12 Sep 2017 | News, Volume 46.03 Autumn 2017
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”The number of people listening to radio stations is on the rise, and with the arrival of podcasting this old form of media is having a rebirth, argues Rachael Jolley”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
A LONG TIME ago my friend Tom told me that for many people there were only two states of mind: talking, and waiting to talk. In effect as his simple description suggests, no one was listening to what anyone else had to say.
This was way before social media got to the state it is in today. In 2017 we have all become transmitters, broadcasting our micro thoughts and reactions almost incessantly. Sometimes I worry that people spend so much of their time on Twitter that they can’t have time to fit in basics like eating, cooking, sleeping, and doing a job.
Listen to a radio show, and you might be provoked, informed or excited about a new subject. But in listening you are doing something that is a little out of fashion, contemplating what others are saying, not writing down some angry instant response, or even just posting the first thought that comes into your head. Surprisingly radio is on the rise again (Americans listened to 11.5 billion hours of news across Nielsen’s portable people meter markets in 2016, up from 10.5 billion in 2015), its audience is growing across various age groups, and part of the reason might be because we are all tired of transmitting constantly. Instead we appear to be happier to settle down and listen to radio and, particularly its news programmes, again.
In the summer of 2017, around 48.2 million people in Britain listened to the radio at least once a week, up 0.9% from 2016. And in 2017 across the Atlantic, the USA is seeing a surge in listeners for news and talk radio. Of particular interest is the steady growth in those who listen to the radio for news in the 18-35 age group. Radio was thought to be going out of fashion as new technologies elbowed it out of the way, but instead it’s back and gathering new audiences. Part of the reason might be growing awareness that someone’s ramblings are not necessarily a reliable source of information.
Meanwhile, according to the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism at Oxford University, figures show that in most countries the proportion of the public using social media as a source for news has stagnated. In Portugal, Italy and Australia it has declined.
So why is radio so important? It has a particular strength over other forms of media and communication. You might only need a battery to give it life. And you can listen to radio anywhere without wifi, without a plug point, without being able to read, and without much fuss. That makes radio an essential for anyone living in a remote location, who hasn’t got access to newspapers or internet. It can bring the news and information about what is happening in the world to you, and if you live in a country where you don’t want people to track you, then a battery-operated radio is the way to go.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”Digital technologies have given radio a new lease of life.” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
In remote regions of Africa and India, where few other options are available, radio is massively important as a means of finding out what is going on locally, and internationally.
Radio is an old technology. It is the wrinkly old guy against the bouncing baby that is Twitter. The first voice broadcast was in 1900, and it’s come a long way since then.
After television came along, some thought it was the end for radio. But it wasn’t. Then along came the internet, and again some thought it was the last long days of summer for radio. But in fact digital technologies have given radio a new lease of life. Podcasting has kicked a whole new audience radio-wards, while retaining some of its old audience. Podcasts are portable, of course, and can be listened to on the way to work.
According to data from US-based Edison Research, audiences for podcasts in Australia and the United States are seeing steady growth. In Australia, among those who listen to podcasts, 30% listen to more than five hours a week, either at home or in their cars.
Not only have podcasts given us a new form of radio, but they have opened up new opportunities for people who want to make their own programmes. Anyone can now be the equivalent of a radio reporter by making their own podcast at very little cost. With some basic skills and nothing more than a smart phone, you can record interviews, and add an introduction. You can even cut them together on a phone app, or a free internet programme, before publishing your programme on a platform like Soundcloud.
Podcasting has given investigative reporting a boost too, as those who listened to the award-winning Serial will recognise. Meticulous and detailed research went into the journalism for the first series of Serial, which reinvestigated a murder in Baltimore. Millions of people tuned in around the world to find out what each episode would unveil. But unlike the old days of radio, listeners didn’t always have to listen at the same time every week, or sit around an old set in the corner of their living room. The podcast could be downloaded to phones, or iPads for a long journey, or even just live streamed.
While journalists are using radio to bring information to hard to reach places, the bad news, which we report in this issue, is that others are trying to stop them.
In India, the government still tightly controls news radio, so only the state can broadcast, despite having hinted over the past few years that things might change. This is a country where radio is vital for millions of people. The Indian government should be rethinking its approach to radio as innovative radio pioneer Shu Choudray argues (p17).
In Somalia, radio journalist Marwan Mayow Hussein checks under his car for bombs before going off to work. The work he does is dangerous, and certain people would rather he didn’t broadcast, as Ismail Einashe reports in this magazine (p8). Meanwhile in Iraq, the team at Alghad FM in Mosul don’t make their names public in order to stay a little safer as they continue to work in a war zone. Laura Silvia Battaglia went there to meet them (p41).
