19 Jun 2014 | China
China’s censors have a hard time stamping out memes.
Memes are proving one of the most powerful weapons Chinese netizens can use to fight online censorship. In the weeks on either side of this year’s 25th anniversary of Tiananmen Square, Chinese censors blocked a variety of terms on social media, including “blood”, “May 35” and even “today”, but references to the event kept on emerging in memes. Images alluding to the infamous “Tank Man” took on a variety of forms, using heads of Mao, tractors, lego and the iconic Hong Kong rubber duck in lieu of circulating the actual iconic photo.
The concept of the meme was coined by Richard Dawkins in 1976 to explain certain ideas, catchphrases, trends and other pieces of cultural information that replicate through a population. In its current usage, memes are defined as cultural items in the form of an image, video or phrase that spreads via the internet and are often altered in a creative or humorous way.
They’ve been part of the Chinese blogosphere for years and in many ways are ideally suited to the Chinese context. In part this is because Mandarin as a language allows for a playful form of double entrendre. Due to its many tones even the slightest shift in pronunciation can change a word’s meaning, while still sounding similar enough to invoke comparisons. The most famous Chinese meme, which parodies censorship itself, is that of the grass mud horse — caonima. In certain tones caonima means an alpaca; in other tones it’s a famous Chinese profanity. A few years back a video depicting a grass mud horse defeating a river crab, hexie, which is a homonym for the propaganda catchword “harmony”, went viral. To this day memes relating to this still emerge to poke fun at Chinese authorities.
Herein lies the strength of memes; their ability to evolve quickly and to imply rather than state makes them very difficult to detect and delete. After all, it’s hard enough for Chinese censors to keep track of and block all search terms directly referencing taboo topics. It’s harder still to block the infinite variations of words and images that might allude to controversy.
“Due to advanced and pervasive censorship, Chinese netizens are often forced to use coded language and images to talk about the social and political issues they find important,” says Ben Valentine, strategist and contributing writer for The Civic Beat, which examines social change memes and viral media.
“Images are much harder to algorithmically block because machines have trouble understanding visual content. While online writing directly talking about anything to do with Tiananmen Square in 1989 is extremely difficult, some of these memes make it past the censors. This is partially why, despite pervasive censorship, the Chinese web still remains a quite lively and active online space,” he adds.
For David Bandhurs, a researcher at the University of Hong Kong’s China Media Project, anyone who engages on a regular basis with others in the Chinese internet space “understands that irony, parody and other forms of expressive subterfuge are absolutely essential”. Memes “are the very substance of self-expression, of which social and political expression are a part, in a repressive space”.
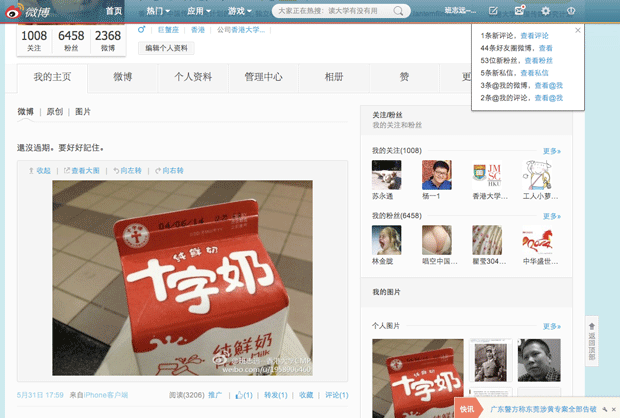
Ahead of the 4th June anniversary, Bandhurs posted a photo of his milk carton to Weibo (China’s Twitter). The expiration date was “04/06/14” and he wrote: “It’s not yet expired. We have to remember.”
“This was a very casual post, its point being to share a momentary thought with my community, a thought which for some might prompt a moment of esprit de corps, or a moment of reflection,” he tells Index.
“A lot of memes emerge, and they emerge constantly, in exactly this way. They encapsulate a thought or a feeling — often with a strong social or political dimension — that cannot be openly expressed. For example, the meme ‘My father is Li Gang’ quickly became emblematic of the injustice and inequality resulting from unchecked power. It was like a key that could open a box of thoughts no one could make very explicit.”
