19 Nov 2013 | Europe and Central Asia, Macedonia, News
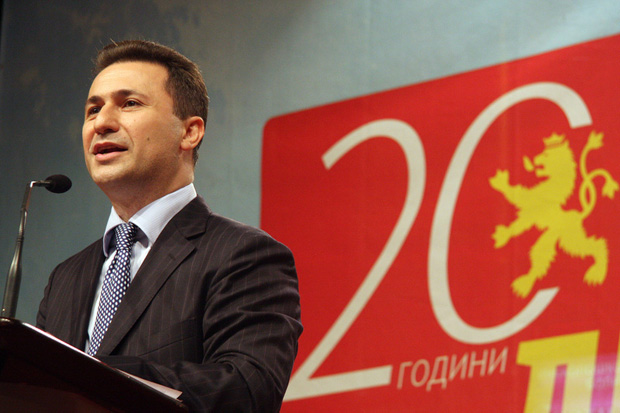

The government of Prime Minister Nikola Gruevski has been heavily criticised for the state of media freedom in Macedonia (Image Toni Arsovski/Demotix)
Media freedom in Macedonia has been deteriorating for some time. The latest case is the arrest of Zoran Bozinovski, the owner of website critical of the government, Burevesnik on espionage charges. Below, Tamara Causidis, President of the Trade Union of Macedonian Journalists and Media Workers and Dragan Sekulovski, the Executive Director of Association of Journalists of Macedonia, chronicles the challenges facing the free press, in their submission to the upcoming International Federation of Journalists conference in Kiev.
—
The media business in Macedonia has been increasingly under attack over the past few years. The EU and the US State Department, as well as renowned non-governmental organisations like Freedom House and Reporters Without Borders, have all called attention to the decline of media freedom in the country. The challenges most often highlighted include imprisoned journalists, restrictive draft media laws, the government’s large advertising share, the lack of transparent ownership, and the polarisation of the media along lines of political and business affiliation. In light of this, freedom of the media and freedom of speech have been marginalised.
Macedonia has almost 200 media outlets, but unfortunately, that does not make the situation better. They all compete in a small, distorted market, covering just over 2 million citizens, where they cannot survive financially unless they align their interests with the governing parties and politically connected, large businesses. Apart from state media, the vast majority of the country’s press is in private hands. However, the government come out top among the 50 biggest advertisers in the country in 2012. The latest European Commission report raised this as a serious concern, and the DG Enlargement report of June says that at least 1% of the annual national budget (20 million Euros) is invested in media outlets through government campaigns and advertising. This highlights the authorities’ huge influence in the media sphere. Bearing in mind that there are no criteria for how to distribute these funds, “governmental friendly” media outlets are favoured over others. Professionals are fired and people with personal integrity are replaced by obedient mouthpieces, while a huge number of journalists are living in professional insecurity. Behind the veil of “economic reasons”, critical media is vanishing.
One of the most striking example of the situation Macedonian media finds itself in, took place on 24 December last year. Journalists reporting on the parliamentary session were expelled from Parliament by security forces without any reasonable explanation. The Association of Journalists of Macedonia (AJM) used all national legal measures to fight this, but so far no public official has been held liable for this breach of Article 16 of the constitution, which guarantees citizens the right to objective information. The next step would be submission of an appeal to the Court in Strasbourg.
In April the government announced a draft media law, now in its final stages within Parliament, which has the potential to further negatively affect media independence and freedom of expression. International and local organisations are concerned about the same issues regarding the bill – the intention to have one regulator for all types of media and the powerful role of this regulator, the issues concerning political independence, sustainable financing and high and disproportionate fines for the media, as well as the messy attempt to adopt definition of a journalist. The main Council of Europe, OSCE and AJM recommendations have not been accepted. In fact, the latest version of the law was updated with amendments which makes the text even more restrictive the before. For instance, it envisaged that authorities to decide which national association of journalists is legitimate, and will have the right to nominate a member to the council of the regulator and the public broadcaster.
