23 Jan 2015 | News
Bahrain
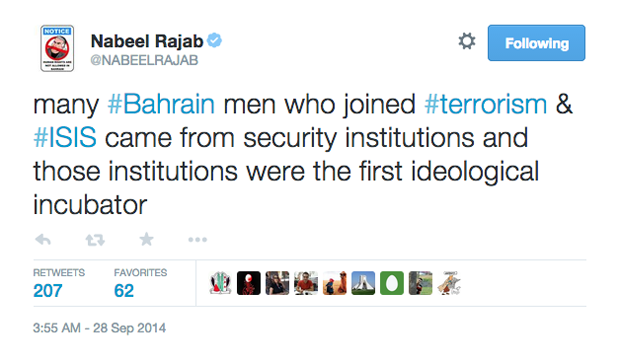
This week, prominent Bahraini human rights activist Nabeel Rajab was handed down a six month suspended sentence over a tweet in which both the country’s ministry of interior and ministry of defence allege that he “denigrated government institutions”. Rajab was only released last May after two years in prison, over charges that included sending offensive tweets. His experience is not unique in Bahrain. In May 2013, five men were arrested for “insulting the king” via Twitter.
Turkey
A former Miss Turkey was recently arrested for sharing a satirical poem criticising the country’s President Recep Tayyip Erdogan on her Instagram account. She is set to go on trial later this year. Turkey has a chequered relationship with social media, temporarily banning both Twitter and YouTube in the wake of the Gezi Park protests, in large part organised and reported through social media. In 2013, authorities arrested 25 individuals for spreading “untrue information” on social media.
Saudi Arabia

(Photo: Gulf Centre for Human Rights)
In late 2014, women’s rights activist Souad Al-Shammari was arrested during an interrogation over some of her tweets. The charges against her include “calling upon society to disobey by describing society as masculine” and “using sarcasm while mentioning religious texts and religious scholars”, according to the Gulf Centre for Human Rights.
France
![(Photo: « Source : Réseau Voltaire » [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Dieudonné_Axis_for_Peace_2005-11-18.jpg)
(Photo: Réseau Voltaire [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons)
Following the series of terrorist attacks in Paris in early January, at least 54 people have been detained by police for “defending or glorifying terrorism”. A number of the cases, including against comedian Dieudonne M’bala M’bala, are believe to be connected to social media comments.
Britain
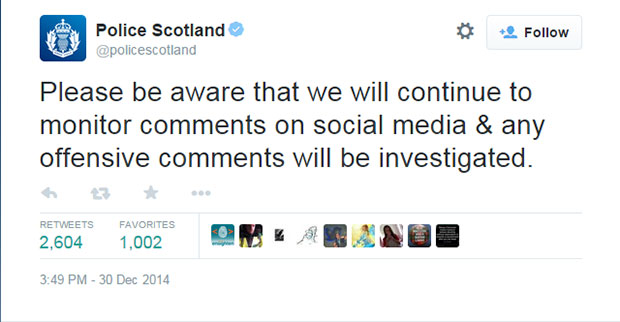
A 22 year old man was arrested in for “malicious communication” following Facebook messages made in response to the murder of soldier Lee Rigby, and another user was arrested after taunting Olympic diver Tom Daly about his dead father. More recently, police arrested a 19-year-old man over an “offensive” tweet about a bin lorry crash in Glasgow that killed six people. TV personality Katie Hopkins, known for her controversial tweets, was also reported to Scottish police following some tasteless tweets about about Scots. The incident prompted Scottish police the to post their now infamous tweet declaring they would continue to “monitor comments on social media“.
China
Online activist Cheng Jianping was arrested on her wedding day in 2010 for “disturbing social order” by retweeting a joke by her fiance. She was sentenced to one year of “re-education through labour”. Twitter is officially banned in China, and microblogging site Weibo is a popular alternative. In 2013, four Weibo users were arrested for spreading rumours about a deceased soldier labelled a hero and used in propaganda posters. The four were said to have “incited dissatisfaction with the government”, according to the BBC.
