23 Jan 2014 | News, Politics and Society, United Kingdom

(Photo illustration: Shutterstock)
The parliamentary struggle over the UK government’s gagging bill, which has overshadowed Westminster in recent months, is all but over. And the end result is bad news for British democracy.
Yesterday ministers secured their final victories against freedom of speech campaigners. Their plans to make it much harder for charities to get their voices heard during election periods – exactly when their contribution is needed most – are about to become law as a result.
The transparency of lobbying, non-party campaigning and trade union administration bill, to give it its full title, has troubled civil liberties activists from start to finish.
Its attempted clampdown on the public affairs industry by forcing third-party lobbyists on to a statutory register, has been roundly dismissed because in-house lobbyists – the vast majority – are simply not included.
This flawed solution to the bill’s main target has been accompanied by a brutal attack on the voluntary sector. The government’s aim was to force small-scale charities, community groups and the like on to a complicated regulatory regime.
Such would have been the chilling effect of this law that most local-issue campaigning during elections would have been stifled when it came to election time. No surprise the legislation was dubbed the ‘gagging bill’.
As it was, bitter opposition to the proposals finally forced ministers to the negotiating table. Instead of lowering the threshold at which charities must begin reporting their activities to the Electoral Commission watchdog, it was increased to £20,000.
This was a major concession. There were other, smaller retreats too, on how long ‘election time’ actually means — it was reduced from one year to 7.5 months — and by excluding some costs like spending on translation into Welsh, or security, from controlled expenditure.
Ultimately, though, these alterations failed to change the bill’s big impact: that important voices encouraging politicians to make promises, and then holding them to their word, are to be stifled.
The Lords did its best to limit the damage. It inflicted embarrassing defeats on the government, which meant when the bill returned to the Commons yesterday MPs had to vote on whether or not to overturn the changes.
As the bill was being debated in the Commons chamber the atmosphere was one of resentment and frustration from the opposition benches — and a smug superiority from ministers. They knew they had already won the war. Now they were about to win the last of its battles, too.
A critical division came over staffing costs. For the bigger household names, like Countryside Alliance or Oxfam, this really matters.
The gagging bill is reducing the total amount a campaigning group can spend in a general election period from £988,000 to £390,000. Say it employs ten staff on a £20,000 salary — by including the staffing costs, the amount actually available to spend on leaflets and demonstrations and advertising is slashed still further.
Yesterday the government whipped its MPs against the Lords amendments. Groups like 38 Degrees had been mobilising their members to urge wavering MPs to rebel. In their offices earlier this week, staff expressed delight as the number of emails sent to backbenchers who’d previously expressed disquiet shot upwards.
Back in parliament, the mood at this campaigning onslaught was grim. One MP I spoke to was so worked up he got his staff to forward me the emails as they came in, to demonstrate just how disruptive they were. The flood which followed was, indeed, deeply irritating – about 50 poured in over the course of just a couple of hours.
Elsewhere, a Tory veteran even phoned up the police to complain about a group of activists wanting to petition him at his home. The bitter irony of this didn’t pass unnoticed.
Ultimately, all the efforts to sway the Commons didn’t make much of a difference. When it came to a vote the coalition’s majority was reduced to 32. But it still won, and the Lords’ improvements were consigned to history.
What caused this diminishing of our democracy? It’s mostly the result of those in power simply not caring much for the views of others. The latest reports from Downing Street indicate that senior No 10 strategists are desperate to find ways of reducing the pledges which candidates make during general elections. It’s much easier to avoid breaking promises, after all, if you haven’t made them in the first place.
And yet that is exactly what democracy, and free speech in Britain, are about: the ability to highlight when politicians are not sticking to their commitments, and the opportunity to encourage them to stick by a cause. Charities are a vital part of this, but the gagging bill is undermining their ability to make the case.
The result is not so much a law which makes it almost impossible for small-scale charities and voluntary groups to campaign during general elections, but one which merely makes the lives of their employees more difficult and awkward.
