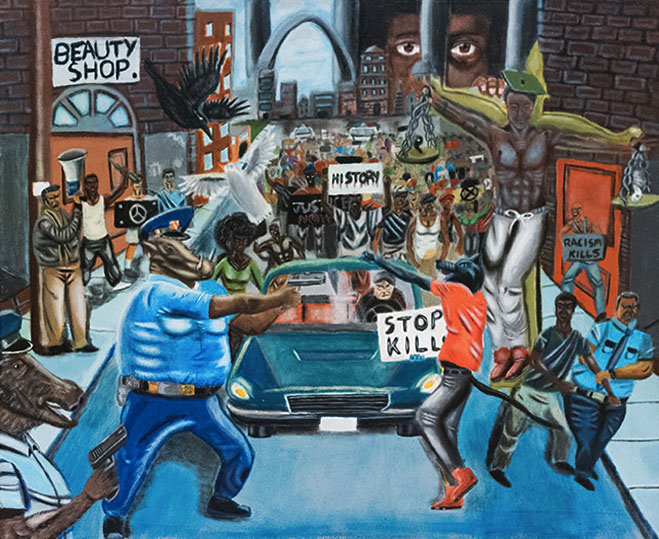21 Nov 2019 | Campaigns -- Featured, Statements, Turkey, Turkey Statements
Turkish authorities re-arrested the internationally known Turkish novelist Ahmet Altan just one week after his release from more than three years in detention. Index on Censorship and 24 other NGOs say that his re-arrest, on 12 November, was an extraordinarily low blow in a case that has been marked by political interference and arbitrariness from start to finish.
In addition to ongoing violations of his right to freedom of expression, stemming from a prosecution that should never have been brought in the first place, his re-arrest is a form of judicial harassment. Altan should be immediately released and his conviction vacated, the organisations say.
On 4 November this year, Altan was convicted of “aiding a terrorist organisation without being its member” and sentenced to 10 years and six months in jail. He was released on bail pending appeal against conviction by the defence. Altan had originally been convicted of “attempting to overthrow the constitutional order” and sentenced to life imprisonment without the possibility of parole. However, that conviction was overturned by the Supreme Court of Appeals who ordered a retrial on the lesser charge.
After the verdict in his retrial was handed down, the prosecutor appealed the decision to release him and on 12 November another panel of judges accepted this appeal and ruled that he should be re-arrested. Altan’s defence lawyers were not formally told of the court’s decision, but instead they learned about it through the pro-government media. Altan was detained later that evening and sent to Silivri Prison the following day.
Article 5 of the European Convention on Human Rights prohibits all arbitrary deprivation of liberty and the European Court of Human Rights has held that arbitrariness can arise where there has been an element of bad faith on the part of the authorities. Altan’s re-arrest and detention gives every appearance of being politically motivated, arbitrary, and incompatible with the right to liberty under Article 5. The organisations pointed to the following aspects of his re-arrest:
- Despite having no right to do so, both the Turkish Presidency and Parliament sought to make representations arguing against the decision to release Altan – a move designed to put political pressure on the court.
- The reasons the judge gave to cancel Altan’s release included that his activities “influenced many sympathisers through the news” and that “those who were interrogated for the same crime but fled the country have engaged in discourse and lobbying against our country’’ – grounds that are both unfounded and lack legitimacy as reasons to deprive someone of liberty. The judge further castigated Altan for refusing to show remorse for a crime he did not commit.
- The judge also considered that Altan was a flight risk and issued a warrant for him to be re-arrested. However, the fact that the decision was almost immediately leaked to the media suggests that the authorities did not genuinely consider him to be a flight risk: Altan could have fled immediately upon hearing the news in the media. Instead, Altan was arrested at his home as he waited for the police. The next day, the court still sent him to prison custody insisting that he was a flight risk.
Thomas Hughes, executive director of ARTICLE 19 said: “The entire process of Ahmet Altan’s trial and retrial, including his prolonged detention, his release and then re-arrest on spurious grounds, has been completely arbitrary.
“The same court that convicted Altan of ‘attempting to overthrow the constitutional order’ then oversaw a retrial and convicted him of ‘aiding a terrorist organisation’, on the same evidence, which primarily consisted of Altan’s writings. That court then released him on bail and another court with no experience of the case ruled for his re-arrest.
“The case of Ahmet Altan is emblematic of the crackdown against writers and journalists in Turkey. Political revenge rather than justice has dominated the proceedings.”
Ahmet Altan’s case challenging his detention is still pending at the European Court of Human Rights. Other decisions by the ECtHR which are binding on Turkey and relate to prosecutions for free speech have had a significant impact on the outcome of the respective trials, including in the case of Ahmet’s brother, Mehmet Altan.
A ruling from the European Court setting out the scope and nature of the violations in Ahmet Altan’s case would likely have a decisive impact on his detention and the appeals process in his case.
We repeat our call for the Turkish authorities to release Ahmet Altan and vacate the conviction against him. The Turkish authorities should cease all judicial harassment of individuals on the basis of their political opinions and for exercising their fundamental right to freedom of expression.