Australia
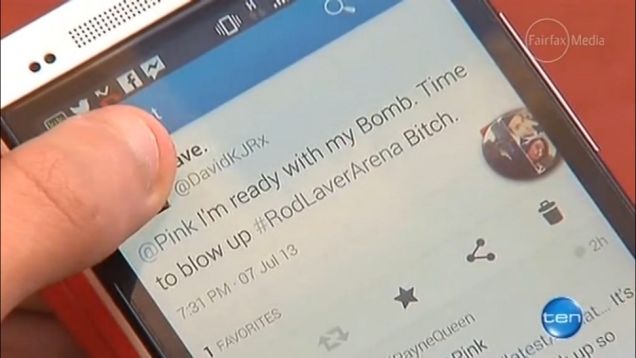
A teen was arrested prior to attending a Pink concert in Melbourne for tweeting: “I’m ready with my Bomb. Time to blow up #RodLaverArena. Bitch.” The tweet referenced lyrics from the American popstar’s song Timebomb.
India
An Indian medical student was arrested in 2012 over a Facebook post questioning why her city of Mumbai should come to a standstill to mark the death of a prominent politician. Her friend was arrested for liking the post. Both were charged with engaging in speech that was offensive and hateful.
United States
Back in 2009, a New York man was arrested, had his home searched and was placed under £19,000 bail for tweeting police movements to help G20 protesters in Pittsburgh avoid the officers. According to Global Voices, it is unclear whether his actions were actually illegal at the time.
Guatemala
A man was arrested in 2009 for causing “financial panic” by tweeting that Guatemalans should fight corruption by withdrawing all their money from banks.
This article was posted on 23 January, 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
16 Sep 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, Netherlands, News
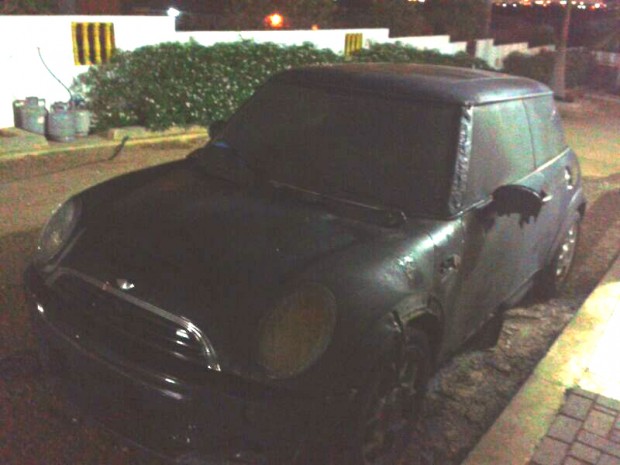

Journalist Richeron Balentien woke up one night to find his car had been torched (Photo: Richeron Balentien)
It’s a Wednesday morning in May 2014, around 3am and still dark outside. Radio journalist Richeron Balentien, his girlfriend and their 2-year-old daughter are sound asleep until the smell of fire wakes them up. When they look out of the window they see Balentien’s car burning in the yard in front of the house. He immediately knows what is going on.
“It was a clear threat,” Balentien told Index on Censorship over the phone. “It was a warning, to shut me up.” The police confirmed the car was purposely set alight. The perpetrator has not been brought to justice.
The Netherlands is always found near the top of press freedom rankings, this year second only to Finland in the Reporters Without Border’s Press Freedom Index. But rarely taken into account, however, are the Dutch islands in the Caribbean sea. The largest of these, Curacao, became a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in 2010.
If Curacao was included in the Netherlands’ press freedom score, it might not place so high on the list. Journalists like Balentien face threats and attacks, as they fight a lonely and dangerous battle to get the truth about corruption and organised crime on the island out.
The attack on Balentien’s car happened just a few hours after Gerrit Schotte, the first prime minister of an autonomous Curacao, was arrested on allegations of money laundering and forgery during his time on power. He was released after a week in custody, but the investigation is ongoing.
Balentien aired the news on his radio station Radio Direct, while many other media outlets kept silent. “This is a small island,” he said. “Everybody knows each other. Most journalists don’t investigate. They don’t want to get into trouble”.
According to a recently published Unesco report, Curacao’s media are “not able to fulfil their role as watchdog of authorities and other powerful stakeholders in society”. It also highlights issues around journalist safety, stating that “some recent cases of harassment of journalists have caused public debate on the issue of safety and are reason for concern”.
The report concludes that social and political pressures lead to self censorship among the press, as “dependency on good relationships with sources of information on one hand and protection of relatives on the other hand is very much a threat”.
