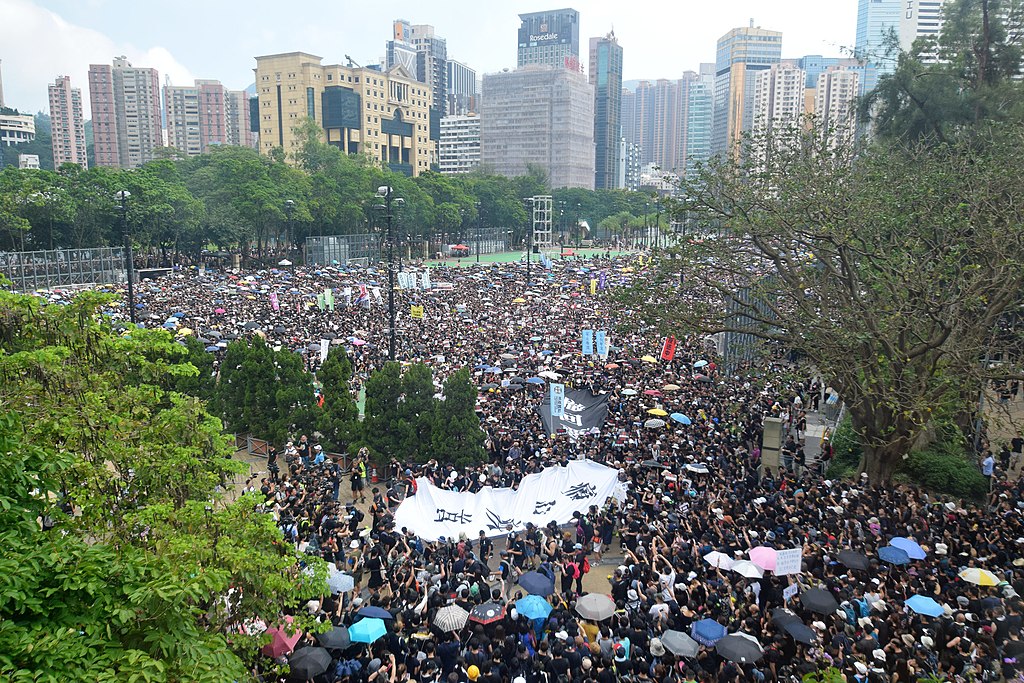
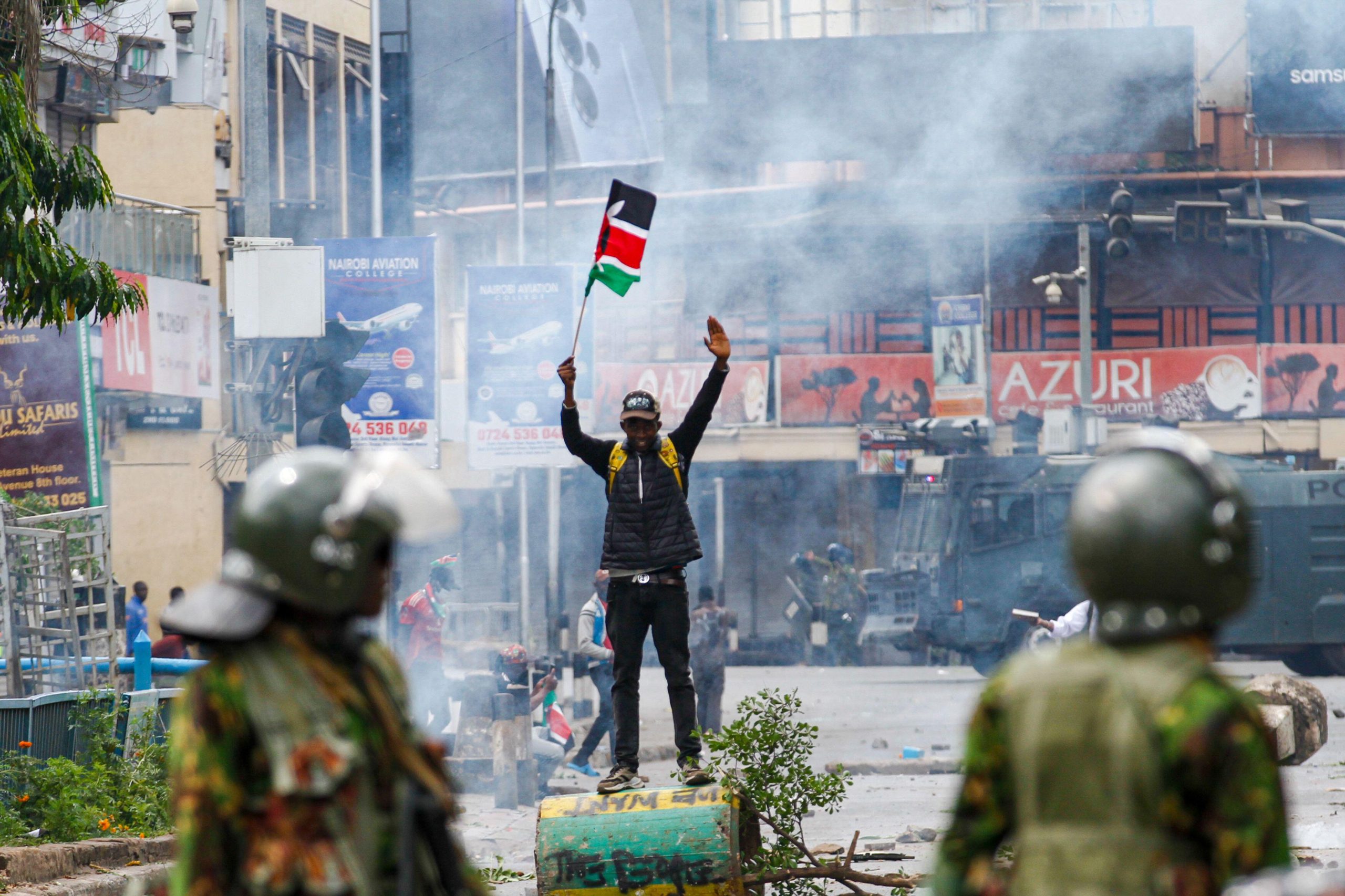Image Adham Khorshed/Demotix
Egypt and China have always ranked poorly on press freedom. In 2013, Egypt ranked 158th while China ranked 173rd out of 178 nations in Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index. In recent months, a government crackdown on free expression in the two countries has shown disturbing similarities with repressive tactics used by the two regimes to silence dissent being invariably the same.
On a recent trip to Beijing, I was struck by how the authorities in both Egypt and China persistently use the media to serve their own interests and to tighten their grip on power. In both countries, opinion leaders, rights activists and critics who challenge those in power are perceived as “a national threat” and often become targets of intimidation, physical assaults, detention and sometimes, even death. The predicament of some journalists and bloggers in the two countries serves as a chilling reminder of the hazards media workers are subjected to as they strive to tell the story.
Thanks to heavy internet censorship in China — including the blacklisting of a host of foreign websites — the country has been described by free speech advocates as “a world leader in repression of the internet”. A draconian campaign against online “rumourmongers” has recently fuelled fears of even tighter government control on social media and online expression and increased self-censorship in China.
The so-called “anti rumour” campaign unveiled on 9 September allows Chinese authorities to arrest and jail internet users accused of “spreading false rumours” for up to three years. The ruling applies to internet activists who deliberately post what the government perceives as “false information” which is then shared by at least 500 others or is viewed at least 5,000 times. Critics warn the campaign will give the government an excuse to crush rights activists, bloggers and independent news providers who challenge the authorities or report abuses by the government as well as those demanding greater freedom and democracy.
In a widening crackdown on free expression in recent weeks , China has seen sweeping arrests of government critics, rights activists and opinion leaders accused of “disturbing public order”. While many of them remain in custody, 16-year-old Yang Hui–a school student who had been among the first group of bloggers jailed on charges of “spreading online rumours”– was released late September after spending a week behind bars in Gansu province. He remains under police surveillance however, and has been prohibited from speaking publicly. Yang was detained after questioning an investigation into the death of a man whose body had been found outside a karaoke club. Police had claimed that the man had fallen to his death from the building and had closed the case, but Yang insisted that the case should have been probed further. Moreover, he had posted comments daring the authorities to arrest him.
