27 May 2016 | About Index, Azerbaijan, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News
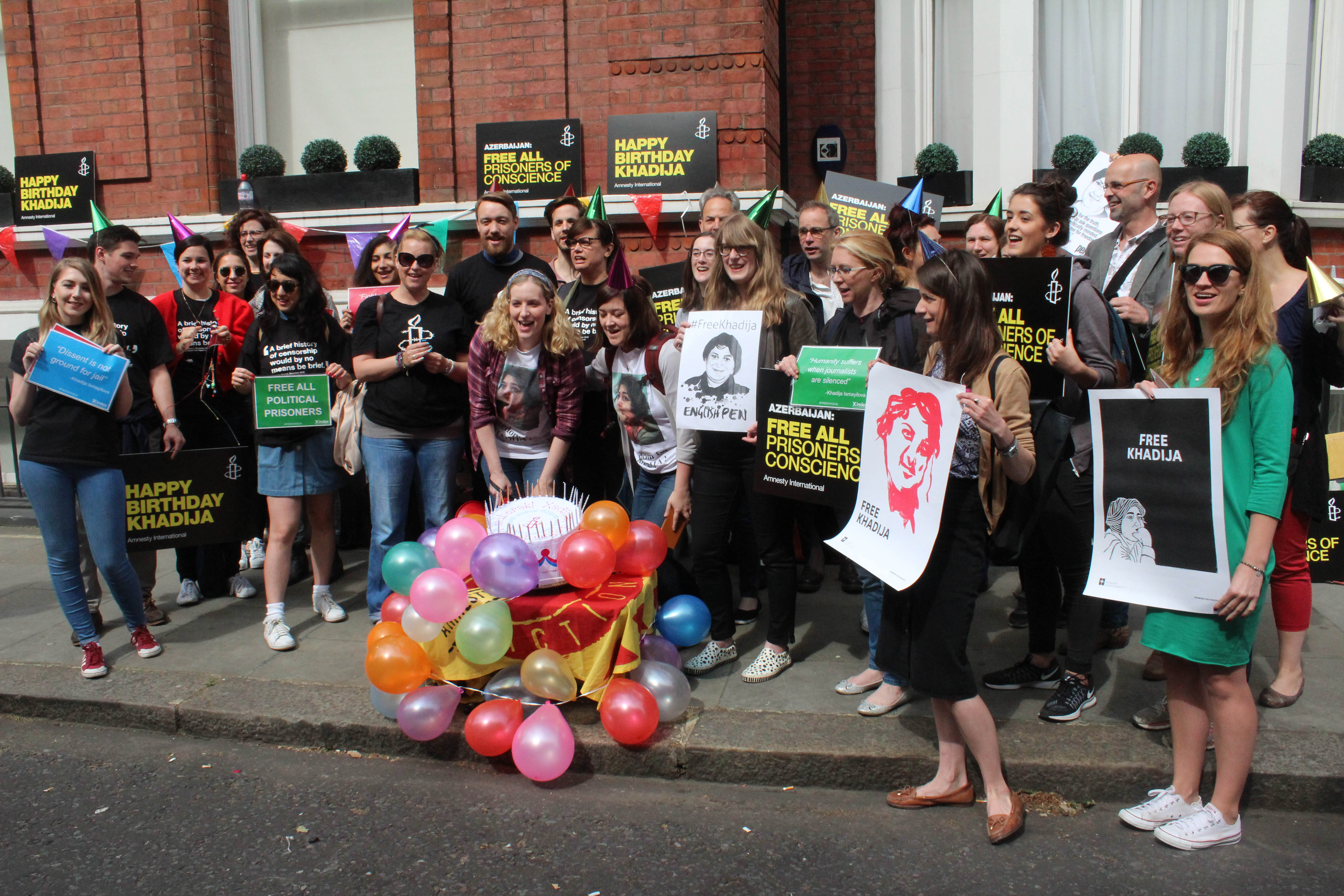
Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
Azerbaijani investigative journalist Khadija Ismayilova may have been released from prison on Wednesday, but two trumped-up charges against her — illegal entrepreneurship and tax evasion –remain. Her seven-and-a-half-year jail sentence has only been reduced to a three-and-a-half-year suspended term and she isn’t free to leave the country.