In May 2013 the island was shocked by a political murder. Helmin Wiels, a popular politician determined to rid the island of high level corruption, was shot dead by an assassin in broad daylight.
The atmosphere on the island has been tense ever since, Balentien said. “Nobody thought it was possible that someone of that calibre could get killed. It shocked the entire island,” he explained. “The atmosphere changed. Everyone is afraid.”
Two men were sentenced to life in prison for killing Wiels, but it’s still unclear who gave the orders. Many believe they came from high up. There has been speculation that former Prime Minister Schotte knew about the plan, said Balentien — something Schotte himself denies. Wiels had accused the state telecommunications company of involvement in illegal sales of lottery tickets.
The Wiels case is one of Balentien’s ongoing investigations. “I feel everything is being done to keep the truth about this murder behind closed doors,” he said. “We need to know who gave the orders.”
A 2013 Transparency International study shows “a general lack of trust in key institutions” in Curacao. The anti-corruption watchdog labels this “a major obstacle” which will “limit the success of any programme addressing corruption and promoting good governance”. As for the media, the report highlights the lack of trained journalists, with content open to influence by the private financiers and advertisers on which “many media companies are heavily dependent”. Few requirements to ensure the integrity of media employees also “undermines the independence and accountability of the media,” according to the group.
Balentien is sure that former prime minister Schotte gave the order to attack his car. “Sources told me that it was discussed within the party to set my car alight to frighten me,” he said. “I have never been afraid to talk about Schotte, his party or the corruption.”
Dick Drayer, the Curacao correspondent for the Dutch national broadcaster NOS, also believes there was a political motive behind the attack. “Schotte’s party is behind this, everybody knows that,” he told Index on Censorship.
Drayer has been working as a journalist on the island for nearly ten years. “I see is an increase of intimidation towards journalists. Journalists here are taught not to ask questions. There is verbal and physical violence. When you dig in dirty business in Curacao, you know you can get into trouble. That leads to self censorship,” he said. “In Netherlands the media controls the power, in Curacao it’s the other way around.”
While the island has had its own government since 2010, ties with the Netherlands are still strong. Corruption and organised crime in Curacao are occasionally discussed in Dutch parliament and the Dutch police is involved in the Wiels murder investigation.
But “the relationship is disturbed,” according to Dryer. “The Netherlands is careful to intervene when things are going the wrong way on the islands, because they’re afraid to be seen as the coloniser.” He thinks his country could be more involved when it comes to corruption and organised crime. “They should speak up more. The Netherlands worries about human rights in China, but when it comes to Curacao they say it’s an internal matter.”
After the car incident, Balentien’s station Radio Direct continued to receive anonymous phone threats. “I am aware,” he said. “I look around. I turn to see who’s driving behind me. I check my house before I enter.”
Despite this, he maintains he will keep up his investigative reporting on high level corruption and the Wiels murder case.”Because I don’t want this island to be ruined by these people anymore”.
More reports from The Netherlands via mediafreedom.ushahidi.com
Bloemendaal municipality accused of censoring local newspaper
Journalists attacked during anti-ISIS protest in The Hague
Journalist on trial for defamation
Photographer assaulted by housing corporation employee
Restrictions on filming inside parliament building
This article was posted on 16 Sept 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
21 Jul 2014 | Mapping Media Freedom, Netherlands, News
Separatists in East Ukraine threatened journalists reporting on the Malaysia Airlines MH17 disaster. The plane was downed on Thursday 18 July killing 298 people, including 193 Dutch citizens.
Writing for The Daily Beast, Anna Nemtsova and two colleagues were detained at the morgue by separatists.
On Monday 21 July, Rudy Bouma, a reporter for the Dutch TV broadcaster Nieuwsuur, took photos of rebels carrying weapons at the train station in Donetsk. The separatists controlled the train that was carrying the bodies of the victims.
More reports from The Netherlands via mediafreedom.ushahidi.com
Journalist denied entrance to public court hearing
‘Rules for using drones by journalists too restricted’
Journalists’ cameras seized by police
Dutch magazine on trial for photographing princess
This article was posted on July 21, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
![(Photo: « Source : Réseau Voltaire » [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Dieudonné_Axis_for_Peace_2005-11-18.jpg)