At the end of it all, democracy in Britain has got just a little bit worse. Our future elections will be slightly poorer affairs than before. The country we were in 2013 is not the country we shall be when, in a short while, the Queen finally hands royal approval to her government’s gagging bill.
This article was published on 23 January 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
15 Jan 2014 | News, Politics and Society, Tunisia

(Photo illustration: Shutterstock)
Tunisia’s National Constituent Assembly (NCA) is voting on a 146-article constitution, following a political crisis which put the country’s democratic transition on hold after the assassination of opposition deputy Mohamed Brahmi last July.
The NCA, where the Islamist Ennahdha Movement enjoys a 40% majority, was elected in October 2011 to draft a new constitution. To be adopted, each article requires a simple majority vote. NCA deputies will then have to approve the text in its entirety by a two-thirds majority.
Articles that guarantee freedom of expression, the rights to access information, protest and assembly, and to form unions, associations and parties were adopted last week. The charter also bans prior censorship on freedoms of thought, conscience, expression and publication (article 30) and enshrines freedom of creation (article 41) and the right to privacy and personal data protection (article 23). Article 48 further states that no future constitutional amendments that violate human rights and freedoms could be introduced to the text.
But, ironically, Tunisia’s self proclaimed progressive and secular opposition stand behind the introduction of an anti-free speech clause in the text. The NCA adopted an amendment to article 6 of the draft constitution banning Takfir (apostasy accusations). Article 6 guarantees freedoms of belief, conscience and religious practice.
On 5 January, the vote on the constitution was interrupted over death threats received by Popular Front deputy Mongi Rahoui. He said he received death threats following declarations made by Habib Ellouze, another NCA representative from Ennahdha. Speaking to the media, Ellouze referred to Rahoui as an “enemy to Islam”. The Interior Ministry confirmed the death threats against Rahoui and placed him under police protection.
“What [Ellouze] said yesterday, that I am an enemy of Islam, has lead to death threats against me”, Rahoui said at the assembly’s plenary session of 5 January. “How much more blood must there be before we understand that we are united”, he added. Rahoui was referring to the assassination of two other fellow Popular Front leaders, Chokri Belaid and Mohamed Brahmi. Belaid, in particular, a staunch critic of Islamists was before his assassination subject to fatwas labelling him as a ‘Kafir’ and an ‘enemy to Islam’ who should be killed.
Following Rahoui’s declaration, NCA deputies from the opposition demanded a revote on article 6 to add a clause ‘banning takfir and incitement to violence’. The clause was approved by 131 votes. But by moving to ban Takfir, Tunisia’s opposition acted out emotionally and without taking into consideration the chilling effect a similar clause could have on free speech. The banning of “apostasy accusations” could only open the door to more restrictions on free speech.
“In just few hours, we will be able to say that the opposition put up in place the first rock in the way of free expression”, Amira Yahyaoui, president of Albawsala, a transparency NGO tracking the NCA’s activities, tweeted before the vote. “How is it nice to watch our representatives unanimously voting in favour of draconian laws”, she added in another tweet.
Following to the opposition’s demands for a constitutional ban on Takfir, Ennahdha’s deputies also called for criminalisation of blasphemy. But, for lack of consensus among the negotiating NCA representatives, the suggestion was not submitted for a vote.
Initially, Tunisia’s Ennahdha did seek to ‘criminalise attacks on sanctities’ in a first draft of the constitution. However, those plans were dropped following negotiations with the other two parties in the ruling coalition. Article 6, still however includes a vague phrase tasking the State with “protecting sanctities” without specifying how, or defining and listing these sanctities.
Meanwhile, Tunisia’s recently established broadcast media regulator, the Independent High Authority for Audiovisual Communication (better known as HAICA) repeatedly expressed its reservations about the draft constitution. HAICA was established by decree 116 on freedom of the media, which was issued on 2 November 2011, to regulate the broadcast media sector.
