Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.

The shocking news of the death of democracy advocate and widely acclaimed Egyptian blogger, Bassem Sabry on April 29, hit me like a lightning bolt.
My short friendship with Bassem dates back to the early days of the January 25 uprising a little over three years ago when, without knowing me personally, Bassem had telephoned to congratulate me on quitting my job at Egypt’s state-run Nile TV in protest at the station’s biased coverage of the protests in Tahrir Square. Although we only met a couple of times after that conversation, I have since considered Bassem “a friend” mainly because of our shared aspirations for a better Egypt.
I learned of Bassem’s death from the flood of Twitter tributes to him from his friends, associates and fellow revolutionaries posted a couple of hours after he had passed away in what his family members describe as a “tragic accident.” Like many of his friends, I had hoped the Twitter eulogies were a sick joke. Unfortunately, they weren’t.
Bassem’s death was confirmed shortly afterward by news reports that said he had fallen to his death from a 10th floor balcony of his apartment after he reportedly “went into a diabetic coma”.
In an outpouring of love and grief, many of Bassem’s comrades in the struggle for a free and democratic Egypt — and some admirers who had never met him but who knew Bassem from his honest and insightful writings and commentaries on Egyptian politics, post-revolution — wrote moving eulogies to him on Twitter .
“Only the good die young but a great loss for those who still have hope for a better Egypt,” prominent human rights lawyer Ragia Omran said via her Twitter account.
“I never knew him but I knew his work. I saw the impact he had and his determination to make things better,” wrote Jeremy Walker, a journalist who has worked for the BBC World Service.
In other online tributes to Bassem, he was fittingly described as “an inspiration”, “a voice of reason”, “a true patriot” and “a champion of civil rights.” Highly respected for his reasoned analysis of regional politics for several international and local media outlets (including Al Monitor, Foreign Policy, the Huffington Post and the independent Egyptian daily Al Masry El Youm), Bassem’s ability to rise above the deeply divided political fray has earned him respect from across the political spectrum.
“I call on the youth of the revolution to pray for a companion and a noble person whom we lost,” exiled Nobel Peace Prize winner Mohamed ElBaradei said on Wednesday via his Twitter account. Bassem had briefly worked as a strategist for Al Dostour Party — the political party founded by ElBaradei after the January 2011 uprising. That however, did not stop him from criticizing the liberal politician’s “one foot inside, one foot outside” attitude vis-à-vis Egyptian politics, which Bassem deemed “frustrating to his supporters”.
Nader Bakkar, the spokesperson for the ultra-conservative Salafi Al Nour Party also expressed his condolences following Bassem’s death, describing him as “a moral person who loved his country”.
Bassem has also been hailed by analysts as a “voice of moderation and conciliation” — a title he deservingly earned for his repeated pleas for unity in the bitterly divided country. In an article published by Ahram Online on June 18, 2013 — just two weeks before Islamist President Mohamed Morsi was toppled by military-backed protests — Bassem had expressed his anxiety and frustration at the discord and deepening polarisation in Egypt. He wrote:
“It is utterly frustrating, disheartening and troubling to see where we are after more than two years of a revolution that was meant to end injustice, political exclusion and repression and hopefully unify most of the country around the dream of rebuilding a strong and vibrant nation. Instead, much of that injustice, exclusion and repression still exists. What’s worse, we’re more divided than ever as a people, and more exclusionary, while the voices of reconciliation and bridge-building are finding themselves more and more unpopular.”
In the same article, Bassem also expressed fear that the deep divisions in Egypt would lead to more blood-letting and violence in the months ahead.
“The fact that we are likely to see some violence and casualties on all sides fills me with dread,” he wrote, noting that clashes between Morsi supporters and opponents had already erupted in Fayoum and Menoufiya. Bassem’s fears were not unfounded: the country has since slipped into a spiral of violence and counter-violence with security forces using lethal force to disperse “anti-coup” protests and militants retaliating with attacks on military and security installations.
Meanwhile, an Arabic essay written by Bassem in October 2012 — around his 30th birthday — and which was published in the independent Al Masry El Youm, reflects his admirable traits of tolerance and compassion while demonstrating his strong urge to embrace all of humanity. In the essay titled Eleutheria, Bassem shared with readers the lessons that life had taught him. Many of those who have read the piece were amazed by the foresight and wisdom of someone so young. The essay was later translated into English and posted on his blog site, becoming one of the most read articles in 2012.