Signatories:
ARTICLE 19
Association of European Journalists (AEJ)
Amnesty International
Articolo 21
Cartoonist’s Rights Network International (CRNI)
Danish PEN
English PEN
European Centre for Press and Media Freedom (ECPMF)
European Federation of Journalists (EFJ)
German PEN
Human Rights Watch
IFEX
Index on Censorship
International Federation of Journalists (IFJ)
International Press Institute (IPI)
Norwegian PEN
Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso Transeuropa
PEN America
PEN Canada
PEN International
P24, Platform for Independent Journalism
Reporters Without Borders (RSF)
South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO)
Swedish PEN
World Association of News Publishers (WAN-IFRA)
Background
Ahmet Altan is an internationally known Turkish novelist who was convicted to life imprisonment without parole in February 2018 for “attempting to overthrow the constitutional order” in an unfair trial that primarily relied on his writings and comments in the media. His case was overturned by the Supreme Court of Appeals in July, who recommended a retrial on equally bogus charges of “aiding a terrorist organisation without being its member”. On 4 November this year, Altan was convicted on the new charges and sentenced to 10 years and six months in prison. He was released on bail pending appeal, after having served more than three years in detention, awaiting trial or appeal. On 12 November he was returned to prison, just one week after his release.
In its verdict on 4 November, the judge ruled that the parliament and the presidency could not intervene in the case as victims. Despite this, on 5 November parliament made an application challenging, inter alia, Altan’s release. It also made a separate application challenging the verdict.
On 6 November, the prosecutor also challenged the decision to release Altan on the grounds that there was a flight risk, despite the fact that a foreign travel ban had been put in place.
On 7 November, Istanbul Heavy Penal Court No 26 reviewed the legal challenges and confirmed its previous decision to release him and the case file was referred to the Heavy Penal Court No 27 for review.
On 8 November, the presidency challenged the verdict, including the release of Altan, stating that all defendants should be charged on the basis of the initial indictment.
On 11 November, the presiding judge and prosecutor of Heavy Penal Court No 27 were changed.
On 12 November, the court, with a new judge and prosecutor, reviewed the legal decision of Court No 26 and issued a ruling. The ruling was not provided to the defence lawyers, but was leaked to the pro-government press which immediately reported that an arrest warrant had been issued. Ahmet Altan was re-arrested that evening, before the decision was communicated to him, or his lawyers, officially.
On 13 November, Altan was taken before the presiding judge at Heavy Penal Court No 27 to review his arrest and decide on his transfer to prison. The judge ruled that he should be returned to prison.
Note: ARTICLE 19 submitted an expert opinion to the court during the first trial, which examined the coup-related charges and evidence against international standards on the right to freedom of expression. Human Rights Watch also assessed the indictment and, like ARTICLE 19, found that the journalistic works cited expressed political opinions and did not incite or advocate violence. No new evidence was presented at the retrial on terrorism charges.
13 Dec 2017 | Campaigns -- Featured, Digital Freedom, Digital Freedom Statements, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship rejects many of the suggestions made in a report into intimidation of UK public officials by a committee tasked with examining standards in public life.
The report recommends — among other things — creating legislation to make social media companies liable for illegal content and increasing the use of automation to remove content that is not only illegal but “intimidatory.”
“Like many such reports, the report from the Committee on Standards in Public Life makes the mistake of lumping together illegal content, intimidatory content — which the committee itself admits is hard to define — and abusive content,” said Jodie Ginsberg, chief executive of Index on Censorship.
“While some content outlined in the report — such as threats of rape — can clearly be defined as harassing or intimidatory in nature, deciding whether content is illegal or not largely depends on understanding the context — and that is something that neither ‘automated techniques’ nor speedy removals can address.
“We are deeply worried by the growing trend in which democratic governments devolve responsibility for making decisions that should be made by the police or the judiciary to unaccountable private bodies to censor speech. [/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-times-circle” color=”black” background_style=”rounded” size=”xl” align=”right”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”3/4″][vc_column_text]
Intimidation in Public Life uses language that would not be out of place in any dictator’s handbook
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]In addition to a number of recommendations for social media companies to take action, the committee’s report also recommends that press regulators should extend their codes of conduct to include “intimidatory behaviour”.
“This report uses language that would not be out of place in any dictator’s handbook,” said Ginsberg. “The idea that the press should include in their code of conduct an element that addresses whether content could ‘unduly undermine public trust in the political system’ sounds like a gift to any politician wanting to challenge reports with which they disagree. Rather than enhance democracy and freedoms, as this report claims to want to do, this risks damaging it further.”
Index welcomes the fact that the committee deemed new criminal offences specific to social media unnecessary, but cautions that devolving power to social media companies to police content could have significant risks in scooping up legitimate as well as illegal content because of the sheer volume of material being posted online every second.
Index would also strongly caution against any engagement with other governments at the international level on “what constitutes hate crime and intimidation online” that could result in a race to the bottom that adds further global restrictions on speech.[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Don’t lose your voice. Stay informed.” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship is a nonprofit that campaigns for and defends free expression worldwide. We publish work by censored writers and artists, promote debate, and monitor threats to free speech. We believe that everyone should be free to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution – no matter what their views.