On a positive move, the constituent assembly incorporated HAICA into the draft constitution. However, the HAICA board criticised provisions in the text threatening the authority’s independence and limiting its prerogatives. Article 122 of the draft constitution states that the Parliament shall elect HAICA’s board members. The media regulator says that this selection process will ‘strip HAICA from its independence’ and make it ‘submissive to the [parliamentary] majority’. Under article 124, HAICA has an ‘advisory’ mission and is not attributed ‘regulatory’ powers which would allow it to regulate and organise the broadcast sector as it is stipulated by decree 116.
The two articles are awaiting NCA’s approval as deputies will first have to discuss and vote on chapters related to the executive branch and the judiciary.
This article was posted on 14 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
15 Jan 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, European Union, Index Reports, News, Politics and Society
This article is part of a series based on our report, Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression
Beyond its near neighbourhood, the EU works to promote freedom of expression in the wider world. To promote freedom of expression and other human rights, the EU has 30 ongoing human rights dialogues with supranational bodies, but also large economic powers such as China.
The EU and freedom of expression in China
The focus of the EU’s relationship with China has been primarily on economic development and trade cooperation. Within China some commentators believe that the tough public noises made by the institutions of the EU to the Chinese government raising concerns over human rights violations are a cynical ploy so that EU nations can continue to put financial interests first as they invest and develop trade with the country. It is certainly the case that the member states place different levels of importance on human rights in their bilateral relationships with China than they do in their relations with Italy, Portugal, Romania and Latvia. With China, member states are often slow to push the importance of human rights in their dialogue with the country. The institutions of the European Union, on the other hand, have formalised a human rights dialogue with China, albeit with little in the way of tangible results.
The EU has a Strategic Partnership with China. This partnership includes a political dialogue on human rights and freedom of the media on a reciprocal basis.[1] It is difficult to see how effective this dialogue is and whether in its present form it should continue. The EU-China human rights dialogue, now 14 years old, has delivered no tangible results.The EU-China Country Strategic Paper (CSP) 2007-2013 on the European Commission’s strategy, budget and priorities for spending aid in China only refers broadly to “human rights”. Neither human rights nor access to freedom of expression are EU priorities in the latest Multiannual Indicative Programme and no money is allocated to programmes to promote freedom of expression in China. The CSP also contains concerning statements such as the following:
“Despite these restrictions [to human rights], most people in China now enjoy greater freedom than at any other time in the past century, and their opportunities in society have increased in many ways.”[2]
Even though the dialogues have not been effective, the institutions of the EU have become more vocal on human rights violations in China in recent years. For instance, it included human rights defenders, including Ai Weiwei, at the EU Nobel Prize event in Beijing. The Chinese foreign ministry responded by throwing an early New Year’s banquet the same evening to reduce the number of attendees to the EU event. When Ai Weiwei was arrested in 2011, the High Representative for Foreign Affairs Catherine Ashton issued a statement in which she expressed her concerns at the deterioration of the human rights situation in China and called for the unconditional release of all political prisoners detained for exercising their right to freedom of expression.[3] The European Parliament has also recently been vocal in supporting human rights in China. In December 2012, it adopted a resolution in which MEPs denounced the repression of “the exercise of the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly, press freedom and the right to join a trade union” in China. They criticised new laws that facilitate “the control and censorship of the internet by Chinese authorities”, concluding that “there is therefore no longer any real limit on censorship or persecution”. Broadly, within human rights groups there are concerns that the situation regarding human rights in China is less on the agenda at international bodies such as the Human Rights Council[4] than it should be for a country with nearly 20% of the world’s population, feeding a perception that China seems “untouchable”. In a report on China and the International Human Rights System, Chatham House quotes a senior European diplomat in Geneva, who argues “no one would dare” table a resolution on China at the HRC with another diplomat, adding the Chinese government has “managed to dissuade states from action – now people don’t even raise it”. A small number of diplomats have expressed the view that more should be done to increase the focus on China in the Council, especially given the perceived ineffectiveness of the bilateral human rights dialogues. While EU member states have shied away from direct condemnation of China, they have raised freedom of expression abuses during HRC General Debates.