Today is Ismayilova’s 40th birthday and to mark the occasion, protesters gathered at 40 different demonstrations from around the world, not just to celebrate, but to call for all charges against her to be quashed. Index joined other members of the Sports for Rights coalition at the Azerbaijani embassy in London (see above).
“Let’s take a moment to celebrate the work that’s been done by this remarkable woman,” Rebecca Vincent, the co-ordinator of the Sport for Rights campaign, told demonstrators.
Currently, around 70 political prisoners — including journalists, bloggers, activists and religious followers — sit in Azerbaijani jails, and Vincent called on protesters to sustain their focus on all of them. “That’s what Khadija has asked for for her birthday,” she said.
Seymur Hezi is an Azerbaijani journalist serving a five-year prison sentence on charges of “aggravated hooliganism”. Hezi, who contributed to the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award-winning newspaper Azadliq, was sentenced on 29 January 2015. He was arrested on 29 August 2014 following an altercation in which the journalist was defending himself from a physical assault and harassment, according to his lawyers. “His case doesn’t get enough international attention, possibly because he is not an English speaker and not well networked,” Vincent said.
Other political prisoners include Ilgar Mammadov, the opposition politician who leads Azerbaijan Republican Alternative Movement, who has been in jail for over three years, and Ilkin Rustemzade, the activistt originally jailed following his Harlem Shake video filmed in Baku.
On the same day Ismayilova was released, two more political prisoners, a youth activist and a journalist, were arrested.

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
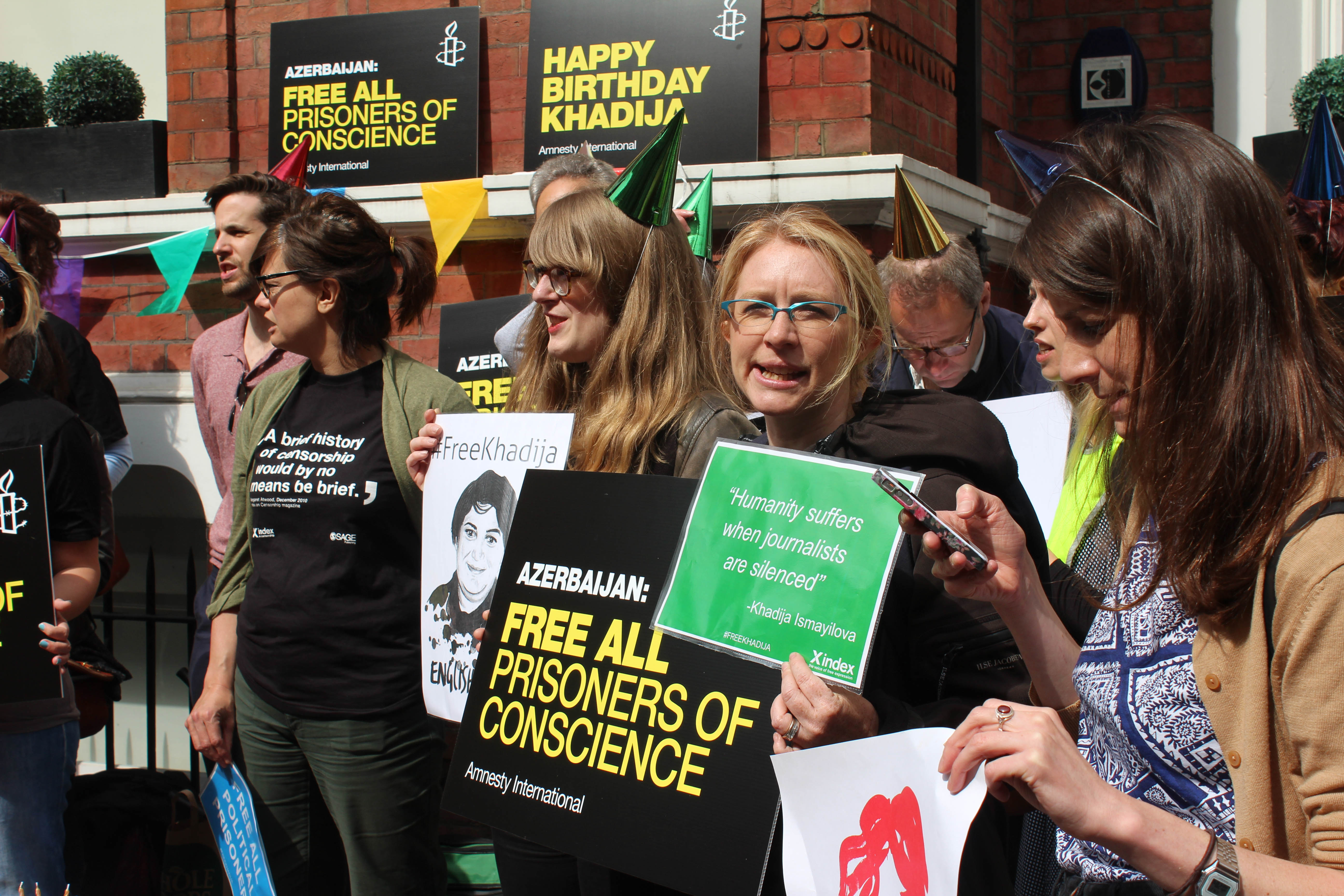

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen

Protest for Khadija Ismayilova, Azerbaijan embassy, London. Credit: Cat Lucas, English Pen
Many more protests took place today. Here are some of them:
Paris, France
Washington DC, USA
Brussels, Belgium
Oslo, Norway
16 May 2016 | Art and the Law Commentary, Artistic Freedom Commentary and Reports, Campaigns -- Featured, mobile, News
Julia Farrington, associate arts producer, Index on Censorship, participated in the Theatre UK 2016 conference on 12 May 2016. This is an adapted version of her presentation.
In January 2013 I organised a conference called Taking the Offensive for Index on Censorship, in partnership with the Free Word Centre and Southbank Centre. The conference was held to debate the growth of self-censorship in contemporary culture, the social, political and legal challenges to artistic freedom of expression and the sources of these new challenges.
