Risky business: Bookselling in Libya
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”The dangers of selling “the wrong” kind of book in Libya are many and varied and yet one chain of bookshops is still open for business. Charlotte Bailey speaks to a bookseller in Tripoli”][vc_column_text]

A street in Tripoli. Credit: David Stanley/Flickr
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
“One of my brothers is still active with the bookshop. The other two, they are kind of scared. They don’t go much anymore,” said Ghassan Fergiani, managing director of the London-based Darf Publishers.
His brothers run Dar Fergiani, a bookselling and publishing business in the Libyan capital Tripoli. The bookshops have remained open despite the brutal civil war that started in 2011, killing thousands and splintering the country into three governments and a vast number of militia groups.
“They got tired of it, the fear,” he continued.
Dar Fergiani is a family firm and what Fergiani calls his legacy. His father, Mohammed Fergiani, started out with three bookshops in Tripoli in 1952 and, a few years later, opened a publishing house. In Libya’s post-independence period, he enjoyed relative freedom to publish and sell the books.
“There was some censorship, but not much,” said Fergiani.
But in 1969 Muammar Gaddafi seized power and four years later launched what he called a cultural revolution, with the aim of removing all traces of imported ideologies and all signs of foreign influence. Books the authorities considered problematic were burned. A few years later Gaddafi published his Green Book, which outlined his governing principles. The chapter on the media banned private ownership of publishing companies.
“In the late 1970s, they confiscated all his shops, all his stock, all his staff, everything,” Fergiani said.
Arrests and assassinations then forced Mohammed Fergiani to London. “My father feared for his life,” Fergiani explained. Not knowing when, or if, he would be able to return, he founded Darf Publishers in the UK.
But after Gaddafi implemented a series of more internationally friendly policies in the 1990s, Mohammed Fergiani decided to go back. He repurchased the stock the government had seized and began cautiously selling books again. “He had to be very careful,” said Fergiani.
A key demand of the protesters who overthrew Gaddafi in the 2011 revolution was freedom of expression. And, in the immediate aftermath, there was more space for different voices. Citizen journalism became more common and there was a proliferation of television, radio and print publications.
“Everybody was excited. We started selling books critical of Gaddafi. We published a book about democracy.”
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”2/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”We started selling books critical of Gaddafi. We published a book about democracy” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
The different types of books available, from niche non-fiction to international bestsellers, and a renewed interest in Libya more generally, led to a spike in demand at the stores. People flocked to the three smart, airy shops with their white stone floors and large windows in the Italian-era streets that lead off from Martyrs’ Square in the north and Hay Al Andalus further west.
The initial excitement did not last long. This area, where once the well-heeled frequented cafes and did their shopping, has become the site of violent clashes. This violence alone has put people off visiting the bookshops.
Today, the legal environment in Libya remains poor for booksellers and publishers. While a constitutional declaration passed in August 2011 provides limited protection for freedom of opinion, communications and the media, it does not fully reflect international standards for freedom of expression and does not abolish censorship. Under Law 5, passed in 2014, any statements that could harm or prejudice the 2011 revolution or insult the executive, judiciary or legislature, are punishable by up to 15 years in prison.
The deteriorating political and security situation has created a chaotic and dangerous media environment. Foreign journalists hardly ever visit.
The Tripoli-based internationally-backed Government of National Accord operates a censorship board, which Fergiani said has a haphazard approach that makes it difficult to predict what will be allowed. After success with Chewing Gum, the debut novel of the Libyan author Mansour Bushnaf with Darf Publishers in London, Fergiani tried to publish it in Arabic with Dar Fergiani in Tripoli. “We submitted it to the censorship board, but they rejected it,” Fergiani said. The board gave no reason for its decision.
