidential – capacity on Friday, Hollande described the publication as an “attack on the right to privacy” but did not deny the allegation. On Sunday, the spokeperson of his partner, Valérie Trierweiler, announced she had been admitted to a hospital due to stress prompted by the publication and that she would leave the hospital on Monday.
For the president to have a mistress would not seem surprising in a country with a long history of presidential mistresses and most French people are likely to remain unfazed. According to a poll commissioned by Le Journal du dimanche, 77% of French people feel that the alleged relationship between Hollande and Gayet does not concern them and don’t feel shocked by the allegation. What is new is the way in which Closer has intruded on the president’s private life.
Traditionally, French presidents’ affairs go unreported. François Miterrand’s double life and the fact that he had a daughter with his long-term mistress was only revealed at the end of his presidency and when his daughter was 20, in 1994, by Paris Match. At the time, the magazine had sought the president’s approval before publication.
Of course, things have changed. Nicolas Sarkozy is known to have blurred the lines between his public and private life, orchestrating the media coverage of his relationship with ex model Carla Bruni, whom he married during his presidential term. In 2011, the Dominique Strauss-Kahn scandal triggered a debate in the French media: had the French press been overprotective of the private life of one of its politicians, failing to report on DSK’s alleged track record of violence against women?
France’s strict privacy laws make it a criminal offence to publish information about someone’s private life without their consent. In 2012, the magazine was sentenced for publishing stolen photos of a topless Kate Middleton sunbathing with Prince Williams. The magazine had to take down the photos from their website and to return them to the couple. Following a complaint by Gayet’s lawyer, Closer has already taken down the allegations of a relationship between the actress and the president from their website. But, as happened with the breasts of the Duchess, the damage is done, and the allegations of an affair between Hollande and Gayet are now everywhere.
Gayet gate: a public affair?
As Closer’s allegations become public, France’s main news publications have started to report on the claims and what seemed to be only a private matter has started to seem much more interesting.
The allegations of a presidential affair raise the question of the status of Hollande’s current official girlfriend Valérie Trierweiler, a former political journalist, who has an office at the presidential palace, employs five people and accompanies the president on official occasions and trips abroad. France, unlike the United States, has no defined role for a “first lady” and the wives or partners of successive French presidents have occupied a blurry zone between the private and the public sphere. A certain confusion has presided over Trierweiler’s involvement in Hollande’s presidency. In June 2012 she committed a gaffe by tweeting her support for a rival to Ségolène Royal, Hollande’s former partner with whom he has four children. Closer’s allegations are likely to force Hollande to clarify the status of his relationship with Trierweiler, a personal matter, which also takes a public dimension.
Lastly, an interesting line of investigation has been opened by the online magazine Mediapart which claimed that the flat used for the alleged encounter of Gayet and Hollande is under the name of Michel Ferracci, suspected to have ties with the infamous Corsican Gang de la Brise de Mer, and his ex wife, an actress and a friend of Gayet. Hollande is believed to have come to the flat regularly, followed by police officers acting as bodyguards, which raises questions for his personal security.
This article was posted on 14 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
14 Jan 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, European Union, News, Politics and Society

This article is part of a series based on our report, Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression
In the aftermath of the Arab Spring, the EU shifted its neighbourhood policy in the southern neighbourhood. In response to the revolutions and social movements in the region, the EU shifted the focus of its neighbourhood policy from economic development towards human rights. On 8 May 2011, the EU High Representative and the European Commission issued a joint communication proposing “A partnership for democracy and shared prosperity with the southern Mediterranean“.
The EU now emphasises the “three Ms”: money, market access and mobility, with the first “M” addressing the EU’s commitment to financially support transition to democracy and civil society. The strategy also heralded the creation of the Civil Society Facility for the neighbourhood (covering both the southern and eastern neighbourhoods), with an overall budget of €26.4 million for 2011 to strengthen civil society. In parallel, the European Instrument for Democracy and Human Rights (EIDHR) deployed a number of operations in the region to protect and promote freedom of expression, often without the consent of the host country.
