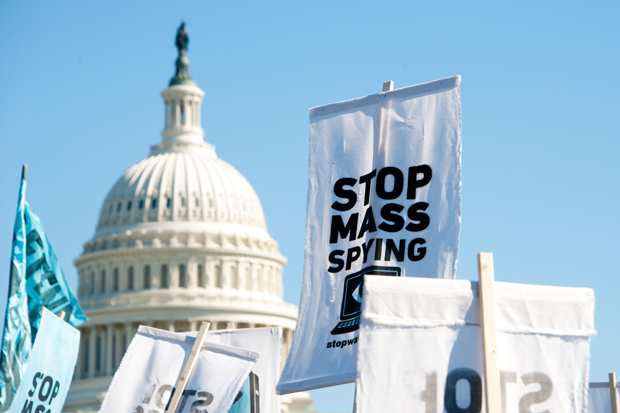
29 May 2014 | India, News and features, Politics and Society
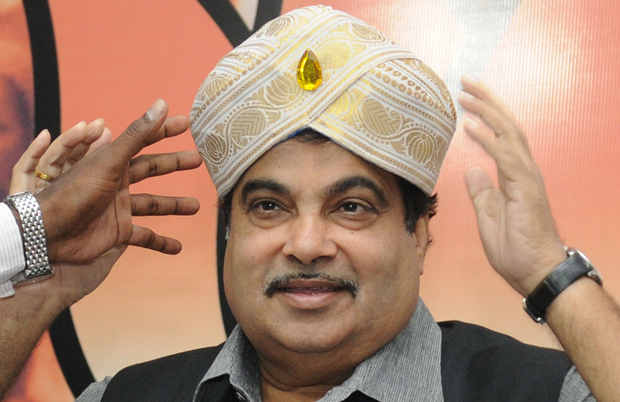

Nitin Gadkari, a politician with a chequered, if not dubious record of integrity and probity, had a political opponent arrested for slander. (Photo: Amit Kumar/Demotix)
Once, President Lyndon Johnson was caught in the crossfire of an anti-Vietnam war protest. A placard was shoved in his face: “LBJ pull out, like your daddy should have done.” Sure, LBJ got the pun, as would have Anthony Weiner in our present times, but he remained unperturbed. Consider Lady Violet Bonham Carter’s biting repartee to an irresolute Sir Stafford Cripps, saying he “has a brilliant mind — until it is made up”.
Mordant wit is what makes politics and political debates sparkle with brilliance, besides deflating windbags and putting stuffed shirts in their place. Even if the “sourcasm” is discounted, plainspeak and no-holds barred verbal duels contribute in no small measure to ensuring accountability, for who isn’t mortally petrified of lacerating criticism?
Turns out that in India, folks with brittle egos and skeletons stacked up in their closets, can and will wield the law to clam a critic’s mouth shut, and even have them put in jail. And this is irrespective of resorting to some risqué puns.
Arvind Kejriwal, founder of the Aam Aadmi (Common Man) Party, who is out on a limb to eradicate the scourge of corruption, realised this to his peril when Nitin Gadkari, a politician with a chequered, if not dubious record of integrity and probity, had him arrested for slander. Slander? No, Gadkari wasn’t invoking some law of the Middle Ages or the Victorian Era. He was merely invoking Sections 499 and 500 of the Indian Penal Code which criminalise defamation, both in writing as well as verbal statements. Kejriwal called Gadkari “corrupt” because not very long ago, the latter did come under the scanner for alleged massive illegalities in his business dealings, but managed to wriggle out since no legal investigation or prosecution were launched.
These two provisions are so broad in scope that every insinuation, unless proved to have been made in “good faith”, can land someone in prison. Someone like Kejriwal, who was incarcerated for six days until he was let out on bail yesterday. Now how does one prove “good faith”, that too, “beyond reasonable doubt”, since that remains the standard of proof in criminal law? Worse, a person can be taken into custody even while this seemingly Herculean task is getting done.