The Common Foreign and Security Policy and human rights dialogues
The EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) is the agreed foreign policy of the European Union. The Maastricht Treaty of 1993 allowed the EU to develop this policy, which is mandated through Article 21 of the Treaty of the European Union to protect the security of the EU, promote peace, international security and co-operation and to consolidate democracy, the rule of law and respect for human rights and fundamental freedom. Unlike most EU policies, the CFSP is subject to unanimous consensus, with majority voting only applying to the implementation of policies already agreed by all member states. As member states still value their own independent foreign policies, the CFSP remains relatively weak, and so a policy that effectively and unanimously protects and promotes rights is at best still a work in progress. The policies that are agreed as part of the Common Foreign and Security Policy therefore be useful in protecting and defending human rights if implemented with support. There are two key parts of the CFSP strategy to promote freedom of expression, the External Action Service guidelines on freedom of expression and the human rights dialogues. The latter has been of variable effectiveness, and so civil society has higher hopes for the effectiveness of the former.
The External Action Service freedom of expression guidelines
As part of its 2012 Action Plan on Human Rights and Democracy, the EU is working on new guidelines for online and offline freedom of expression, due by the end of 2013. These guidelines could provide the basis for more active external policies and perhaps encourage a more strategic approach to the promotion of human rights in light of the criticism made of the human rights dialogues.
The guidelines will be of particular use when the EU makes human rights impact assessments of third countries and in determining conditionality on trade and aid with non-EU states. A draft of the guidelines has been published, but as these guidelines will be a Common Foreign and Security Policy document, there will be no full and open consultation for civil society to comment on the draft. This is unfortunate and somewhat ironic given the guidelines’ focus on free expression. The Council should open this process to wider debate and discussion.
The draft guidelines place too much emphasis on the rights of the media and not enough emphasis on the role of ordinary citizens and their ability to exercise the right to free speech. It is important the guidelines deal with a number of pressing international threats to freedom of expression, including state surveillance, the impact of criminal defamation, restrictions on the registration of associations and public protest and impunity against human right defenders. Although externally facing, the freedom of expression guidelines may also be useful in indirectly establishing benchmarks for internal EU policies. It would clearly undermine the impact of the guidelines on third parties if the domestic policies of EU member states contradict the EU’s external guidelines.
Human rights dialogues
Another one of the key processes for the EU to raise concerns over states’ infringement of the right to freedom of expression as part of the CFSP are the human rights dialogues. The guidelines on the dialogues make explicit reference to the promotion of freedom of expression. The EU runs 30 human rights dialogues across the globe, with the key dialogues taking place in China (as above), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Georgia and Belarus. It also has a dialogues with the African Union, all enlargement candidate countries (Croatia, the former Yugoslav republic of Macedonia and Turkey), as well as consultations with Canada, Japan, New Zealand, the United States and Russia. The dialogue with Iran was suspended in 2006. Beyond this, there are also “local dialogues” at a lower level, with the Heads of EU missions, with Cambodia, Bangladesh, Egypt, India, Israel, Jordan, Laos, Lebanon, Morocco, Pakistan, the Palestinian Authority, Sri Lanka, Tunisia and Vietnam. In November 2008, the Council decided to initiate and enhance the EU human rights dialogues with a number of Latin American countries.
It is argued that because too many of the dialogues are held behind closed doors, with little civil society participation with only low-level EU officials, it has allowed the dialogues to lose their importance as a tool. Others contend that the dialogues allow the leaders of EU member states and Commissioners to silo human rights solely into the dialogues, giving them the opportunity to engage with authoritarian regimes on trade without raising specific human rights objections.