“I have met Hindus, Buddhists, Christians, the non-religious, the still-searching, and others. And I have met those of all skin colours. And I have found them to all be like myself. We became friends, and I became wealthier in spirit as a human being. And I learned that mankind was one, that coexistence was possible, that we must ostracise the hate-mongers amongst us. We can achieve with the pen and the word much more than what we can achieve with guns and loud angry rhetoric – and achieve that more rapidly ”
Unlike many Egyptian journalists who practice self-censorship in the current repressive climate of fear since the coup, Bassem had refused to be intimidated and had managed to remain neutral and objective throughout. He refused to take sides in the ongoing conflict between the military and the Muslim Brotherhood, designated as a terrorist organization in December. A few weeks ago when asked by a fellow journalist whose side he was on, he replied: “Nobody’s, I simply support my country.”
Close friends and secular activists describe him as “an optimist to a fault”. In recent months however, Bassem’s optimism had waned and he became increasingly frustrated with the political turmoil, violence and above all, with the military-backed government’s repressive policies. In a tribute to Bassem published in the independent news portal Mada Masr on Thursday, his friend H. A. Hellyer, a non-resident Associate Fellow at the Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies in London and the Brookings Institution wrote: “Bassem at heart was a great optimist. However, and he was very reserved about this fact, he was deeply and terribly pained by the experience of particularly the last year. The pain he felt, as he saw Egyptian turn on Egyptian, troubled him tremendously. He lived to see the revolution that so many Egyptians of his generation wanted to be a part of — but he was also profoundly wounded to see the failure of Egyptians to live up to that revolution.”
Bassem himself had expressed his dismay at the turn of events in Egypt, post-revolution, blaming the messy transition on the lack of vision of the country’s political elite. In an article published by Ahram Online in June 2013, he lamented that “the political elites, on every side of the spectrum, have profoundly failed the nation in varying ways down the road through an astonishing alternation (or even, at times, a blend) of lack of vision, displays of ineptitude, an improper balance of idealism and pragmatism, inability to know when to lead the street and their political biases and when to defy them for a greater good if necessary, and more.”
I last met Bassem for dinner at a restaurant overlooking the Nile River in the affluent neighbourhood of Zamalek one week before his death. That evening, he did not drink and left his food untouched. I also noticed that he had lost his infectious vigour and enthusiasm; it was clear he had been weighed down by the news of daily killings and detentions of both secular activists and Muslim Brotherhood supporters, the targeting of journalists by security forces and the recent mass death sentences handed down to Morsi loyalists. We talked about the ongoing events and about the presidential elections scheduled for the end of this month. Bassem told me that he had joined leftist politician Hamdeen Sabahy’s presidential campaign. I was not surprised. After all, most young revolutionaries do not want to see Egypt return to oppressive military rule and Sabahy is the sole candidate contesting the presidential elections against Field Marshal Abdel Fattah El Sisi. Despite joining protests demanding the downfall of the Muslim Brotherhood regime in July 2013, many of them are waking up to the realization that their uprising has paved the way for the return of the old police state that existed under Hosni Mubarak. The jailing of prominent secular activists, the return of media censorship and the recent outlawing of the April 6 group — the movement that helped ignite the January 2011 mass protests — are all signs that the revolution has once again been stolen and that this is the counter-revolution, lament the young activists.
In a message posted on his Twitter account on March 24, 2013 Bassem had quizzed: “Why is it that all the good people die in this country?” He had posed the question in the wake of violent demonstrations against the Muslim Brotherhood and clashes between secular activists and Brotherhood supporters outside the Islamist group’s Cairo Headquarters. Earlier that same day, Morsi had warned he would take “necessary measures” against any politicians and Mubarak loyalists shown to be involved in the violence and rioting.
At the time, Bassem was probably unaware that his question was a premonition of his own death. It is a question that many of his young activist friends are echoing today.
“Why is it that all the good people die in this country?” Rest in Peace, Bassem. You will be sorely missed.