Just how effective are these memes? When shared instantly and abundantly across platforms like Weibo, they can be very powerful. In some instances Chinese memes have spurred a call to action, as was the case with those that knocked Beijing’s poor air quality. Until recently, the government denied the extent of the pollution. Conversation on the topic was silenced. Then photos of blue sky days and other related memes emerged. Now the government is approaching the topic with more transparency.
As for those topics which still remain off limits, memes provide an alternative form of political discourse. The China Digital Times sees caonima specifically as the “the icon of online resistance to censorship”.
Memes represent a way in which Chinese people momentarily seize control of conversations. For example, when blind activist and lawyer Chen Guangcheng was arrested, thousands of people posted photos of themselves wearing sunglasses in protest. While it might not seem like the biggest act of defiance, it’s still something in a nation where free speech and collective action are strictly controlled.
“These memes allow for more expression, a political conversation to start, for humor around a taboo subject; this is an incredibly empowering feeling. The ability to connect, talk, laugh, and touch on politics feels good,” explains Valentine.
Speaking of memes more generally, Cole Stryker, author of Epic Win for Anonymous: How 4chan’s Army Conquered the Web, tells Index:
“The power of politically-oriented memes is that they can be used in a playful way that isn’t necessarily directly confrontational to a regime. In some cases, the regime doesn’t even realize they’re being undermined. This allows activists to openly protest with impunity or even anonymity.”
At the same time, it’s important not to overstate the power of memes in China. Most vanish in the cyberspace vortex. Bandhurs’ milk carton post, for example, had more than 3,000 views, but could not be shared or commented upon, taking the sting out of it.
Memes are also predominantly harmless and politically apathetic. An office worker in Beijing, Wang Meimei, 28, said she and her friends constantly share memes. These solely relate to entertainment, not politics, because “we’re not interested in that”.
Meanwhile, 35-year-old Huang Yeping, who works in news media in Beijing, says none of the recent memes he has seen capture any form of zeitgeist.
“Is it me or have Chinese become even more subdued in terms of political expression, so much so that they haven’t been able to create anything as infectious as grass mud horse or a derivative of the tankman?” he asks, then adds:
“There has been this chill spreading across the cyber world.”
And as this indicates, taken alone memes cannot supersede collective action, nor do most have that in mind. They can spark a discussion, yes, yet remain as entertainment without the other key elements that bring about concrete action. What memes can do is allow for everyday Chinese to seize control of conversations — whether they be of a social, political or cultural nature — even if only for a few hours or days before the army of censors step in. And as Valentine says, that “feels good”.
This article was published on June 19, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
23 May 2014 | China, News and features

(Photo: Yo Hibino/Wikimedia Commons)
“Keep quiet and carry on” is the slogan that can best describe China’s take on the approaching 25th anniversary of the 1989 Tiananmen Square massacre.
This is the yearly Tiananmen anniversary crackdown, and people within China know what to expect; slower internet, blocked search terms, more military personnel in public and the arrest of high profile individuals. But this year’s crackdown appears particularly thorough, either a reaction to dissent being higher than usual or a perception that it is in light of the milestone anniversary.
The Chinese government has already jailed scores of lawyers, activists and intellectuals, sending a chilling message to any other would-be agitators. Of the most widely reported was the arrest of Pu Zhiqiang, a prominent human rights lawyer who helped organise the 1989 protests. His detention came three days after he joined a private panel discussion on the massacre. Around 15 people were at the event, five of whom have since been detained. Then there was the airing of confessions on state media by journalist Gao Yu and citizen journalist Xiang Nanfu this May, which echoes Maoist propaganda tactics.
As we get closer to 4 June actions against freedom of expression will grow. Yvonne Shen, who is Asia News Digest Editor at Freedom House, an NGO committed to tracking violations to free expression, says the Chinese government “step up their censorship efforts in the days surrounding that date”. Within a week the organisation anticipate spikes in suspicious activity online. They are keeping a close eye on social platform WeChat in particular, given its current popularity.
“There was a leaked document dated 31 May, 2011, from the Beijing Municipal Government, that suggested the authorities had launched a ‘wartime coordination mechanism’ that required all units to report suspicious information during the “sensitive period,” Shen tells Index of the government’s usual tactic.
China forbids open discussion of the Tiananmen Square crackdown, in which soldiers fired on crowds of unarmed pro-democracy protesters, killing hundreds if not thousands (no official death toll has ever been released). On top of arrests, an army of censors work overtime to ensure mentions of the event are quickly removed. Sites are blocked and words that allude to or directly reference it vanish.