As if criminalisation of libel isn’t bad enough, punishing “slander” grants almost instant impunity if one is strategic enough. Take Kejriwal’s example, again. In October and November last year, he addressed a press conference and read out from a list of charges against business tycoon Mukesh Ambani. The businessman lost no time in slapping legal notices against every television channel which broadcast the conference. Libel chill, without a shred of doubt, for all the channels went silent. Whether Ambani’s fleece is as white as snow isn’t the question; his dark deeds of pulverising criticism are, and deserve the most trenchant critique.
It is encouraging to note that already demands are being made for decriminalising libel, but unless slander is banished from the statute books, dangers would continue to lurk. The Law Commission of India has taken a laudatory and timely step by releasing a consultation paper which seeks to unshackle the media from apprehensions of libel chill. But what happens to individuals — political activists, or whistleblowers? A possible solution lies in Gertz v. Robert Welch, Inc. wherein the Supreme Court of the United States extended the Sullivan privilege (named after the legendary NYT v. Sullivan case) — that only statements made with naked malice or reckless disregard for the truth shall be held as defamatory — available to media houses, to certain categories of individuals also. Those “seeking governmental office” and those who “occupy positions of such persuasive power and influence that they are deemed public figures for all purposes” were accorded protection. Recently, this has been adopted in international money laundering law of PEPs or Politically Exposed Persons. It includes, “individuals who are or have been entrusted domestically with prominent public functions, for example, heads of state or of government, senior politicians, senior government, judicial or military officials, senior executives of state-owned corporations, important political party officials”.
Back in 2011, the UNHRC (United Nations Human Rights Committee) issued a declaration condemning Philippines’ provisions of criminal libel as a violation of the ICCPR. One hopes India wouldn’t require such a slap on the wrists to amend the repugnant law which rewards dishonest claims of calumny.
This article was published on May 29, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
28 May 2014 | Digital Freedom, News and features, Politics and Society, United States
Last week saw a flurry of legislative to-and-fro on the Hill as the US House of Representatives pondered the passage of legislation aimed at ending bulk-collection by the US National Security Agency. The USA Freedom Act, or HR. 3361, was passed on Thursday in a 303-121 vote, and was hailed by The New York Times as “a rare moment of bipartisan agreement between the White House and Congress on a major national security issue”. Congressman Glenn ‘GT’ Thompson (R-Pa.) tweeted that he was the proud cosponsor of a bill “that passed uniting and strengthening America by ending eavesdropping/online monitoring.”
It was perhaps inevitable that compromise between the intelligence and judiciary committees would see various blows against the bill in terms of scope and effect. When legislators want to posture about change while asserting the status quo, ambiguity proves their steadfast friend. After all, with the term “freedom” in the bill, something was bound to give.
Students of the bill would have noted that its main author, Rep. Jim Sensenbrenner (R-Wi.), was also behind HR. 3162, known more popularly as the USA Patriot Act. Most roads in the US surveillance establishment tend to lead to that roughly drafted and applied piece of legislation, a mechanism that gave the NSA the broadest, and most ineffective of mandates, in eavesdropping.
Then came salutatory remarks made about the bill from Rep. Mike Rogers[2], who extolled its virtues on the House floor even as he attacked the Obama administration for not being firm enough in holding against advocates of surveillance reform. There is a notable signature change between commending “a responsible legislative solution to address concerns about the bulk telephone metadata program” and being “held hostage by the actions of traitors who leak classified information that puts our troops in the field at risk or those who fear-monger and spread mistruth to further their misguided agenda.”
Even as Edward Snowden’s ghost hung heavy over the Hill like a moralising Banquo, Rogers was pointing a vengeful finger in his direction. There would, after all, have been no need for the USA Freedom Act, no need for this display of lawmaking, but for the actions of the intelligence sub-contractor. Privacy advocates would again raise their eyebrows at Rogers’s remarks about the now infamous Section 215 telephone metadata program under the Patriot Act, which had been “the subject of intense, and often inaccurate, criticism. The bulk telephone metadata program is legal, overseen, and effective at saving American lives.”
