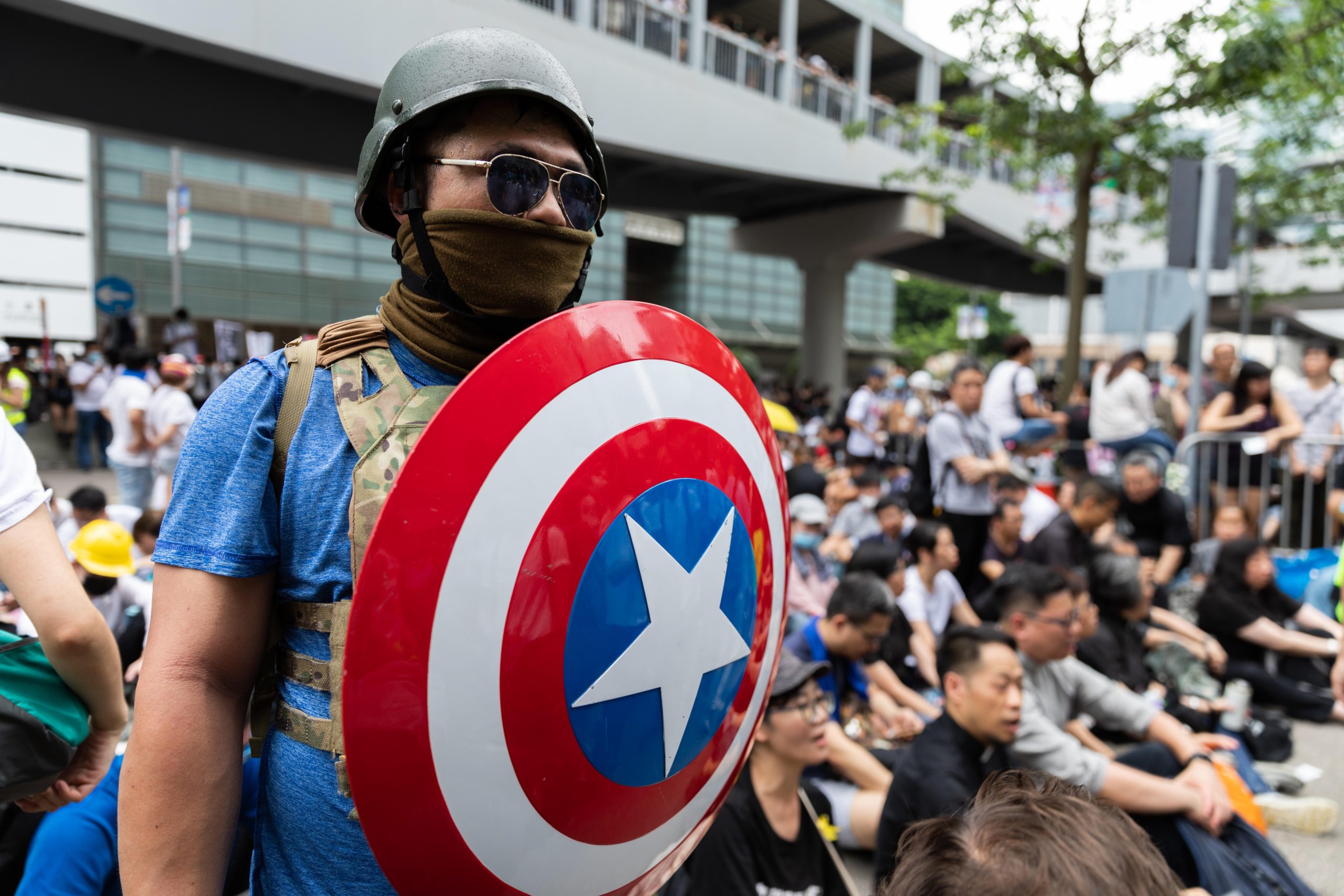
A former food delivery worker calling himself a “second-generation Captain America” and who would turn up at protests in Hong Kong with the Marvel superhero’s instantly recognisable shield has been convicted for violating the country’s national security law (NSL).
On 11 November, Adam Ma Chun-man was sentenced to five years and nine months for inciting secession by chanting pro-independence slogans in public places between August and November 2020.
Evidence cited by a government prosecutor in the court case against Ma included calls for independence he had made in interviews.
Ma becomes the second person to be found guilty under the law imposed by Beijing in July last year. He has lodged an appeal against the verdict.
The first person sentenced under the NSL was former waiter Tong Ying-kit who was jailed in late July for nine years for terrorist activities and inciting secession. Tong was accused of driving his motorcycle into three riot police on 1 July 2020 while carrying a flag with the protest slogan “Liberate Hong Kong. Revolution of our times.”
