16 Dec 2015 | Awards, Events, mobile, Press Releases
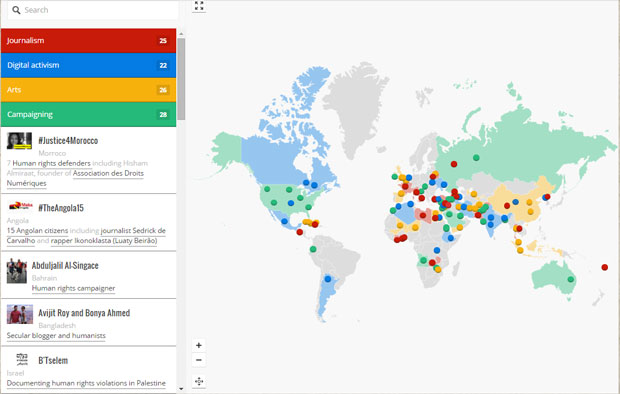
A graffiti artist who paints murals in war-torn Yemen, a jailed Bahraini academic and the Ethiopia’s Zone 9 bloggers are among those honoured in this year’s #Index100 list of global free expression heroes.
Selected from public nominations from around the world, the #Index100 highlights champions against censorship and those who fight for free expression against the odds in the fields of arts, journalism, activism and technology and whose work had a marked impact in 2015.
Those on the long list include Chinese human rights lawyer Pu Zhiqiang, Angolan journalist Sedrick de Carvalho, website Raqqa is Being Slaughtered Silently and refugee arts venue Good Chance Calais. The #Index100 includes nominees from 53 countries ranging from Azerbaijan to China to El Salvador and Zambia, and who were selected from around 500 public nominations.
“The individuals and organisations listed in the #Index100 demonstrate courage, creativity and determination in tackling threats to censorship in every corner of globe. They are a testament to the universal value of free expression. Without their efforts in the face of huge obstacles, often under violent harassment, the world would be a darker place,” Index on Censorship CEO Jodie Ginsberg said.
Those in the #Index100 form the long list for the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards to be presented in April. Now in their 16th year, the awards recognise artists, journalists and campaigners who have had a marked impact in tackling censorship, or in defending free expression, in the past year. Previous winners include Nobel Peace Prize winner Malala Yousafzai, Argentina-born conductor Daniel Barenboim and Syrian cartoonist Ali Ferzat.
A shortlist will be announced in January 2016 and winners then selected by an international panel of judges. This year’s judges include Nobel Prize winning author Wole Soyinka, classical pianist James Rhodes and award-winning journalist María Teresa Ronderos. Other judges include Bahraini human rights activist Nabeel Rajab, tech “queen of startups” Bindi Karia and human rights lawyer Kirsty Brimelow QC.
The winners will be announced on 13 April at a gala ceremony at London’s Unicorn Theatre.
The awards are distinctive in attempting to identify individuals whose work might be little acknowledged outside their own communities. Judges place particular emphasis on the impact that the awards and the Index fellowship can have on winners in enhancing their security, magnifying the impact of their work or increasing their sustainability. Winners become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for the year after their fellowship on one aspect of their work.
“The award ceremony was aired by all community radios in northern Kenya and reached many people. I am happy because it will give women courage to stand up for their rights,” said 2015’s winner of the Index campaigning award, Amran Abdundi, a women’s rights activist working on the treacherous border between Somalia and Kenya.
Each member of the long list is shown on an interactive map on the Index website where people can find out more about their work. This is the first time Index has published the long list for the awards.
For more information on the #Index100, please contact [email protected] or call 0207 260 2665.
19 Jun 2012 | Middle East and North Africa, Volume 41.02 Summer 2012
 The Syrian regime has gone to great lengths to silence the satirical commentary of Ali Ferzat. But the celebrated cartoonist and Index award winner has no intention of letting the censors keep him down. Malu Halasa reports
The Syrian regime has gone to great lengths to silence the satirical commentary of Ali Ferzat. But the celebrated cartoonist and Index award winner has no intention of letting the censors keep him down. Malu Halasa reports
Three months before the start of the Syrian revolution in March last year, Ali Ferzat broke with his own satirical convention: he stopped using symbolism in his cartoons to criticise the regime and began to target identifiable individuals, including the president himself. He describes the shift as pushing through “the barrier of fear”. The first cartoon in Ferzat’s new series showed President Bashar al Assad agitated at seeing the traditional day of mass demonstrations against the regime, Friday, marked on a wall calendar. Another had him hitching a lift from Gaddafi making his own getaway in a car. The third featured the “chair of power”, one of Ali Ferzat’s iconic symbols, with the springs popping out of the cushion and Bashar hanging onto its arm.
