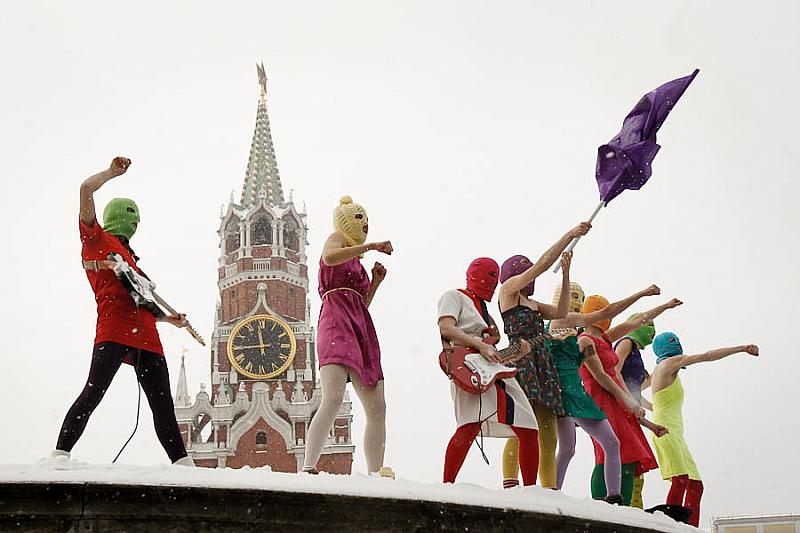8 Jul 2013 | Comment, Europe and Central Asia, News
 Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
(more…)
14 Jun 2013 | Comment, Europe and Central Asia, News
Russia’s new blasphemy law is censorship under the guise of protection for believers, says Padraig Reidy

In his speech on Russia’s Constitution Day in December 2012, Vladimir Putin bemoaned the decline of spiritual values.
“Today, Russia suffers an apparent deficit of spiritual values,” said Putin, as his Orthodox ally Patriarch Kirill nodded along.
The former KGB man continued: “We must wholeheartedly support the institutions that are the carriers of traditional values.”
So far, so Mother Russia.
What was interesting was that the president went on to say that it would be “amoral” to create laws governing spirituality. Putin commented ““Any attempts of the government to intervene with people’s beliefs are effectively a sign of totalitarian rule. It’s absolutely out of the question. It’s not our way.”
This would seem at odds with this week’s passing of a new blasphemy law, which will impose prison sentences and fines on people convicted of “public actions expressing clear disrespect for society and committed with the goal of offending religious feelings of the faithful”.
But it is in fact very much in the mould of the current trend for religious defamation law.
Traditionally, blasphemy was the crime of causing offence to God himself; now it is recast as causing offence to believers. Blasphemy laws are here to protect us. Look back at the testimony durings Pussy Riot’s trial, and again and again you hear the stories of poor innocent believers who were shocked by the women’s behaviour; even if the Patriarch and the president had wished to forgive the punk group, they had to think of the poor pious babushkas who had been rocked to the very core by an act that some admitted to not actually having witnessed.
Shamefully, Ireland has led the way in this trend. The Irish Defamation Act of 2009 established definitions and punishments for blasphemy where none had previously existed (in spite of the fact that the 1937 constitution recognised blasphemy as a crime, it did not define what blasphemy was, and thus, there had never been a conviction for blasphemy, or even a full trial, in the country).
The Irish law defines religious defamation as any action likely to cause “outrage among a substantial number of the adherents of [a] religion”, with fines of up to e25,000 payable by those found guilty.
The wording of the Irish bill was used as a template in the Organisation of Islamic Conference’s attempts to get the UN to recognise religious defamation as a crime.
Of course, the old-fashioned definitions of blasphemy still exist: in Egypt this week, writer Amer Saber was given a five-year sentence for “contempt of religion” for authoring a short story collection called “Where is God?”. And in Syria, a teenager was reportedly shot in front of his family merely for uttering the name of Muhammad. The abuses of blasphemy law in Pakistan are only too well known.