The report from the conference concluded that censorship and self-censorship are significant influences in the arts, creating a complex picture of the different ways society controls expression. Institutional self-censorship, which many acknowledged suppresses creativity and ideas, was openly discussed for the first time.
Lack of understanding and knowledge about rights and responsibilities relating to freedom of expression, worries about legal action, police intervention and loss of funding, health and safety regulations, concern about provoking negative media and social media reaction, and public protests are all causing cultural institutions to be overly cautious.
One speaker at Taking the Offensive suggested that we are fostering a culture where “art is not for debate, controversy and disagreement, but it is to please”.
There is above all, unequal access to exercising the right to artistic freedom of expression, with artists from black and minority ethnic encountering additional obstacles.
Many felt that far greater trust, transparency and honesty about the challenges being faced need to be developed across the sector; dilemmas should be recast as a necessary part of the creative process, to be shared and openly discussed, rather than something to keep behind closed doors. This will make it possible for organisations to come together when there is a crisis, rather than standing back and withholding support: “if we collectively don’t feel confident about the dilemmas we face how can we move on with the public?”
I think there have been significant changes in the three years since the conference and, whilst I think the same challenges persist, there have been some really positive moves to tackle self-censorship within the sector. The growth of What Next? has created precisely the platform to debate and discuss the pressures, dilemmas and controversies that the conference identified. What Next? has produced guidance on navigating some of these issues and is developing more resources on how organisations can support each other when work is contested.
Index on Censorship responded to the clear call from the conference for the need for guidance about legal rights and responsibilities if we are to create a space where artists are free to take on complex issues that may be disturbing, divisive, shocking or offensive.
We have published information packs around five areas of law that impact on what is sayable in the arts: Public Order, Race and Religion, Counter Terrorism, Child Protection and Obscene Publications. They are available on the website under our campaign Art and Offence. These have been well received by the sector and read by CPS and police and we are developing a programme of training which will, if all goes well, include working with senior police officers.
At the same time, pressures from outside the sector have intensified.