Such assertions are remarkable, more so for the fact that both the Privacy and Civil Liberties Oversight Board and the internal White House review panel, found little evidence of effectiveness in the program. “Section 215 of the USA Patriot Act,” claimed the PCLOB, “does not provide an adequate basis to support this program.” Any data obtained was thin and obtained at unwarranted cost.
Critics of the bill such as Centre for Democracy and Technology President Nuala O’Connor expressed concern at the chipping moves. “This legislation was designed to prohibit bulk collection, but has been made so weak that it fails to adequately protect against mass, untargeted collection of Americans’ private information.” In O’Connor’s view, “The bill now offers only mild reform and goes against the overwhelming support for definitively ending bulk collection.”
Not so, claimed an anonymous House GOP aide. “The amended bill successfully addresses the concerns that were raised about NSA surveillance, ends bulk collections and increases transparency.” Victory in small steps would seem to have impressed the aide. “We view it as a victory for privacy, and while we would like to have had a stronger bill, we shouldn’t let the perfect being the enemy of the good.”
Various members of the House disagreed. Rep. Zoe Lofgren (D-Calif.) noted that the bill had received a severe pruning by the time it reached the House floor, having a change “that seems to open the door to bulk collection again.” Others connected with co-sponsoring initial versions of the bill, among them Rep. Jared Polis (D-Colo.) and Rep. Justin Amash (R-Mich.) also refused to vote for the compromise.
What, then, is the basis of the gripe? For one, the language “specific selection term”, which would cover what the NSA can intercept, is incorrigibly vague. The definition offers the unsatisfactory “term used to uniquely describe a person, entity or account.” What, in this sense, is an entity for the purpose of the legislation? The tip of the iceberg is already problematic enough without venturing down into the murkier depths of interpretation.
Even more troubling in the USA Freedom Act is what it leaves out. For one thing, telephony metadata is only a portion of the surveillance loot. Other collection programs are conspicuously absent, be it the already exposed PRISM program which covers online communications, Captivatedaudience, a program used to attain control of a computer’s microphone and record audio, Foggybottom – used to note a user’s browsing history on the net, and Gumfish, used to control a computer webcam. (These are the choice bits – others in the NSA arsenal persist, untrammelled.)
Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Amendments (FISA) Act, the provision outlining when the NSA may collect data from American citizens in various cases and how the incorrect or inadvertent collection of data is to be handled, is left untouched. On inspection, it seems the reformist resume of the Freedom Act is rather sparse.
Ambiguities, rather than perfections, end up being the enemy of the good. Laws that are poorly drafted tend to be more than mere nuisances – they can be dangerous in cultivating complacency before the effects of power. Well as it might that the USA Freedom Act has passed, signalling a political will to deal with bulk-collection of data. But in making that signal, Congress has also made it clear that compromise is one way of doing nothing, a form of sanctified inertia.
This article was posted on May 28, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
28 May 2014 | News and features, Religion and Culture, Spain, Turkey
Last year, the exhibition Here Together Now was held at Matadero Madrid, Spain. Curated by Manuela Villa, it was realised with the support of the Turkish Embassy in Madrid, Turkish Airlines and ARCOmadrid. But in the exhibition booklet, the explanatory notes to artist İz Öztat’s work “A Selection from the Utopie Folder (Zişan, 1917-1919)” was censored upon the request of the Turkish Embassy in Madrid, and the expressions “Armenian genocide” and the date “1915” were taken out.The case shows how the Turkish state delimits artistic expression in the projects it supports, and how it silences the institutions it cooperates with.