In October 2013 Macedonia became the only country in south-east Europe with imprisoned journalists. Tomislav Kezarovski, from the daily Nova Makedonija, was sentenced to four and a half years in prison for in 2008 revealing the identity of a protected witness in a murder trial. The witness recently testified that he had given false evidence against the accused killers. The Trade Union of Macedonian Journalists and Media Workers (SSNM) and AJM organised two protests in front of court in Skopje, raising the issue in the international community, but despite this Kezarovski was sentenced on October 21.
It should also be noted that at the time, he was investigating the mysterious death of prominent journalist Nikola Mladenov, founder of the weekly Fokus and one of the biggest activists for press freedom in the country. AJM is taking daily initiatives to raise the visibility of this case, to try to convince authorities that this sends terrifying message to all journalists and endangers freedom of press even more.
Finally, many colleagues in the media cannot rely on any of the basic rights guaranteed by the Labour Law. They are working without contracts, insurance, paid vacation, overtime hours and sick leave, and minimum wage is not regulated. There aren’t any internal rules or statutes defining the rights and obligations of owners, editors and journalists, and there are instances of both direct and indirect bans for organising into workers unions. The journalists themselves are barely educated about what a union is and how they can organise through it. In the face of fierce criticism from AJM, the government has developed the Macedonian journalists association, designed not only to diminish critics and open confrontation but also to impose artificial support for the proposed media laws.
This text is drafted based on a draft report on the media situation in Macedonia by Tamara Causidis, President of the Trade Union of Macedonian Journalists and Media Workers and Dragan Sekulovski, Executive Director of Association of Journalists of Macedonia. It will be published at the upcoming conference organised by the International Federation of Journalists in Kiev.
This article was originally published on 19 Nov 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
11 Nov 2013 | Americas, News
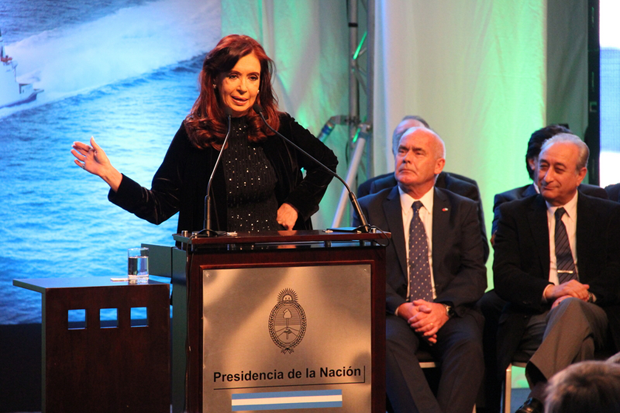

While president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner’s government took a hit during midterm elections, Argentina’s supreme court ruled her restrictions on the country’s media were constitutional. (Photo: Claudio Santisteban / Demotix)
The Argentinian supreme court recently ruled to uphold the country’s controversial media law. The decision represents a big victory for President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, who argued that the law helps break up the power concentrated in the hands of Argentina’s biggest media conglomerate Grupo Clarín. Opponents, however, says it stifles freedom of expression and press as it would force media companies to sell off some of their outlets. Concerns have also been raised about the law being a way of punishing Clarín, which fell out with the government after negative coverage during tax protests in 2008.
This is only the latest chapter in the ongoing story of the media business in some Latin American countries, with left wing governments and private companies locked in a decade-long fight for control of what will be shown on TV, heard on the radio, printed in newspapers, and posted on websites. New communications laws, persecution of journalists and closure of television networks, however, shows who is really in charge.
Governments like Venezuela and Argentina are waging war against big media companies, while more moderate ones, like Brazil, are using milder means to try and balance the power of communication in their countries. But far from being presented as a straightforward issue of freedom of expression, most of these cases have two opposing and radical interpretations.
On one side, there is the pro-government camp. They believe the governments are democratising the media, which has traditionally been in the hands of the few. In Brazil, for example, eight families control almost 80% of all traditional media companies. The aforementioned Grupo Clarín owns national and regional newspapers, radios, TV channels and more.
Those opposing these measures, however, say they amount to censorship. Again, a good example comes from Argentina: there are some rumours that Kirchner’s administration is trying to suffocate Grupo Clarín by not allowing big chain stores to advertise in their papers. There is also the infamous case of the the closure of Venezuela TV channel RCTVI in 2010.
