22 Nov 2013 | Americas, Asia and Pacific, Azerbaijan News, Europe and Central Asia, News

Tomorrow is International Day To End Impunity. “When someone acts with impunity, it means that their actions have no consequences” explains IFEX, the global freedom of expression network behind the campaign. Since 1992, 600 journalists have been killed with impunity — that is 600 lives taken with all or some of those culpable not being being held responsible. Countless others — writers, activists, musicians — have joined their ranks, simply for exercising their right to freedom of expression.
This year has only added to the grim statistics. By the middle of January, six journalists had already been murdered. We are now getting close to the end of 2013, and 73 more journalists and two media workers have suffered the same fate — 48 in cases directly connected to their work, 25 with motives still unconfirmed. Out of these, 15 were killed without anyone — perpetrators or masterminds — convicted.
Russia is notorious for its culture of impunity. In July this year, Akhmednabi Akhmednabiev, a Russian journalist reporting on human rights violations in the Caucasus, was shot dead. In 2009 he had been placed on an “execution list” on leaflets distributed anonymously, and had in the past also received death threats. In January he survived an assassination attempt which local authorities reportedly refused to investigate. His case is still classed as murder with impunity.
Pakistan is also an increasingly dangerous place to work as a journalist. Twenty seven of the 28 journalists killed in the past 11 years in connection with their work have been killed with impunity. In the last year alone, seven journalists have been murdered. Express Tribune journalist Rana Tanveer told Index he has received death threats and been followed for reporting on minority issues. In October, Karak Times journalists Ayub Khattak was gunned down after filing a report on the drugs trade.
In July, Honduran TV commentator Aníbal Barrow was kidnapped together with his family and a driver. The others were released, but after two weeks, Barrow’s body was found floating in a lagoon. He was the second journalists with links to the country’s president Porfirio Lobo Sosa — they were close friends — to have been killed over the past two years. Four members of the criminal group “Gordo” were detained in connection with the case, but at one point, there were at least three other suspects on the run.
In September, Colombian lawyer and radio host Édison Alberto Molina was shot four times while riding on his motorcycle with his wife. His show “Consultorio Jurídico” (The Law Office), aired on community radio station Puerto Berrío Stereo, and often took on the topic of corruption. The Inter American Press Association in October called on authorities to open “a prompt investigation into the murders” of him and news vendor and occasional stringer José Darío Arenas, who was also killed in September.
Meanwhile in Mexico, a country for many synonymous with impunity for crimes against the media, three journalists were murdered in 2013. The state public prosecutor’s offices has yet to announce any progress in the cases of Daniel Martínez Bazaldúa, Mario Ricardo Chávez Jorge and Alberto López Bello, or disclose whether they are linked to their work. Notorious criminal syndicate Zetas took responsibility for the murder of Martínez Bazaldúa and warned the police about investigating the case. He was a society photographer and student, only 22 at the time of his death. Chavez Jorge, founder of an online newspaper, disappeared in May and his body was found in June, but in August the state attorney’s office said they did not have a record of his death. López Bello was a crime reporter who had published stories on the drugs trade.
This year, 20 journalists — from Naji Asaad in January to Nour al-Din Al-Hafiri in September — have also lost their lives covering the ongoing tragedy of the Syrian civil war. Their loved ones, like those of all the civilians killed, will have to wait for justice.
It is also worth noting that while an unresolved or uninvestigated murder is the most serious and devastating manifestation of impunity, it is not the only one. Across the world, journalists are being attacked and intimidated without consequences. In August there was a two-hour long raid on the home of Sri Lankan editor and columnist Mandana Ismail Abeywickrema, who recently started a journalists’ trade union. Despite her receiving threats related to her work prior to the attack, it was labelled a robbery by the police. Bahraini citizen journalist Mohamed Hassan experienced similar incident, also in August, when he was arrested and his equipment seized during a night-time raid. His lawyer Abdul Aziz Mosa was also detained and his computer confiscated, after tweeting about his client being beaten. In October, a group of Azerbaijani journalists were attacked by a pro-government mob while covering an opposition rally in the town of Sabirabad. One of the journalists, Ramin Deko, told Index of regular threats and intimidation.
International Day To End Impunity is a time to reflect on these staggering figures and the tragic stories behind them. More importantly, however, it represents an opportunity to stand up and demand action. Demand that Russia’s President Vladimir Putin, Mexico’s President Enrique Peña Nieto, Pakistan’s President Mamnoon Hussain and the rest of the world’s leaders provide justice for those murdered. Demand an end to the culture of impunity in which journalists, writers, activists, lawyers, musicians and others can be intimidated, attacked and killed simply for daring to speak truth to power. Visit the campaign website to see how you can take action.
23 Oct 2013 | News, Pakistan, Religion and Culture
It’s been over two weeks now that Rana Tanveer, a reporter in Lahore at the English daily, Express Tribune, has not gone to work.
Early this month, he received a one-page letter, in the Urdu language, terming him an apostate and accusing him of writing in favour of Ahmadis and Christians.