This article was posted on May 6, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
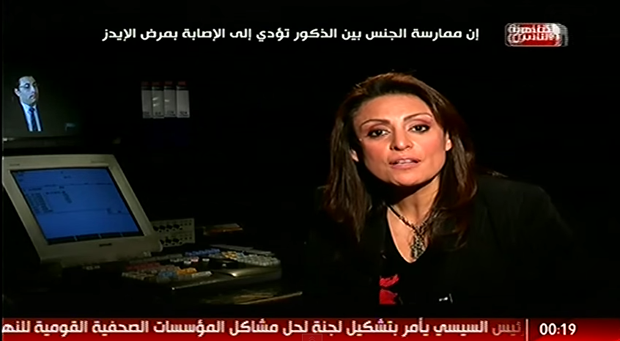
Journalist Mona El Iraqi colluded with security forces in a raid on a public bathhouse allegedly frequented by gay people (Image: Al Kahera Wal Nas TV Network/YouTube)
When prominent Egyptian actor Khaled Abul Naga criticised President Abdel Fattah El Sisi counter-terrorism policies in Sinai in a video posted on the El-Bawaba news website last November, he was slammed by government loyalists and Egypt’s pro-regime media.
Lawyer Samir Sabry, notorious for filing legal complaints against opposition activists, filed a lawsuit against Abul Naga accusing him of “treason” and “inciting anti-government protests”. In a telephone interview with the Egyptian privately-owned satellite channel Sada El Balad, Sabry said “those who go against the will of the people who elected El Sisi, must be punished”.
Abul Naga’s prosecution reflects the growing intolerance in Egyptian society and the persistent intimidation of dissenters since the ouster of Islamist President Mohamed Morsi some eighteen months ago. Since the military takeover of the country on 3 July, 2013, anyone expressing a view that runs counter to the official narrative is labeled a “traitor” and a “spy” by supporters of Egypt’s military-backed regime.
Even more disturbing than the criminal charges faced by Abul Naga is the barrage of insults hurled at him by government loyalists in the media who poked fun at the actor’s alleged sexual orientation.
Talk show host Tawfiq Okasha scandalously mocked Abul Naga’s sexuality, hinting that the actor was gay.
“Why do you sleep on your stomach and not on your back?” the controversial TV presenter (and owner of Faraeen Channel) asked, adding that there must have been a reason why Abul Naga was exempted from military service.
Mazhar Shaheen, a pro-government cleric who presents a talk show on a privately-owned satellite channel, also scoffed at Abul Naga, suggesting that he leave the country.
“If you are not happy with the military’s performance, you should go to either Syria or Iraq,” he said, addressing Abul Naga.
“But watch your pants while you are there,” he sarcastically warned.
Abul Naga’s lampooning by the pro-government media reflects the shrinking space for free expression in today’s Egypt. It also highlights the increased vulnerability of and continued discrimination against the LGBT community in Egypt’s deeply conservative society.
In recent months, Egypt’s gay population have increasingly been targeted amid a brutal crackdown that has seen 150 suspected homosexuals arrested and detained since November. While Egyptian law does not expressly ban homosexuality, gay people are frequently charged with “debauchery” and detained. Muslim scholars and prosecutors have condoned the arrests, arguing that “homosexuals are shameful to God” and that “it is the government’s duty to protect morality” — a conservative view that is widely shared by the Egyptian public. A Pew survey conducted in 2013 found only three per cent of Egyptians accept homosexuality.
While disdain for homosexuality is not new in Egypt, inflammatory reporting by Egypt’s pro-government media has in recent months further fuelled prejudice against gay people and deepened the stigma associated with homosexuality.
Last month, TV reporter Mona El Iraqi who works for the privately-owned Al Kahera Wal Nas TV channel, colluded with security forces in a raid on a public bathhouse in downtown Cairo, allegedly frequented by gay people. Iraqi used her cell phone to take pictures of 26 half-naked men wrapped only in bath-towels as they were arrested. After sending undercover agents to the bathhouse to spy on visitors, she alerted the police, claiming that “promiscuous orgies” were taking place there. On 7 December, police — accompanied by Iraqi’s camera crew stormed the bathhouse and indiscriminately arrested the suspects.
Iraqi unashamedly posted pictures of the half-naked men on her public Facebook page. The images were removed a couple of hours later after she was lambasted by rights activists enraged by what they described as her “insensitivity” and “flagrant intolerance”. Defending her actions in a Facebook post, she insisted that the bathhouse was a “hotbed of immorality” and was “helping spread HIV and AIDS in Egypt”.
Despite the outpouring of horror over the bathhouse raid on social media networks, Iraqi’s episode was broadcast to “mark World AIDS Day and spread awareness about the causes of HIV and AIDS in Egypt” — according to Iraqi.