The apparent efforts to promote freedom of expression in the southern neighbourhood after the Arab Spring are in stark contrast to the multilateral partnerships that the EU actually established, often with the now overthrown dictatorships. The Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (EUROMED), also known as the Union for the Mediterranean (UfM) and formerly known as the Barcelona Process, was re-launched in 2008 as a multilateral partnership between the EU member states and 15 Mediterranean partner countries in the EU’s southern neighbourhood. Of the UfM’s six key initiatives launched prior to the Arab Spring, none related to the promotion of human rights. EU member states that border the Mediterranean Sea, in particular Italy, Spain and France, emphasised cooperation on migration, energy supplies and help with counter-terrorism, while adopting a relatively passive approach toward democracy and human rights.
Critics contend the UfM was overly concerned with regional security and economic partnership at the expense of human rights, including the right to freedom of expression. For example, in spring 2010, the EU began negotiations with Tunisia on advanced status within the European Neighbourhood Policy, with clear economic benefits for the country, even though, at the same time, the Ben Ali regime was clamping down on freedom of expression. Ben Ali’s government even introduced a draconian NGO law during the period of the advanced status talks, in an attempt to prevent Tunisian activists from lobbying the EU to be tougher on human rights issues. As a result, even with the new “three Ms” strategy, the EU and its member states suffer from a legacy credibility problem in the region and are often seen as former allies of repressive regimes.
The EU has continued to lack unity on the use of conditionality to enhance political and human rights reform. Germany, Finland and the Netherlands have generally been more supportive of this reform, whereas Italy and Portugal are less keen on penalising countries for failing to introduce reform. According to a survey of over 700 experts initiated by the European Commission, both the UfM and the EU have failed to deliver the expectations of key regional actors, 93% of those interviewed called on the EU to have a greater role in the region. The survey indicated that Turkey was perceived as the most active country in the region on the promotion of human rights, ahead of the US, followed by all EU countries combined.
In its near neighbourhood, the EU has had mixed levels of success in promoting freedom of expression. Enlargement continues to be the most effective tool at the EU’s disposal in incentivising countries to improve their domestic situation for freedom of expression. With enlargement slowing, this leverage may diminish and other levels have become important. Therefore, it is arguable that the Eastern Partnership and southern neighbourhood policy are test cases for how effective the EU can be beyond enlargement. Yet, with key regional actors in both the eastern and southern neighbourhoods all too aware of the EU’s failings, and with expectations high as to what the EU can achieve, ensuring these policies are strategic and sustained in their demands for freedom of expression is essential.
13 Jan 2014 | Egypt, News, Politics and Society, Religion and Culture
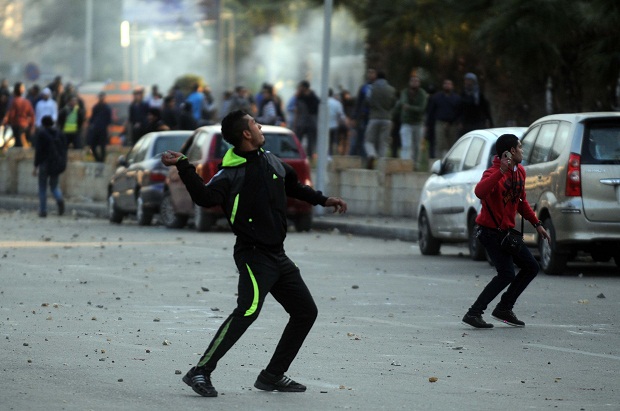

An alleged supporter of ousted President Mohamed Morsi clashes with Egyptian security forces in front of Cairo University, Egypt 12th January 2014 (Image: Nameer Galal/Demotix)
Egyptians head to polling stations on Tuesday to vote on a revised constitution heralded by Egypt’s military-backed government as a” first step in the country’s democratic transition” and billed as a blueprint for the “new Egypt.”