The role of the police in managing the public space when controversial art leads to protest has come into sharp relief over the past two-three years where they have repeatedly “advised” venues to remove or cancel work that has caused protest or may cause protest.
I did a case study on the policing of the picket of Exhibit B at the Barbican in London which is available on the Index website; and in the same year, the Israeli hip hop opera the City was closed in Edinburgh on the advice of the police.
More worryingly the police “advice” has also led to the foreclosing of work that is potentially inflammatory – as in Isis Threaten Sylvannia an art installation by Mimsy, that was removed from an exhibition called Passion for Freedom from the Mall Gallery last year.
With the removal of Isis Threaten Sylvania, we see a shift from the police advising closure following protest to the police contributing indirectly or directly to the decision to remove work to avoid protest.
In this case freedom of expression was actually given a price — set at £7,200 per day for the five days of the exhibition — the price set by the police for their services to guarantee public safety.
The police took the view that a perfectly legal piece of art, which had already been displayed without incident earlier in the year, was inflammatory. And in the balance of things as they stand, this opinion outweighs:
- the right of the artist to express him or herself;
- the organisation’s right to present provocative political art;
- the audience’s right to view it;
- and those that protest against it, the right to say how much they hate it, including when that means that they want the art removed.
This new chapter in the policing of controversial art sets alarm bells ringing and represents a very dangerous precedent for foreclosing any work that the police don’t approve of.
But going against police advice is problematic.
In Index’s information pack on Public Order we asked our legal adviser, working pro bono, questions that many artists and arts managers are concerned about:
What happens if police advise you not to continue with presenting a piece of work because they have unspecified concerns about public safety – and yet tell you it is your choice and they can only advise you?
The artist would in principle be free to continue with the work. It would be advisable, however, to ensure that the reasons held by the police were understood. It may also be prudent to take professional advice…
And then what responsibilities for safety do employers have to staff and the public in relation to continuing with an artwork that has been contested by the police?
An organisation also has duties to their employees and members of the public on their premises. These duties may extend to making an organisation liable in the event of injury to a person resulting from the unlawful act of a third party if, for example, that unlawful act was plainly foreseeable – in other words the police have given their warning.
What are the options for an arts organisation to challenge police advice at the time of the protest itself?
If the organisation believes that it has grounds to challenge police directions to avoid a breach of the peace, it can seek to take legal action on an urgent basis. Realistically…legal action will not be determined until some time later and until it is determined by the courts, the organisation and/or its members or employees would risk arrest if they do not comply with police directions.
So – what starts out as police advice which implies genuine choice, on closer inspection transforms into a Hobson’s Choice where failure to follow that advice could lead to arrest.
On this evidence, both self-censorship and direct censorship are the undesirable outcomes of this as yet unchallenged area of policing.
But the Crown Prosecution Service has read and approved the packs and our law packs are in the system with the police.
The ideal policing scenario is to keep the space open for both the challenging political art and the protest it provokes. Both are about freedom of expression, what we have to avoid is the heckler’s veto prevailing.
Going back to other recent examples of censorship — questions remain about the role of the police in the decision to cancel Homegrown the National Youth Theatre production of a play about the radicalisation of young Muslims by writer Omar El-Khairy and director Nadia Latif. This was followed earlier this year by the presentation, without incident, of Another World: Losing our Children to Islamic State at the National Theatre, play on similar themes by Gillian Slovo and Nicolas Kent.
I mention Another World because it is important to state the obvious, that all the work that has been contested by the police and been cancelled, relates to work about race and religion and the majority of artists involved in work that has been foreclosed are from black and minority ethnic communities.
Looking through the lens of freedom of expression, each case of censorship gives a valuable opportunity to view a specific snapshot of relationships within society and to analyse the power dynamics operating there, both directly around the censored work — whose voices are and aren’t being heard in the work itself, and in the field and context in which the work is taking place and again looking at who is in control, who decides what voices are heard. I don’t have time here to go into an analysis of each case, but what emerges is that freedom of expression is, as it stands, a biased affair in the UK and I believe will remain so while our society and our culture are not equal.
As well as these new cases of censorship that we have seen since the 2013 conference, we have also seen new government policy, legislation and regulations which place increasingly explicit controls on what we can say and have a chilling effect on many areas of expression and communication, and interaction with government.