In Rwanda, radio is vital, Peter Kettler who ran an NGO called Coffee Lifeline there, told Index: “Radio is far more powerful than messages on mobile phones. In Rwanda you are dealing with a heavily illiterate population, but everyone has a radio or access to a shared radio.” During the period of genocide radio was used to incite violence. Graham Holliday investigates the role of radio in Rwanda today (p51), and finds it faces censorship and banning orders. The BBC World Service in English and Kinyarwanda have been banned by the president, and journalists are fleeing the country.
The new rise of radio allows more opportunities to discuss and debate than ever before, but we must also fight for radio stations to be unbound from state control and to be able to broadcast news freely.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Rachael Jolley is the editor of Index on Censorship magazine. She recently won the editor of the year (special interest) at British Society of Magazine Editors’ 2016 awards
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89165″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/03064220100390021001″][vc_custom_heading text=”Radio waves” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F03064220100390021001|||”][vc_column_text]June 2010
Liam Hodkinson and Elizabeth Stitt compile comprehensive facts on radio usage throughout the world.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”90954″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064229408535741″][vc_custom_heading text=”Death by radio” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064229408535741|||”][vc_column_text]September 1994
If Rwandan genocide comes to trial, owners of Radio des Milk Collines should be head of the accused.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89165″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422010372565″][vc_custom_heading text=”Going local” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422010372565|||”][vc_column_text]June 2010
Jo Glanville explains how radio has the most impact on the local level than any other media platform.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Free to air” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F09%2Ffree-to-air%2F|||”][vc_column_text]Through a range of in-depth reporting, interviews and illustrations, the autumn 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine explores how radio has been reborn and is innovating ways to deliver news in war zones, developing countries and online
With: Ismail Einashe, Peter Bazalgette, Wana Udobang[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”95458″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/09/free-to-air/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
16 Aug 2017 | Magazine, News, Volume 46.02 Summer 2017
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
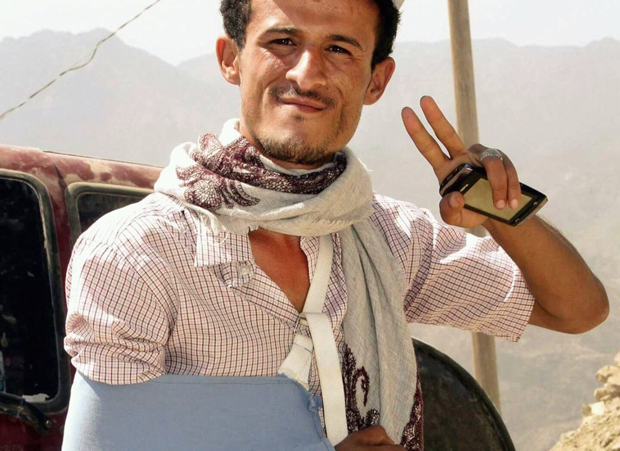

Yemeni journalist Abdulaziz Muhammad al-Sabri wears a sling after he was shot by a sniper in 2015
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Yemeni journalist Abdulaziz Muhammad al-Sabri details the dangers of reporting in his country. Interview by Laura Silvia Battaglia”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Abdulaziz Muhammad al-Sabri is smiling, despite everything. But he cannot fail to feel depressed when he sees the photos taken a few months ago, in which he is holding a telephoto lens or setting up a video camera on a tripod: “The Houthis confiscated these from me. They confiscated all my equipment. Even if I wanted to continue working, I wouldn’t be able to.”
Al-Sabri is a Yemeni journalist, filmmaker and cameraman, and a native of Taiz, the city that was briefly the bloodiest frontline in the country’s civil war. He has worked in the worst hotspots, supplying original material to international media like Reuters and Sky News. “I have always liked working in the field,” he said, “and I was really doing good work from the start of the 2011 revolution.”
But since the beginning of the war, the working environment for Yemeni journalists has progressively deteriorated. In the most recent case, veteran journalist Yahia Abdulraqeeb al-Jubaihi faced a trial behind closed doors and was sentenced to death after he published stories critical of Yemen’s Houthi rebels. Many journalists have disappeared or been detained, and media outlets closed, in the past few years.
“The media industry and those who work in Yemen are coming up against a war machine which slams every door in our faces, and which controls all the local and international media bureaus. Attacks and assaults against us have affected 80% of the people employed in these professions, without counting the journalists who have already been killed, and there have been around 160 cases of assaults, attacks and kidnappings. Many journalists have had to leave the country to save their lives. Like my very dear friend Hamdan al-Bukari, who was working for Al-Jazeera in Taiz.”
Al-Sabri wanted to tell his story to Index on Censorship without leaving out details “because there is nothing left for us to do here except to denounce what is going on, even if nobody is listening to us”. He spoke of systematic intimidation by the Houthi militias in his area against journalists in general, and in particular against those who work for the international media: “In Taiz they have even used us as human shields. Many colleagues have been taken to arms depots, which are under attack from the [Saudi-led, government-allied] coalition, so that once the military target has been hit, the coalition can be accused of killing journalists.”
