8 Apr 2020 | Hungary, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Viktor Orbán Credit: European People’s Party/Flickr
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]Hungary’s prime minister Viktor Orbán, leader of right-wing nationalist party Fidesz, has responded to the coronavirus crisis by pushing through sweeping emergency laws that have no time limit and have enormous potential to limit media freedom.
These laws essentially allow Orbán to rule by decree, which presents a huge threat to democracy and freedom of expression. While Index acknowledges that extraordinary measures need to be taken to protect lives, the passing of emergency laws of this nature for an indefinite time period was described in an Index statement as “an abuse of power”.
Under the emergency laws, journalists can be imprisoned for up to five years for publishing what the authorities consider to be falsehoods about the outbreak or measures taken to control it. But what exactly constitutes falsehoods is open to interpretation.
As Index notes, Hungary already has “one of the worst free speech records in Europe”. This further blow to journalists’ ability to report freely and objectively on the actions taken by the government is crippling for press freedom. It follows a pattern of state authorities infringing on press freedom under the guise of quashing “fake news” that Index has recorded happening globally in the wake of the crisis.
Transparency about the official numbers of those infected and those who have died from Covid-19 is critical for public safety. The scale of the outbreak will inform public behaviour and support for health services. Authoritarian regimes around the world such as North Korea and Turkmenistan have reported zero cases, the implausibility of which suggests censorship of the real figures by these countries’ despotic leaders.
Orbán is on the road to joining these leaders as, under the emergency laws, journalists are unable to hold the government to account over the accuracy of the data. Orbán has singular control of the public knowledge of the number of confirmed coronavirus cases, which, according to a government website, is 817 to date. See more here about this on the Index map tracking attacks on media freedom in Hungary.
Hungary’s neighbour Austria, which has a smaller population and recorded its first cases just 8 days before Hungary, has to date recorded 12,206 cases.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”3″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1586344862424-03642fb1-d46b-2″ taxonomies=”4157″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
7 Aug 2018 | Campaigns -- Featured, Hungary, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”102023″ img_size=”full”][vc_column_text]Frans Timmermans, First Vice-President, European Commission
Mariya Gabriel, Commissioner, European Commission
Tibor Navracsics, Commissioner, European Commission
Antonio Tajani, President, European Parliament
7 August 2018
OPEN LETTER – Media freedom in Hungary and the case of Hir TV
The undersigned media freedom organisations are writing to draw your attention to the deteriorating situation of press and media freedom in Hungary, in particular the recent case of Hir TV.
Hir TV was the last domestically-owned independent TV company in Hungary. On 1 August 2018 a sudden change in ownership resulted in dismissals of outspoken leading journalists and an abrupt change of editorial policy. Programmes that had previously reflected independent views were cancelled and replaced with government-friendly programmes. One cancelled talk show was replaced with a broadcast of a speech that Viktor Orbán had made some days earlier.
The case of Hir TV has been reported to Index on Censorship’s platform Mapping Media Freedom, which monitors threats, limitations and violations related to media freedom in Europe.
The loss of independence of the last remaining domestically owned TV company in Hungary is deeply discouraging. It demonstrates a fundamental lack of respect for media freedom and shows how far Hungary has distanced itself from European values.
We ask you to condemn these developments in the strongest possible terms.
We strongly urge the European Union to strengthen the link between eligibility for funding under the next Multiannual Financial Framework and respect for media freedom.
European Centre for Press and Media Freedom (ECPMF)
Index on Censorship
International Press Institute (IPI)
South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO)[/vc_column_text][vc_separator][vc_column_text]
Hungarian media freedom violations reported to and verified by Mapping Media Freedom since May 2014.
[/vc_column_text][vc_raw_html]JTNDaWZyYW1lJTIwd2lkdGglM0QlMjI3MDAlMjIlMjBoZWlnaHQlM0QlMjIzMTUlMjIlMjBzcmMlM0QlMjJodHRwcyUzQSUyRiUyRm1hcHBpbmdtZWRpYWZyZWVkb20udXNoYWhpZGkuaW8lMkZzYXZlZHNlYXJjaGVzJTJGODUlMkZtYXAlMjIlMjBmcmFtZWJvcmRlciUzRCUyMjAlMjIlMjBhbGxvd2Z1bGxzY3JlZW4lM0UlM0MlMkZpZnJhbWUlM0U=[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1533629513035-b3d8ca8c-d3a9-4″ taxonomies=”6534″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
17 Jan 2018 | Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News and features, Uncategorized
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Last year was a bleak one for press freedom in Hungary. A series of transactions saw the purchase of every local newspaper — more than 500 in all — by businessmen close to the government. Papers like Somogyi Hírlap have become reliable trumpets for the government with a biased and centralised editing team in charge of political stories.
Public media has been broadcasting government propaganda for many years and the few remaining independent online media outlets have a limited reach. Many Hungarians living in the provinces have no access at all to news critical of the government and the ruling party, Fidesz.