Join our mailing list (or follow us on Twitter or Facebook) and we’ll send you our weekly newsletter about our activities defending free speech. We won’t share your personal information with anyone outside Index.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][gravityform id=”20″ title=”false” description=”false” ajax=”false”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1513167851048-354a7311-4d5b-3″ taxonomies=”16928″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
20 Jan 2017 | Statements
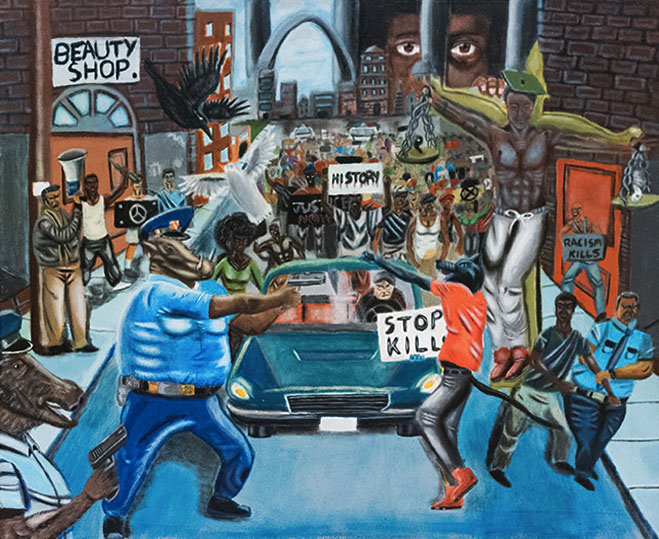
Untitled #1, by David Pulphus
As organisations devoted to promoting the arts and freedom of expression, we condemn the recent removal of a student painting from a public passageway on Capitol Hill. The removal shows a deep disregard of a young person’s constitutional right to free expression and is a flagrant violation of the principles underlying the nation’s commitment to the protection of free speech. It is a sad day when elected representatives of the people of the United States send a message to young people in this country that they should stifle passionate expression concerning important issues of public policy.
The painting, by St. Louis High School Senior David Pulphus, is among the winners of the annual Congressional Art Competition. It depicts, in an allegorical manner, a young artist’s vision of one of the facts of our recent past: a protest against police violence. Pulphus’ painting was selected through a process set by the Competition, which included a review by the office of the Architect of the Capitol. It was approved and remained on display for six months until conservative news outlets built up a controversy around it in late December.
The media-generated controversy was followed by multiple attempts on the part of several Republican Representatives to take down the work with their own hands (each time, Representative Clay (D-Mo) put it back up). On Friday, January 13th, Stephen Ayers, the Architect of the Capitol, ordered the painting’s removal on the basis that it violated competition guidelines stipulating that “subjects of contemporary political controversy or a sensationalistic or gruesome nature are not allowed.”
The retroactive use of the very guidelines by which the painting was selected in the first place to remove the work only serves to draw attention to the how vague these guidelines are. Worse, the fact that the decision to censor the work was made under strong political pressure coming from one side of the aisle proves how easy it is to use the vague guidelines to suppress political viewpoints.
What is “controversial” is entirely subjective and thus open to abuse and the enforcement of political bias: Indeed, many other artworks in the exhibition may be deemed controversial, including a depiction of white police officers harassing an African American playing checkers, a portrait of Bernie Sanders and another of President Obama. And, of course, portraits and statuary on permanent display in Congressional buildings represent many political figures that are controversial. That Pulphus’ painting of police protests was singled out among all these for a hasty removal, after partisan political pressure by representatives who claimed the work was offensive to law enforcement, only deepens our concerns about the elected representatives enforcing political bias and stifling speech.
Political artistic expression is protected speech, no matter how controversial or offensive some may find it. Criticism of government actors such as law enforcement officials is one of the foremost reasons why we have the First Amendment. Citizens’ freedom to speak out against perceived governmental abuses and injustices is necessary to the health of our democracy: were government able to silence such criticisms, meaningful political discourse would be rendered impossible.
Removing the work sends a message to young people – and everybody else – that they should not depict the world around them for fear of offending our political representatives. At a time when we have a new administration and nationwide concerns about free speech, the censoring of an artwork because of its viewpoint is a deeply disturbing and divisive act in an already polarised nation.
We urge the Architect of the Capitol to take the time to consider arguments from both sides of the aisle and make a decision that upholds one of the nation’s most cherished values, a value that should not be subject to partisan strife: the value of free speech. We hope that rather than exacerbating partisan conflict, the controversy around this young person’s painting becomes a unifying educational opportunity to reinforce free speech principles across both sides of the aisle.
National Coalition Against Censorship
American Civil Liberties Union
American Civil Liberties Union of the District of Columbia
American Society of Journalists and Authors
Authors Guild
College Art Association
Comic Book Legal Defense Fund
Free Speech Coalition
Index on Censorship
PEN America
Vera List Center for Art and Politics
Washington Area Lawyers for the Arts