[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Fifty years after 1968, the year of protests, increasing attacks on the right to assembly must be addressed says Rachael Jolley”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
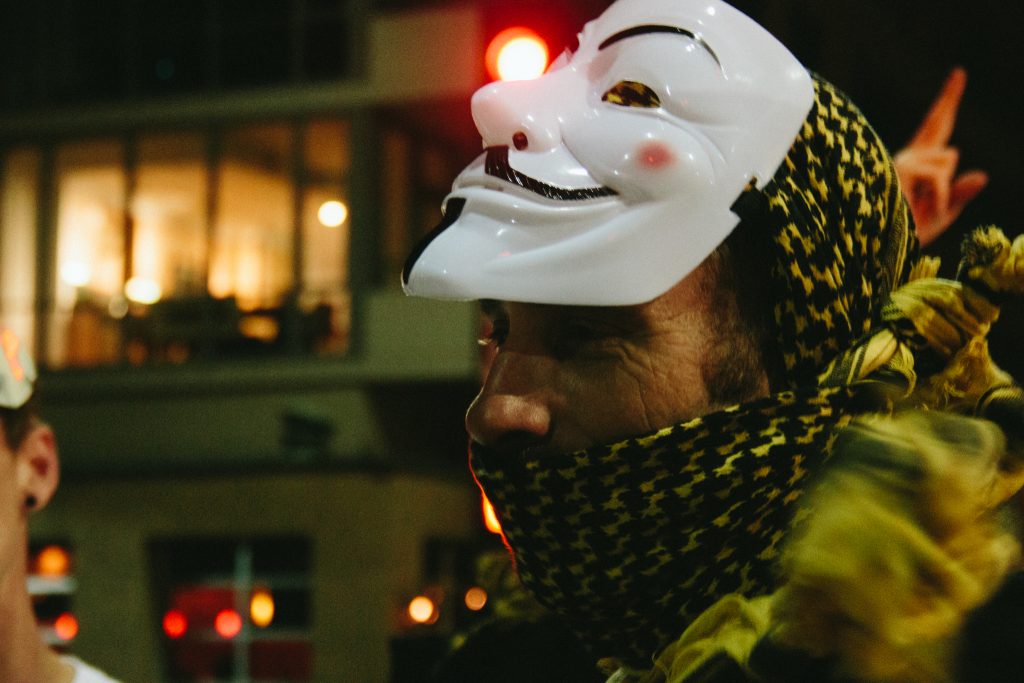

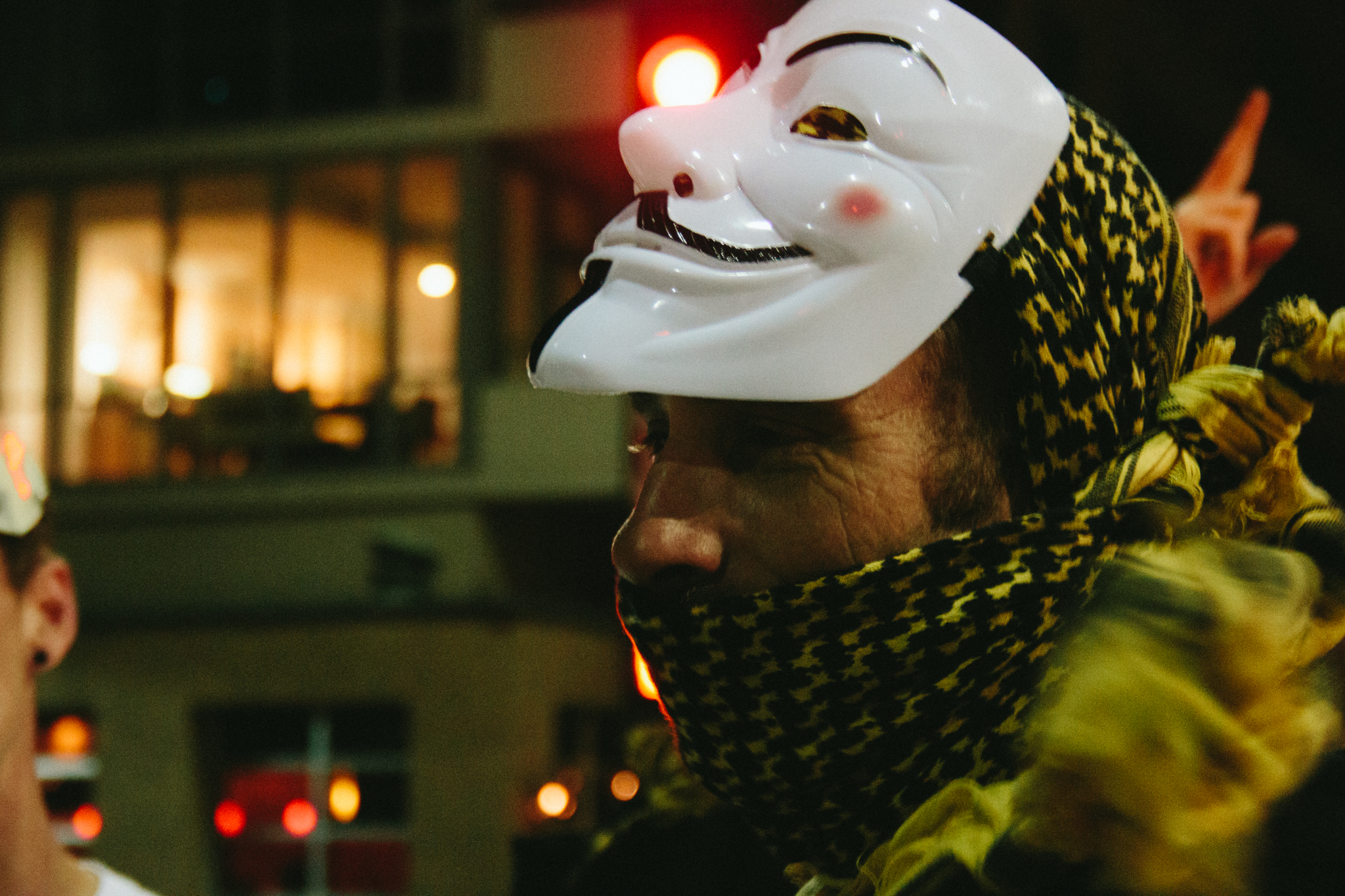
A protester wears the Anonymous mask during a protest. Credit: Sean P. Anderson/Flickr
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Close to where I live is a school named after an important protester of his age, John Ball. Ball was the co-leader of the 14th century Peasants’ Revolt, which looked for better conditions for the English poor and took to the streets to make that point. Masses walked from Kent to the edges of London, where Ball preached to the crowds. He argued against the poor being told where they could and couldn’t live, against being told what jobs they were allowed to pursue, and what they were allowed to wear. His basic demands were more equality, and more opportunity, a fairly modern message.
For challenging the status quo, Ball was put on trial and then put to death.
These protesters saw the right to assembly as a method for those who were not in power to speak out against the conditions in which they were expected to live and taxes they were expected to pay. In most countries today protest is still just that; a method of calling for change that people hope and believe will make life better.
However, in the 21st century the UK authorities, thankfully, do not believe protesters should be put to death for asserting their right to debate something in public, to call for laws to be modified or overturned, or for ridiculing a government decision.
Sadly though this basic right, the right to protest, is under threat in democracies, as well as, less surprisingly, in authoritarian states.
Fifty years after 1968, a year of significant protests around the world, is a good moment to take stock of the ways the right to assembly is being eroded and why it is worth fighting for.
In those 50 years have we become lazier about speaking out about our rights or dissatisfactions? Do we just expect the state to protect our individual liberties? Or do we just feel this basic democratic right is not important?
Most of the big leaps forward in societies have not happened without a struggle. The fall of dictatorships in Latin America, the end of apartheid, the right of women to vote, and more recently gay marriage, have partly come about because the public placed pressure on their governments by publicly showing dissatisfaction about the status quo. In other words, public protests were part of the story of major social change, and in doing so challenged those in power to listen.
