Reporting rights? Media freedom in the Balkans since the wars
Today the bulk of the media in the Balkans has “been bought by people with no history in, or understanding of, the media business; they promote narrow interests of their owners or new political elites; sometimes without even pretence of objectivity,” said Kemal Kurspahic, former editor of Oslobodjenje, an independent newspaper published during the Bosnian war, reflecting on the development of media freedom over the past 25 years.
While in the 1990s nationalism was the order of the day, today a whole host of challenges – including murky media ownership – face independent journalists across the region. The Balkan Investigative Journalism Network in Serbia, for instance, has documented the campaign against them from authorities and pro-government press on a dedicated website, BIRN Under Fire. Television journalist Jet Xharra and BIRN Kosovo took the government to court over the right to report on the prime minister’s accounts, and to set a legal precedent for press freedom in the state. But Xharra, country director of BIRN in Kosovo, said there is a sense of disbelief among those who had to report during war, that these kinds of battles still need to be fought.
“We cannot understand why, 20 years later, you have to deal with [such] a strain on your reporting,” said Xharra.
During the war years that tore Yugoslavia apart, press freedom, like pretty much every other aspect of society, experienced a profound crisis. Large swathes of the media in the former republics became propaganda tools for ruling elites, even before the fighting started. In fact, concerted media campaigns of hate and fear-mongering played an important part in priming people who had lived side by side for decades for war. As British historian Mark Thompson put it in his 1999 book Forging War, on the media’s role in the conflicts in Bosnia, Croatia and Serbia: “War is the continuation of television news by other means.”
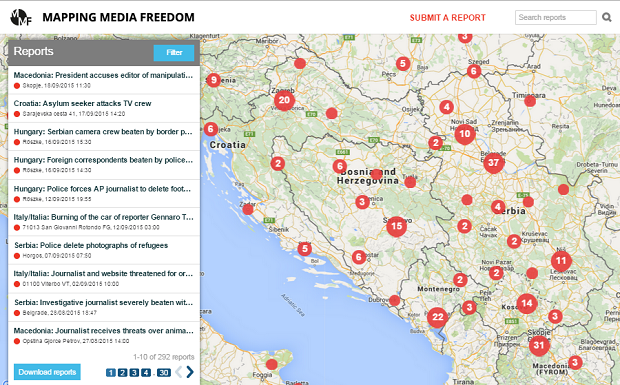
Dangers of reporting in the BalkinsAttacks on journalists and journalism in the Balkans, compiled from Index’s Mapping Media Freedom project SERBIA MONTENEGRO BOSNIA CROATIA MACEDONIA SLOVENIA KOSOVO Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project launched as in 2014 to record threats to media freedom throughout the European Union and EU candidate countries. It has recently expanded to cover Russia and Ukraine. |
Yet during the Balkan wars beginning in the 1990s there were local journalists who, in the face of enormous pressure, rejected nationalist and propagandist lines, and attempted to sift truth from lies and distortion. Beyond the daily struggle that came with just existing in a war zone, independent journalism was dangerous work. As Human Rights Watch points out in a new report on the state of media freedom in the Balkans, journalists who were, at the time, “critical of official government positions were often labelled as traitors or spies working on behalf of foreign interests and against the state”.
Serbia’s B92, a rare dissenting voice in a media landscape shaped by President Slobodan Milosevic’s propaganda strategy, is perhaps the most famous example of independent journalism. Set up in 1989 as a youth-focused radio station (later branching out into TV and web platforms), B92 bravely covered a turbulent time – from the war in Bosnia, to the Nato bombing of Serbia, to the protest movement that eventually saw Milošević ousted. For this, it was continuously hounded by the government. At one point in 1999 authorities commandeered its offices and radio frequency, forcing the station off air, before it could resume broadcasting from a different studio and frequency, under the name B2-92.
In Croatia, President Franjo Tudjman also made sure ultra-nationalism had a place in column inches and on airwaves. Feral Tribune, which started out in 1983 as a satirical supplement in the newspaper Slobodna Dalmacija, had other ideas. Under sustained pressure from the authorities, it covered stories of human rights and conflict that many other outlets avoided, in addition to its biting satire. It was taken to court, publicly burned, and one journalist was even drafted into the army after Feral published an edited photo of Tudjman and Milosevic in bed together on the front page.