While in China and Central Asia the EU’s human rights dialogues have had little impact, elsewhere the dialogues are more welcome. The EU and Brazil established a Strategic Partnership in 2007. Within this framework, a Joint Action Plan (JAP) covering the period 2012-2014 was endorsed by the EU and Brazil, in which they both committed to “promoting human rights and democracy and upholding international justice”. To this end, Brazil and the EU hold regular human rights consultations that assess the main challenges concerning respect for human rights, democratic principles and the rule of law; advance human rights and democracy policy priorities and identify and coordinate policy positions on relevant issues in international fora. While at present, freedom of expression has not been prioritised as a key human rights challenge in this dialogue, the dialogues are seen by both partners as of mutual benefit. It is notable that in the EU-Brazil dialogue both partners come to the dialogues with different human rights concerns, but as democracies. With criticism of the effectiveness and openness of the dialogues, the EU should look again at how the dialogues fit into the overall strategy of the Union and its member states in the promotion of human rights with third countries and assess whether the dialogues can be improved.
[1] It covers both press freedom for the Chinese media in Europe and also press freedom for European media in China.
[2] China Strategy Paper 2007-2013, Annexes, ‘the political situation’, p. 11
[3] “I urge China to release all of those who have been detained for exercising their universally recognised right to freedom of expression.”
[4] Interview with European diplomat, February 2013.
12 Dec 2013 | Digital Freedom Reports, Europe and Central Asia, European Union, Index Reports, News, Politics and Society
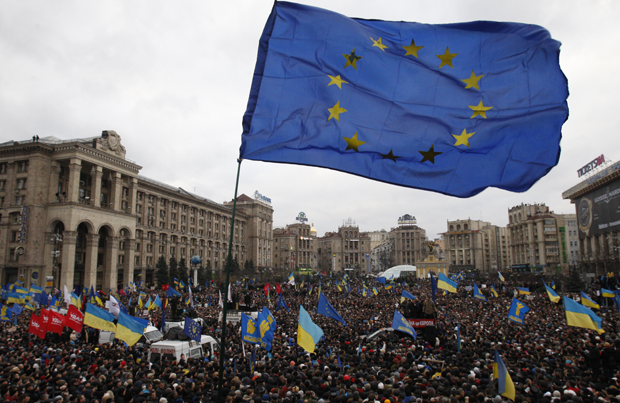

As Ukraine experiences ongoing protests over lack of European integration, Index’ new report looks at the EU’s relationship with freedom of expression (Photo: Anatolii Stepanov / Demotix)
Index on Censorship’s policy paper, Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression, looks at freedom of expression both within the European Union’s 28 member states, which with over 500 million people account for about a quarter of total global economic output, but also how this union defends freedom of expression in the wider world. States that are members of the European Union are supposed to share “European values”, which include a commitment to freedom of expression. However, the way these common values are put into practice vary: some of the world’s best places for free expression are within the European Union – Finland, Netherlands, Denmark and Sweden – while other countries such as Italy, Hungary, Greece and Romania lag behind new and emerging global democracies.
This paper explores freedom of expression, both at the EU level on how the Commission and institutions of the EU protect this important right, but also across the member states. Firstly, the paper will explore where the EU and its member states protect freedom of expression internally and where more needs to be done. The second section will look at how the EU projects and defends freedom of expression to partner countries and institutions. The paper will explore the institutions and instruments used by the EU and its member states to protect this fundamental right and how they have developed in recent years, as well as the impact of these institutions and instruments.
Outwardly, a commitment to freedom of expression is one of the principle characteristics of the European Union. Every European Union member state has ratified the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR); the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and has committed to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. To complement this, the Treaty of Lisbon has made the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights legally binding which means that the EU institutions and member states (if they act within the scope of the EU law) must act in compliance with the rights and principles of the Charter. The EU has also said it will accede to the ECHR. Yet, even with these commitments and this powerful framework for defending freedom of expression, has the EU in practice upheld freedom of expression evenly across the European Union and outside with third parties, and is it doing enough to protect this universal right?