But the justification for blasphemy laws, as with many other censorious impulses, is increasingly tied up in the idea that people should be protected from offence, from controversy, even from being challenged.
Perhaps the most offensive notion is that we cannot deal with ideas, even aggressively expressed ideas, that we disagree with. Government’s such as Putin’s are all too happy to shut down free speech and repackage censorship as benign protection.
24 May 2013 | Europe and Central Asia
A year after the mass protests marking Vladimir Putin’s controversial presidential win, Elena Vlasenko reports from Moscow on the heavy-handed repression confronting the Russian opposition.
On 6 May 2012, the day before Putin’s inauguration, tens of thousands marched towards Moscow’s Bolotnaya Square, protesting against his return to power, fuelled by allegations of election fraud.

Russian President Vladimir Putin visited the Netherlands in April 2013. (Photo: Pierre Crom / Demotix)
The rally was to be the culmination of the historic peaceful protests for fair elections in late 2011. The plan had been to end the march with a rally in the sqaure, where the throng of protesters were funneled through metal detectors. A splinter group launched smoke bombs at the police, which erupted into violent clashes with security forces. Hundreds were arrested — including opposition leaders Alexei Navalny and Sergei Udaltsov — and many faced criminal charges for participating in “mass riots.”
Days later, when 200 protesters protested the Bolotnaya Square arrests, organisers of the encampment were arrested. Criminal charges were brought against almost 30 protesters, most of whom, according to rights activists, were either mistakenly prosecuted or should have faced lesser administrative charges.
In April 2013, a public inquiry led by members of Russia’s opposition and human rights activists refuted the official narrative around the 6 May rally. The inquiry found that the response of protesters was an act of “self-defence”, provoked by “police officers and masked men”. Despite the findings, there is an air of pessimism about the political climate.
The deterioration of the free expression environment in Russia has accelerated since Putin’s inauguration. Authorities prosecuted Pussy Riot and instituted of a number of repressive laws against non governmental organisations, rally organisers, and re-criminalised defamation. There is also an ever-growing blacklist of websites. The second reading of the so-called “homosexual propaganda” law is planned. Yet, none of these recent actions have been met with a substantial response from Russia’s opposition.
Student Blog Competition
Think you have what it takes to be published by Index on Censorship? Here’s your chance to find out. More >>>
Index on Censorship Events
Caught in the web: how free are we online? June 10, 2013
The internet: free open space, wild wild west, or totalitarian state? However you view the web, in today’s world it is bringing both opportunities and threats for free expression. More >>>
Last October, groups opposed to the Kremlin created the “Opposition coordinating council” — an online, elected pseudo-parliament meant to legitimise opposition leaders. Throughout its young existence it has received criticism — not from pro-Kremlin media or activists, but from people who voted for them or participated in the elections — for using expensive facilities for their monthly meetings. In fact, most elected opposition leaders don’t attend these meetings, which means that the council doesn’t have the quorum to make decisions. The council’s decisions are also minor administrative details about bylaws, and have less to do with fighting to change the current system.
The council, created to form a united opposition strategy, still hasn’t decided whether it should criticise Putin and demand his resignation, or to call on him to implement radical reforms.
Even though it has failed to give a strong response to the Kremlin’s attempts to silence dissidents, the opposition has faced criminal prosecutions of its leaders. Sergei Udaltsov is currently under house arrest on charges of organising “mass riots” and political activist Alexei Navalny is facing charges of fraud. The result has been to blunt the rising political power of Udaltsov and other members of the opposition’s leadership.
When this year’s 6 May anniversary rally ended, demonstrators were made to pass long lines of soldiers blocking their way to the Red Square and many other places, forcing the protest’s traffic towards Moscow’s metro stations. One could hardly call the picture of protesters winding through rows of soldiers, police and military cars, one of freedom. Without much to expect from either the government or the opposition a general feeling of entrapment hung over Bolotnaya Square’s anniversary protests.
 Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights