Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
Index on Censorship recently appointed a new youth advisory board who attend monthly online meetings to discuss current freedom of expression issues and complete related tasks. As their first assignments they were asked to provide a short bio to introduce themselves, along with a photograph of them holding a quotation highlighting what free expression means to them.
Simon Engelkes 
I am from Berlin, Germany, where I study political science at Free University Berlin. I have worked as an intern with Reporters Without Borders and RTL Television, which made me passionate about the importance of freedom of speech.
I believe that freedom of expression forms an important cornerstone of any effective democracy. Journalists and bloggers must live without fear and without interference from state or economic interests. Unfortunately, this is not the case. Journalists, authors and everyday citizens are imprisoned or killed by radicals, state agencies or drug cartels. Raif Badawi, James Foley, Khadija Ismayilova, Avijit Roy – the list is endless.
We need to remind ourselves and the powerful of today, that freedom of expression as well as freedom of information are basic human rights, which we have to defend at all costs.
 Mariana Cunha e Melo
Mariana Cunha e Melo
I am from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. I graduated from law school in Rio and I have a degree from New York University School of Law. My family has taught me about the dangers of censorship and dictatorship, so I have always been interested in studying civil rights. This was the main reason I decided to study law.
I grew up listening to stories about the media censorship in Brazil during the military dictatorship. The fight against the ghost of state censorship has always sounded very natural to me – and, I believe, to all my generation. When I finished law school I found out that the new villain my generation has to face is the censorship based on constitutional values. The argument has changed, but the censorship is not all that different. So I decided to dedicate my academic and my professional life as a lawyer to fight all sorts of institutionalised censorship in Brazil.
 Ephraim Kenyanito
Ephraim Kenyanito
I was born and raised in Kenya, and I am currently working as the sub-Saharan Africa policy analyst at Access Now, an international organisation that defends and extends the digital rights of users at risk around the world. My role involves working on the connection between internet policy and human rights in African Union member countries. I am an affiliate at the Internet Policy Observatory (IPO) at the Center for Global Communication Studies, University of Pennsylvania. I also currently serve as a member of the UN Secretary General’s Multi-stakeholder Advisory Group on internet governance.
The reason why I have always been passionate about protecting the open internet is that it is a cornerstone for advancing free speech in the post-millennium era and there is a great need to build common ground around a public interest-oriented approach to internet governance.
Emily Wright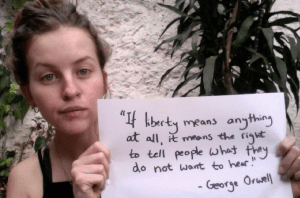
I grew up in Portugal, and I am now based between London and Bogotá, Colombia. I am a freelance filmmaker and journalist. Working in documentary production and community-based, participatory journalism informed a growing interest in journalistic practices, freedom of expression and access to information.
I believe that one of the greatest threats to freedom of expression is the flagrant violation of civil liberties under the banner of national security. The war on terror, underscored by Bush’s declaration “You’re either for us or against us”, has collapsed the middle ground, suppressing any struggles that challenge that statement. Freedom of expression has become a pretext for silencing those who have the least access to it; those who do not fall in line with the global order’s supposed defence of freedom against barbarism and obscurantism.
 Mark Crawford
Mark Crawford
I’m originally from Birmingham, and now a postgraduate student at University College London, specialising in Russian and post-Soviet politics. This has inevitably educated me on the pressures exerted upon freedom of expression in Russia, whose suffocated and disenfranchised opposition journalists I am currently investigating.
Hostility to free expression has become a staple of my university life. Rather than developing a coherent set of ideologies to challenge toxic values in the open, it has become mainstream for students of the most privileged universities in the world to veto them on behalf of everyone else, no-platforming and deriding free speech.
I am convinced that there is no point fighting for an egalitarian society if any monopolies over truth are permitted. Freedom of speech is, therefore, something I am keen to promote in whatever small way I can.
Madeleine Stone 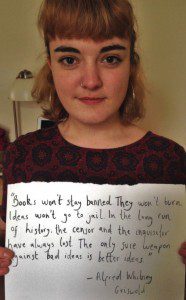
My home is in south-east London but I spend most of my time in York, studying for my bachelor’s degree in English and related literature. I am currently the co-chair of York PEN, the University of York’s branch of English PEN, and a founding member of the Antione Collective, a human rights-focused theatre company.
