7 May 2014 | Asia and Pacific, China, News
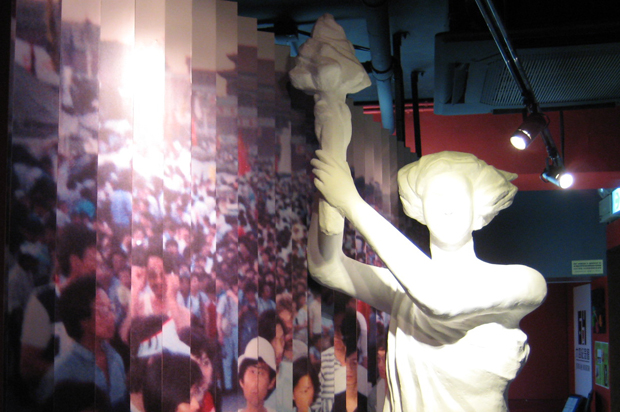

(Photo: Hannah Leung)
The world’s first museum dedicated to the 1989 pro-democracy protests in Beijing’s Tiananmen Square opened in Hong Kong last Saturday to mark the 25 year anniversary. Named the June 4 Memorial Museum, it hopes to educate the millions of mainland tourists who visit Hong Kong each year.
The violent suppression of student protests in Tiananmen Square remains a taboo topic in mainland China, banned from official discourse. Beijing considers the weeks of peaceful protest by students and workers a “counter-revolutionary” revolt and defends its decision to send in the army. To this day no official numbers of the death toll have been released and many young Chinese in particular are unaware of its occurrence.
Index visited the museum a few days after its launch. Located in the busy district of Tsim Sha Tsui, the bustling side streets of Hong Kong’s main Korean centre, the museum sits on the fifth floor of a commercial building. Inconspicuously sandwiched in the throngs of bars and Korean fried chicken joints, discretion is key. It’s easy to walk past the museum if you don’t know what you are looking for and signs of its existence are only given at the floor directory located by the elevator.
A curator at the museum tells Index that since its opening the museum has received around 300 visitors per day, with an even split between mainlanders and Hong Kong residents. At the time of our visit, there were mostly Hong Kong residents in attendance, with a sprinkling of mainland visitors. It’s also packed. Despite being a normal weekday and an hour before closing time, a queue weaves out the door. The sense of eagerness to discover something is palpable amongst the patrons.
The space is modest – 800 square feet in total – with both people and information meticulously squeezed in. School children browse through books and pamphlets found on a bookshelf. Some pose for pictures with a Goddess of Democracy statue located by the entrance. The statue is a replica of one created by the protesters in the days before the crackdown.
Copies of newspaper clippings, photos, videos and an interactive feature on the configuration of the protestors at Tiananmen Square, which went on for a month, are all on display. The centrepiece is a video of the Tiananmen Mothers, a group of activists personally affected by the protests, some of whom lost children or relatives in the crackdown. Testimonies given in the clips go through the agony of losing a university-aged child, and the subsequent upset of being forced to lie about the way their children died. They have been forbidden by the government, then and now, to reveal the truth.
One young woman, a tourist from mainland China, is visibly in tears as she watches the documentary. Others are less moved and some attendees have criticised the museum for not being sombre enough. A couple, also from the mainland, fiddle with the interactive feature found in the centre of the museum before the man, seemingly bored, says he wants to leave.
That visitors are here however, is a feat in and of itself. While free speech is protected in Hong Kong in theory under the One Country Two Systems agreement, closer ties to the Chinese mainland in recent years have led to incursions on free speech, as Index recently reported. In the weeks leading up to the museum’s unveiling many were sceptical about whether it would open at all. Occupants of the same building called for its closure, citing safety concerns. The museum’s backers believe Communist Party officials were behind these efforts. In another incident, Yang Jianli, a US-based activist who participated in the protests in 1989, was refused entry to Hong Kong to attend the opening ceremony. The launch was greeted by more protests from pro-China demonstrators.