The 26 men who were arrested were charged with “debauchery” and subjected to intrusive anal checks to determine their sexuality. Human Rights Watch has decried the anal examinations, describing them as being in violation of “international standards against torture“. The forensics report claimed that two of the 26 defendants may have been subjected to rape as signs of struggle were evident on the bodies of the men in question. At the trial last Sunday, defence lawyers argued however, that it was almost impossible to verify whether the men had indeed practiced homosexuality. They also slammed the decision to allow Iraqi to film the arrests, describing the move as “unconstitutional”. Denouncing the arrests, they said it was only natural for the men to have been naked “for they were either in the shower or the steam bath when police stormed the premises”. Khaled Naqash, one of the defence lawyers meanwhile, claimed his client had been fully dressed but was stripped naked by the police before his arrest. The defendants’ families were barred from entry into the courtroom and complained they were “ruffled up” by security guards who had apparently already condemned the defendants even before the verdict has been pronounced. The trial has been adjourned until 12 January when the fate of the men will be decided.
The latest mass arrests are reminiscent of the 2001 so-called “Queen Boat raid“, when security forces stormed a floating nightclub moored on the Nile in Cairo’s affluent neighbourhood of Zamalek, arresting 52 men. That incident sparked international outrage and condemnation and sent a chilling message to Egypt’s LGBT community. Rights advocates say the latest arrests are even more disturbing than the Queen Boat incident as they show media colluding with the police instead of holding security forces to account for their actions.
The bathhouse raid also comes hot on the heels of similar raids on gay hangouts in Cairo in recent months including cafes, bars and even private house parties. In March last year, four men were arrested in a raid on a house party after police allegedly found the men dresses in women’s clothing. The men were accused of “debauchery” and sentenced to eight years in prison. In September, a video of an alleged “gay wedding ceremony” posted online prompted the arrest of another eight men including the alleged “gay couple” who were seen in the video exchanging rings and hugging. While all the men had reportedly tested “negative” for homosexuality, they were nevertheless, sentenced to three years in prison each. A Cairo appeals court later reduced the sentences to one year in prison. The court also ruled however, that the men would remain under police surveillance after completing their jail terms. Last Sunday, El Youm El Sabe’ reported that two men were arrested in Alexandria by “morality police” and charged with “debauchery” and “destroying public morals”.
The recent spate of mass arrests of gay suspects has sparked serious concerns for Egypt’s LGBT community.
“I no longer feel safe,” Karim, a 26 year-old Egyptian homosexual told Index. “Egypt has never been safe for us but things are worse now under the military-backed authorities because we know we are being targeted.” He explained that the current regime was trying to woo the conservatives in the society by “appearing more Islamist than the ousted Islamist regime”.
“I’m always looking over my shoulder now and constantly live in fear,” said Mohamed, 32, another member of Egypt’s LGBT community. “I would leave Egypt if I could.”
For Mohamed and other gay people in Egypt, what is even more worrying than persecution and prosecution is the humiliation and shame they may bring onto their families if their identities were revealed — as has happened with the defendants in the recent bathhouse case.
“Now that the media is aligned with the police, we are at serious risk of public defamation and loss of dignity,” he lamented.
“What is even sadder is that few Egyptians are denouncing the arrests of gays as some media are telling the public that homosexuality is a disease that will destroy public morality and hence, it is necessary to rid the society of the scourge,” he added.
Buthayna Haleem ( her name has been changed to protect her identity) an Egyptian lesbian writer is one of the few people in Egypt condemning the raids.
“It is not something that concerns others,” she told Agence France Press in a recently televised interview. “This is oppression against people.”
Update: An earlier version of this article incorrectly stated Mona Iraqi had removed the images posted to Facebook. Facebook removed the images because they violated the service’s terms.
This article was published on 6 January 2015 at indexoncensorship.org

Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El Sisi has tightened the screws of the country’s journalists. (Photo: Wikipedia)
In a rare show of defiance, hundreds of Egyptian journalists have objected to a “statement of allegiance” to the government signed by editors-in-chief of the main state-owned and independent newspapers.
More than 600 Egyptian journalists signed an online petition defending press freedom and rejecting censorship in all its forms. The move came in response to a loyalty pledge by 17 editors-in-chief of newspapers to refrain from criticizing the police, the military and the judiciary at this sensitive time when Egypt was “at war with terrorism.”
The journalists dismissed the editors’ statement as “a futile attempt to create a one-voice media,” arguing that “fighting terrorism had nothing to do with voluntary abandonment of freedom of speech.”