“It warned me to stop writing ‘against’ Islam and seek ‘forgiveness’ from God,” he said over the phone from his home in the Punjab province.
It further warned him that if he did not desist, he would be killed — since that is the punishment of a person declared an apostate.
“I can’t work like this; no reporter can, if he cannot roam about freely,” said Tanveer.
Initially, he did not take the letter too seriously, but a week after he received the letter, he felt he was being followed on a motorbike. “It’s a scary experience,” he conceded, adding: “I made a few turns just to be sure that this was not a figment of my imagination, but the man on the motorbike persisted. I knew then that this was no joke and I had to do something.”
His seniors at work advised him to at least file a complaint with the police, which he did, but he did not name anyone “due to security reasons”.
“My editor told me to keep a low profile and not to report on minority issues for a while, and if I had to, it would go without by byline,” said the journalist.
Farahnaz Zahidi, features editor in the same paper as Tanveer’s feels very strongly about one’s byline being taken away. “As a journalist, perhaps the biggest satisfaction in this otherwise perilous and often under-paid profession is one’s by-line; it also lends credibility.”
However, she added, by shooting the messenger, society loses out. “The right to information is threatened when media persons threatened.”
Tanveer finds a plethora of minority rights abuses strewn around his city but says few journalists feel inclined to take up these issues.
“Mine seems to be a lone battle,” he said. “I am often scorned by my colleagues for reporting ‘chooras’ (derogatory term used for Christians, also among the poorest sections of society and consigned to menial janitorial jobs) and ‘Qadianis’ (also a derogatory name for those belonging to the Ahmadi faith, declared non-Muslims by state in 1974),” he said.
But it’s not indifference to these rights issue alone that keeps journalists from reporting on them. Senior journalist and communication expert, Babar Ayaz, says it is also quite dangerous to write about “the victimisation of Ahmadis, Christians or Hindus”.
Nevertheless, he added: “Journalists have to write what is right. Threats and killings are hazards of this job living in an increasingly intolerant society.”
He remembered when he wrote a piece on the attack on the massacre of Ahmadis in Lahore [in May 2010], he received a couple “abusive phone calls”. He also received some angry messages on a chapter in his book titled: What’s Wrong With Pakistan? The book, which was published in August criticises Islamic laws in Pakistan.
“But we are small fry,” said Ayaz. “When Nawaz Sharif expressed condolence on the killings of ‘our Ahmadis bhais [brothers]’ some mullahs said that by calling them ‘bhai’ he had committed a sin. The extremists have no logic but they have muscle power,” he added.
According to Aamer Mahmood, who heads the press section of the Ahmadiyya Jammat, and is in regular touch with several journalists: “The fear among them is palpable. While many empathise with us for the way our rights are trampled, they say their hands are tied. Some are scared of the wrath of the extremists; others fear they will lose their jobs.”
“It is indeed becoming more dangerous to write on these issues, in any language,” agreed Kamila Hyat, a rights activist and former editor of English daily The News. “I believe that while sections of the English language press remain relatively liberal, more and more are succumbing to the bias and intolerance we see everywhere,” she pointed out.
“The manner in which the ‘agenda’ for news is set, notably by the electronic media, also shoves minority issues to the sidelines, and intolerant mindsets exist everywhere — even among the educated,” she said.
With seven journalists having lost their lives since January this year, according to the 2013 Impunity Index report by the Committee to Protect Journalists (CJP), just last year, Pakistan which was ranked tenth, has moved two spots up at eighth position for the worst place for the press. Further, it has been declared more dangerous than Russia, Brazil, Nigeria and India.
According to the CJP, 28 Pakistani journalists have been murdered since 1992 in connection with their work, 27 of whom were killed with impunity. The deaths of 24 additional killed during the same period cannot be confirmed as “targeted.”
“Doing journalism in Pakistan is not easy, which is ranked the third most dangerous country for reporting after Syria and Egypt,” observes Mazhar Abbas, former secretary general of the Pakistan Federal Union of Journalists, a formidable voice fighting for the rights of journalists. While journalists continue reporting despite threats particularly those working in the Federally Administered Tribal Area (FATA), Balochistan and even in the southern port city of Karachi, Abbas said, reporters from the Punjab province seemed comparatively safer.
But not anymore, it seems.
Abbas said every threat should be taken seriously. “The letter to Tanveer could be an individual act or from a group. The government and administration need to probe this matter and find out about the person who sent this letter in the first place. Journalists reporting on sensitive issues should do so responsibly; their reports should be factually correct with minimum expression that can lead to stoking up controversy.”
