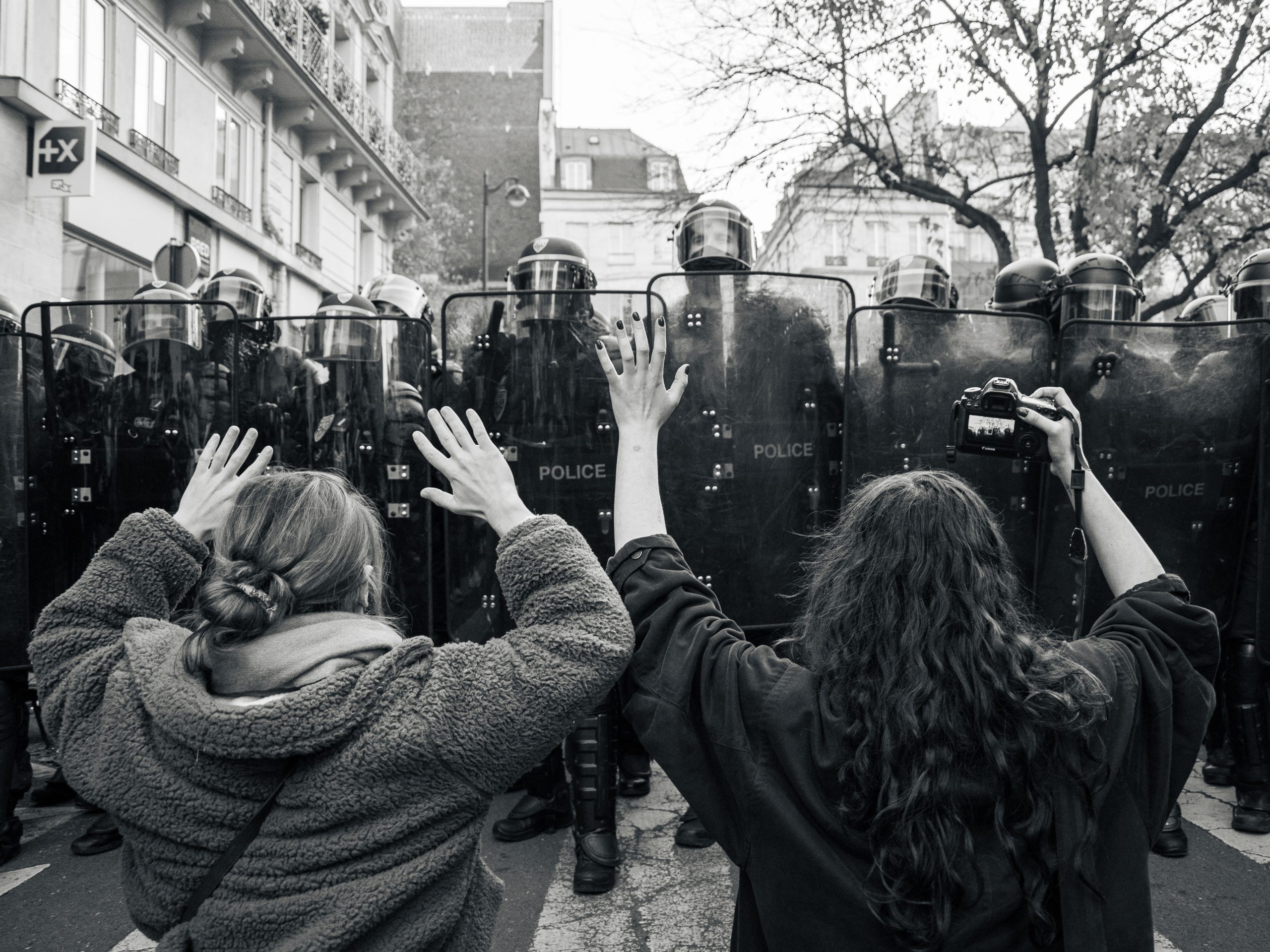Physical attacks on journalists have increased dramatically over the past year, according to the latest annual report from the Council of Europe Platform on media freedom in Europe.