Repressive measures to silence dissent are not peculiar to the Chinese government. In recent days, a leaked video posted by activists on YouTube has shown Egyptian military generals discussing plans for a media clampdown similar to that imposed by the Chinese authorities . The footage — which appears to have been shot some months before Islamist President Mohamed Morsi was toppled: The video shows officers wearing winter uniforms — shows Defense Minister Abdel Fattah El Sissi addressing the officers . The recording starts with a senior officer urging El Sissi to re-establish red lines for the media and find new ways of “neutralizing media outlets”. He also calls on El Sissi to engage with owners of media outlets directly. “There are twenty to twenty five people controlling the media in Egypt, ” the senior officer notes. “We could either win them over or terrorize them”, he adds. El Sissi jokingly responds that he knows how to win them over but asks how he could possibly terrorize them?
That however does not rule out plans by the military generals to control the media. El Sissi acknowleges in the video that “we have been concerned with controlling the media” since the army took over power in February 2011. He goes on to affirm that the military was working on doing so and was achieving positive results but “we are yet to achieve what we want”, he says.
Since Morsi’s ouster, the tone of Egyptian media has shifted, reflecting the interests of those now in power. Print journalists and TV talk show hosts have persistently cheered on the powerful armed forces as “the guardians of the revolution” while demonizing the Muslim Brotherhood as a ” terrorist organization”.
Meanwhile, the military-backed interim government has cracked down on journalists covering the anti coup protests. In recent weeks, several journalists have reported harassment by police and soldiers including physical assaults, molestation, confiscation of their equipment and detentions. Worse still, journalists at the frontlines are getting caught in the crossfire. Mick Deane, a British Sky News cameraman, was shot and killed while covering the violent breakup of a pro- Morsi protest camp in Cairo in August. Egyptian Journalist Habiba Ahmed Abd Elaziz was also shot dead near the Rabaah al-Adawiya mosque in Cairo the very same day as security forces moved in on the pro- Morsi sit-in demanding the reinstatement of the toppled Islamist President. Abu Dra’aa , a Sinai-based journalist working with the independent Al Masry El Youm recently faced a military tribunal for a post on his Facebook wall suggesting that the military was misinforming the public about its offensive in Sinai. He was handed a six month suspended jail sentence. A number of other journalists including several working for Al Jazeera (which has been accused of being biased towards the Muslim Brotherhood) remain in custody. Several pro- Muslim Brotherhood channels (including Al Jazeera Mubasher) and Al Faraeen, a private channel owned by controversial talk show host Tawfeek Okasha, have been shut down. While the latter has recently been allowed back on the air, its temporary closure sends a powerful warning message to other channels to “adopt the pro-military state line or risk a similar fate.”
Meanwhile, the military has been using the media to fuel xenophobic sentiment: In remarks to state owned daily Al Ahram,after the brutal massacre outside the Republican Guard Headquarters in July, an unnamed military source warned that “the foreign press is inciting sedition between the army and people. ” With the surge in xenophobic sentiment gripping the country in the aftermath of the June 30 military takeover, foreign correspondents covering the Tahrir rallies commemorating the October 1973 War last Sunday expressed concern on Twitter about possibly being mistaken for “foreign spies”.
“There are rumours of a no-foreigner rule in Tahrir Square today. Can anyone confirm?” asked Louisa Loveluck, a freelance journalist based in Cairo . The BBC’s Middle East Correspondent Quentin Sommerville meanwhile posted a picture of himself near a military tank in Tahrir Square ahead of the protests with the sarcastic byline “foreign spy in Tahrir” before quickly deleting it , possibly for fear it may evoke unwarranted anger.
Nationalistic fervour and a rising tide of xenophobia are characteristics shared by all countries where autocratic regimes use the media to consolidate their grip on power. Egypt and China are no exception to the rule. The muzzling of the press through continued intimidation and the sweeping arrests of journalists, bloggers and rights activists bears testimony to the fact that neither country is serious about carrying out the desired democratic reforms.
This article was originally posted on 7 Oct 2013 at indexoncensorship.org