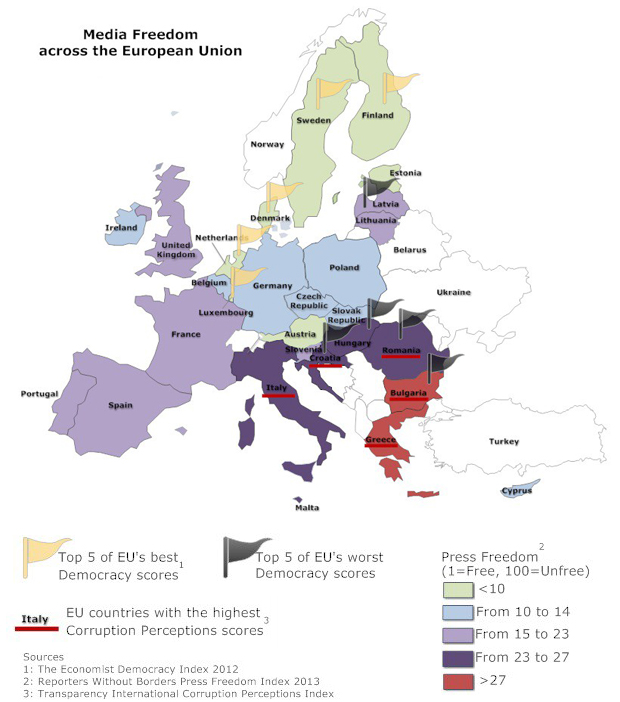
Within the European Commission, there has been considerable analysis about what should be done when member states fail to abide by “European values”, Commission President Barroso raised this in his State of the Union address in September 2012, explicitly calling for “a better developed set of instruments” to deal with threats to these perceived values and the rights that accompany them. With threats to freedom of expression increasing, it is essential that this is taken up by the Commission sooner rather than later.
To date, most EU member states have failed to repeal criminal sanctions for defamation, with only Croatia, Cyprus, Ireland and the UK having done so. The parliamentary assembly of the Council of Europe called on states to repeal criminal sanctions for libel in 2007, since then little action has been taken by EU member states. There also remain significant issues in the field of privacy law and freedom of information across the EU.
While the European Commission has in the past tended to view its competencies in the field of media regulation as limited, due to the introduction of the Charter of Fundamental Rights into EU primary law, the Commission is looking at a possible enhancement of its role in this area.
With media plurality limited across Europe and in fact potentially threatened by the convergence of media across media both online and off (and the internet being the most concentrated media market), the Commission must take an early view on whether it wishes to intervene more fully in this field to uphold the values the EU has outlined. Political threats against media workers are too commonplace and risks to whistleblowers have increased as demonstrated by the lack of support given by EU member states to whistleblower Edward Snowden. That the EU and its member states have so clearly failed one of the most significant whistleblowers of our era is indicative of the scale of the challenge to freedom of expression within the European Union.
The EU and its member states have made a number of positive commitments to protect online freedom, including the EU’s positioning at WCIT, the freedom of expression guidelines and the No-Disconnect strategy helping the EU to strengthen its external polices around promoting digital freedom. These commitments have challenged top-down internet governance models, supported the multistakeholder approach, protected human rights defenders who use the internet and social media in their work, limited takedown requests, filters and others forms of censorship. But for the EU to have a strong and coherent impact at the global level, it now needs to develop a clear and comprehensive digital freedom strategy. For too long, the EU has been slow to prioritise digital rights, placing the emphasis on digital competitiveness instead. It has also been the case that positive external initiatives have been undermined by contradictory internal policies, or a contradiction of fundamental values, at the EU and member state level. The revelations made by Edward Snowden show that EU member states are violating universal human rights through mass surveillance.