Over in a small area by the exit, memorabilia is sold. USB memory drives are also available upon enquiry containing information and images related to the killings. Museum founders hope visitors will smuggle these over the border into mainland China, and in so doing force the Communist government to admit its crimes. They might be an overly optimistic aim, but at least the June 4 museum is confronting China’s recent past in an honest, open way.
This article was published on May 7, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
2 May 2014 | China, News, Religion and Culture, United States
Chinese fans of American TV have been dealt a serious blow after some of their favorite shows were removed from the country’s main video streaming websites. On Saturday, The Big Bang Theory, The Good Wife, NCIS and The Practice all disappeared from the sites of Sohu TV, iQiyi and Youku. Immediately after, fans took to online forums to voice their disapproval. Netizens lashed out at the government, referring to China as “West North Korea,” a phrase that was quickly blocked from online searches.
No one knows exactly why the government has ordered the shows offline. Others, such as House of Cards and Breaking Bad, both of which have gained huge followings in China and present darker material, remain unscathed. Speculating in the state-controlled newspaper Global Times, leading film critic Tan Fei argued that “the machetes the monitoring departments waved to the U.S. dramas are not only aimed at protecting teenagers’ physical and mental health but, on a deeper level, are aimed at protecting our weak domestic film industry.”
Of Fei’s last point, it’s worth noting that until recently, the main video providers have been free to broadcast shows without the hurdle of obtaining official approval. China’s TV stations, by contrast, are heavily restricted when it comes to content. Poorly acted soap operas and over-the-top dramas about corrupt emperors and the Sino-Japanese War are the mainstay of these channels. As a result, viewers have fled to the more free and entertaining realms of online TV.
In order to lure people back, state-owned television channels have started to broadcast some of the same shows as Chinese streaming platforms, albeit censored versions. China’s national TV broadcaster CCTV will soon air The Big Bang Theory and has recently introduced a dubbed version of Game of Thrones to its paid channel.
Li Bingwen, who has worked for Chinese state media and is now at a western publication, watches a range of popular US shows, including the ones that have been removed. For Li, who tells Index that Chinese TV shows make him “doze off”, the latest government move is “cynical.”
“Forcing video web sites like Youku.com to remove The Big Bang Theory from their play lists is the most cynical act by Chinese censors ever. Banning speech for ideological reasons is evil but understandable. Taking a show off the site of a private company just so a state-owned broadcaster can air it is the new height of hypocrisy.”
Commerce doesn’t explain the move entirely though. The development comes as the government is tightening control of all areas online, particular the areas that attract the most attention, which these shows do.
“There’s been a tendency for the government to treat different forms of communication differently when it comes to censorship, being most restrictive about the media that reach the broadest spectrum of people,” explained Jeffrey Wasserstrom, a prominent academic and author of China in the 21st Century: What Everyone Needs To Know.
“The internet was seen for a time as having less broad a reach than film and television, so you were given more latitude for what you said online as opposed to in a television show. Now, of course, streaming content and growing numbers of people who go online regularly blurs that distinction,” he added.
While people of all ages within China watch these shows, it is the youth who tune in the most, and are therefore the most affected. On top of making up the biggest proportion of online users, the under-30 demographic are particularly drawn to the themes of the shows, and disillusioned by those themes presented on Chinese TV. For example, the story of science geeks trying to find their way in the world post graduation, as is illustrated in The Big Bang Theory, resonates with millions of young Chinese. With the job market in China becoming fiercely competitive and living costs soaring across major cities, graduates are now finding their dreams scuppered, much like the characters of this show.
Today’s Chinese youth also see US and UK shows as windows to foreign cultures, and more importantly, as exercises in English. For many of these people then, who might be politically apathetic, or at least profess to be so, the recent attack will be a first direct taste of censorship.
“Moves like this, which limit access to works of western popular culture, are particularly significant for Chinese youth,” Wasserstrom said.
“When people in China go online, as when people in other places do this, they often do so in search not of news but of entertainment and other kinds of non-political things, such as information about restaurants. Being suddenly unable to access a favorite television show is both annoying and a reminder of the prevalence of the government’s ability to exert control over many different aspects of life, when it wants to.”