After Turkey was chosen as the country of focus for the 2013 edition of the ARCOmadrid International Contemporary Art Fair, the designated curator Vasıf Kortun and assistant curator Lara Fresko started to work with the galleries that would join the fair. They helped in fostering connections between the Madrid arts institutions and artists in Turkey; as well as with the embassy officers in charge of the financial support of events such as Here Together Now, which would run as a parallel event to the main fair. The embassy indicated that it would support this exhibition with the generous sum of €250,000. However, it did not provide any written documentation guaranteeing this support, and outlining the mutual duties and responsibilities of the parties involved. Likewise, during the realisation of the project, there was no written communication between the embassy and Matadero Madrid, and all negotiations took place verbally, over the phone. It was in this manner that, from the very beginning, the state kept the exact conditions of its support ambiguous and created a tense situation for the organisers. Ultimately, this working practice gave the Embassy the possibility of denying the promised support, in the event that their request was not carried out.
This is not the first case of the Turkish state censoring an arts event it sponsors abroad. We frequently hear about such cases off the record, and at times through the media. One of the best-known cases of state intervention took place in Switzerland, during the 2007 Culturespaces Festival. Director Hüseyin Karabey’s film Gitmek – My Marlon and Brando, which had received support from the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism, was taken out of the festival program at the very last minute, at the request of an officer from the General Directorate of Promotion Fund, on the pretext that “a Turkish girl cannot fall in love with a Kurdish boy” as was the case in the film. The officer threatened the festival organisers with withdrawal of sponsorship totaling €400,000 — much like the case of the Madrid exhibition. The festival director decided that they could not go ahead with the event without this support, ceded to the censorship request, and accepted to take the film out of the program. However, independent movie theaters in Switzerland criticised this decision and ended up screening the film independently of the festival.
Both examples show that the state controls the content of the projects it sponsors abroad, interferes with the organisations on arbitrary grounds, and violates artists’ rights by threatening the very institutions it collaborates with.
The administrative channel for the state’s support to events outside of Turkey is the Ministry of Culture and Tourism’s Promotion Fund Committee, established under law 3230 (10 June, 1985) with the aim of supporting activities that “promote Turkey’s history, language, culture and arts, touristic values and natural riches”. The Committee reports directly to the Prime Minister’s office, and is presided over either by the Prime Minister himself, the Vice Prime Minister or a minister designated by the PM. It has five more members: Deputy Undersecretaries from the Prime Minister’s Office, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, as well as the general managers of the Directorate General of Press and Information, and the Turkish Radio and Television Corporation (TRT). The objective of the fund is “to provide financial support to agencies set up to promote various aspects of Turkey domestically and overseas, to disseminate Turkish cultural heritage, to influence the international public opinion in the direction of our national interests, to support efforts of public diplomacy, and to render the state archive service more effective”.
The Committee convenes at least four times a year upon the invitation of its president to evaluate project applications. The only criterion in accepting a project is whether it complies with the objectives mentioned above. After the Committee carries out its evaluation, the projects are put into practice upon the approval of the PM. Representative offices of the Promotion Fund Committee monitor whether the projects are implemented in compliance with the principles of the fund. In the case of the Madrid exhibition, the Turkish Embassy assumed the role of representative office. In this respect, as per the relevant regulation, the embassy was in charge of controlling the project, signing protocols with project managers to outline mutual duties and responsibilities, making the necessary payments, and delivering the project report to the Committee. As such, the embassy’s avoidance of all written documentation is in breach of the principles and modus operandi established by its own regulations.
Overall, it can be said that the Promotion Fund Committee does not meet the criteria of transparency and accountability generally expected from a public agency. The dates when the committee convenes to evaluate the projects are not announced, and the committee members, annual budget, sponsorship priorities and selection criteria are not made public. The sums paid to projects sponsored and the content of the projects are not disclosed officially. In other words, there is no transparency about the distribution of the funds, or about the auditing procedures. Such structural problems make it even harder to reveal and question the state’s violation of the right to artistic expression.