Studying literature from across the globe has introduced me to issues of freedom and censorship, and the devastating effects censorship can have on national progress. Freedom of expression on campuses is hugely important to me as a student and it is currently under threat. Well-meaning individuals are shutting down the open debate that is vital to academic institutions. The only way to fight harmful ideas is to engage them head-on and destroy them through academic debate, not to ban them.
Layli Foroudi 
I am a journalist and student currently studying for a MPhil in race, ethnicity and conflict at Trinity College Dublin. It was studying literary works from the Soviet period during my undergraduate degree in Russian and French at University College London that initially highlighted the issue of censorship for me. The quote I selected, “manuscripts don’t burn”, is from the book Master and Margarita by Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov. He wrote about the hardship that many writers faced as they had to adjust their own writing in accordance with the authority, as well as the fact that not all that is written can be taken to be true.
I think that these themes are very relevant today. Whether people are censored or self-censor out of fear of punishment or of being wrong, limiting freedom of expression results in loss of debate, of exchange and of creativity. Being denied freedom of expression is being denied the right to participation in society.
 Ian Morse
Ian Morse
I have been involved in journalism since I began studying at Lafayette College, Pennsylvania, USA, and have been engaged in press freedom and reporting in three countries since then. I studied in Turkey last spring, where I interviewed and wrote about journalists and press freedom. It motivated me to begin researching and writing on my own about these topics. Now, as I study for a semester in Cambridge in the UK, I continue to talk about and advocate for free speech and press.
I find it absolutely amazing the power words and information can have in a society. It becomes then extremely damaging to realise that some things cannot be published because they conflict with those in power. Free speech is now becoming a hot topic around the world, particularly among youth, and it makes it all the more important to be able to approach freedom of expression critically and objectively.

Seymur Hezi was sentenced to five years in prison for “aggravated hooliganism” on 29 January 2015.
On the anniversary of Azerbaijani journalist Seymur Hezi’s sentencing to five years imprisonment for “aggravated hooliganism,” the country’s authorities have continued to target journalists, independent media and human rights activists.
Hezi, who contributed to the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award-winning newspaper Azadliq, was sentenced on 29 January 2015. He was arrested on 29 August 2014 following an altercation in which the journalist was defending himself from a physical assault and harassment, according to his lawyers.
Rahim Haciyev, acting editor of Azadliq, told Index in September 2015 Hezi’s prosecution was due to his critical articles of the Azerbaijan authorities in the newspaper, as well as critiques he had made in his online TV programme, Azerbaijan Hour.
Haciyev said Hezi’s health is “very bad” due to the Azerbaijan’s awful prison conditions. Despite this, he said the journalist is working on articles about the country’s recent political history — some of which have been published in Azadliq.
In Hezi’s final statement given during his trial, he noted his belief in the shared struggle “with my dear friends at prison”. He also said: “It is not just a confrontation between the government and the opposition. It is the struggle between the good and the evil.”
After a year activism and journalism dedicated to free expression within the restricting country, not much positive change can be seen. Investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova remains in jail, doing everything in her power to continue spreading the message of truth and resistance. Human rights lawyer Amal Clooney recently offered to take Ismayilova’s case to the European Court of Human Rights.
Azadliq, which was one of Azerbaijan’s only remaining independent news outlets operating inside the country, was forced to discontinue publishing a daily print edition of the newspaper in July 2014, due to its financial situation. The paper was hit with enormous fines following multiple defamation suits in 2013, and its journalists — including Hezi — have been targeted by authorities with politically motivated charges.
“The repression and detainment of journalists are continuing,” Haciyev said. “[The] government has started to arrest Facebook activists.”
Haciyev said that because the government cannot solve its country’s main problems, they try to create new problems for society through eliminating any chance of other opinions being promoted.

Khadija Ismayilova
On the eve of the anniversary of the arrest of journalist Khadija Ismayilova, members of the Sport for Rights coalition and the Civic Solidarity Platform underscore the unprecedented nature of the repression that has taken place in Azerbaijan in the year that has passed. The groups reiterate their call for the immediate and unconditional release of Ismayilova and Azerbaijan’s other political prisoners, and for the international community to take steps to hold the Azerbaijani government accountable for its human rights obligations as matter of urgent priority.
“Ismayilova’s arrest a year ago signalled an escalation of repression in Azerbaijan”, noted Karin Deutsch Karlekar, Director of Free Expression Programs at PEN American Center. “Independent voices are being silenced at an unprecedented rate, and we urge the authorities to cease the legal and extra-legal harassment of journalists and media outlets immediately”.
