[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Syrian citizen journalist HAZZA AL-ADNAN writes in the summer 2016 Index on Censorship magazine on the realities of reporting in a country where a pseudonym and bulletproof vest offer little protection from constant danger” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
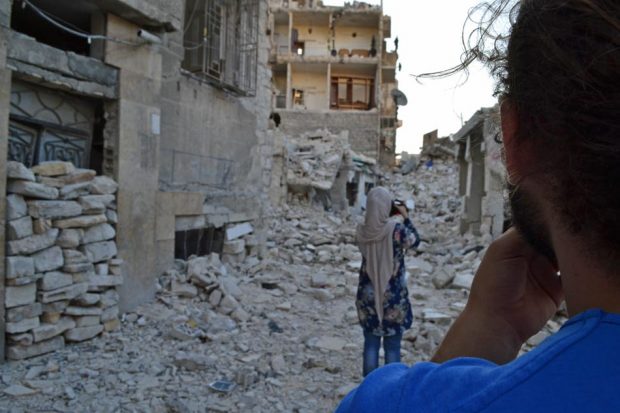

Aleppo: Somehow destroyed buildings and massacres become part of the daily view and even marks to guide people to places. (Photo: Zaina Erhaim)
“THE PSEUDONYM HELPS me to feel safe,” said Ali, a citizen journalist who works under a false name in Syria’s government-held regions. “I always pretend to be completely loyal to Bashar al-Assad’s regime while at the same time I am documenting the abuses perpetrated by his government against the activists and civilians.” Because of fear, many of the journalists inside Syria work under pseudonyms, especially in the government-held areas and those controlled by IS.
Despite the dangers of working as a journalist in Syria, there are still many who strive to report the truth, while trying to minimise the risks to themselves as much as possible. They receive some support and training from Western institutions, from time to time. But most work with local or Middle Eastern media agencies.
“If your aim is to report the truth, you cannot work in areas under government control, because it doesn’t want the truth to come out. You can work in the opposition-controlled areas, but you have to keep hidden from the government forces’ aircraft, and the Russian aircraft, and the IS organisation’s intelligence apparatus,” said Mounaf Abd Almajeed, 26, who works for Fresh Radio, a radio station in Idlib, northwest Syria.
“The government accuses us of terrorism, and the majority of the armed opposition factions do not look upon us favourably, because they confuse intelligence work with journalism,” Abd Almajeed added. “We always have to convince these factions that we are journalists, and not agents of the intelligence organisations of the US or Saudi Arabia or Qatar and so on.”
Some armed opposition factions are extreme Islamists, some of them are moderate Islamists and some of them belong to civilian or secular groups, and there is a state of cold – and sometimes hot – war among them. Abd Almajeed thinks that even if a journalist can gain the trust of a particular faction, the battle is not yet won, because he must now convince the other factions that he has not picked a side or become an agent.
Abd Almajeed tries to minimise the risks of the work by wearing a helmet and bullet-proof jacket when going to areas where clashes are taking place. He rarely works at night for fear of being kidnapped, and he doesn’t ever go to areas held by IS or the government. He believes these precautions have helped him to avoid many injuries, especially around seven months ago, when he was covering one of the battles between government and opposition forces around Aleppo, in northern Syria. When the trench that he was hiding in was targeted in an air raid, which he believes was conducted by Russian aircraft, four journalists were killed, but Mounaf was only slightly injured.
Abd Almajeed believes that Western media NGOs could do more to help by offering the required support to journalists inside opposition areas, but rather have confined their support to Syrian press organisations outside the country.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”However much we try to minimise the risks; hardly a week goes by without our losing a friend or colleague” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:left|color:%23dd3333″ google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic” css_animation=”fadeIn”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
But Ahmed Jalal, 35, editor of the local magazine Al-Manatarah, does not agree. He thinks that the diminished support is due to concern for the safety of their employees, and Syrians working with them, after the country became so dangerous for journalists.
As for the burden of responsibility laid on the journalists inside Syria, Jalal said: “In the early stages of the revolution we did not have a great responsibility to convey the truth to the international community because the door was open to journalists from all over the world, and many of them came in and reported the truth to their communities. But after a year or two of the revolution everything changed because Bashar al-Assad succeeded in getting his propaganda message across to the West that he was fighting terrorists and that the alternative to him was chaos and terrorism.”