The battle is not over yet. In the wake of the ban, people have started exploring alternative methods to access the shows. Committed viewers like Li can still gain access to the programmes. Li is boycotting CCTV and says he will explore unsanctioned methods to access the shows.
“If you are really serious, you can find them, maybe on someone’s virtual hard drive that they make accessible to everyone. A friend for example goes to a place to download tons of shows shortly after they air in the US. He is very discreet about that place and he is helping me now.”
Less tech savvy fans will have to await the airing of The Big Bang Theory on Chinese TV and hope it’s not too sanitised. Wang Meimei, another fervent Big Bang fan who Index spoke to, says she’s not holding her breath. She’ll tune in anyway.
“I want to see how much they will ruin a good drama,” explains the 26-year-old curtly.
This article was published on May 2, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
2 Apr 2014 | Asia and Pacific, News, North Korea
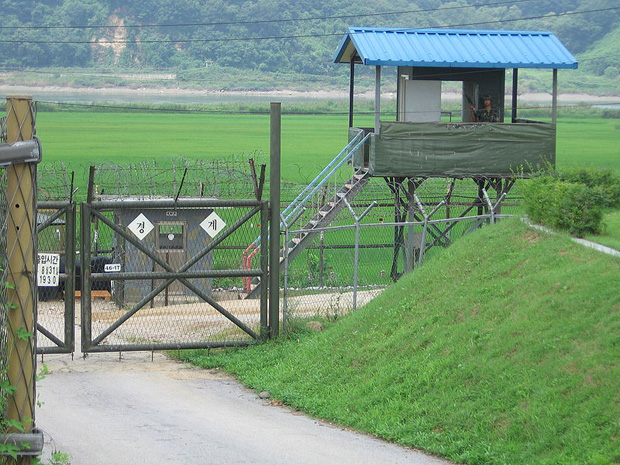

A view into South Korea from North Korea (Image: Johannes Barre/iGEL/Wikimedia Commons)
North Korea hit global headlines again last week. This was in part because of the UN resolution condemning the catastrophic, ongoing abuses against its people, in the wake of a 400-page report chronicling the country’s countless human rights violations. However, as much attention, if not more, was devoted to the curious case of state-imposed hairstyles. Again it seemed the world’s focus was fixed on the bizarre end of the spectrum of outrageous stories coming out of the hermit kingdom. But while reports of haircuts, hysterical grieving masses, Dennis Rodman and killer dogs — true or not — have spread like wildfire across social media, Kim Young-Il has gone about his work of fighting for the often forgotten rights of North Korean defectors.
Kim escaped North Korea himself in 1996. Forced to join the army as a teenager, he soon discovered that the military, like the rest of the country, suffered from malnourishment. North Korea experienced devastating famine throughout the 1990s, in no small part down to mismanagement by authorities. Together with his parents, he made the gruelling journey to China, where they stayed for four-and-a-half years as illegal immigrants. “I had every job you can imagine,” he says. Finally, tired of living in constant fear of deportation, they made their way to South Korea. Kim went to university, where he says frequent questions from fellow students writing on North Korea, made him think about his heritage. After graduating he set up the non-governmental organisation PSCORE to help those who, like he did, make the difficult decision to escape.
The risks of defecting are huge. Many are put off even trying by widespread rumours backed up by state propaganda, of defectors being interrogated and killed by South Korean authorities. The country’s near complete lack of freedom of expression makes such stories difficult to debunk. Simply getting out of North Korea is no guarantee of freedom either. Many defectors have to go through China, the regime’s powerful ally, which operates a strict returns policy for defectors. Returnees face a multitude of possible punishments, from forced labour to execution. “If China changes their stance, that wholly changes the situation,” Kim says. At present, however, there is little to suggest they will. For those managing to avoid return, the threat to family left behind looms large. Kim’s sister-in-law is a political prisoner today for speaking on the phone to his wife.