This article was originally posted on 23 Oct 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
22 Oct 2013 | Africa, News, Politics and Society
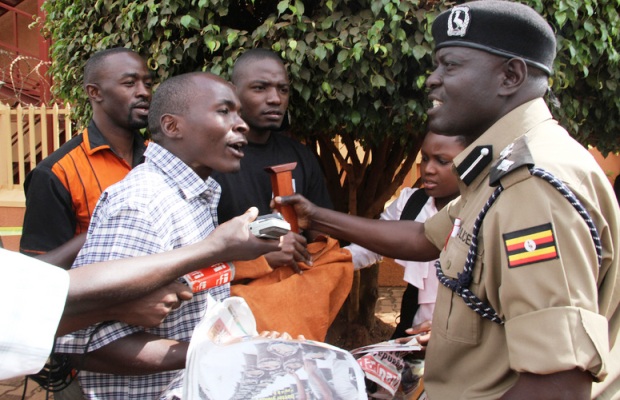

In June 2013, police and protesters clashed at the offices of the Daily Monitor, Kampala. Picture Isaac Kasamani/Demotix
In the age of technology with high-speed Internet access and smart phones, it is sometimes easy to imagine that all journalists’ working lives are the same: deadlines, insufficient resources, worrying about the threats of digital media and the race to break news.
In some ways these concerns are indeed universal. However, what journalists in North America and Europe hardly ever have to worry about is their basic right to report the news. It is true that in a post-Wikileaks and News of the World journalistic environment, all reporters have had to consider their fundamental role in providing news and information and analysis ethically. However, in Africa many journalists find themselves carefully tiptoeing through minefields of media laws which limit their ability to report accurately and truthfully on the news of the day, particularly when reporting on activities of the powerful in government.
Recently in Swaziland, a journalist has been charged with contempt of court for reporting the fundamental issue of whether or not the Chief Justice is fit to hold office, given that he is the subject of impeachment proceedings back in his own country, Lesotho. Several Zambian journalists were brought to court earlier this year, initially accused of sedition. In Ethiopia, journalists are serving time in prison, sentenced for threatening the state with their reports.
Besides individual actions taken against journalists, whole media enterprises are also at risk. In Tanzania, the two newspapers Mwananchi and Mtanzania have been suspended by the unilateral action of the Minister of Information citing breach of the peace concerns – Mwananchi was reporting on new salary structures in the government. Earlier this year, the newsroom of the Ugandan newspaper Daily Monitor was under siege for over a week, while police was trying to find letters that were exchanged between editors and a source.
There is no doubt that much state action against journalists and media houses is unconstitutional. However, there is also no doubt that Africa’s media laws do make provision for draconian action to be taken against journalists and publications.
The Konrad Adenauer Stiftung’s Media Programme has recently published a two-volume Media Law Handbook for Southern Africa, written by Justine Limpitlaw. The handbook is available for free download on the internet. One of the most important aims of the handbook is simply to provide information about what the law is in a number of southern African countries. Statutes are often not available electronically and many journalists simply have no idea about what the laws governing the media are.
A key characteristic of many southern African countries is a media law landscape with a relatively benign liberal constitution at the apex. All constitutions protect freedom of expression to some extent. However, very few changes have been made to media legislation to ensure that the legislation accords with the constitutional right to freedom of expression. Despite oft-expressed anger at the colonial era and its on-going repercussions for the continent, African political elites have essentially retained colonial era media laws as is.
One only has to list many in-force statutes to note that African media law appears to have stultified in the early or mid-20th century. Both Lesotho’s and Swaziland’s Sedition legislation dates back to 1938. Swaziland’s Cinematograph Act is from 1920. Many countries’ Penal Codes date back to the 1960s – prior to their independence from Colonial powers. These Penal Codes criminalise many forms of expression including defamation, insult and false news, and provide for significant jail sentences.
Sadly few attempts have been made to update African media laws. On the rare occasion where a country has engaged in media law reform, the results have been decidedly mixed. South Africa’s attempt to update apartheid-era security laws has been roundly condemned for promoting governmental secrecy at the expense of the public interest.
There is hope. In 2010, the African Commission on Human and People’s Rights adopted Resolution 169 on Repealing Criminal Defamation Laws in Africa. The resolution calls on states parties to repeal criminal defamation and insult laws which impede freedom of speech. In May 2013, the Pan African Parliament adopted the Midrand Declaration on Press Freedom in Africa. The Pan African Parliament resolved to launch a campaign entitled “Press Freedom for Development and Governance: Need for Reform” in all five regions of Africa. These initiatives by intergovernmental African organisations are historic and represent a real opportunity for media law reform. There is also significant pressure being brought to bear on a number of countries to enact access to information laws.
The objective link between a free press and accelerated development is clear. Sadly governments appear all too willing to forego development in their desire to retain political control. Journalists are under real threat in many countries in Africa and the threats are not only from rogue police officers but also from ordinary police officers and other state functionaries merely carrying out the letter of the law.
The Konrad Adenauer Stiftung believes that the media Law handbook could act as a catalyst for bringing together journalists, media owners, members of the judiciary, government officials and media activists to have a serious look at African media law with a view to taking it out of the colonial era. Together with the Pan African Parliament’s and the Comission’s efforts, this is a great opportunity to make Africa a place where journalists can report the news of the day accurately and fairly without fear of arrest and imprisonment.
This article was originally posted on 22 Oct 2013 at indexoncensorship.org