“The editors’ statement is not worth the ink used in writing it,” Dina Samak, deputy editor-in-chief of the English language semi-official Ahram Online and one of the journalists who signed the petition, told Index on Censorship.
“The terrorists will win when they can control the media, and the state will fall when it agrees on the same goal,” said Khaled El Balshi, a journalist and board member of the Journalists Syndicate, who helped draw up the petition for press freedom.
In a show of solidarity with Egypt’s military-backed regime, the editors had gathered at El Wafd newspaper headquarters on 26 October to forge “a united front against terrorism”, expressing their “rejection of attempts to cast doubt on state institutions.” They also vowed to take measures to halt what they called the “infiltration by elements supporting terrorism” in their publications — a reference to supporters of the outlawed Muslim Brotherhood, designated as a terrorist group by Egypt last year.
While the move did not come as a surprise to many — as it was already clear that the majority of media outlets had aligned themselves closely with the government since the military takeover of the country in July 2013 — the “loyalty pledge” by the editors was nevertheless unusual even in a country where the media was in lockstep with the regime.
The signatories to the declaration — the editors-in-chief of the three main state-owned dailies Al Ahram, Al Akhbar, Al Gomhouria and those of the independent Al Masry Al Youm, Al Watan, Al Shorouq, El Tahrir, El Ahali, Al Fajr , El Messa, El Esboo, El Youm el Sabe and El Gamaheer newspapers — argued however that “crisis situations” required “exceptional measures”.
Defending the editors’ statement, Emad El Din, editor-in-chief of the independent Al Shorouk denied that the editors’ loyalty declaration gave journalists the green light to practice self censorship.
“We wanted to deliver a message to citizens that the media is with the state in fighting terrorism,” he told NPR Radio shortly after signing the statement.
“At this time of heightened nationalism, the climate does not allow for any criticism of the government,” he added.
The move came in response to a call by President Abdel Fattah El Sisi for Egyptians to rally behind him in his fight against terrorism following two deadly militant attacks on an army checkpoint in North Sinai on 24 October that killed 33 army soldiers and injured at least a dozen others. The militant assaults were the latest in a string of attacks targeting mainly security forces — but at times, also civilians — since the overthrow of Islamist President Mohamed Morsi in July 2013. The attacks have prompted a surge in nationalism and a heralding of a so-called “war on terrorism” waged by the military against suspect-militants in the Sinai Peninsula. The violence has also resulted in a massive government crackdown on dissent that has targeted all opposition including journalists critical of regime policies.
Six journalists have been killed and dozens detained since the military took power in July 2013, according to the New York-based Committee for the Protection of Journalists. While most have been released, at least 11 journalists remain behind bars for no crime other than being at — or near — Muslim Brotherhood protest sites. Among the detained are three journalists working for the Al Jazeera English news network who have been sentenced to between seven and 10 years in jail on charges of “threatening national security, fabricating news and aiding a terror group”.
The crackdown on the media has led many journalists to practice self-censorship for fear of being imprisoned, killed or labeled “unpatriotic” by an unsympathising Egyptian public. Meanwhile, the statement released by the editors has fueled fears among press freedom advocates of a further shrinking in the already-dwindling space for freedom of expression in Egypt.
Adel Hamouda, an Egyptian journalist and former editor-in-chief of Al Fajr, meanwhile, criticised the editors’ statement as “uncalled for“.
“It is an attempt by the editors to win favour with the regime for the sake of personal gains,” he told Index. He explained that all Egyptians — except those supporting the Muslim Brotherhood — support the state in its war on terror so it is “meaningless” to publicly assert their support. He further noted that all media organisations were required to seek approval from the Armed Forces Morale Affairs Department before publishing or broadcasting any news about the military.
The majority of the independent media outlets that signed the statement belong to wealthy businessmen with close links to the ruling military-backed regime. They are fully aware that publishing any criticism of government policies would ruffle feathers and likely jeopardize their business interests. All top editors were appointed by the Higher Press Council shortly after Morsi’s overthrow in July 2013. Their selection was clearly based on their willingness to cooperate with the regime rather than their merits. Shortly after Morsi’s ouster, a leaked video on YouTube showed then-Defence Minister Abdel Fattah El Sisi asking senior generals to “establish partnerships with media outlets to curb any criticism of the military”. An independent journalist who spoke on condition of anonymity told Index that days before Morsi’s ouster, she had been approached by security officials who promised her “fruitful rewards” if she joined the “winning side” — a clear reference to the country’s powerful security apparatus that drove the uprising against the democratically-elected president.