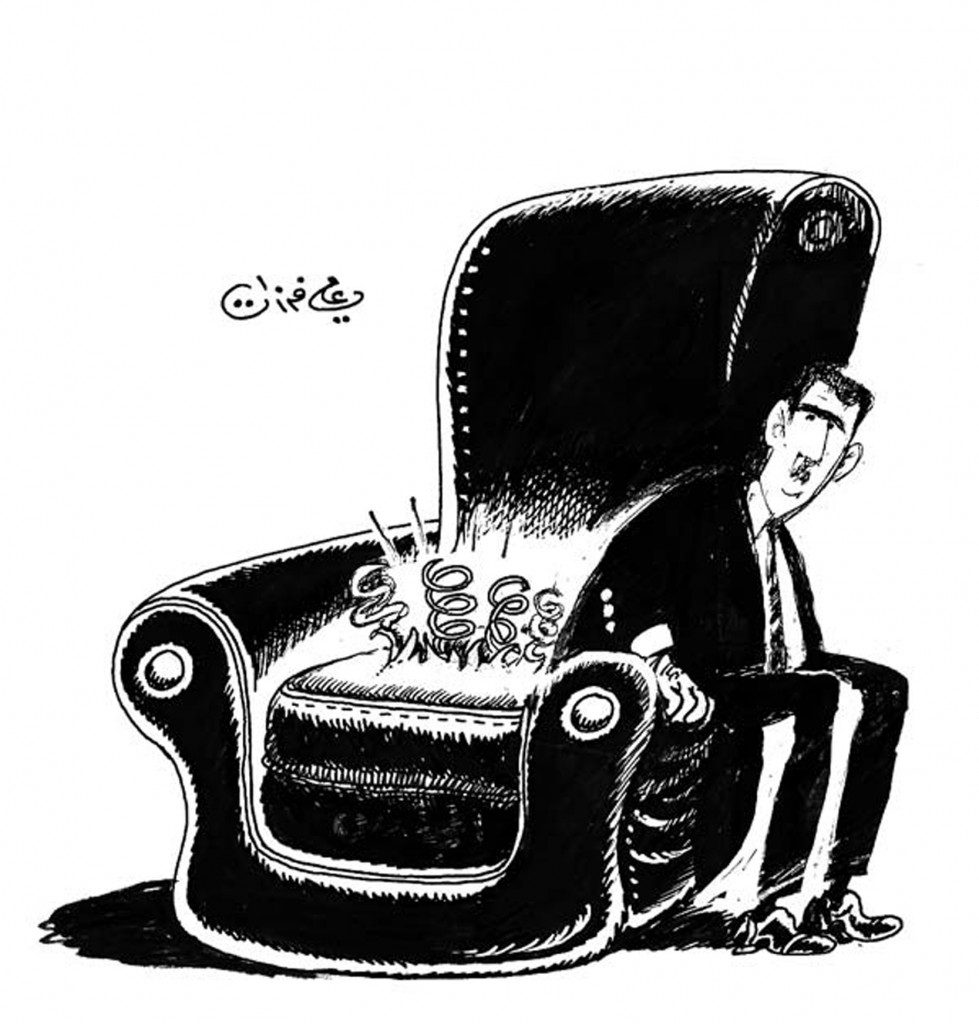 Drawing the president, Ferzat admits, was a personal and political breakthrough — if not foolhardy. “It is quite suicidal to draw someone who is considered a godlike figure for the regime and the Ba’ath party, but still I did it and people respected that courage and started carrying banners with caricatures in the protest to show how they feel about things.”
Drawing the president, Ferzat admits, was a personal and political breakthrough — if not foolhardy. “It is quite suicidal to draw someone who is considered a godlike figure for the regime and the Ba’ath party, but still I did it and people respected that courage and started carrying banners with caricatures in the protest to show how they feel about things.”