The platform, of which Index on Censorship is a partner, reports on serious threats to the safety of journalists and media freedom in Europe in order to reinforce the Council of Europe’s response to the threats and member states’ accountability.
The new report, Defending Press Freedom in Times of Tension and Conflict, reveals that the number of cases involving the safety and physical integrity of journalists has jumped by 51% year-on-year, with 82 cases reported to the platform.
Many of the attacks on journalists have taken place during public protests.
“Violence against journalists during street protests is fed by a wave of media bashing and an avalanche of hate speech on social networks – very often prompted by political figures – which directly target journalists, questioning their independence and legitimacy and therefore making them more vulnerable to physical aggression,” the report says.
Overall, the number of alerts in all categories published by the CoE platform has sky-rocketed to 280 in 2021, up from around 200 in 2020 and more than double the level reported in 2016. Of the 280 alerts, 110 related to the harassment and intimidation of journalists.

Index’s policy and campaigns manager Jessica Ní Mhainín
Speaking at the launch of the report, Index’s policy and campaigns manager Jessica Ní Mhainín highlighted cases of impunity in CoE’s report.
“Impunity for crimes against journalists refer to failure of states to identify, prosecute and punish anyone including the assailants and masterminds involved in committing a crime against a journalist,” she said. “Cultures of impunity contribute to self-censorship by making journalists more vulnerable to pressures out of fear of reprisals or harm.”
Some 35 cases of impunity have been registered on the platform since 2015 and two new impunity cases – those of Turkish journalist Uğur Mumcu, murdered in 1993, and Turkish-Cypriot journalist Kutlu Adalı, murdered in Cyprus in 1996 – were added to the impunity category during the year.
“In 2021, we welcomed the Slovak Supreme Court’s decision to overturn the not-guilty verdicts of the suspected masterminds of the 2018 murder of journalist Ján Kuciak and his fiancée Martina Kušnírová. The case will be heard in the Specialized Criminal Court later this year,” said Ní Mhainín.
Last year also saw the publication of a 438 page-report from the public inquiry into the assassination of investigative journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia, which concluded that the state of Malta “must bear responsibility for the assassination because it created an atmosphere of impunity”.
“We once again call on the Maltese authorities and the Commission of Experts to implement the recommendations of the Public Inquiry,” said Ní Mhainín.
Russia, Turkey and Ukraine account for 60% of all the cases relating to impunity on the platform. Last October marked the 15th anniversary of Russian journalist Anna Politkovskaya’s murder.
Ní Mhainín said, “The masterminds of her murder are still at large, sending the incredibly dangerous message that killing a journalist is a low-risk crime.”
Yet impunity is not restricted to these countries.
A BBC Spotlight investigation has uncovered serious concerns over the police investigation and the failure to prosecute those behind the murder of Irish journalist Martin O’Hagan, who was killed in September 2001 for his reporting on paramilitary activities in Northern Ireland. The concerns raised in the programme, which aired on 2 March 2022, came in the wake of several Police Ombudsman reports that uncovered collusive behaviour between the police and loyalists in Northern Ireland. According to the BBC’s investigation, police did not act on important information – including individual names – that were handed over to them within 48 hours of the murder. The journalist’s family are now taking legal action against the Police Service of Northern Ireland (PSNI) and the Ministry of Defence.
“Press freedom is the canary in the coal mine – it is a key indicator of the clear and worrying degree of democratic backsliding that is taking place across Europe,” said Ní Mhainín. “That’s why we once again call on Council of Europe member states to ensure that the highest priority is given to conducting thorough and transparent investigations into all crimes against journalists and we remind member states of the 2016 Recommendation of the Committee of Ministers which requires states ‘adopt appropriate criminal law provisions to prevent impunity’”