In the coup’s aftermath, most editors and TV talk show hosts have persistently lionised Sisi and cheered on the military while demonising the Muslim Brotherhood, the Islamist group from which former President Mohamed Morsi hailed.
The media in Egypt has traditionally been a propaganda tool for whoever is in power. Various successive regimes have used the state media as a mouthpiece to further their political gains. Under Mubarak, all editors-in-chief of the state-owned newspapers were handpicked by his powerful Minister of Information Safwat El Sherif who presented the list of chosen candidates to the Shoura or Consultative Council, the upper house of parliament dominated by members of the then-ruling party, the National Democratic Party, for ratification.
In the months following the fall of Mubarak, there was a brief period of free expression and a loosening up of restrictions on the media. Press freedom — one of the major gains of the 2011 mass uprising — was short-lived however as the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces (SCAF) which replaced Mubarak, quickly moved to exercise control over the media. During its one year in office, the SCAF confiscated newspapers, ransacked the offices of foreign news networks and investigated journalists critical of the military. Shortly after Morsi won the elections — becoming the country’s first democratically elected president — he too reneged on his election promises to promote freedom of speech, appointing a Muslim Brotherhood member as minister of information. The Muslim Brotherhood-dominated Shoura appointed regime loyalists as senior editors of state-owned dailies, repeating the Mubarak-era practice that allows tight government control over the media. The move provoked an outcry from non-Islamist journalists who held protest rallies and threatened to resign their posts.
Almost immediately after Morsi’s overthrow, all Islamist-leaning newspapers and TV channels were shut down by the new authorities — a move that sent a message to journalists that there was little tolerance for dissent in Egypt, post-3 July. The last sixteen months have seen a return of the media censorship reminiscent of that which prevailed under Mubarak. Newspapers that published articles deemed “controversial” by the authorities, have been pulled off newsstands and confiscated. In October 2014, a print edition of the independent Al Masry Al Youm was confiscated by government censors for publishing an interview with former national security intelligence chief Mohamed Gebril in which he was quoted as saying that “no Israeli spy has ever been executed in Egypt”. The paper later appeared on newsstands, albeit without the interview. Months earlier, columnist and screenwriter Belal Fadl resigned from the independent Al Shorouk after the paper’s management allegedly refused to publish his column ridiculing the promotion of Sisi (who was defence minister at the time) to the rank of field marshal. Fadl was accused by pro-military commentators of being a “traitor” and “a fifth columnist plotting to destroy the country”.
Several editors who signed the statement of support to the government are also known to be part of a fake opposition created by Mubarak to give a semblance of free speech and democracy. Like other pro-regime editors, they too have persistently glorified the military and vilified the Muslim Brotherhood. And they have gone a step further, slandering the January 25 Revolution as a “foreign conspiracy” and labelling the secular opposition activists who mobilised public support for the 2011 mass protests “traitors” and “foreign agents.”
Mostafa Bakri, editor-in-chief of Al Osbou — and one of the editors who signed the loyalty pledge — has recently been summoned by the public prosecutor after several legal complaints were filed against him by private citizens for “fabricating news” and “slandering the January 25 Revolution”.
Meanwhile, the journalists behind the online petition for press freedom are planning to form an independent association to advocate freedom of expression. While this is a step in the right direction, press freedom advocates fear the negative effects of the editors’ pledge of allegiance are already being felt.
“Their statement was perceived as a warning message by the younger, less skilled journalists, many of whom are now practicing self-censorship for fear of losing their jobs or in a bid to win favour with the management and get promoted,” lamented Dina Samak.
Despite the setback, the battle for press freedom is on.
“It is a battle pitting the younger, pro-reform journalists against the old regime loyalists, resisting change,” Amany Kamal, a former radio presenter told Index. Kamal was forced to quit her job as a broadcaster with a state-run radio channel after being accused by the management of sympathising with the Muslim Brotherhood. “But we shall win,” she said.