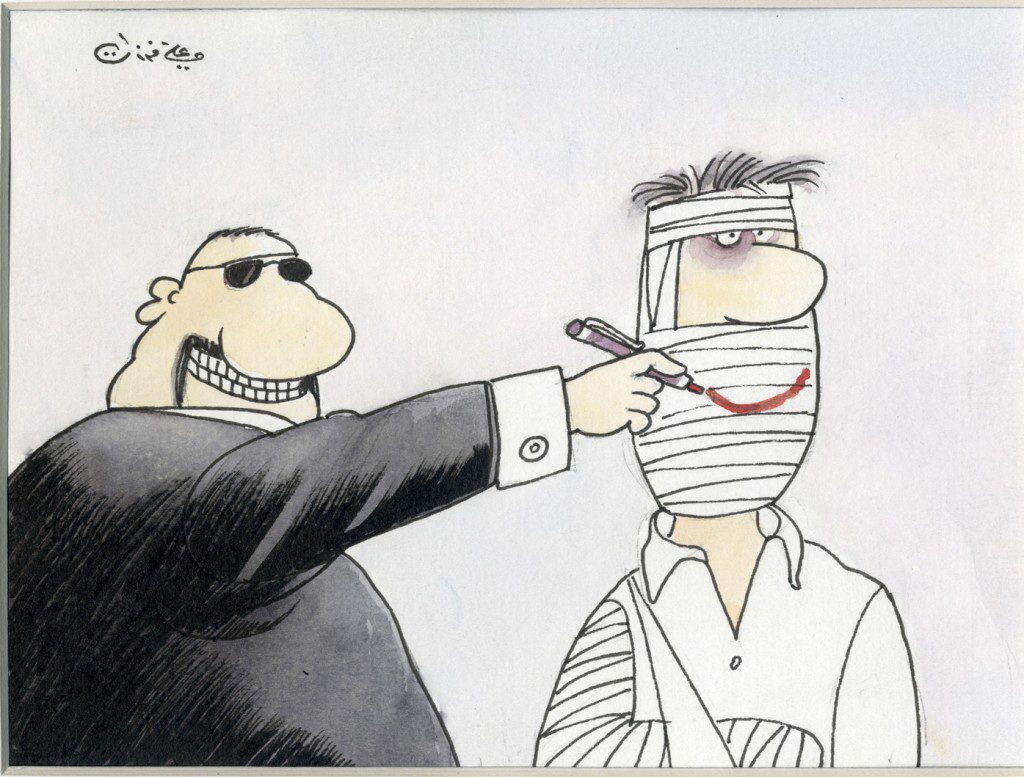
Ferzat must have anticipated that his actions might lead to violent repercussions. Last August, pro-regime forces viciously assaulted him and broke both his hands. During the attack, one of the assailants yelled at him, “Bashar’s shoe is better than you.” Article 376 of the Syrian penal code makes it an offence to insult or defame the president, and carries a six-month to three-year prison sentence.
The most lauded cartoonist of the Arab spring, Ferzat has won countless international prizes — including this year’s Index Freedom of Expression Award for the Arts. For more than 40 years, he has been delivering his own scathing messages to dictatorship. Published daily in al Thawra (the Revolution) newspaper in Damascus for a decade, he was a thorn in the side of Hafez al Assad. In the early noughties, the launch of his satirical newspaper al Doumari (the Lamplighter) was considered a hopeful sign in the nascent presidency of Hafez’s heir. Last December, when Bashar al Assad was asked about the attack on Ali Ferzat by the American news commentator Barbara Walters, he responded, “Many people criticise me. Did they kill all of them? Who killed who?’” Such comments made little sense and attest to Ferzat’s power, whether convalescing in a hospital bed or through his drawings.
There are two cartoons by Ferzat embedded in my own visual consciousness of Syria during years of visiting and writing about the country. The first is a drawing of a man whose head has been sliced and popped open at the airport. Instead of searching the luggage on the rack, a uniformed authority figure inspects the contents of the man’s brain. The other is of a dismembered prisoner hanging in a cell, body parts everywhere, while the jailer sits on the floor, sharp implements to hand, crying over a television soap opera. Both of them were a comment on the secret life that routinely takes place in Syria, the self-censorship that is sometimes needed to survive and the ongoing activities inside prisons that are rarely officially acknowledged in the state media.