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”In Taiz they have even used us as human shields” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
This sort of intimidation is one of the reasons why researching and reporting on the conflict is very difficult. “In Taiz and in the north, apart from those working for al-Masirah, the Houthis’ TV station, and the pro-Iranian channels, al-Manar and al-Alam, only a few other journalists are able to work from here, and those few, local and international, are putting their necks on the line,” said al-Sabri.
“You’re lucky if you can make it, otherwise you fall victim to a bullet from the militias, attacks, kidnappings. Foreigners are unable even to obtain visas because of the limitations imposed by [Abdrabbuh Mansour] Hadi’s government and the coalition. The official excuse is that the government ‘fears’ for their lives, since if they were kidnapped, imprisoned or died in a coalition bombardment, it would be the Yemeni government’s responsibility.”
Al-Sabri has personal experience of the violence against journalists in Yemen. In December 2015, he was wounded in the shoulder by a sniper who was aiming at his head. On another occasion, he was kidnapped, held at a secret location for 15 days, blindfolded, threatened with death and tortured.
The full article by Laura Silvia Battaglia is available with a print or online subscription.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Award-winning journalist Laura Silvia Battaglia reports regularly from Yemen. Translated by Sue Copeland.
This article is published in full in the Summer 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine. Print copies of the magazine are available on Amazon, or you can find information about print or digital subscriptions here. Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), and Home (Manchester). Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80562″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422014550963″][vc_custom_heading text=”The future of Yemeni journalists” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422014550963|||”][vc_column_text]September 2014
The Yemeni government should not be the ones judging the objectivity of reporting, but there is hope for more freedom.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80569″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422016657007″][vc_custom_heading text=”Journalists face increasing threats” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422016657007|||”][vc_column_text]June 2016
Rachael Jolley explains why journalists around the world, especially near the Middle East, are facing increasing threats.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80562″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422014548392″][vc_custom_heading text=”Journalists should ignore technology” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422014548392|||”][vc_column_text]September 2014
Journalists in war zones may need to ignore technology and go back to old ways to avoiding surveillance, says Iona Craig.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row content_placement=”top”][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”100 Years On” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F06%2F100-years-on%2F|||”][vc_column_text]Through a range of in-depth reporting, interviews and illustrations, the summer 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine explores how the consequences of the 1917 Russian Revolution still affect freedoms today, in Russia and around the world.
With: Andrei Arkhangelsky, BG Muhn, Nina Khrushcheva[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91220″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/06/100-years-on/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ css=”.vc_custom_1481888488328{padding-bottom: 50px !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
4 Aug 2017 | Germany, Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Journalists covering the G20 Summit in Hamburg in July were subject to assaults, intimidation and some lost their accreditation, according to verified incidents documented by Index on Censorship’s project Mapping Media Freedom.
Several journalists reported that they were assaulted by police while covering protests against the meeting, which included leaders of the 19 largest industrial nations in the world plus the EU. Leading up to the summit, freelance journalist Martin Eimermacher was assaulted while police were clearing a protest camp in Hamburg on 2 July, according to Netzpolitik and Jetzt.
Police had demolished protesters’ tents when Eimermacher tried to leave the area, telling police he felt unwell. He said that officers pushed him and several other journalists to the centre of a field. He showed his press card, which was slapped out of his hand by a police officer who then pepper sprayed him.
“In my opinion the most dangerous thing is that this sets an example within Germany and beyond, that such treatment of journalists is acceptable,” Mapping Media Freedom Germany correspondent Pascale Müller said. “There seemed to have been, on an individual level of police officers, a severe lack of understanding of the rights of the press and their role as an observer and part of a healthy democracy.”
On 7 July, ITN News journalist Flo Smith, his producer and cameraperson were all pepper sprayed by police. Photojournalist Henry Langston of Vice UK was struck by a police water cannon. RT UK published a video in which police assaulted and injured photojournalist Zino Peterk, who later had to go to the hospital for his injuries.
On 8 July, Spiegel Online photographer Chris Grodotzki said police assaulted him with pepper spray while he was covering protests in Schulterblatt. Taz reporter Martin Kaul sustained minor injuries when he was hit by protesters while live-streaming the demonstration, according to Deutschlandfunk. Müller noted that some attacks by protesters targeted journalists they perceived as right-wing, “but in some cases it seems that people were already so ‘high on violence’ that they hurt journalists regardless of their political affiliation.”[/vc_column_text][vc_separator][vc_custom_heading text=”Media freedom is under threat worldwide. Journalists are threatened, jailed and even killed simply for doing their job.” font_container=”tag:h3|text_align:left” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fcampaigns%2Fpress-regulation%2F|||”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Index on Censorship monitors press freedom in Germany and 41 other European area nations.