Kim’s reasoning was that he’d rather face these dangers than the prospect of starving to death in his home country. It appears many agree. Nobody knows the exact number of defectors, as many keep quiet about it due to dangers posed to loved ones. What is certain is that it has shot up because of the devastating effects of the famine. This has also changed the demographic of defectors. While it used to be an option utilised mainly by relatively high-level North Koreans, today people from all sections of society are making big sacrifices in hope of a better life abroad.
Part of the reason could also be that in the some 60 years since its establishment, life in the Democratic Republic has shown no signs of improving. Kim tells of a complex and rigid class system, explaining that records of your grandparents’ position and occupation are used to determine your standing in society. The state decides who can be a doctor and who can be a farmer. Women have some possibilities for upward social mobility through marriage, but on the whole, your path in life is determined almost entirely by factors outside your control. That is, with one notable exception: “It’s difficult to move up, but very simple to drop down.”
This system, reassuring many North Koreans that there is always someone worse off than you, has played its part in deterring popular dissent and large-scale social uprising, Kim explains. That, and the crippling fear of a brutal regime acting with impunity. Asked whether any noticeable changes came with the change of leader, Kim said that any hope of the country opening up when Kim Jong-un took power following the death of his father, was quickly extinguished. The issue of South Korean pop culture is striking example. Kim Jong-un and his family are big consumers of their neighbours’ booming entertainment industry, while the official line is that it’s strictly prohibited. Kim says a man as recently found to be selling CDs with South Korean films and music. He was publicly executed to set an example for others.
So many head for China and hope. In China is where PSCORE’s work starts. Kim travels over several times a year to meet defectors and bring them to South Korea. Finding them isn’t always easy, and when he does, many are afraid to speak. “We don’t ask questions immediately. We try to identify with them first,” he explains, mindful of the rumours and propaganda they have been subjected to in the north. Many have gruelling journeys behind them. Nam Bada, PSCORE’s General Secretary, showed Index pictures of a girl’s feet, disfigured by frostbite. She lost her shoes travelling on foot in the snow. Others have used brokers; locals living in the border areas, charging to help defectors cross. The brokers are “just interested in profit, not human rights” says Kim, and estimates the price is currently between $2000-6000. The practise puts defectors, especially female ones, at risk of human trafficking. PSCORE have helped a number of women from being sold by brokers.
Once they reach South Korea, they’re interrogated by authorities. “90% of South Korea’s information about North Korea comes from defectors,” Kim explains. After that, they’re enrolled in a basic, three-month education programme, and then more or less left to their own devices. The transition from arguably the most closed society in the world, to one of the most open ones can be difficult. Kim highlight language as a big hurdle. North Korean has been completely shielded from outside influence for decades, while South Korean has been free to develop. And while there is no discrimination against defectors legally and on paper, Kim says they are often discriminated against.
It’s against this backdrop PSCORE are providing education to defectors and helping them adjust to their new lives. Kim compares the process to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: “At first, people are just glad to be fed, but later they want more.” They also continue to campaign against North Korean human rights violations, which the aforementioned UN report described as “systematic, widespread and gross” and in many instances constituting crimes against humanity. Something to keep in mind the next time North Korea is in the news because of haircuts.
Support PSCORE’s work here
This article was posted on April 2, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
25 Mar 2014 | Asia and Pacific, China, News
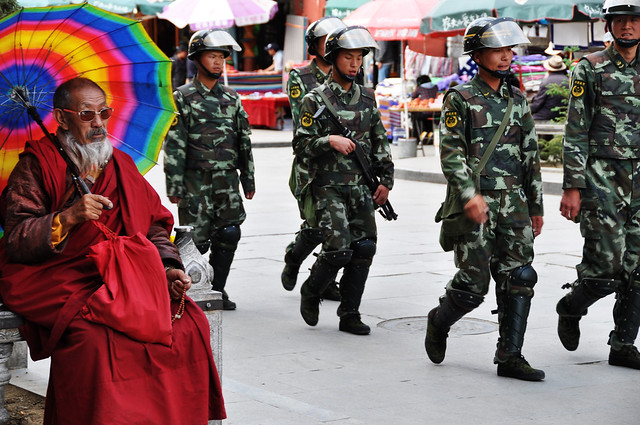

Lhasa, Tibet (Image: Prasad Kholkute/Creative Commons)
“What kind of device is that sniper on the rooftop using?”