Speaking the truth
In a recent exhibition of Ali Ferzat’s work at the MICA gallery in London, there were numerous examples of his coded messages: the armchair of salat (representing ruling power), the shortened ladder to suggest the gulf between the political elite and the nobodies (sometimes in a hole) or the ever busy authority figure waving a roll of toilet paper like a flag. The messages are inescapably clear but their target is not always what one might expect. In one colourful drawing, a man is trying to pluck fruit from a tree, but the three ladders on which he is standing have been laid horizontally, not vertically. Pausing beneath this picture, Ferzat points out: “Yes, I always speak truth to power. Sometimes it’s not only the president to be blamed but the people too.” The gallery, usually closed at the weekend, was filled with Syrians and their families within minutes of its unscheduled opening. Everyone, from grown men to children of all ages, photographed the cartoons on the walls with their mobile phones.
Ferzat’s unique visual vocabulary, developed in extreme circumstances, has had an unexpected reach:
To survive and get around censorship, my caricatures had to be speechless and rely instead on symbols. That gave them an international aspect I did not intend in the first place. So I managed to get the voice of people inside Syria to the outside, through channels of common human interest.
During his stay in London in the spring, Ferzat received good news. There is an interest in reviving al Doumari, with plans to publish it in exile in Dubai and, ultimately, hopefully back home as well. One gets the impression that no matter where Ferzat is — he currently resides in Kuwait because his family thinks it is too dangerous for him to be in Damascus — living away from the revolution has been frustrating. He spends most nights watching the Arabic news channels and drawing until the early hours. His right hand, which was fractured in the attack last summer, remains a little stiff, although that is not evident in the first two cartoons he drew when he was able to move his fingers. One shows an armoured Trojan warhorse with marauding tanks for hooves. The second is, again, a tank poised on its back wheels, ready to crush a lone green shoot sprouting from the ground.
False springs
The Syrian people are a major influence on his work. “Drawing is first of all a means and not a purpose in itself,” he says.
The artist is always the one who produces an idea, but if that person is not living within his community then how can he reflect what his community is going through? Art is about being with your own people and having a vision of what they need. You can’t sit in your room isolated behind your window and draw about life — it doesn’t work like that.
The revolution was sparked in March 2011 when young graffiti artists in Deraa, between the ages of nine and 15, were arrested and tortured for writing government slogans on the walls. The sale of spray paint is now banned in Syria unless ID papers are shown.
There have been many false springs in the country’s turbulent political history. A decade ago, and just a few months after Bashar al Assad assumed the presidency, Syrian artists and intellectuals were hopeful that change was possible in their country, a sentiment that began in Ferzat’s case when Bashar al Assad, a “tall dude with a large entourage”, walked into his exhibition filled with censored cartoons. (Ferzat always shows banned cartoons in his exhibitions.) When the new president asked Ferzat how he might be able to gauge popular opinion, the cartoonist urged him to simply talk to the people. Eventually Bashar telephoned him and said he was having a Pepsi with ordinary folk in the street. This was during the so-called Damascus spring of the early noughties, when the regime was courting artists and intellectuals. Imbued by optimism in 2001, Ferzat started his satirical newspaper al Doumari, but as the mood of the political elite reverted to tried and trusted methods, so did the fortunes of his weekly. By the time it closed in 2003, 105 issues later, he had survived two assassination attempts that were never investigated. Thirty-two court cases had been filed against the newspaper and advertisers had stopped advertising.
An incredible heritage: satire in the Middle East
Historically, cartoonists have been astute in their circumvention of censorship. As Fatma Müge Göçek has shown, under the Ottoman press laws of the early 1900s, they sent erasable drawings to the censors and, after approval, substituted other images in their place. Newspapers at that time also appeared with black boxes where a cartoon had been censored. As the gap widened between official pronouncements and reality – or as Václav Havel once said, ‘People know they are living a lie’ – caricatures became an important means of expression in the Middle East. Now cyberspace provides a comparatively safe haven for pictures and ideas that cannot be expressed in print.

Editorial cartooning, like journalism, is considered a western invention, but the convention of satire in the Middle East is as old as the stories of Alf Laila wa Laila (A Thousand and One Nights). Ferzat’s peers include the Egyptian Baghat Othman, who parodied Sadat, Palestinian Naji al Ali, creator of the Palestinian barefoot boy Hanzala (with his back always to the reader in rejection of the world around him) and Algerian Chawki Amari, now in exile in Paris after serving a three-year sentence in his country for drawing the country’s flags in a cartoon that was seen as ‘defacing’ a national symbol. The Syrians also bring something new to the mix, which springs from a sense of humour coloured by the experience of dictatorship, coupled with sexual innuendo. This blend is nicely demonstrated by a joke from the 1980s that is still pertinent, as recently told to me by a political activist.