Many campaigners and charities see the Criminal Justice and Courts Act 2015 as designed to deter charities from intervening in judicial reviews — the most important legal channel we have to call authorities to account; the Investigatory Powers Bill, better known as the Snoopers’ Charter gives the surveillance state more powers; the Prevent Strategy requires us to police each other – surveillance and policing our neighbours — two nasty authoritarian tactics, and most recently the anti-advocacy clause would effectively ban organisations from using government funds for lobbying — stifling dissent. It was due to come into law on 1 May but the consultation period was extended and it might be kicked into the long grass.
The government has made it clear that it wants us to see ourselves predominantly if not exclusively as businesses and in response we have successfully made the case that the arts contribute massively to the economy.
But we know we are so much more. The arts are a vital, at best magnificent and effective player in civil society — especially when you define civil society as “a community of citizens linked by common interests and collective activity”.
With our core values and freedoms under attack, the arts and other civil society bodies are responding. The discussion about the role of the artist in taking on the big issues in society — from climate change to the refugee crisis — has, from where I stand, definitely intensified and gone up the agenda over the past three years, both here and internationally, as the pressure on our freedoms and values also intensifies domestically and internationally.
To fully participate in society and to create art that calls power to account, we need to continue to identify, analyse and tackle the causes of self-censorship within the sector, and stand together to enter into dialogue with the various agents of control that we identify in the process.
Art can help us imagine and bring about a more equal and just future.
16 Mar 2016 | Campaigns, European Union, Statements, Turkey, Turkey Letters
The President of the European Council
Donald Tusk
General Secretariat of the Council of the European Union
Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat 175
B-1048 Bruxelles/Brussel
Belgique/België
CC:
Federica Mogherini, High Representative of the European Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy
Stavros Lambrinidis, EU Special Representative for Human Rights
Elmar Brok, Chair of the European Parliament Committee on Foreign Affairs
Johannes Hahn, Commissioner for European Neighbourhood Policy and Enlargement Negotiations
Martin Schulz, President of the European Parliament
Dear President Tusk,
We, the undersigned press freedom and media organisations, are writing ahead of the upcoming meeting between EU leaders and Ahmet Davutoğlu, Prime Minister of Turkey, to express our concern over the collapse of media freedom in Turkey.
In the past six months, we have recorded 50 incidents in clear breach of international standards with regards to media freedom and pluralism in the country.[1] These violations include the recent government takeovers of the Feza media group and the Koza İpek Group; the prosecution and jailing of daily Cumhuriyet editor-in-chief Can Dündar and Ankara bureau chief Erdem Gül on politically motivated charges of terrorism, espionage and revealing classified information; the police raids of Bugün TV; the assault of journalist Ahmet Hakan; and the blocking of Dicle News Agency’s website.
Many of these violations took place against the backdrop of the migration and refugee crisis or are related to reporting on sensitive issues such as the banned Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) or Turkey’s security operations in the south. Hence we believe the Council has the mandate to address these violations during the specific working session on EU-Turkey cooperation.
This mandate stems from the Council’s commitment to the rights to freedom of expression including freedom of the press, which was reaffirmed when adopting the EU Human Rights Guidelines on “freedom of expression online and offline” on 12 May 2014.[2] By doing so, the Council pledged that “through its external policy instruments, the EU intends to help address and prevent violations of these rights in a timely, consistent and coherent manner.”
The guidelines also state that “all appropriate EU external financial instruments should be used to further protect and promote freedom of opinion and expression online as well as offline.”
While we welcome the fact that you discussed the situation of the media in Turkey with Prime Minister Davutoğlu last week, we believe the EU must not reach a deal without a specific conditionality clause that requires Turkey to improve the environment for freedom of expression and freedom of the media.
When meeting Prime Minister Davutoğlu on 18 March 2016, you have the unique opportunity to not only discuss the press freedom situation in Turkey, but to bring forth concrete measures that Turkey ought to take in order to start reversing its unrelenting crackdown on the media. Without taking these measures Ankara cannot and must not be considered a trustful strategic partner for the European Union. Specifically, we ask that you make any EU-Turkey agreement conditional on the release of the more than dozen journalists currently jailed for their work;[3] the immediate return of the media outlets belonging to the Feza and Koza İpek groups to their rightful owners and editorial boards; and the abandonment of Turkey’s official practice of using vague anti-terror laws to equate press coverage with criminal activity.