“People’s Armed Police are everywhere.”
“Emerging from military compounds are Special Police, all driving mighty armoured vehicles.”
These are the messages sent by ordinary Chinese tourist about their trips to Tibet, collected by the International Campaign for Tibet, and published on their website.
While Tibetans themselves face fierce internet restrictions and harsh penalties if they try to spread information about the military occupation, Chinese tourists appear to be inadvertently breaching “the great Firewall of China” by sharing holiday snaps with friends back home. The messages and photos, which have been leaking out fairly infrequently since 2009, represent a rare source of information for those interested in repression in Tibet.
The tourists post photos of the considerable military presence — despite occasional warnings. Most comment on the large numbers of troops deployed.
“You can see People’s Armed Police troops everywhere in Lhasa. A guard post every ten meters…”
“Every three steps there’s a heavily armed People’s Armed Police checkpoint, there are armoured vehicles and tanks which you wouldn’t dare to photograph.”
“The Jokhang [most sacred temple in Tibet] is surrounded by heavily armed, fire-extinguisher toting People’s Armed Police.”
One photo shows a column of a hundred or so Chinese soldiers marching down a street. Another shows armoured cars on the move, and another a cohort of tanks. A picture sneakily snapped behind some marching soldiers shows fire extinguishers strapped to their backpacks.
Also striking amongst the comments are what appear to be genuinely held fears by Han Chinese tourists about the Tibetan residents.
“The number of Tibetans going back and forth on the streets made us worry about our safety, but when we asked the officer on duty they said it was safe, no problem.”
“Tibetans have a very strange look in their eyes, especially at night. It’s best not to do anything on the street by yourself,” said one, who admitted to carrying a Swiss Army knife during his trip, for protection.
These images are precious. Research in 2012 showed that half of all Weibo posts originating from Tibet were being deleted, compared to just 12% in Beijing. Last year, authorities installed a new system for monitoring both internet and phone traffic — while Tibetans living in nearby Sichuan province have seen their internet connections shut down en masse.
Anne Henochowicz, Translations Editor for China Digital Times, remembers a recent crackdown: “For several weeks in early summer 2012, Tibet was sealed off from all foreign visitors,” she told Index. “It was following two self-immolations in Lhasa in May. Chinese tourists were still allowed entry, and posted photos of armed troops in the city streets, along with posts describing increased security measures.”
Translations of the messages were posted on China Digital Times, an independent news website with a focus on freedom of expression in China’s complex and highly restricted online space.
Dechen Pemba, UK resident but editor of the Tibetan website High Peaks Pure Earth, put the leaked images in perspective: “Tibetans are not free to comment, document or report on their own situations. You only have to look at what happened to Dhondup Wangchen in 2008,” she told Index.
Wangchen was sentenced on 28 December 2009 following a secret trial in Xining city, western China, receiving six years in prison for producing a documentary film interviewing 100 Tibetans. He is one of many Tibetan political prisoners in China.
“Tibetans are well aware of the risk of using Weibo and public platforms online,” says Pemba. “Despite controls, Tibetans are also finding other ways to speak out and express themselves such as through poetry and song.” Pemba’s blog has been key in highlighting this trend — offering translations of works by Tibetans.
During high-tension periods, Chinese forces are not afraid to take special measures. In 2011, Pemba points out, searching Chinese social media site Weibo for mentions of “self immolations” yielded zero results. This was strange, given seven self-immolations had occurred in the past three weeks.
“After the riots in 2012,” continues Pemba. “Internet connections and mobile phone signals were cut off for over 50 kilometres around the areas affected.”
The Save Tibet campaign continues to document all of these images, under the title “Has life here always been like this?”. It has been extremely difficult to find information about Tibet without either going there, or relying on opportunistic citizen journalism. Chinese tourists, snapping away and posting to Weibo, provide a surprising back-channel into the Tibetan struggle.
This article was published on 25 March 2014 at indexoncensorship.org