On 5 December 2014, prominent investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova was arrested on charges of inciting a local man, Tural Mustafayev, to attempt suicide. Two months later, authorities slammed her with additional politicised charges of embezzlement, illegal business, tax evasion, and abuse of power. After eight months in pre-trial detention, Ismayilova’s trial started on 7 August at the Baku Court of Grave Crimes.
Ismayilova referred to the proceedings as an “express trial”, and observers noted it was rife with due process violations, with the judges rarely granting any motions made by the defence. During the trial, Mustafayev publicly told the court that prosecutors forced him to make a statement against Ismayilova, and withdrew his accusations. Additionally, Ismayilova’s lawyer told the court that her employer did not report any funds missing, that she was not authorised to hire or dismiss other journalists, and that she was not engaged in any commercial enterprise.
On 1 September, the court convicted Ismayilova of the charges of embezzlement, illegal entrepreneurship, tax evasion, and abuse of office, and sentenced her to 7.5 years’ imprisonment. She was acquitted of the charge of inciting Mustafayev to attempt suicide. On 25 November, the Baku Court of Appeals upheld this conviction, and Ismayilova was transferred to Prison Number 4 on 27 November.
Sport for Rights considers the charges against Ismayilova to be politically motivated and connected to her work as an investigative journalist, particularly her exposure of corruption among the ruling elite. Sport for Rights believes that in jailing Ismayilova, the Azerbaijani authorities sought to silence her critical voice before the country faced increased international media attention during the inaugural European Games, which took place in Baku in June. For this reason, Sport for Rights has referred to Ismayilova as a “Prisoner of the Games”.
“Ismayilova’s imprisonment is emblematic of the Azerbaijani authorities’ repression of independent journalists and human rights defenders”, said Melody Patry, Senior Advocacy Officer at Index on Censorship. “Every day Ismayilova and the other political prisoners spend in jail is another reminder to the world that the Azerbaijani government fails to respect and protect the democratic principles and fundamental rights it has committed to upholding”.
Ismayilova is one of dozens of political prisoners in Azerbaijan. Other prominent cases include journalists Nijat Aliyev, Araz Guliyev, Parviz Hashimli, Seymur Hezi, Hilal Mammadov, Rauf Mirkadirov, and Tofig Yagublu; bloggers Abdul Abilov, Faraj Karimli, Omar Mammadov, Rashad Ramazanov, and Ilkin Rustamzade; human rights defenders Intigam Aliyev, Rasul Jafarov, Taleh Khasmammadov, Anar Mammadli, Arif Yunus, and Leyla Yunus; NIDA civic movement activists Rashadat Akundov, Mammad Azizov, and Rashad Hasanov; opposition activist Yadigar Sadikhov; and opposition REAL movement chairman Ilgar Mammadov.
Besides politically motivated arrests and imprisonment, the Azerbaijani authorities continue to employ a wide range of tactics as part of an aggressive crackdown to silence the country’s few remaining critical voices. Independent online television station Meydan TV has been a particular target, with its staff and their relatives threatened, detained, and otherwise pressured in connection with Meydan TV’s critical news coverage of Azerbaijan. Other independent NGOs and media including the Institute for Reporters’ Freedom and Safety and its online television project Obyektiv TV, as well as Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty’s Baku office, have also been aggressively targeted over the past year.
In addition to the post-European Games crackdown, the Azerbaijani authorities also worked to silence criticism ahead of the 1 November parliamentary elections. For the first time, the elections took place with almost no credible international observers, and with the majority of the traditional opposition boycotting. Independent domestic observers reported widespread fraud, such as carousel voting and irregularities in the vote counting and tabulation process. Now, in the run-up to the Formula One European Grand Prix, which will take place in Baku in June 2016, the crackdown shows no signs of relenting.
These issues and more are detailed in a new Sport for Rights report, No Holds Barred: Azerbaijan’s Human Rights Crackdown in Aliyev’s Third Term, which also contains specific recommendations to the Azerbaijani authorities and the international community on urgent measures needed to improve the dire human rights situation in the country. Sport for Rights and the Civic Solidarity Platform particularly urge the international community to sustain focus on Azerbaijan over the coming months, when critical voices will need concrete support more than ever before.