This article was published on 24 November 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
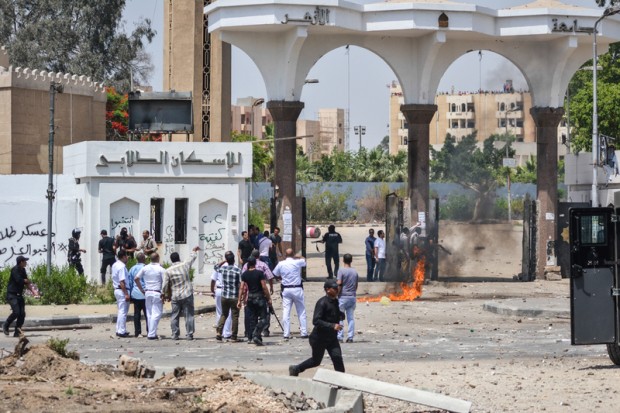

In May 2014, Egyptian security forces entered a student housing area of Al-Azhar University, during clashes with student protesters in Cairo. (Photo: Ahmed Hendawy /Demotix)
With just a few weeks to go before Egyptian universities open their gates to students for the start of the new academic year, the Egyptian authorities are feeling jittery — and rightly so.
The previous academic year saw an unprecedented wave of violence at universities across the country with clashes between “anti-coup” student-protesters and security forces on an almost daily occurrence that forced the repeated postponement of exams. At least 14 students were killed in the violence, hundreds of others were detained and hundreds more were expelled for organising or taking part in protests, according to Al Ahram.
Ahead of the new academic year, the authorities have taken some new, stringent measures to ensure the past year’s scenario is not repeated. They have also issued stern warnings to students that they will adopt a “zero tolerance approach” towards dissent. Any student who criticises President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi or any “symbol of the state” face repercussions. According to warnings issued last week by two major state universities –Ain Shams and Bani Suef — students who violate university regulations by “defaming public officials” will be subject to an internal disciplinary investigation and risk expulsion.
The announcement drew angry outcries from students and rights advocates who expressed their concern on social media. Critics fear the new regulation would curb the rights to free speech and expression. Since the 3 July ouster of Islamist President Mohamed Morsi by military-backed protests, the Egyptian authorities have imposed sweeping restrictions on freedom of expression. The massive security crackdown on dissent has targeted Islamists, liberal activists , journalists and academics.
A draconian law passed last November bans protests without prior permission from the authorities. Scores of liberal opposition activists including several prominent figures in the January 2011 mass uprising have been imprisoned for protesting against the repressive legislation. Hundreds of Muslim Brotherhood supporters also languish behind bars for staging “anti-coup” protests following the overthrow of Morsi.
In February, an Egyptian court approved the stationing of police forces at universities, overturning a 2010 verdict banning police presence at educational institutions. The Ministry of Interior hailed the latest court decision, saying the police deployment was “necessary” to quell opposition protests led by supporters of the outlawed Muslim Brotherhood (designated by Egypt as a terrorist organisation following Morsi’s ouster). The beefed-up security presence at universities has resulted in the arrests of hundreds of students and the deaths and injuries of dozens of others over the course of the past year. Many of the detained students have been sentenced to between 3 and 17 years in jail on charges of staging unauthorised protests, having links to a terror group and inciting violence.
Meanwhile, Minister of Endowments Mokhtar Gomaa has called for a purge of Islamist-leaning deans, staff and faculty members from state universities. The independent Mada Masr quoted Minister Gomaa as saying that universities should be “cleansed of academics sympathetic to the banned terrorist group”. He has also demanded that firm action be taken against the so-called “Academics Against the Coup” — an Islamist partisan group of scholars whose members are purportedly connected Al-Azhar University’s board of directors.
In another restrictive move, Cairo University Head Gaber Nassar has called for the dissolution of student groups or organisations of any political affiliation at all universities. According to Al Youm El Sabe’ newspaper, new students enrolling at universities will now be requested to sign a document pledging not to engage in any political activities on campus.
While the government insists the new measures are part of its ongoing war against terrorism and claims that the upsurge in violence at universities is “an extension of the nationwide Muslim Brotherhood insurgency”, a security source told Index that the ban on student protests goes beyond suppressing the Muslim Brotherhood rebellion. Speaking on condition of anonymity, he said that “the ban is not just aimed at restoring stability”.
“The government wants to spread a culture of submission and fear similar to that which prevailed under Hosni Mubarak. It is trying to instil the idea that the opposition is evil and must be crushed,” he added, warning that “students engaging in political activities will be accused by both the authorities and ‘patriotic’ government supporters of being affiliated to the terrorist group.”
