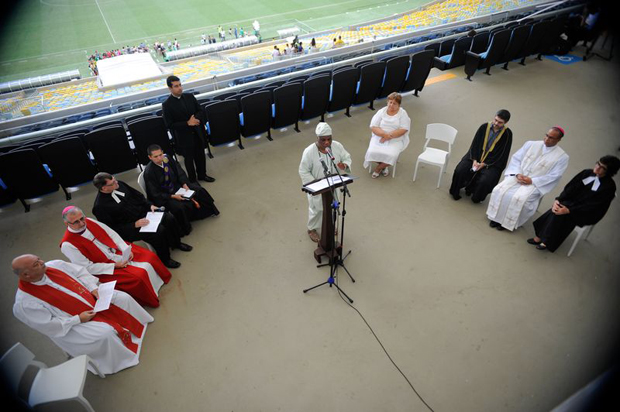
An inter-religious meeting at the Maracanã stadium in Rio de Janeiro to mark the beginning of the Peace Cup campaign (Tomaz Silva/Brazil Agency)
A request to remove 16 videos from YouTube has sparked a broad debate on the limits of freedom of speech and religious expression in Brazil. According to the complaint by the National Association of African Media, filed to the Regional Prosecutor’s Office of Rio de Janeiro (MPF), the videos encourage intolerance and prejudice against religious practices of African origin (Candomblé and Umbanda). The videos were posted by the Igreja Universal do Reino de Deus (IURD), a Neo-Pentecostal church.
The federal prosecutors from the MPF asked Google Brazil to remove the videos. But Google refused, arguing that the material disclosed “would be nothing more than the manifestation of the religious freedom of the Brazilian people” and that the videos “did not violate the company’s policy”.
On 17 May, the issue was taken to the federal court in Rio de Janeiro. There, judge Eugenio Rosa de Araújo denied the request for the removal of the videos. “Its contents are manifestations of free expression of opinion,” he stated. He argued that “the African-Brazilian religious practices do not constitute a religion” because “the religious manifestations (African) do not contain necessary traits of a religion”. He stated that a religion needs to have traits such as a baseline text (“as the Bible or the Koran”), a hierarchical structure and one God to be worshiped.
Notably, the ruling has two parts: the first determines that the videos are to be kept online, and is based on the right to freedom of expression. In the second part of the sentence, the judge defines what religion is, and excludes religions with African-Brazilian origin from this scope.
The representative of the Commission Against Religious Intolerance, Ivanir dos Santos, accused the judge of encouraging prejudice. “He is an employee of a laic State and is submitted to the Brazilian constitution and laws. He violated the constitution and the law against the racial discrimination.”
Facing such strong reaction, the judge Eugenio de Araujo Rosa went back on his decision. In a statement, he admitted he made a mistake and revised his sentence. “The strong support of the media and civil society demonstrates unquestionably the belief in the worship of such religions,” he said, referring to African-Brazilian beliefs.
But the original position of the judge is still causing reactions. The Order of Lawyers of Brazil repudiated the ruling, while the MPF has filed an appeal, arguing that “the decision mistreats the awareness, the honour and the dignity of millions of Brazilians who recognise themselves in these religions”. Protests by African-Brazilian culture organisations were held in at least seven cities. Leaders of all Brazilian beliefs gathered at Maracanã Stadium, calling for more peace and religious tolerance.
In addition, representatives from the MPF will file a lawsuit to the Superior Court of Justice (STJ), one of the highest organisations in the Brazilian judiciary system, against Judge Eugênio Rosa de Araújo. “Our intention is to remove the videos. It is not about freedom of expression, but about the spread of hatred,” said Santos.
On 28 May, the Federal Regional Court (TRF) received a petition with 1,000 signatures, demanding the removal of the videos. The petition was organised by the Commission Against Religious Intolerance and the National Association of African Media. The representatives of the afro culture argue the court’s decision to keep the videos on the internet violates the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Article 129 of the Brazilian Constitution, and the Statute of Racial Equality (Law 12.288/2010). The statute stipulates that the government must protect the communities of African origin from hateful content in the media. The law forbids “the use of the media to disseminate images and contents that expose a person or group to hatred or contempt on the grounds of religion with African roots”.
FuA national demonstration against prejudice towards African-Brazilian religions has been scheduled. The event is organised by various associations for the defence of black culture, with the support of the Order of Lawyers of Brazil, the National Council of Justice (CNJ), the Human Rights Commission of Congress national and the Organization of American States (OAS). In congress, the Parliamentary Front in Defence of “Traditional Peoples of Terreiro” was created, aiming to institutionalise the defence of religions of African origin. The bloc will be a counterpoint to the Evangelical Parliamentary Front, which brings together 77 congressmen who form the base of support for the government of Dilma Rousseff.
“The theme is of utmost importance, because [it] involves guarantees which the constitution itself assures. I hope that it resolves itself quickly,” the President of the Federal Court, Sérgio Schwaitzer, told the Jornal do Brasil.
According Edson Santos, the deputy of PT (Workers Party) and former minister of racial equality, the judge encouraged the prejudice against African-Brazilian sects. He argued that the magistrate will be denounced at the National Council of Justice. “The decision was absurd and deeply regrettable, because it hurts the constitution”, he told to the newspaper Folha de S. Paulo.
“This conflict of law is challenging and raises questions about the limits of freedom of expression,” said Professor of Philosophy of Law José Rodrigo Rodriguez, of Law School of São Paulo from the Fundação Getúlio Vargas. Analysing the topic in an article, he argues that “one can say, without fear of any excess, that the decision has a clear discriminatory effect, despite the certainly good intention of the judge”.
This article was posted on June 4, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org