The amended document has also been hailed by analysts as one that “enshrines personal and political rights in stronger language than in previous constitutions.” Rights advocates however, have expressed fears that the enormous powers and privileges the ‘new’ charter grants the military could undermine those rights, rendering them meaningless .
The public is being reassured that the revised charter is “a vast improvement to the 2012 Muslim Brotherhood constitution” that was scrapped when the Islamist former President Mohamed Morsi was toppled by military-backed protests in July. In an Op-Ed published in the New York Times last week, Amr Moussa, a former Foreign Minister under deposed President Hosni Mubarak and the Head of the 50-member committee that amended the 2012 Constitution, said that the document –in its new form– “meets the needs and aspirations of all Egyptians” unlike the previous charter which he said, “had been rushed through by a single dominating political faction and answered only to its priorities”.
Ads in the local media and on billboards across the country promote a ‘yes’ vote on the charter, portraying its ratification as a ‘patriotic’ act. Public service messages broadcast on radio and TV stations tell Egyptians that even if they disagree with some of its provisions, the charter is “not permanent—Egypt is.” A ‘yes” vote will “complete the unfinished revolution Egyptians began on June 30,” intones the broadcaster in reference to the day millions took to the streets demanding the downfall of the Islamist regime.
The new charter grants Egyptians greater freedom of expression and belief and ensures equality between men and women. The provision on women’s rights says the state must take necessary measures to guarantee women have proper representation in legislative councils, hold senior public and administrative posts, and are appointed to judicial institutions. It obligates the state to provide protection to women against any form of violence. Meanwhile, articles that gave the previous constitution an “Islamist flair” have either been removed or replaced by others that limit the scope of Islamic law or Shariah. The charter also reaffirms the country’s commitment to its obligations under all previously signed international treaties and agreements including human rights covenants. It also empowers lawmakers to remove the president with a two-thirds majority, obliges the president to declare his financial assets and bans political parties founded on religion, sect or region. All of the above signal victory for Egypt’s liberals and rights advocates who had been vocal in their concerns about flaws in the previous constitution including provisions on religious freedoms and other liberties and rights of women and minorities.
But skeptics caution it may be too early to rejoice.
While some analysts hail a provision banning the prosecution of journalists for ‘publication offences’ as one that will “reinforce press freedom,” a widening government crackdown on critical voices in recent weeks has dashed hopes for greater freedom of expression. Secular revolutionary activists, bloggers and journalists have been targeted along with thousands of Brotherhood supporters and sympathizers, the majority of whom have been imprisoned on trumped up political charges. Four prominent activists (including iconic symbols of the 2011 Revolution Alaa Abdel Fattah and Ahmed Maher) languish behind bars for “taking part in unauthorized protests.” Meanwhile, three journalists working for the Al Jazeera English service remain in custody pending investigations on charges of ‘spreading lies and belonging to a terrorist cell.”
Another provision banning the closure of media outlets for what they broadcast or publish would have been plausible had it come before all channels linked to the Muslim Brotherhood were shut down in the wake of the military takeover of the country in July.
Critics meanwhile, cynically dismiss the provision giving citizens the right to freedom of assembly and demonstrations. They argue that a controversial new law criminalizing protests without prior permission from the authorities nullifies the provision.
And while the revised charter says freedom of belief is “absolute’–whereas the previous charter said it was “protected’– the freedom to practice religion and to establish places of worship is restricted to believers in the three “divine faiths’: Christianity, Islam and Judaism. This leaves the country’s Baha’is –who have long suffered discrimination –without protection or rights and may subject them to further persecution. Shia Muslims too face harassment in Egypt, according to the US State Department’s religious freedom 2012 report. Persistent hate speech culminated in the lynching of four Shias by a mob of ultraconservative Salafis in the village of Abu Musallim in Greater Cairo in June Earlier this month, a group of Canadian Shia pilgrims were barred entry into the country and were turned back by security officials.