The watershed ruling on Tong has profound implications for freedom of expression and judicial independence in Hong Kong.
The “Captain America” case has further fuelled fears about the rapid erosion of the city’s room for freedom and the strength of the court in upholding civil liberties.
Like the Tong case, the Ma judgement has significant implications for related cases but the ruling has attracted far less attention. The general public reacted with indifference mixed with a feeling of futility and helplessness. It does not bode well for civil rights and liberties in the city.
The significance of the Ma case lies with the judge’s ruling on what constituted incitement.
Ma’s lawyer said Ma had no intention whatsoever of committing a crime, but was just expressing his views. Merely chanting slogans should not be deemed as a violation of the NSL, the lawyer argued. That he urged people to discuss the issue of independence in schools did not necessarily mean the result of the discussions would be a yes to independence. It could be a no.
Importantly, his lawyer argued Ma had merely expressed his personal views without giving thought of how to make it happen through an action plan. Referring to Ma’s slogan “Hong Kong people building an army”, his lawyer said it was just an empty slogan, again, without a plan.
In sentencing, judge Stanley Chan described the case as serious. He rejected the argument by Ma’s lawyer that the level of incitement in his speeches was minimal, saying Ma could turn more people into the next Ma Chun-man.
Put simply, judge Chan said that although the actual impact of Ma’s speeches in inciting others has been minimal, this was insignificant when determining whether his act constituted incitement.
This view is markedly different from the reaction of the media and the public over Ma’s political antics.
Ma had drawn the attention of journalists when he turned up in protests for obvious reasons. But no more. The lone protester neither had a sizable group of followers nor electrified the sentiments of the crowd at the scene.
The heavy sentencing of Ma will worsen the chilling effect of the national security law on freedom of expression. Importantly, it will have serious implications for a list of incitement cases currently in the process of trial.
In a statement on the sentencing, Kyle Ward, Amnesty International’s deputy secretary general said: “In the warped political landscape of post-national security law Hong Kong, peacefully expressing a political stance and trying to get support from others is interpreted as ‘inciting subversion’ and punishable by years in jail.”
With no sign of an easing of the enforcement of the law 16 months after it took effect, the international human rights group decided to shut down its local and regional offices in the city by the end of the year. They said the Beijing-imposed law made it “effectively impossible” to do its work without fear of “serious reprisals” from the Government.
Hong Kong chief executive Carrie Lam responded by saying no organisation should be worried about the national security law if they are operating legally in Hong Kong, adding Hong Kong residents’ freedoms, including that of speech, association and assembly were guaranteed under Article 27 of the Basic Law, the city’s mini-constitution.
To a lot of Hongkongers, the assurance, which is an integral part of the former British colony’s “one country, two systems” policy, is an empty promise.
The power of the national security law in curtailing freedoms in other aspects of everyday life in Hong Kong has been widely felt.
In October, the legislature rubber-stamped an amendment to the film censorship ordinance, giving powers to the authorities to ban films that are considered as “contrary to the interests of national security.” The phrase, or “red line” in the law, is much broader than the original version, which targeted anything that might “endanger national security.”
Even before the bill was passed, a number of films and documentary films relating to the 2019 protest were not allowed to be shown in public locally. They include the award-winning Inside the Red Brick Wall and Revolution of Our Times, a nominee in the 2021 Taiwan Golden Horse Film Award.
Moves to revive political censorship in film are part of the authorities’ intensified campaign against threats to national security. While targeting political activists, the net has been widened to curb what officials described as “soft confrontation” and “penetration” through films, art and culture and books.
The University of Hong Kong has called for the Pillar of Shame, a sculpture by Danish artist Jens Galschiot, to be removed from the campus, citing concern over the national security law.
On the legislative front, security minister Chris Tang has given clear reminders that more needs to be done to protect national security, pointing to crimes in Basic Law Article 23 that have not been covered in the national security law.
He has vowed to target spying activities and to plug loopholes following the social unrest in 2019. Tang cited the example that helmets and free MTR tickets were distributed free to protesters during the protests, claiming there were state-level organising behaviours, potentially by actors from outside the country.
Both the central and Hong Kong authorities have labelled the movement as a “colour revolution” with hostile foreign forces behind it, without giving concrete evidence.
In addition to spying, a bill on Article 23 will also cover theft of state secrets and links with foreign organisations. Officials gave no timetable. But it is expected to be at the top of the agenda for the new legislature, which is due to be formed after an election is held on 19 December.
Officials are also looking at introducing a law on “fake news” to eliminate what they deem as lies and disinformation, which went viral on social media during the 2019 protest. The Government and the Police claimed they were major victims of this false information.
Looking back to mid-2020 when the idea of a national security law was first mooted, officials assured Hongkongers the law would only “target a very small number of people”.
Nothing can be further from the truth.