The private realms of emails and direct messages are also monitored, as Louisa Lim, author of upcoming book The People’s Republic of Amnesia, Tiananmen Revisited, describes: “I wrote my book on a brand-new laptop that had never been online. Every night I locked it in a safe in my apartment. I never mentioned the book on the phone or in e-mail, at home or in the office — both located in the same Beijing diplomatic compound, which I assumed was bugged.”
Chinese journalists are trained “not to ever touch Tiananmen with a 10 foot pole,” Beijing-based journalist Eric Fish tells Index. He too perceives a recent shift: “The atmosphere for Chinese journalists has tightened quite a bit in general since Xi Jinping came to power. It feels like they’ve clamped down a lot more than normal in the lead-up to this anniversary.”
As Fish says, the detentions form part of a broader crackdown on free speech. When Xi Jinping came to power in 2012, there were hopes he would relax censorship. These hopes were quickly dashed. Index recently reported on a ban of seemingly innocent US TV shows, which shows just how pervasive the attack has been.
Even foreign journalists, who are usually granted more leeway, have experienced “a big uptick in pressure over the past two years,” says Fish, a reference to several prominent cases of journalist visas being revoked.
This is a fact Steven Levine has had to accept. “I anticipate being refused a Chinese visa the next time I apply to visit China as this is one way in which the Chinese authorities punish foreigners who criticise their human rights practices,” explains the retired professor of Chinese history and politics, who coordinates the Tiananmen Initiative Project — an individual effort aimed at focussing attention on the Tiananmen Movement and government crackdown.
Levine’s project has already been banned from the Chinese online world; within days of launching last November, the site had been blocked. Levine will not be deterred and continues to correspond with Chinese individuals inside the country, as well as with exiled Chinese who were either leaders or active in the 1989 movement. For him, being refused a visa is a price worth paying. It’s a different story for those inside of China, who take a much bigger gamble.
That said many have come up with creative ways to circumvent censorship. For example, prominent writer Murong Xuecun avoided the censors by using the politically neutral word “tractors” instead of the highly provocative “tanks”. And while “4th June” is blocked, the new code of “May 35th” has filled its place — a count of that month’s 31 days plus four in June.
It’s a game of cat and mouse. Ultimately, the cat is winning, but the mice aren’t going down without a fight.
This article was posted on May 23, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
25 Mar 2014 | China, Digital Freedom, News and features

(Photo illustration: Shutterstock)
The Chinese government has revealed it is expanding their censorship of the internet with a new training programme for the estimated two million “opinion monitors” Beijing organised last year.
Training will target civil servants in all aspects of government – from the police force to the judiciary, to academic institutions, and even to the press offices in large and medium sized enterprises, many of which are state-owned, according to the offical state news agency Xinhua.
“The training courses actually began some years ago, I had attend it in 2006 when I was working for Yangcheng evening news in Guangdong province. But this is the first time it has been publicised so widely”, Yunchao Wen, a Chinese anti-censorship activist and social media expert, told Index.
The training course will reportedly cost 6,800 yuan ($1,108) and graduates will receive a certificate according to one of five levels – assistant analyst, analyst, senior analyst, manager and senior manager. The test will take three hours and participants will be required to take a “refresher” course at a later date.
Once trained, monitors will “supervise” the posting of social media messages, deleting those that are deemed harmful. Beijing claims to have deployed “advanced filtering technology” to identify problematic posts, and will need to “rapidly filter out false, harmful, incorrect, or even reactionary information,” according to Xinhua.
Internet monitoring in China is an intensive process. Censored search terms are often placed on the list and then removed as a situation develops.
A recent example saw searches for “terrorist” with “Xinjiang” placed back on a list of banned keywords, after reports of a terrorist attack in Kunming surfaced. Over 140 were injured and 33 were reportedly killed. Weibo quickly turned to theories about Uyghur separatists from the northern province of Xinjiang. “Terrorist” and “Xinjiang” were periodically blocked over similar incidents in 2013 and 2011. Similarly “children stabbed and killed” also re-appeared on the ban list.
Beijing also issued strict instructions to media:
Media may publish a moderate amount of criticism and internet commentary which oppose terrorism and violence and which condemn the killers. However, do not hype this incident.