Another important aspect of this case is that the state constantly tries to reproduce its dominant discourse based on the denial of past and ongoing human rights violations such as forced displacement, genocide, political murders, burning of villages, enforced disappearances, rape, and torture through security forces; and does its utmost to silence any expression which contests this discourse. The centenary of the Armenian genocide, 2015, is drawing near. As such, it becomes even more important to demand that the Turkish state be held accountable for this human rights violation.
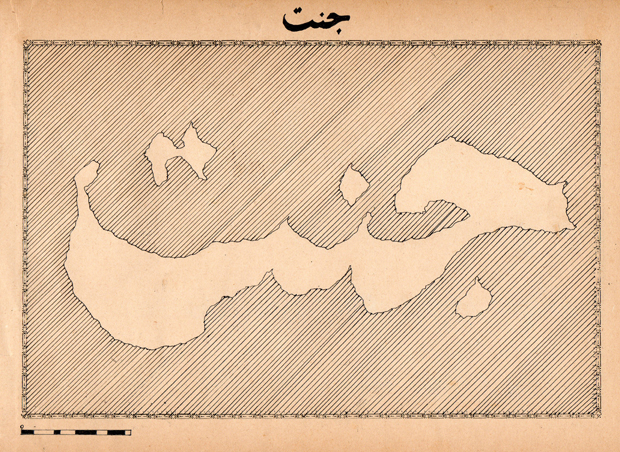
Map of Cennet/Cinnet (Paradise/Possessed Island). Zişan, 1915-1917. Ink on paper, 20×27 cm. Dedicated to the Public Domain
Siyah Bant is a research platform that documents and reports on cases of censorship in arts across Turkey, and shares these with the local and international public. In the context of this work, we wanted to investigate the censorship that occurred at Here Together Now. In accordance with the Right to Information Act, we asked the Turkish Embassy in Madrid and the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, to explain the legal basis of the censorship they imposed on the booklet. In response, the Ministry of Culture and Tourism indicated that Matadero Madrid and curator Manuela Villa were the only authorities in charge of selecting the artists who would participate in the workshops of ARCOmadrid, designating the content of the works to be produced during the workshops, and preparing all printed matter in connection to the event. We were unable to obtain an official statement from curator Manuela Villa, despite several inquiries. Finally, we conducted an interview the artist İz Öztat to understand how the censorship took place, and how she experienced the process.
How did you come to be involved in the exhibition?
I was invited by Manuela Villa, curator of Matadero Madrid, after meeting her in Istanbul. Matadero planned for a residency program and an exhibition project titled Here Together Now to take place concurrently with the 2013 edition of the ARCOmadrid Art Fair that had a section consisting of invited galleries from Turkey. By the time I signed the contract with Matadero Madrid, I knew that the project was partially supported by the Turkish Embassy in Madrid and Turkish Airlines.
Here Together Now was a process that allocated the resources with an emphasis on living and working together. Cristina Anglada (writer), Theo Firmo, Sibel Horada, HUSOS (a collective of architects), Pedagogias Invisibles (art mediation collective), Diego del Pozo Barrius, Dilek Winchester and I had six weeks together, during which we figured out common concerns, negotiated our relationship to the institution’s public, designed the working and exhibition space, collaborated and produced our works.
Can you tell us about the nature of contract with the institution and if there were any limitations indicated as to the nature of your work?
We signed a very detailed contract with Matadero Madrid that laid out the responsibilities of the institution and the artist in relation to the production and authorship of new work but there were no limitations outlined in the contract. I took it for granted that the artist has freedom of expression and institutions do not interfere in the produced content.
The institution was extremely supportive of the project. They were engaged in our discussions and ready to help once we started producing the work.
Could you talk a bit about the work that you prepared for Matadero Madrid?