A guy used to talk about the president. The mukhabarat, secret police, picked him up and started beating and torturing him. They told him, ‘Stop making jokes about the president. Stop talking about the president. You can tackle whatever issues you want, but in the end you always have to say: this has nothing to do with the president. The president is not aware of this.’ So the minute the guy is released, he sees his family waiting by the door and says, ‘Have you heard, the wife of the president is pregnant and the president has nothing to do with it. He’s not even aware of it.’
Even in his comic strips for juveniles, Ferzat has challenged traditional sensibilities in Syria, a country known for channelling propaganda through state-sponsored children’s publications. Ferzat was 26 years old when he created ‘The Travels of Ibn Battuta” for the popular Usama magazine, published in 1977. In the strip, the famous medieval Arab traveller Ibn Battuta is depicted with a moustache and beard, wearing a turban in the shape of the globe. Ferzat demystifies Ibn Battuta by drawing Muhammad Ali, Omar Sharif and the pop singer Abdel Halim Hafiz, with a turban globe on their heads; as avatars of Ibn Battuta, they respectively box, hug a leading lady and sing. Later in the strip, as the historic traveller pulls his donkey into the present day, his size shrinks, suggesting he is overwhelmed by modern life.
A letter sent to the editor of Usama complained about this portrayal of Ibn Battuta. Ferzat did not use one of the traditional Arab figures of ridicule such as the poet Abu Nuwas or the folk character Juha as his fumbling protagonist, but instead a notable historical personage, which the letter writer found highly insulting. This was at a time when the magazine was already starting to change, and was publishing less controversial material, as Allen Douglas and Fedwa Malti-Douglas show in their study of Arabic comic strips.
Self censorship, survival and living without boundaries
Originally from a Sunni Muslim family in Homs, Ferzat describes freedom of the press as “a responsibility”. He stresses:
It’s not as if I should do whatever I feel like doing, regardless of the consequences. It is a matter of moral commitment at the end of the day and varies between countries, depending on the culture and civil liberties. You have to find the right balance. Some newspapers have no obligation, not even morally, and they refrain from nothing and then call it ‘freedom’. Meanwhile other newspapers censor human interest stories. I see both as bad — whether too much suppression in the name of commitment, or too much unethical commitment in the name of freedom. They are both the same.
During prolonged periods of dictatorship, there have been unexpected chinks in the wall of silence, which Lisa Weeden outlines in her tour de force Ambiguities of Domination. One way ordinary Syrians thwarted the cult of Hafez al Assad that pervaded their daily lives was in their choice of newspapers. Throughout the 1970s, al Thawra published a daily editorial cartoon by Ferzat. When he was dropped from the newspaper, al Thawra experienced a 35 per cent drop in sales and was forced to ask the cartoonist to return. Ferzat’s stories about his days there are particularly amusing and they reveal just how much leeway can exist in what at first glance appears to be a monolithic system. In some instances, the offending cartoon would be published in the paper. Then the abusive phone calls from the minister of information would begin.
Ferzat continues:
They came with this new procedure. First the editor-in-chief had to look at the caricature. If he approved it, he had to send it to the general manager. If he approved it, or if he found it controversial and difficult to understand, he had to send it to the minister of information. Take into consideration that the minister of information was a bit of an ass, he would say ‘Yes’ because he didn’t understand it and the next day the people would get the meaning because it only took commonsense. Suddenly the angry phone calls would start all over again.
According to Italian visual critic Donatella Della Ratta, Bashar al Assad’s Syria is ruled by what she calls “a whispering campaign” waged by competing elites, the secret police, the official media and finally the president and his inner circle. All of the different factions are involved in censorship: it takes many pillars of society to control the flow of information and ideas in a totalitarian state.
In such a society, what is the difference between self-censorship and survival for someone like Ferzat? “What I can tell you is that I have no boundaries,” he says.
I don’t have a censor or a policeman in my head before I draw. However, it is not requested of fedayeen — freedom fighters — to be suicidal. As an artist, I’m not going to go and find a landmine and sit on top of it. I invented the symbols that actually manipulate the censor and survive the dangers of punishment. I put simple codes and symbols in my drawings, and anyone who has the capacity to notice things would understand them. That is what I do to secure myself and not be suicidal.