As of 4/8/2017, there were 101 verified incidents associated with Germany in the Mapping Media Freedom database.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship campaigns against laws that stifle journalists’ work. We also publish an award-winning magazine featuring work by and about censored journalists. Support our work today.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][vc_column_text]“Many journalists who covered the protest directly and that I have spoken to were emotionally and physically affected even a week after” Müller said. The press freedom violations were widely condemned, but according to Müller “The most shocking revelation came after the protests, when Sueddeutsche Zeitung revealed that the BKA had monitored selected journalists during their summit coverage over the past 10 years. This was very disturbing and lead to a certain level of insecurity within the profession. “
Other journalists reported the use of intimidation tactics by police. In the Schanze neighbourhood, Frank Schneider, a reporter for Bild, tweeted that police told journalists to “leave or you’ll go to the hospital”. F-Mag journalist Wiebke Harms reported on Twitter that police in Schanze told her: “Your press card is worth nothing.” Freelance journalist Reuben Neugebauer was told “now press freedom is over”.
Thirty-two journalists had their accreditation revoked by federal police on 7 and 8 July. German government spokesperson Steffen Seibert cited ‘security concerns’ as the rationale for the loss of access to the summit.
Journalists who lost accreditation include the photographer Björn Kietzmann, Rafael Heygster (Weser Kurier), photographer for Junge Welt, Willi Effenberger Alfred Denzinger (Beobachter News), photographer Chris Grodotzki (Spiegel Online), Adil Yigit (Avrupa Postasi), editor Elsa Koester (Neues Deutschland) and freelance photographer Po Ming Cheung.
When trying to enter a press area, Grodotzki and Yigit were told by police that their accreditation was no longer valid. Photographers Björn Kietzmann for Weser Kurier and Rafael Heygster were also not allowed to enter the press area.
Müller does not think that this treatment will intimidate journalists into stepping back from events like this in the future. “Quite the opposite, I think that many journalists and their outlets are quite resilient against such types of violence or blocked access. G20 brought press freedom issues to the forefront in Germany and made journalists even more aware of their role as critical observers, even in the middle of such violent tension and intimidation attempts.”[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1501833910854-5bf94268-20d1-5″ taxonomies=”77″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
2 Aug 2017 | Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News
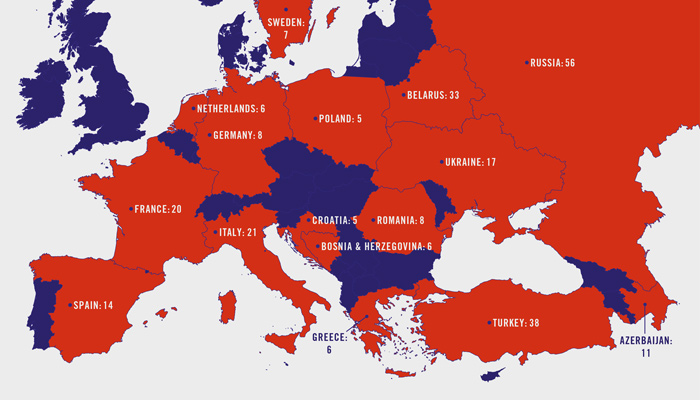
Journalists continue to face unprecedented pressure in Europe as reports submitted to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom platform in the first quarter of 2017 demonstrate. Media professionals—primarily in Turkey, Russia, Belarus and Ukraine—were arrested at an alarming rate, more than a fourfold increase over the fourth quarter of 2016.
“During the first quarter of 2017, the MMF database registered several trends that we find to be acute challenges to media freedom. Some European governments have clearly interfered with media pluralism. Others have harassed, detained and intimidated journalists. All of these actions debase and devalue the work of the press and undermine a basic foundation of democracy,” Hannah Machlin, project manager at Mapping Media Freedom, said.
During Q1, authorities in multiple countries shut down critical and independent media outlets and intimidated reporters who asked challenging questions. Turkey continues to be the largest jailer of journalists in the world with a total of 148 journalists in prison by the end of March according to the Platform for Independent Journalists P24, a Turkey-based MMF partner, which monitors the number of arrests in the country.
Even reporters in countries often thought to respect freedom of the press, such as Sweden, France and Germany, faced obstacles to performing their professional duties. They were abused by the leaders of extreme populist movements and their supporters, who encouraged a distrust of “mainstream media”; and blocked by nervous politicians who were seeing, particularly in France, the old political certainties swept away.
Between 1 January and 31 March 2017, Mapping Media Freedom’s network of correspondents and other journalists submitted a total of 299 violations of press freedom to the database.
The full report can be found online at Mapping Media Freedom or in PDF format.

![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]