Both sides talk of freedom of expression, arguing they want to show what is better for the public. But the public – those with the most to benefit from a good and transparent media – are not being allowed to decide for themselves. This is not happening just in Argentina and Venezuela, but across the continent – in Ecuador, Nicaragua and Bolivia, and, albeit in a much gentler way, in Brazil.
Professor Mirta Varela, specialist in history of the media at the University of Buenos Aires, is among those who believe governments are not repressing the big companies or trying to dominate the industry. “The measures taken have shown the political and economic power of the main companies, the spurious origin of their economic growth and their relationship with the dictatorship”, she explains, referencing Grupo Clarín and the military regimes that held power in almost all the Latin American countries from 1960 to 1980. But she also sees some problems with this polarisation: “There is a little room to set a new agenda; to make independent criticism, not overtly for or against the government.”
Cecilia Sanz works for Argentinian TV show “Bajada de línea”, which roughly translates to “Under the Line”. The show is hosted by Uruguayan Victor Hugo Morales, a well-known journalist connected to what Sanz calls “the progressive governments” in Latin America. Here she groups together a number of different left-leaning governments from across the continent – from moderates Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff in Brazil, to the more radical Evo Morales in Bolivia and Rafael Correa in Ecuador.
The show comments on the state of the media in Latin America, mainly arguing against the big private companies. “Our main goal is to put in context and show how the media owners have the intention, above all else, to accomplish their economic objectives,” she says. “The are using ‘freedom of expression’ as an excuse for this”. She mentions the case of powerful Mexican TV Azteca, which according to her, supports all the candidates from the hegemonic party PRI, and Chilean paper “El Mercurio”, which used to attack Chilean ex-president Salvador Allende in the 1970s – again putting very different cases in the same group.
The more radical of these “progressive governments” accuse the media industry of trying to destabilise the authorities or to encourage coups d’état. Venezuela’s putsch in 2002 is always mentioned. In this case factions of the media was directly fighting against Hugo Chávez – so Chávez took them off the air.
“This is an insult to the audience because in all of cases it is about the most popular media channels”, counters Claudio Paolillo, president of the freedom of press and expression commission of SIP, Sociedad Interamericana de Prensa (the Inter-American Press Society). “No one has put a gun to the audience’s head to force them to choose what to read, listen or watch, and on what channel.”
Paolillo says the government engages in “Goebbels’ style” propaganda, sustained by public resources, to oppress independent or critic media and journalists. He adds that, ironically, these radical “progressive governments” act like the conservative military regimes of the past. “It is an ideological posture. They want to nationalise communications media as if it was a regular business that offers services or products.”
Paolillo says SIP is against Latin Americas state-controlled monopolies or oligopolies, but reaffirms it is the audience that has the real power to decide what to watch, and where. If they want to watch the same news program, the government shall not interfere. “Unfortunately in Argentina as in Venezuela (and we must add here Ecuador, Nicaragua and Bolivia), governments have created their own media companies, expropriated and bought private ones – in some cases even working through a figurehead”, he complains.
Brazilian political scientist Mauricio Santoro brings up another common problem in the region – organised crime targeting reporters in Mexico and Colombia. But he says this is not a new situation. In his opinion, what is new, is “progressive governments” using the power of the state to control its opponents.
“The alternative proposed by these leftist governments is not based on the construction of an alternative model that privileges pluralism and gives a voice to social and community movements. It is about breaking business groups and giving power to a state press that acts like a government representative and not a public one.”
Worried about the poor quality of the media across Latin America, Santoro suggests the continent needs a more dynamic media, more capable of listening and understanding the true necessities of the people of a region going through “profound change”.
“Looking at the local scene”, he asks, “are we able to find any country where the traditional media meets this expectation?”
Not really.
This article was originally posted on 11 Nov 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
8 Nov 2013 | Europe and Central Asia, Macedonia, News
Zoran Bozinovski, the owner of website Burevesnik, was arrested Thursday night in Novi Sad, Serbia. Bozinovski is charged with foreign espionage and criminal association.