But the government’s grip on the flow of information is being challenged by a movement resembling the underground “samizdat” publications of the Soviet Union known for skirting government censorship. “While in larger cities we use term ‘samizdat’ ironically, in small communities our readers actually perceive our newspaper as an illegal publication distributed without the consent of those in power,” János László, the leader of the Nyomtass Te Is (Print Yourself) movement, tells Mapping Media Freedom.
“Our first priority is to help people access news that is censored in the newspapers, TV stations and radio stations close to the government,” László, a former newspaper editor says. “There are still a few independent newspapers and online news websites that work honestly, but they have a limited reach. Our goal is to provide people living in the countryside with points of view other than the severely biased and the unscrupulous propaganda.”
The Nyomtass Te Is editorial team provides a weekly overview of the independent press, selecting stories from outlets such as a 444.hu and merce.hu which aren’t very well known in rural areas, about poverty, corruption, the state of the education and the health system, and rewrite them into short, easily understood articles. Page four of each publication is reserved for local news, where local activists and journalists can suggest pieces. One such article, written by an anonymous author, broke the news of Tibor Balázsi, a former press aide of the mayor of Miskolc, becoming the editor-in-chief position at a local newspaper, Észak-Magyarország.
Activists edit and lay the articles out on A4 pages. These pages are then printed in 50 different locations across the country, put in mailboxes, handed out to people on the street and at bus stations, and left in public places.
The publication is uploaded to the movement’s website, where it is downloaded and printed by the activists who distribute the newspaper. Because the whole process is decentralised and anyone can download and print the newspaper, it is difficult to know just how widely circulated it is, but, according to László, 5,000-10,000 copies are printed weekly. In a city like Miskolc, around 3,500 copies are distributed weekly, while in other places numbers are in the dozens.
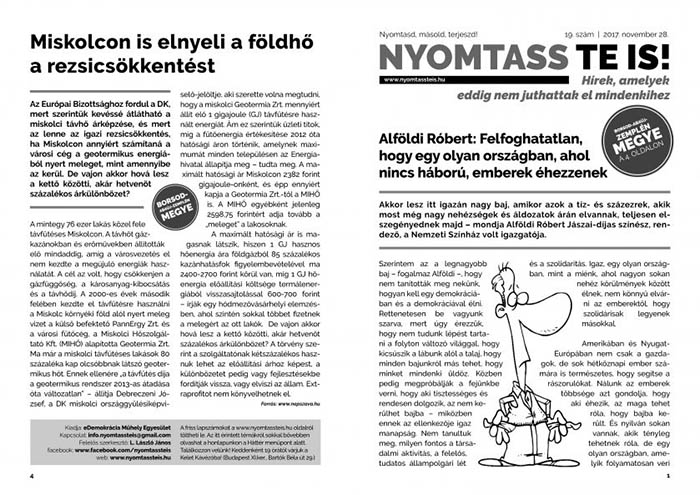
“Right now we are present in more than 50 places,” László says. “Our goal is to start from county towns, and from there, to reach the smallest villages. As of January 2018, we have local partners and activists in every county.”
When his crackdown on media freedom is criticised, prime minister Viktor Orbán usually argues that one can publish anything in Hungary, so the press is free, László says, pointing out that press freedom also means a citizen’s right to easily access diverse and comprehensive information regarding public affairs.
The right to be informed is even guaranteed by the Hungarian constitution, but the majority of people living in rural areas still have no access to information other than public media, local newspapers edited by the local government and county newspapers under government control. Every city council publishes a newspaper. Because the most city councils have a Fidesz majority, and the mayor is also from Fidesz, these newspapers are totally biased towards the party.
Unsurprisingly, then, reactions from readers on Nyomtass Te Is’s circumvention efforts are almost always supportive. “Since we started, we have received emails and Facebook messages on an almost daily basis. Most of them are receptive to the idea, and only a small fraction contain anything negative. We receive many ideas on how our publication can be improved and what stories we should cover. We increased the size of our fonts after receiving complaints about readability.”
According to the editor, until now there have been no attempts to their work. “However, in small settlements, our activists are distributing copies of Nyomtass Te Is only at night and in secret.”
The movement is functioning without big donors. Instead, it relies on a lot of voluntary work and small private donations of around of 5-10 thousand forints (€15-30). The money is spent almost exclusively on printing.
As for the future, they are planning to apply for the funding opportunity titled Supporting Objective Media in Hungary by the US. Department of State, which would mean a funding of $700,000 for media operating outside the capital in Hungary to produce fact-based reporting.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1516198972987-f974cdff-ca3f-7″ taxonomies=”2942″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
27 Sep 2017 | Europe and Central Asia, Hungary, Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Viktor Orban (Credit: European People’s Party)
As Hungary prepares for parliamentary elections, independent journalists have become a target of the pro-government media outlets. This follows a speech by Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orban at the end of July at Tusványos, the annual Fidesz jamboree in Băile Tușnad, Romania, during which he said: “We must stand our ground against the Soros mafia network and bureaucrats in Brussels, and will have to go to battle against the media they operate in the coming months.”