He concludes: “At the end of the day, my drawings and caricatures are part of the daily culture of the street. I want to represent the consciousness of the street, of the people, and I do, and that gives my work value.”
As Ferzat and the graffiti artists of Deraa, who sparked a revolution over a year ago, have shown: Sharpie pens and spray paint can be the most effective tools against a brutal regime.

Malu Halasa is a writer and editor. Her books include The Secret Life of Syrian Lingerie (Chronicle Books)
This article appears in the new edition of Index on Censorship. Click on The Sports Issue for subscription options and more

29 Feb 2012 | Awards
Recognising artists, filmmakers and writers whose work asserts artistic freedom and battles against repression and injustice
Voina, performance artists, Russia
 Voina, meaning “War”, is a collective of radical Russian anarchist artists who combine political protest and performance art.
Voina, meaning “War”, is a collective of radical Russian anarchist artists who combine political protest and performance art.
Voina’s carries out actions directed against the authorities. In June 2010, members painted a 65-metre phallus on a drawbridge in St Petersburg which, when raised, faced the city headquarters of the federal security service.
Voina members Vorotnikov and Leonid Nikolayev were imprisoned from November 2010 to February 2011 in connection with an anti-corruption protest and, in July 2011, Russian police issued an international arrest warrant for Vorotnikov. A warrant for the arrest of fellow artist Natalia Sokol was issued in December 2011.
Ai Weiwei, artist, China
 AiWeiwei is a Chinese artist and activist whose work incorporates social and political activism. He has investigated corruption and cover-ups and openly criticised the Chinese government’s record on human rights.
AiWeiwei is a Chinese artist and activist whose work incorporates social and political activism. He has investigated corruption and cover-ups and openly criticised the Chinese government’s record on human rights.
Ai’s 81-day detention in 2011 caused international uproar. He was arrested in April, alongside several of his friends and colleagues. Since the Chinese authorities released him on bail in June 2011, he has been fined $2.4 million in back taxes and penalties. Though officials arrested Ai for alleged economic crimes, supporters say he was punished for his activism and vocal critiques of the government. He paid a $1.3 million bond with loans from supporters, who contributed online and in person and even throwing cash over the walls of his studio in Beijing.
In November 2011, after Ai announced that authorities were investigating his cameraman for pornography in connection with photos that featured the artist and four women naked, internet users responded tweeting nude photos of themselves in support.
Ali Ferzat, cartoonist, Syria
 Syrian cartoonist Ali Ferzat has been called “an icon of freedom in the Arab world”. He has spent decades ridiculing dictators in more than 15,000 caricatures. His depictions of President Assad and the police state have helped galvanise revolt in Syria.
Syrian cartoonist Ali Ferzat has been called “an icon of freedom in the Arab world”. He has spent decades ridiculing dictators in more than 15,000 caricatures. His depictions of President Assad and the police state have helped galvanise revolt in Syria.
In August 2011, Ferzat was wrenched from his vehicle in central Damascus by pro-Assad masked gunmen who beat him badly and broke his hands. Passers-by found Ferzat dumped at the side of a road; his briefcase and the drawings inside it had been confiscated by his attackers.
Ferzat earned regional and international recognition in the 1980s with stinging cartoons of officials, autocrats and dictators including Saddam Hussein and Muammar Gaddafi. Saddam Hussein called for Ferzat’s death in 1989 after an unfavourable portrait of him was exhibited in Paris and Ferzat’s cartoons have been banned in numerous Arabic countries.
Min Htin Ko Ko Gyi, poet, Burma
 Min Htin Ko Ko Gyi, a poet, filmmaker and screenwriter, co-founded Burma’s inaugural Arts of Freedom Film Festival, which took place in early January 2012.
Min Htin Ko Ko Gyi, a poet, filmmaker and screenwriter, co-founded Burma’s inaugural Arts of Freedom Film Festival, which took place in early January 2012.
Burmese citizens were invited to create a short film on the theme of freedom. Despite the state media’s refusal to cover the announcement, Ko Ko Gyi and his organisers received 188 submissions. Thousands gathered in Rangoon under the banner “Free Art, free thought, freedom”, to watch the selected films. More than 7,000 attendees voted for Cut This Scene to win one of five awards. The film is a satire of a government censorship committee struggling to set the criteria by which to censor films.