Bosnia was the country in the region that would be by far the hardest hit by fighting. But even as war came to Sarajevo, independent journalism survived in some small way. Oslobodjenje, which started out as an anti-Nazi paper in 1943, had a track record of editorial independence. In 1988, staff for the first time voted for their own editor – Kemal Kurspahic – instead of accepting one appointed by the authorities. Just three years later they fought for their freedom again, this time in the constitutional court, as the newly elected nationalist parties agreed to adopt a law whereby they could appoint the editors and managers of Bosnian media. In 1992 came their toughest challenge yet. With the two towers of their office building under fire – in one night they lost six floors on one side and four on the other – they decided to go underground, and continue their work from a nuclear bomb shelter, with no newsprint supplies and no phone links.
“If dozens of foreign journalists could come to report on the siege of Sarajevo and Bosnian war, how could we – whose families, city and country were under attack – stop doing our job?” Kurspahic, now managing editor of Connection Newspapers, told Index. They felt an obligation to their readers: “We could not leave them without news at the worst time of their lives.”
Oslobodjenje even celebrated its 50th anniversary during the war, with 82 papers around the world printing some of their stories. With that they achieved “the ultimate victory”, Kurspahic said, “if the aim of the terror against Oslobodjenje was to silence us as a voice of multiethnic Bosnia”.
“People were getting killed, so we were reporting it. The risk was physical at that time to journalists,” Xharra told Index. Today she hosts Kosovo’s most watched current affairs programme, as well as fulfilling her role at BIRN Kosovo. But she cut her reporting teeth as a translator, fixer and field producer for UK broadcasters – the BBC and Channel 4 – during the Kosovo war. She recalled going through frontlines for a story, and hiding tapes from paramilitary checkpoints, painting a vivid picture of a time when practicing journalism in the western Balkans meant near constant risk of physical harm.
Journalists could be caught in crossfire, or targeted specifically for their work. Kurspahic remembers the Oslobodjenje reporter Kjasif Smajlovic in Zvornik, who sent his wife and children away, and stayed to report on the fall of the town until he was killed by Serbian paramilitary forces in April 1992. In 1999, Slavko Curuvija, known for his critical reporting, was shot 17 times in a Belgrade side street, just days after a pro-government daily had labelled him a Nato supporter. In many cases, there has been little to no accountability for such crimes, breeding a culture of impunity that still hangs over the region.
Because while the darkest days for press freedom in the Balkans came during wartime, peace has not brought the improved conditions many hoped for. At a talk in March, Dunja Mijatovic, the OSCE’s free expression representative, went as far as to say that the situation now is worse than in the aftermath of the conflicts.
And today the media itself remains part of the problem, especially when journalists turn on their colleagues. One prominent example is the story of BIRN Serbia. Following their critical investigation into a state-owned power company, Prime Minister Aleksandar Vucic labelled the group liars who had been funded by the EU to speak against his government. That attack was then taken forward by the pro-government Serbian press, including in the newspaper Informer. Just one example where the media has been a less than staunch defender of its own rights.
Data from Index’s Mapping Media Freedom project, which tracks media freedom across Europe, indicates that worries of threats to media rights are justified. In just over a year it has received more than 170 reports of violations from the countries of the former Yugoslavia. Incidents included a Croatian journalist who received a letter saying she would “end up like Curuvija”; a Bosnian journalist threatened over Facebook by a local politician; Kosovan journalists depicted as animals on several billboards; a Montenegrin daily that had a company car torched; a Macedonian editor who had a funeral wreath sent to his home; and a Slovenian who faced charges for reporting on the intelligence agency. Online and offline, physical and verbal, serious threats to press freedom remain, some 20 years on.
© Milana Knezevic
This article is part of the autumn issue of Index on Censorship magazine looking at comparisons between old censors and new censors. Copies can be purchased from Amazon, in some bookshops and online, more information here.