Orban’s message at Tusványos is considered a preview of what to expect from the Hungarian government in the following months. A few days after the speech, Magyar Nemzet daily reported that the prime minister’s words signal a clear change in tactics: instead of defaming independent media outlets and their owners, pro-government media outlets started going after prominent journalists, known for their work of exposing the corruption of the Hungarian government.
During September 2017, pro-government media outlets started publishing articles discrediting leading Hungarian journalists critical to Orban’s regime.
On 5 September 2017, 888.hu published a list of journalists accused of being “mouthpieces” for George Soros, who has been called a “national security risk” and a “public enemy” by Orban for allegedly supporting the mass immigration of Muslims into Europe.
“The international media, with a few exceptions, generally write bad things about the government because a small minority with great media influence does everything to tarnish the reputation of Hungary in front of the world — prestige that has been built over hundreds of years by patriots,” 888.hu wrote.
Among those listed are Lili Bayer, a journalist working for Politico, László Balogh, a Pulitzer-winner photographer, Márton Dunai, Gergely Szakács and Sándor Pető, journalists working for the Reuters news agency, as well as Zoltán Simon, a journalist working for Bloomberg, and ZDF producer István Sinkovicz.
“The article is indicative of the extent to which the pro-government press seems willing to carry out the political orders of prime minister Viktor Orbán,” Budapest Beacon commented, adding that the editor in chief of 888.hu is Gábor G. Fodor, deputy chairman of Századvég Foundation’s board of trustees. Századvég is a think-tank and consultancy that has been embroiled in numerous scandals involving large government orders since 2010. The publisher of 888.hu is Modern Media Group Zrt., a company owned by Árpád Habony, an informal advisor to the prime minister.
The list was condemned by the 3,500-member National Association of Hungarian Journalists (MUOSZ). The body said that there is no evidence of any contact between Soros and the journalists named in the piece. “Stigmatising colleagues by using listing methods that hark back to former anti-democratic times is far from the practice of democratic journalism and informing (the public),” said MUOSZ.
The campaign against journalists continued on 11 September 2017 with a piece on 888.hu attacking Gergely Brückner, one of Hungary’s leading business journalists working at index.hu. The piece accused Brückner of writing an article about the political-diplomatic background of several millions of dollars transferred to Hungary from an Azerbaijani slush fund without any evidence.
“I was not particularly bothered by the editorial, although I don’t think he understands correctly where the trenches in the Hungarian media landscape are,” Gergely Brückner told Index on Censorship. “He also exaggerates my importance (of course, I felt flattered), and for sure he does misunderstand the goals I had with my articles.”
“It is known that the ruling party is always looking for enemies, these being refugees, Soros, the EU, NGOs and independent journalists, all of which are under attack,” Brückner added. “This is how they are trying to keep their core voters engaged.”
Unfortunately, ordinary media consumers have a difficulty in making a distinction between independent, fact-based journalism and biased, post-truth journalism, as Brückner explains. “I am not disturbed at being targeted and it does not influence my work or my sources. They had an obviously exaggerated opinion about me, but they did not have false statements. In the latter case, I would seek legal redress.”
On 14 September 2017, Attila Bátorfy, a data journalist at investigative website Atlatszo.hu and research fellow at CEU’s Center for Media and Communication Studies was also the target of a defamatory article published on an obscure blog, Tűzfalcsoport. The piece, illustrated with a photo of enlarged mites, is claiming that Bátorfy’s piece on the spread of Russian propaganda in Hungary is based on faulty evidence.
A day later, on 15 September 2015, Pesti Srácok, another website close to the government published an article about András Földes, a journalist working for index.hu who reported extensively on the migration crisis. The piece is a list of Földes’s more important reports, along with “ironic” commentary.
“When he goes to war zones, he watchfully takes a peek on the trenches, carefully avoiding danger, then he presents the things he saw as he wishes (…). His extraordinary talent is also shown by the fact that he believes anything to 17-year old immigrant men born on 1 January. At least we hope he naively believes the overstatements he writes about, and these (overstatements) are not invented by him,” the article goes.
Even if the readership of such a blog or website is relatively small, these articles are usually echoed in the media universe loyal to Orban and are often referenced by the public media as well, meaning that the allegations reach a considerable audience.
The recent defamatory pieces are only the tip of the iceberg of the attacks on press freedom in Hungary. Since 2010, the Hungarian government led by Orbán is working systematically to silence critical voices by changing the legal framework regarding media, redrawing the advertising market, introducing preferential taxes that only hit certain, independent broadcasters, buying up media companies, or simply closing them down, as happened with the largest opposition newspaper, Népszabadság.
The most alarming recent incidents regarding press freedom in Hungary:
Police check IDs of TV crew filming new PM office
Journalist assaulted at a Fidesz public forum
Largest opposition daily suspended
Parliamentary amendment restricts access to public information[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1506503807710-1289f6d8-e51b-2″ taxonomies=”2942″][/vc_column][/vc_row]