Burevesnik is known for its critical coverage of the Macedonian government, led by Prime Minister Nikola Gruevski.
Macedonian authorities accuse Bozinovski of being part of a spy-ring working for a foreign government. He has previously denied the charges, telling Macedonian independent news site NOVA TV in September that “all the information that I gather I publicly declare my website Burevesnik.” He now faces 30 days in detention and extradition to Macedonia.
This comes only a day after journalist Tomislav Kezarovski was released from prison and put under house arrest. He was sentenced to four and half years in jail in October for reporting on the identity of a witness in a murder trial in 2008. The sentence came under criticism both nationally and internationally, with OSCE Media Freedom Representative Dunja Mijatovic declaring it had “serious consequences for free expression and media freedom” in the country.
Press freedom in Macedonia has been deteriorating for some time, with repressive legislation and increased hostility towards critical press from the government. The country ranks 116th out of 179 countries in the 2013 Reporters Without Borders press freedom index.
This article was originally posted on 8 Nov 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
30 Sep 2013 | News, Politics and Society, Sudan

The two most influential independent newspapers in Sudan, Al-Sahafa and Al-Kartoum, have recently been bought by the National Intelligence
Security Service (NISS).
The NISS now owns 90% of all the independent newspapers in the country, according to Alnoor Ahmed Alnoor, the ex-editor in chief of Al-Sahafa.
The NISS purchased 65% of Al-Sahafa’s stock from a company called Bayader and a further 25% from Sideeq Wadaa, a businessman and member of the ruling NCP Party (with the remainder retained by the paper’s founder, Taha Ali Albashir). This follows the purchase of 80% of the stock of Al-Khartoum from its owner, Albagir Abdellah, five months ago.
Ownership represents the final stage in the Sudanese government’s campaign to silence independent voices in the media. Newspapers that refused to tow the NCP line or implement its agendas faced harassment, and fifteen newspapers were forcibly closed following the independence of South Sudan in 2011. Punitive taxes were also imposed, as was the case with the Al-Sudani between 2006 to 2011, which eventually forced the paper’s owner to sell it to a member of the NCP.
Khalid Abdelaziz, a one-time editorial manager of Al-Sudani says: “They used to demand about US$400,000 a year in their campaign against us while leaving their own newspapers paying little tax. They also used regulations to prevent us from the advertising. They gave us a choice, to implement their agendas or to sell our newspaper. We took the second choice”.
The new ownership has been followed by the resignation of key journalist. Interference led to Mozdalfa Osman to step down as editorial manager at Al-Khartoum: “I resigned because of the negative influence on my job and the implementing of NISS’s agenda, which contradicted my professionalism”.
Those that remain face increasing harassment, such as Al-Khartoum’s Mohamed Salih, winner of this year’s Peter Mackler prize, who faces pressure from his new editor-in-chief: “He calls me four times weekly asking to change some of the ideas in my column. I have never worked under such conditions before”.
Independent reporting in Sudanese has had a checkered history. The free press thrived for 57 years from 1903 to 1960 when first dictatorship came to the power. After the revolution of October 1964 independent newspapers once more operated until the second dictatorship in 1969, which nationalized all newspapers considered to have had a socialist orientation. With the second period of democracy, following the revolution of March 1985, another tranche of independent newspapers came into existence. However this once more came to an end when the current regime came to power in a military coup in June 1989.
Before the peace agreement with Sudan people liberation movement (SPLM) in 2005, NCP created shell companies to buy stakes in the newspapers, such as Alrai Alaam one of the oldest newspapers in Sudan. It has been published since 1948. The shell companies began buying stakes in 2002. The same process has been used with Alsahafa and Alkhartoum.
Hayder Almukashfi, who is responsible for the opinion pages on Al-Sahafa, said the newspaper has been greatly influenced by the new owners: “All the pages have been affected by the new polices and the opinion pages have been affected the most. The new owners sacked the previous editor in chief, who had been in the job for years, and have brought another one is a member of ruling NCP. This is an awful situation for freedom of speech in Sudan. The government can now claim there’s no censorship of the press because now the government is the press”.
This article was originally posted on 30 Sept 2013 at indexoncensorship.org