Rigid and deferential societies, such as China, do not take kindly to people gathering in the street and telling the grand leaders that they are wrong. And with China racheting up its censorship and control, it’s no wonder that protesters risk punishment for public protest.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”Protecting protest is vital, even if it doesn’t feel important today. ” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
But it is not just China where the right to protest is not being protected. Our special report on the UK discovers that public squares in Bristol and other major cities are being handed over to private companies to manage for hundreds of years, giving away basic democratic rights like freedom of speech and assembly without so much as a backwards glance.
Leading legal academics revealed to Index that it was impossible to track this shift of public spaces into private hands in detail, as it was not being mapped as it would in other Western countries. As councils shrug off their responsibilities for historic city squares that have been at the centre of shaping those cities, they are also lightly handing over their responsibilities for public democracy, for the right to assembly and for local powers to be challenged.
The Bristol Alliance, which already controls one central shopping district with a 250-year lease, is now seeking to take over two central thoroughfares as part of a 100,000-square-metre deal (see page 15). And the people who are deciding to hand them over are elected representatives.
In the USA, where a similar shift has happened with private companies taking over the management of town squares, the right to protest and to free speech has, in many cases, been protected as part of the deal. But in the UK those hard-fought-for rights are being thrown away.
Another significant anniversary in 2018 is the centenary of the right to vote for British women over 30. That right came after decades of protests. Those suffragettes, if they were alive today, would not look kindly on English city councils who are giving away the rights of their ancestors to assemble and argue in public arenas.
For a swift lesson in why defending the right to assembly is vital, look to Duncan Tucker’s report on how protesters in Mexico, Argentina, Venezuela and Brazil are facing increasing threats, tear gas and prison, just for publicly criticising those governments.
In Venezuela, where there are increasing food and medicine shortages, as well as escalating inflation, legislation is being introduced to criminalise protest.
As Tucker details on page 27 and 28, Mexican authorities have passed or submitted at least 17 local and federal initiatives to regulate demonstrations in the past three years.
Those in power across these countries are using these new laws to target minorities and those with the least power, as is typically the case throughout history. When the mainstream middle class take part in protest, the police often respond less dramatically. The lesson here is that throughout the centuries freedom of expression and freedom of assembly have been used to challenge deference and the elite, and are vital tools in our defences against corruption and authoritarianism. Protecting protest is vital, even if it doesn’t feel important today. Tomorrow when it is gone, it could well be too late.
But it is not all bad news. We are also seeing the rise of extreme creativity in bringing protests to a whole new audience in 2017. From photos of cow masks in India to satirical election posters from the Two-Tailed Dog Party in Hungary, new techniques have the power to use dangerous levels of humour and political satire to hit the pressure points of politicians. These clever and powerful techniques have shown protest is not a dying art, but it can come back and bite the powers that be on the bum in an expected fashion. And that’s to be celebrated in 2018, a year which remembers all things protest.
Finally, don’t miss our amazing exclusive this issue, a brand new short story by the award-winning writer Ariel Dorfman, who imagines a meeting between Shakespeare and Cervantes, two of his heroes.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Rachael Jolley is the editor of Index on Censorship magazine.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91582″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228808534472″][vc_custom_heading text=”Uruguay 1968-88″ font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228808534472|||”][vc_column_text]June 1988
In 1968 she was a student and a political activist; in 1972 she was arrested, tortured and held for four years; then began the years of exile.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”94296″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228108533158″][vc_custom_heading text=”The girl athlete” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228108533158|||”][vc_column_text]February 1981
Unable to publish his work in Prague since the cultural freeze following the Soviet invasion in 1968, Ivan Klíma, has his short story published by Index. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91220″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422017716062″][vc_custom_heading text=”Cement protesters” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422017716062|||”][vc_column_text]June 2017
Protesters casting their feet in concrete are grabbing attention in Indonesia and inspiring other communities to challenge the government using new tactics.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row content_placement=”top”][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”What price protest?” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F12%2Fwhat-price-protest%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In homage to the 50th anniversary of 1968, the year the world took to the streets, the winter 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine looks at all aspects related to protest.
With: Micah White, Ariel Dorfman, Robert McCrum[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”96747″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/12/what-price-protest/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ css=”.vc_custom_1481888488328{padding-bottom: 50px !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]