But the biggest disappointment for secular activists and pro-democracy groups has been the retention of disputed provisions giving the military special privileges and allowing the continuation of military trials for civilians. Article 204 says that “civilians can be tried by military judges for attacks on armed forces, military installations, and military personnel.” Critics fear the provision could be applied to protesters, journalists and dissidents. For the next two presidential terms, the armed forces will also have the right to name the defense minister — an arrangement that positions the military as the main power broker, giving it autonomy above any civilian oversight. Moreover, the charter fails to ensure transparency for the armed forces’ budget allowing it to remain beyond civilian scrutiny.
“Failure of the charter to curb the military’s privileges paves the way for a bigger role for the army in becoming the main power broker,” said Hossam el-Hamalawy, a journalist and member of the Revolutionary Socialists Movement which played a key role in the 2011 mass uprising that toppled President Hosni Mubarak.
Despite its shortcomings, the charter is widely expected to be endorsed in the upcoming referendum. The majority of non-Islamists — a term often used to refer to Egypt’s leftists, liberals and Christians — are likely to approve the new charter simply because they yearn for a return to the stability and security they once enjoyed under authoritarian President Hosni Mubarak. An economic recession and rising unemployment have taken their toll on weary Egyptians whose livelihoods have been disrupted by the work stoppages and ongoing street protests. The economy had been on the brink of collapse before Saudi Arabia and other oil-rich Gulf states offered Egypt a multi-billion dollar rescue package to shore it up.
Analysts say the “yes” vote will not be an endorsement of the charter per se but rather, a nod of approval for the return of the military to power. They say the constitution will pass as an endorsement of Defense Minister General Abdel Fattah El Sissi, the country’s de facto ruler, who on Saturday confirmed he would run in the country’s next presidential elections “if the army gives me a mandate and if the people of Egypt ask me to do so”. General Sissi is idolized by millions of Egyptians who see him as the “saviour of the Revolution” despite the repressive measures used by the military to silence dissent since Morsi’s ouster.
Meanwhile, supporters of the ousted Islamist president have vowed to boycott what they call the “military” vote and are urging others to do likewise. Sheikh Youssef Qaradawi, a prominent Qatari-based Muslim Brotherhood cleric — who faces trial in absentia after the interim government branded him a ‘terrorist’ — has issued a religious edict or “fatwa” prohibiting Egyptians from voting in the referendum.
Some political groups have also declared their intention to boycott the vote while others have announced their outright rejection of the charter. The Strong Egypt Party, established in 2012 by former Brotherhood member Abdel Moneim Aboul Fottouh has said it opposes the constitution on grounds that “it fails to promote social justice and gives too much power to the President.” Four of the party’s members were arrested last week in Cairo for hanging up posters promoting a “no” vote. The April Six Movement — one of two main groups that organized and planned the mass protests that led to Hosni Mubarak’s overthrow — has also announced it would stay away from the ballot box, citing “the violent crackdown on Islamist protesters” as a reason. Other revolutionary groups like the Third Square — a loose coalition of leftists, liberals and moderate Islamists opposing both the military and the Muslim Brotherhood — have also said they would refrain from voting.
The enthusiasm and vigour that characterized the polls held after Mubarak’s overthrow have been replaced by disengagement and the mood of apathy that prevailed during the autocratic era of Hosni Mubarak. When asked if they will vote in the referendum, many ordinary Egyptians will answer, “What constitution? We want food for our children.” Many of them say they will not stand in line and wait for hours as they did in previous polls held during the last three years.
“I voted for Morsi in the last presidential election,” Mohamed Abdalla, a bearded taxi driver said. “What good did that do? Where is my vote now?”
This article was posted on 13 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org