Jalal believes that IS’s pursuit of journalists, and execution of some of them, forced Western agencies to withdraw their correspondents, and then the opposition factions’ media made repeated mistakes until the world began to view the Syrian conflict as a “sectarian war between the Alawites and the Shi’a on the one hand and the Sunnis on the other, or as a fundamentalist Islamic revolution that crossed borders, and not a people’s revolution”.
Jalal sighed, took a drag on his cigarette, and continued: “Our responsibility has become great, it is now up to us to convince the international community that we are reporting the truth, which can be expressed as the aspirations for freedom and justice of a people that a criminal regime is killing – and this is what compels us to risk our lives.”
Working under a pseudonym and wearing bullet-proof jackets is all journalists inside Syria can do to minimise the risks, according to Jalal, because nobody recognises the immunity of journalists, and nobody respects the international laws and conventions governing their work. He said: “We are in a jungle … all we can do is persevere, coping with the fear and the grief. However much we try to minimise the risks; hardly a week goes by without our losing a friend or colleague, who has died covering some battle or other, or in the bombing of civilians by government forces or their allies, or in an execution by Da’esh [IS].”
The editor said: “Hardly a day goes by without our seeing the dead body of a child torn apart by Bashar al-Assad’s aircraft.” In the opposition-held areas, ordinary citizens do not look upon journalists favourably.
Jalal added: “Every time we go to take a photograph we encounter people who refuse and say ‘You media people take photos and rake in the money and we get bombed by Bashar al-Assad’s planes because of you taking pictures.’”
Many journalists inside Syria want their output to reach the international community. “Unfortunately, it rarely gets through because most of the journalists in these areas do not possess English or the skills to communicate with the outside world, so when talking to the world they rely on compassion rather than understanding,” said Jalal.
Jalal wishes the armed opposition factions would invite Western media organisations into their areas and provide them with protection. And if that is impossible, then he asks “powerful news agencies like Reuters, Agence France-Presse and the Associated Press, and powerful networks like the BBC and CNN” to put trust in local journalists or citizen journalists in these areas.
Ahmed said: “We have now got good journalists inside the opposition-held areas who have received training from Western institutions such as the Institute for War and Peace Reporting and Reporters Without Borders and the CFI [run by the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs], and we now have training centres in these areas; all that we lack is the trust of the powerful Western agencies and the networks in us.”
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Translated by Sue Copeland
The writer of this piece, Hazza al-Adnan, was introduced to Index on Censorship by our 2016 Freedom of Expression Award winner Zaina Erhaim.
Erhaim won the journalism award for using her own skills to train other Syrians to be able to tell their stories too.
Erhaim told Index: “Hazza attended the first training I did in Idlib suburb. He is a lawyer and had no experience in journalism at all. After the training, he started publishing on our website [the Institute of War and Peace’s Damascus Bureau], and when their local radio station Fresh was established, he started working as an editor with them. He writes for many Syrian websites and has passed the training I gave to him to more than 30 others.”
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]This article appeared in the summer 2016 issue of Index on Censorship magazine. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80561″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422014535688″][vc_custom_heading text=”Syria tracker: Syria’s inside track” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422014535688|||”][vc_column_text]June 2014
Report on an ambitious project to chart and verify countrywide citizen reports, social media updates and news articles.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89073″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422013511563″][vc_custom_heading text=”Rise of Turkish citizens’ media” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422013511563|||”][vc_column_text]December 2013
Turkey’s mainstream media bias made the public turn to a new type of media outlet for their news.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80562″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422014548623″][vc_custom_heading text=”Holed up in Harare, Zimbabwe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422014548623|||”][vc_column_text]September 2014
Natasha Joseph talks to journalists who walk the line of reporting in Zimbabwe, which is dangerous business.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Danger in truth: truth in danger” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2016%2F05%2Fdanger-in-truth-truth-in-danger%2F|||”][vc_column_text]The summer 2016 issue of Index on Censorship magazine looks at why journalists around the world face increasing threats.
In the issue: articles by journalists Lindsey Hilsum and Jean-Paul Marthoz plus Stephen Grey. Special report on dangerous journalism, China’s most famous political cartoonist and the late Henning Mankell on colonialism in Africa.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”76282″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2016/05/danger-in-truth-truth-in-danger/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]