The Union must ensure that member states are called upon to address their adherence to fundamental principles at the next European Council meeting. The European Council should also address concerns that external government surveillance efforts like the US National Security Agency’s Prism programme are undermining EU citizens’ rights to privacy and free expression. A comprehensive overarching digital freedom strategy would help ensure coherent EU policies and priorities on freedom of expression and further strengthen the EU’s influence on crucial debates around global internet governance and digital freedom. With the next two years of ITU negotiations crucial, it’s important the EU takes this strategy forward urgently.
While the European Commission has in the past tended to view its competencies in the field of media regulation as limited, due to the introduction of the Charter of Fundamental Rights into EU primary law, the Commission is looking at a possible enhancement of its role in this area.
With media plurality limited across Europe and in fact potentially threatened by the convergence of media across media both online and off (and the internet being the most concentrated media market), the Commission must take an early view on whether it wishes to intervene more fully in this field to uphold the values the EU has outlined.
Political threats against media workers are too commonplace and risks to whistleblowers have increased as demonstrated by the lack of support given by EU member states to whistleblower Edward Snowden. That the EU and its member states have so clearly failed one of the most significant whistleblowers of our era is indicative of the scale of the challenge to freedom of expression within the European Union.
Where the EU acts with a common approach among the member states, it has significant leverage to help promote and defend freedom of expression globally. To develop a more common approach, since the Lisbon Treaty, the EU has enhanced its set of policies, instruments and institutions to promote human rights externally, with new resources to do so. Enlargement has proved the most effective tool to promote freedom of expression with, on the whole, significant improvements in the adherence to the principles of freedom of expression in countries that have joined the EU or where enlargement is a real prospect. That this respect for human rights is a condition of accession to the EU shows that conditionality can be effective. Whereas the eastern neighbourhood has benefitted from the real prospect of accession (for some countries), in its southern neighbourhood, the EU has failed to promote freedom of expression by placing security interests first and also by failing to react quickly enough to the transitions in its southern neighbourhood following the events of the Arab Spring. The new strategy for this region is welcome and may better protect freedom of expression, but with Egypt in crisis, the EU may have acted too late. The EU must assess the effectiveness of some of its foreign policy instruments, in particular the dialogues for particular countries such as China.
The freedom of expression guidelines provide an excellent opportunity to reassess the criteria for how the EU engages with third party countries. Strong freedom of expression guidelines will allow the EU to better benchmark the effectiveness of its human rights dialogues. The guidelines will also reemphasise the importance of the EU, ensuring that the right to freedom of expression is protected within the EU and its member states. Otherwise, the ability of the EU to influence external partners will be limited.
Headline recommendations
• After recent revelations about mass state surveillance the EU must develop a roadmap that puts in place strong safeguards to ensure narrow targeted surveillance with oversight not mass population surveillance and must also recommit to protect whistle-blowers
• The European Commission needs to put in place controls so that EU directives cannot be used for the retention of data that makes mass population surveillance feasible
• The EU has expanded its powers to deal with human rights violations, but is reluctant to use these powers even during a crisis within a member state. The EU must establish clear red lines where it will act collectively to protect freedom of expression in a member state
• Defamation should be decriminalised across the EU
• The EU must not act to encourage the statutory regulation of the print media but instead promote tough independent regulation
• Politicians from across the EU must stop directly interfering in the workings of the independent media
• The EU suffers from a serious credibility gap in its near neighbourhood – the realpolitik of the past that neglected human rights must be replaced with a coherent, unified Union position on how to promote human rights
Recommendations
- The EU has expanded its powers to deal with human rights violations, but is reluctant to use these powers even during a crisis within a member state. The EU must establish clear red lines where it will act collectively to protect freedom of expression in a member state
- The EU should cut funding for member states that cross the red lines and breach their human rights commitments
Libel, privacy and insult
- Defamation should be decriminalised in line with the recommendations of the Council of Europe parliamentary assembly, and the UN and OSCE’s special rapporteurs on freedom of expression.