Supporting organisations:
ARTICLE 19
Association of Ukrainian Human Rights Monitors on Law Enforcement
Canadian Journalists for Free Expression
Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
Centre for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights (Russia)
Civil Rights Defenders
Committee to Protect Journalists
Crude Accountability
Freedom Now
Front Line Defenders
Georgian Young Lawyers’ Association
Golos Svobody Public Foundation (Kyrgyzstan)
Human Rights House Foundation
Human Rights Movement “Bir Duino-Kyrgyzstan”
Index on Censorship
Institute for Reporters’ Freedom and Safety
International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH), within the framework of the
Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
International Partnership for Human Rights
Kazakhstan International Bureau for Human Rights and Rule of Law
Kharkiv Regional Foundation – Public Alternative (Ukraine)
Kosova Rehabilitation Centre for Torture Victims
Norwegian Helsinki Committee
PEN American Center
People In Need
Platform
Promo-LEX (Moldova)
Public Verdict Foundation (Russia)
Reporters Without Borders
Sova Center for Information and Analysis (Russia)
World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT), within the framework of the
Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders

November is a month of historical anniversaries. Last Thursday was the annual commemoration of the foiling of the Gunpowder Plot and yesterday the UK fell silent to pay tribute to its war dead on Remembrance Sunday.
A much lesser-known date — at least to anyone outside Azerbaijan — is the country’s Flag Day, the celebration of the tricolour which was first adopted as the national flag on 9 November 1918.
The flag hoisted in the capital city of Baku was once confirmed by the Guinness Book of Records as being the tallest in the world. It flies on a pole 162 meters high and measures 70 by 35 meters. While the flag underwent a hiatus while Azerbaijan was part of the Soviet Union between 1920 and 1991, it is now a proud symbol of the country’s independence.
The tricolour consists of three horizontal stripes, each being deeply symbolic. The blue stripe stands for the Turkish origin of Azerbaijani people and the green stripe at the bottom expresses affiliation to Islam. Neither can be disputed. The red stripe in the middle, however, is problematic. It stands for progress, modernisation and democracy.
But Azerbaijan’s status as a modern democracy is less than convincing. Sure, the country has made some significant strides since the collapse of communism. It boasts a 98.8% literacy rate, and since the early 2000s spending on education has increased five-fold, for example.
However, there is an illusion of material progress in Azerbaijan. As Index on Censorship has been reporting, the country has experienced an unprecedented crackdown on human rights and freedoms.
Little over a week ago, Azerbaijan held a parliamentary election while an estimated 20 prisoners of conscience sat in prison. Azerbaijani journalist Khadija Ismayilova, who was sentenced to seven years and six months in jail in September for exposing state corruption, is one of them. The award-winning journalist was detained on 5 December 2014 and eventually convicted of libel, tax evasion and illegal business activity.
President Ilham Aliyev’s government has long claimed that “all freedoms are guaranteed in Azerbaijan“. Given his government’s lack tolerance for dissent, this clearly isn’t the case. Leyla Yunus, founder and director of the Institute for Peace and Democracy, and her husband, historian Arif Yunus — both outspoken critics of the government — have been detained since summer 2014 when they were arrested on charges of treason and fraud. On 13 August, the Baku Court on Grave Crimes sentenced Leyla to eight years and six months in prison and Arif to seven years in prison.
Democracy activist Rasul Jafarov, human rights lawyer Intigam Aliyev and journalist Seymur Hezi are also serving prison sentences on charges that were widely condemned for being politically motivated to silence outspoken critics of the government of President Aliyev.
The list of journalists and activists who have been arrested, abused, beaten and even killed goes on. In June 2015, on the eve of the inaugural European Games in Baku, activists from Amnesty International and Platform were banned from entering the country. Both organisations have been highly critical of Aliyev’s government, and its continuing targeting, jailing and prosecution dissenters. Even The Guardian was blocked from reporting on the games when its reporter was barred.
The ruling party in Azerbaijan may have won an outright majority in this month’s elections, cementing Aliyev’s hold on power. However, opposition parties boycotted the vote over concerns it was neither free nor fair. Even the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) refused to monitor the election after authorities severely limited its ability to observe the vote effectively. It marks the first time since 1991 that the OSCE has not monitored an Azerbaijani election and highlights that the situation in the country is far from progressive.
Flag Day is set against a backdrop of arrests and human rights abuses. If Azerbaijan is to earn its stripes, the authorities must uphold their human rights obligations, release all prisoners of conscience and allow for elections that meet basic democratic standards.
This article was posted on 9 November 2015 at indexoncensorship.org