The latest restrictions are a far cry from the period between the 1930s and the 1970s when Egyptian state universities were a hotbed for political activism and the student movement was an instrumental political force in Egyptian society. That ended, however, with amendments introduced to the student charter by late President Anwar Sadat in 1979. The changes “essentially were intended to undermine the power and activism of students on campus by dissolving the representative student bodies,” author Hisham Adawi wrote in his book In Pursuit of Legitimacy published in 2004. While Hosni Mubarak, the authoritarian leader toppled by the 2011 protests, was relatively more tolerant of political expression and dissent than his predecessors Gamal Abdel Nasser and Sadat (at least during the early years of his rule), he too cited fears that “the university’s faculties were becoming strong recruiting points for militants”. Using this as a pretext, he again altered the charter to allow further administrative and security intervention in student activities. Mubarak’s amendments drew criticism from rights advocates who sarcastically called it “the State Security Charter” (in reference to the autocratic leader’s detested security apparatus). Despite sporadic periods of heightened tensions — particularly at Al Azhar and Cairo University — there has since been no true revival of the student movement as an influential political force in society.
Despite the recent warnings by the authorities, angry students staged a small rally outside Cairo University last Wednesday to protest the new measures. The protesters denounced the restrictions, chanted anti-government slogans and demanded the release of their detained colleagues and academics. No fewer than 160 faculty members and staff have been arrested and detained since the July 2013 overthrow of President Morsi, according to an April 2014 report compiled by Egyptian academic rights groups and posted on the Al Jazeera Arabic website. Several academics charged with “supporting the outlawed Muslim Brotherhood” remain at large and have either fled the country or gone into hiding.
Dr. Emad Shahin — an internationally renowned scholar of political Islam who has taught at Harvard, Notre Dame and the American University in Cairo — was charged with espionage in January. He is listed as one of the defendants in a criminal case against several Muslim Brotherhood leaders (including the deposed President Morsi) and stands accused of “conspiring with foreign organisations to undermine Egypt’s national security”. An outspoken critic of the bloody crackdown on Morsi’s supporters after the military takeover, Shahin learnt of the arrest warrant against him while on a visit to Washington nine months ago. He has since remained in the United States and has denied the charges in an email to the New York Times. “The accusations against me are baseless, politically motivated and beyond preposterous,” he said.
Amr Hamzawy, a liberal political scientist and former lawmaker and senior associate at the Carnegie Middle East Centre in Beirut, has also been charged with “insulting the judiciary”. In January, a lawsuit was filed against him by a lawyer after he questioned (on Twitter) a verdict against a group of foreign non-governmental organisations. Hamzawy was released after being investigated for several hours by the public prosecutor.
In a new case that has fuelled concern among rights advocates, Dr. Mohamed Tarek, an adjunct professor at the faculty of science at Alexandria University, was arrested, detained and allegedly tortured last week. He was arrested on 29 August from a street near his home in Alexandria, and has been held in custody since. Police later raided his home and confiscated his laptop and other personal belongings. There have been conflicting reports of his arrest: Interior Ministry sources claim they arrested him during a protest march in Moharram Beik district in Alexandria. Rights groups meanwhile, insist he was detained for giving his testimony of last year’s Raba’a massacre to Human Rights Watch. Tarek was injured in clashes with security forces during the forced dispersal of a sit-in staged by supporters of Morsi outside Raba’a El Adaweya Mosque in the Cairo neighbourhood of Nasr City in August 2013. His chilling account of the forced evacuation featured in a damning report released by Human Rights Watch last month.
According to the 195-page report titled All According to Plan, Egyptian police and the army used “grossly disproportionate and premeditated lethal force against overwhelmingly peaceful opposition protesters” resulting in the killings and injuries of hundreds of them in a single day of violence. The report describes the Raba’a deaths as “likely crimes against humanity” and calls for those responsible to be brought to justice. The Egyptian government has dismissed the report as “politicised” and “biased”. Days after the release of the report, Cairo Airport authorities prevented Human Rights Watch staff members from entering the country, saying the organisation “has no legal status that would allow it to operate in the country”. Human Rights Watch said the move was “an attempt by the Egyptian authorities to gag critics”.
While Egyptian authorities are hoping the new proposed measures will help end violence at state universities, sceptics warn the clampdown on freedoms can only further fuel the unrest. With the new academic year scheduled to begin on October 11 (instead of in late September as originally planned), many worry about a fresh eruption of unrest that may well result in even more bloodshed.
This article was posted on 10 Sept 2014 at indexoncensorship.org