Anne Henochowicz, Translations Editor for China Digital Times, told Index about the constantly shifting world of Weibo censorship.
“As a story trends in the news cycle, more terms are blocked on Weibo; and when that story ebbs, many of those words become searchable again,” she explained.
Alongside the announcement about the training course, the government emphasised its concern over “the spreading of rumours,” which have recently become a euphemism for political discussion, including possible corruption of senior officials online. Those who spread “rumors” would be “severely punished,” the statement confirmed.
Ten days ago, opinion monitors identified forty five users of Weibo, who were accused of “spreading rumours” about the deadly knife attack in Kunming. Several of the accounts are operated by well-known figures: Some of whom questioned the veracity of media reports, or speculated about the ethnicity of the attackers. All of the users received an official warning while some were detained.
This article was published on March 25, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
19 Mar 2014 | China, Digital Freedom

WeChat was the darling of the Chinese start-up scene, the sexy competitor to Weibo domestically, and Twitter and WhatsApp, on the global stage. The design of the website meant that freedom of speech was for a while preserved – mainly because messages between users remained relatively private and insulated from the wider internet. But Beijing has orchestrated a sudden clampdown on the service : closing several high-profile accounts, some with hundreds of thousands of followers.
When users access the banned accounts, a Chinese message appears, translated as:
Due to reports from users that have been confirmed, all functions for this public account have been shut down for violating regulations. We suggest you cancel your subscription.
Users operating the site in English received a slightly different message – notably without any mention of “We suggest you cancel the subscription.”
WeChat started as a messaging service – however in 2012 the company behind the app – Tencent, introduced public accounts so that subscribers could follow celebrities, brands and well-known journalists and media outlets.
All of these subscription-based accounts on WeChat come with a “report” button at the bottom right of the content page. Some accounts had hundreds of thousands of subscribers.
Tencent has not stated its reasons for shutting down the accounts. The Chinese authorities have previously warned users that “spreading rumours” online is a crime – “spreading rumours” being a euphemism for speculation about corruption amongst senior Chinese officials.
Users of WeChat had already reported that the app blocked certain sensitive words.
Analysts have said they are not surprised by the censorship – although admit that WeChat has survived longer than most websites in China without restrictions on freedom of speech.
“I don’t find the suspensions surprising, though it’s still disheartening,” Jason Ng, author of Blocked on Weibo and social media expert.
“It would’ve been foolish of authorities not to regulate WeChat, like they do all other social media when they clearly have the capability and the will to do so.” Ng added “The only thing holding them back perhaps was a lack of resources.”
Ng pointed to the original “insular nature” of WeChat messaging, meanig it was less likely for “rumours” to go viral. However since 2012, the introduction of “new public accounts had clearly changed the authorities assumptions [about WeChat]”.
Yunchao Wen, a freedom of speech activist and Chinese social media expert told Index
“The Chinese government have never leaves any permanent space for political expression – sometimes they don’t find them straight away, sometimes they’re too busy dealing with other issues, but they are always censored.”
Wen also stressed that more than two hundred people were jailed by the Chinese authorities over political or human rights issues in 2013, as well as suggesting that the news had been “buried” while journalists were distracted.
“They closed down the Wechat public accounts on the last day of 12th National People’s Congress, trying to make sure foreign journalists didn’t notice,” said Wen.
Speculating on whether the censorship campaign will have hit WeChat commercially, Ng was sceptical.
“I don’t think it’s hit them too hard; it was only 50 or so accounts.” Ng also quipped “One Lionel Messi commercial and this event will probably be forgotten,” referring to the high profile celebrites who are regularly featured on the site.
WeChat was launched in early 2011, reportedly attracting 100 million registered users in its first fifteen months. The company revealed that it had 270 million active monthly users, up 124% from the previous year.
Sina Weibo, a key competitor for WeChat, is gearing up for an IPO on the Nasdaq – targeted to raise $500m. However investors have been warned that China’s censorship policies may negatively affect business – with several paragraphs in their sales materials relating to censorship.
Sina Weibo faced similar censorship to WeChat in 2012, telling investors “we had to disable the comment feature on our platform for three days to clean up feeds related to certain rumors.” Users were speculating about a possible coup d’etat in Beijing.
This article was published on 19 March 2014 at indexoncensorship.org