The work shown in the Here Together Now exhibition was part of an ongoing process, in which I imagine ways to conjure a suppressed past. Since 2010, I have been engaged in an untimely collaboration with Zişan (1894-1970), who is a recently discovered historical figure, a channeled spirit and an alter ego. By inventing an anarchic lineage with a marginalized Ottoman woman, I try to recognize a haunting past and rework it to be able to imagine otherwise. For the exhibition at Matadero Madrid, I produced and exhibited “A Selection from Zişan’s Utopie Folder (1917-1919)” accompanied by works from the “Posthumous Production Series”, in which I depart from Zişan’s work to open a path towards the future in our collaboration. The exhibited work was complemented by a publication with three interviews, which situates the work and builds a discourse around it.
Which aspect of the work was censored? How did the process of censorship occur, and what kind of dilemmas did you face in this process?
Manuela Villa, the curator, met with me in the exhibition space one evening a few days prior to the opening. Officials from the Turkish Embassy had threatened to withdraw their financial support, if the demanded changes were not made. I had to make a decision on the spot and accepted the censorship in the booklet, but not in the publication complementing the work. The exhibition booklet was reprinted and the sentence was changed to “Zişan, born in Istanbul in 1894, is a marginal woman of Armenian descent, who embarks on a European quest.”
As I said before, there was an emphasis on the community we built together during the residency at Matadero and I didn’t want to make a decision alone that would put the whole project at risk. Because of the time constraints, we were only able to meet with the other artists after the opening to discuss the precarious condition that we were all in. The institution didn’t have any signed documents from the Embassy committing to the sponsorship. Everything was communicated verbally and there was no written documentation. I was not able to reach out for a support network to resist the situation, not least due to the immediacy the decision required.
The exhibition booklet that was presented to the embassy was altered but the publication accompanying your work remained unchanged. How did the curator and other artists react to your refusal to change the publication?
I could not stand my ground with regard the exhibition booklet because it concerned everybody in the project. Yet, I was able to take full responsibility of my own work. We were informed that officials from the embassy will visit the show prior to the opening and I was ready to withdraw the work, if there was any interference. Everybody was supportive of my decision.
What happened on the day of the opening? Did you feel the need to prepare yourself?
In the end, none of the officials from the embassy came to the opening or the exhibition. There was no confrontation regarding the work. There might be a few reasons for this that I can think of. Maybe, they felt entitled to interfere with the content of the exhibition booklet because it had the logo of the embassy and could dismiss my publication since it only had the logo of Matadero Madrid. It was not of benefit for the embassy to confront me in a situation that would have made the case public.
As Siyah Bant we inquired both with the curator and the Ministry of Culture and Tourism in order to understand how this censoring motion played out. Given that the ministry rejects any responsibility and instead assigns all responsibility to the curator, and that the curator was acting under the duress of loosing all funding last minute, where does this leave you as the artist? How do you make sense of what happened to your work?
Since I accepted the censorship, my only option was making the situation public after the fact. I have been working in cooperation with Siyah Bant since I got back from Madrid. It took a few months to receive an official response from the embassy, which denied all responsibility. We wanted to make the case public after receiving a statement from the curator or the institution. I was unable to receive such a statement, and Siyah Bant is working on that now.
I see it as an experience, in which I was able to test and see the boundaries of government support that is allocated to arts and culture for promoting the country. If you decide to accept this support and challenge official policies, a system of censorship starts to operate.
Next year marks the centenary of the Armenian genocide which will inevitably bring about numerous artistic and cultural reflections on the subject. Given the current climate in Turkey, how confident are you that artistic freedom of expression will be respected?
We are going through a period, in which it is impossible to make predictions about what can happen even the next day. I can only hope that genocide denial at state level comes to an end. I am sure that artists will articulate their own ways of recognising the Armenian Genocide and confronting its denial. You are probably more prepared than I am to predict and know what kinds of mechanisms are at work to limit the production and dissemination of such work.
What would be your recommendations to other artists taking part in cultural events that are supported by the Turkish government?