Speaking to Index from Benghazi in Libya, Nada Elfeituri, founder of the grassroots group Young Writers of Benghazi, said: “It’s frustrating when I can’t find a popular book written by a Libyan inside my own country. Libya doesn’t have many books, libraries or publishing houses.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”2/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Forces loyal to Field Marshall Khalifa Haftar were accused of burning 6,000 books” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
“There were several initiatives to introduce a wider variety of books, even ones that might be considered taboo, but again that became restricted as different government groups controlled the books that entered the country,” she said.
In January, for example, forces loyal to Field Marshall Khalifa Haftar were accused of burning 6,000 books in the east of the country. These books included works of philosophy by Friedrich Nietzsche. In a video of the book seizure posted online, an officer said the books promoted violence, sorcery, eroticism and the Muslim Brotherhood.
Meanwhile, there is a constant threat from militia groups. Numbers suggest there are up to 2,000 militia groups, all with different ideas about what should and shouldn’t be published.
“Sometimes somebody tells them this is a bad book for one reason. Another time, a different militia takes your book out for a different reason,” said Fergiani, who explained that recently a militant came into one of the shops and demanded that they rearrange the show window to give priority to religious books. Three people who work at Dar Fergiani bookshops have also been arrested in Tripoli on different occasions and were only released after a complex set of negotiations.
“That is the pressure that in Libya we live under. It doesn’t have to be a government or a dictator. It can be anybody.
“You start fearing for your life. You start saying – OK I don’t want to do this. What am I in it for?”
These problems are compounded by the exceptionally difficult economic environment in Libya. The World Bank said in 2016 that the economy was on the verge of collapse. The currency has crashed, making Dar Fergiani books expensive. There are regular city-wide power cuts, an intermittent water supply and very little internet.
Despite this, Dar Fergiani has remained open six days a week throughout the war and Fergiani continues to travel to Tripoli frequently for work.
“Just don’t ask us why we do it,” said Fergiani.
When pushed on the answer to that question he added: “As a publisher and a bookseller you want to promote certain books. You want people to be exposed to different ideas.
“But it’s hard.”
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Charlotte Bailey is a freelance journalist writing for newspapers including The Guardian. She used to live in Beirut, Lebanon where she worked for the Daily Star
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80561″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422014535686″][vc_custom_heading text=”Enemies of the people” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422014535686|||”][vc_column_text]June 2014
Writer Matthias Biskupek took part in demonstrations in East Germany as the Berlin Wall came down. He looks back at the attempts to censor books and theatre.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”92001″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/030642208701600510″][vc_custom_heading text=”The media under Gadaffi” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F030642208701600510|||”][vc_column_text]May 1987
An interview with Fadel Al-Messaoudi, who believes the media has been directly controlled by the government since the cultural revolution of 1973.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”94326″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228108533267″][vc_custom_heading text=”Censorship and Col Gadaffi” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228108533267|||”][vc_column_text]October 1981
Libyan journalist exiled in Spain, F. el-Manssoury, reports on soldiers’ accounts of censorship in Libya from first-hand knowledge of the early President Gaddafi’s regime.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Free to air” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F09%2Ffree-to-air%2F|||”][vc_column_text]Through a range of in-depth reporting, interviews and illustrations, the autumn 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine explores how radio has been reborn and is innovating ways to deliver news in war zones, developing countries and online
With: Ismail Einashe, Peter Bazalgette, Wana Udobang[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”95458″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/09/free-to-air/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]



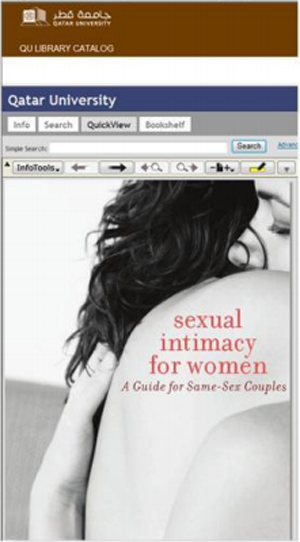 A group of students at the University of Qatar have started a petition to remove “inappropriate” books from the university library.
A group of students at the University of Qatar have started a petition to remove “inappropriate” books from the university library.