- Insult laws that criminalise insult to national symbols should be repealed
Freedom of information
- To better protect freedom of information, all EU member states should sign up to the Council of Europe Convention on Access to Official Documents
- Not all EU institutions, offices, bodies and agencies are acting on their freedom of information commitments. More must be done by the Commission to protect freedom of information
Media freedom & plurality
- The EU must revisit its competencies in the area of media regulation in order to prevent the most egregious breaches of the right to freedom of expression in particular the situations that arose in Italy and Hungary
- The EU must argue against statutory regulation of the print media and argue for independent self-regulation where media bandwidth is no longer limited by spectrum and other considerations
- Member states must not allow political interference or considerations of “political balance” into the workings of the media, where this happens the EU should be considered competent to act to protect media freedom and pluralism at a state level
- The EU is not doing enough to protect whistleblowers. National states must do more to protect journalists from threats of violence and intimidation
Digital
- The Commission must prepare a roadmap for collective action against mass state surveillance
- The EU is right to argue against top-down state control over internet governance it must find more natural allies for this position globally
- The Commission should proceed with a Directive that sets out the criteria takedown requests must meet and outline a process that protects anonymous whistle-blowers and intermediaries from vexatious claims
The EU and freedom of expression in the world
- The EU suffers from a credibility issue in its southern neighbourhood. To repair its standing in the wider world, the EU and its member states must not downgrade the importance of human rights in any bilateral or multilateral relationship
- The EU’s EEAS Freedom of Expression guidelines are welcome. To be effective, they need to focus on the right to freedom of expression for ordinary citizens and not just media actors
- The guidelines need to become the focus for negotiations with external countries, rather than the under-achieving human rights dialogues
- With criticism of the effectiveness of the human rights dialogues, the EU should look again at how the dialogues fit into the overall strategy of the Union and its member states
The European Union contains some of the world’s strongest defenders of freedom of expression, but also a significant number of member states who fail to meet their European and international commitments. To deal with this, in recent years, the European Union’s member states have made new commitments to better protect freedom of expression. The new competency of the European Court of Justice to uphold the values enshrined in the European Convention of Human Rights will provide a welcome alternative forum to the increasingly deluged European Court of Human Rights. This could have significant implications for freedom of expression within the EU. Internally within the EU there is still much that could be done to improve freedom of expression. It is welcome that that the EU and its member states have made a number of positive commitments to protect online freedom, with new action on vexatious takedown notices and coordinated action to protect the multistakeholder model of internet governance. Increasing Commission concern over media plurality may also be positive in the future.
Yet there are a number of areas where the EU must do more. The decriminalisation of defamation across Europe should be a focal point for European action in line with the Council of Europe’s recommendations. National insult laws should be repealed. The Commission should not intervene to increase its powers over national media regulators, but should act where it has clear competencies, in particular to prevent media monopolies and to help deal with conflict of interests between politicians and state broadcasters. Most importantly, discussions of mass population surveillance at the European Council in October must be followed by a roadmap outlining how the EU will collectively take action on this issue. Without internal reform to strengthen protections for freedom of expression, the EU will not enjoy the leverage it should to promote freedom of expression externally to partner countries. While the External Action Service freedom of expression guidelines are welcome, they must be impressed upon member countries as a benchmark for reform.
Externally, the EU has failed to deliver on the significant leverage it could have as the world’s largest trading block. Where the EU has acted in concert, with clear aims and objectives for partner countries, such as during the process of enlargement, it has had a big impact on improving and protecting freedom of expression. Elsewhere, the EU has fallen short, particularly in its southern neighbourhood and in its relationship with China, where the EU has continued human rights dialogues that have failed to be effective.
New commitments and new instruments post-Lisbon may better protect freedom of expression in the EU and externally. Yet, as the Snowden revelations show, the EU and its member states must do significantly more to deliver upon the commitments that have been agreed.
Full report PDF: Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression
This article was posted on 12 Dec 2013 at indexoncensorship.org