Based on my experience, I think that artists and art institutions need to act in solidarity in these situations. If there is funding from the Turkish state, the institutions and artists involved need to be aware that the state monitors the content. The various institutions that distribute state funding do not provide written documents about their commitments and communicate their demands mostly in person or by phone. Demanding written documentation at every step is necessary. Artists who are considering to take parts in projects that receive state funding, can demand from the art institutions to be more transparent about the budget and its workings so that they can be prepared to make alternative plans if the state funding does not come through as promised.
If I encountered the same case of censorship now, I would not feel obliged to make a decision immediately and in isolation. I would consult the rest of the group and demand the involvement of the institution.
This article was posted on May 28 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
27 May 2014 | About Index, Campaigns, European Union, Press Releases
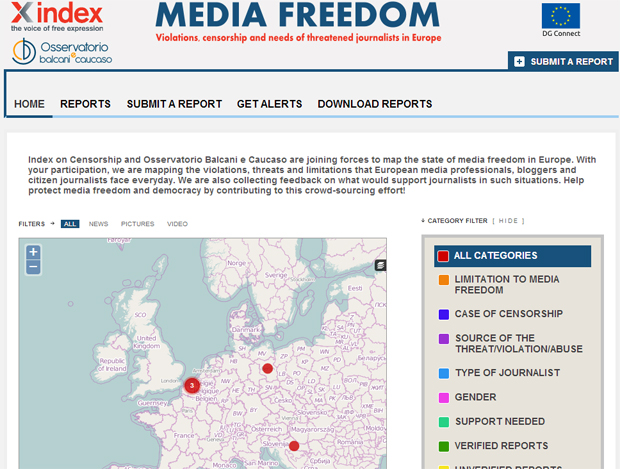
Index on Censorship and Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso are launching mediafreedom.ushahidi.com to track media violations in Europe.
Index on Censorship, (London, United Kingdom) and Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso, (Rovereto, Italy) have launched mediafreedom.ushahidi.com, a website that will enable the reporting and mapping of media freedom violations across the 28 EU countries plus candidate countries. The platform will collect and map out crowd-sourced information from media professionals and citizen journalists across Europe over the course of a year.
Based in London, Index on Censorship is an international organisation that promotes and defends the right to freedom of expression. Since its founding in 1972, Index has used a unique combination of journalism, campaigning and advocacy to defend freedom of expression for those facing censorship and repression, including journalists, writers, social media users, bloggers, artists, politicians, scientists, academics, activists and citizens.
“Index believes that free expression is the foundation of a free society and this website will enable journalists to report incidences of violations as soon as they happen. By mapping these reports online, the entire system will act as an advocacy, research and response tool, highlighting that violations on media freedom still occur in Europe.” explained Melody Patry, Index on Censorship senior advocacy officer.
Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso (OBC) has been reporting on the socio-political and cultural developments of South-East Europe since 2000. Through the online platform, OBC will monitor and document media freedom violations in 11 countries, among which Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Romania, Serbia and others, and collect the needs of journalists under threat.
“We aim at improving the working conditions of media professionals and citizen journalists in Italy, South-East Europe and Turkey and ultimately at enhancing the quality of European democracy,” said Luisa Chiodi, scientific director of OBC.
This new website is part of a European Commission grant project under the EU’s Digital Agenda (DG Connect). In light of remaining violations to media freedom and plurality in Europe, and longer-term challenges in the digital age, the DG Connect launched a call for proposals to address the issue.
The successful candidates- the International Press Institute, Index on Censorship, Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso together with SEEMO, Ossigeno per l’Informazione and Dr Siapera, as well as the European University Institute in cooperation with the Central European University– will spend the next year working on four projects, under the title European Centre for Press and Media Freedom.
For more information on the projects and the website, please read EU project to explore media freedom and pluralism or contact Melody Patry, [email protected], +44 (0) 207 260 2671 or OBC, [email protected].