At a time when the very essence of the European Union is questioned, it is critical to show unity and coherence over one of its core foundations: human rights, and in particular freedom of opinion and expression, which are fundamental elements of democracy.
Yours sincerely,
Jodie Ginsberg, Chief Executive, Index on Censorship
David Diaz-Jogeix, Director of Programmes, Article 19
William Horsley, Vice President and Media Freedom Representative, Association of European Journalists
Nina Ognianova, Europe and Central Asia Program Coordinator, Committee to Protect Journalists
Jo Glanville, Director, English Pen
Mogens Blicher Bjerregård, President, European Federation of Journalists
Barbara Trionfi, Executive Director, International Press Institute
Carles Torner, Executive Director, PEN International
Christophe Deloire, Executive Director, Reporters Without Borders
Deborah Bonetti, President, Foreign Press Association in London
[1] www.mappingmediafreedom.org (verified reports from 1 October 2015 to 14 March 2016)
[2] EU Human Rights Guidelines on Freedom of Expression Online and Offline, adopted by the Council on 12 May 2014 (Foreign Affairs Council meeting)
[3] At least 28 journalists jailed in Turkey (last update: 26 February 2016). Source: European Federation of Journalists and affiliates, http://europeanjournalists.org/journalists-in-jail-europe/
12 Feb 2016 | mobile, News, Youth Board
Index on Censorship recently appointed a new youth advisory board who attend monthly online meetings to discuss current freedom of expression issues and complete related tasks. As their first assignments they were asked to provide a short bio to introduce themselves, along with a photograph of them holding a quotation highlighting what free expression means to them.
Simon Engelkes 
I am from Berlin, Germany, where I study political science at Free University Berlin. I have worked as an intern with Reporters Without Borders and RTL Television, which made me passionate about the importance of freedom of speech.
I believe that freedom of expression forms an important cornerstone of any effective democracy. Journalists and bloggers must live without fear and without interference from state or economic interests. Unfortunately, this is not the case. Journalists, authors and everyday citizens are imprisoned or killed by radicals, state agencies or drug cartels. Raif Badawi, James Foley, Khadija Ismayilova, Avijit Roy – the list is endless.
We need to remind ourselves and the powerful of today, that freedom of expression as well as freedom of information are basic human rights, which we have to defend at all costs.
 Mariana Cunha e Melo
Mariana Cunha e Melo
I am from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. I graduated from law school in Rio and I have a degree from New York University School of Law. My family has taught me about the dangers of censorship and dictatorship, so I have always been interested in studying civil rights. This was the main reason I decided to study law.
I grew up listening to stories about the media censorship in Brazil during the military dictatorship. The fight against the ghost of state censorship has always sounded very natural to me – and, I believe, to all my generation. When I finished law school I found out that the new villain my generation has to face is the censorship based on constitutional values. The argument has changed, but the censorship is not all that different. So I decided to dedicate my academic and my professional life as a lawyer to fight all sorts of institutionalised censorship in Brazil.
 Ephraim Kenyanito
Ephraim Kenyanito
I was born and raised in Kenya, and I am currently working as the sub-Saharan Africa policy analyst at Access Now, an international organisation that defends and extends the digital rights of users at risk around the world. My role involves working on the connection between internet policy and human rights in African Union member countries. I am an affiliate at the Internet Policy Observatory (IPO) at the Center for Global Communication Studies, University of Pennsylvania. I also currently serve as a member of the UN Secretary General’s Multi-stakeholder Advisory Group on internet governance.
The reason why I have always been passionate about protecting the open internet is that it is a cornerstone for advancing free speech in the post-millennium era and there is a great need to build common ground around a public interest-oriented approach to internet governance.
Emily Wright
I grew up in Portugal, and I am now based between London and Bogotá, Colombia. I am a freelance filmmaker and journalist. Working in documentary production and community-based, participatory journalism informed a growing interest in journalistic practices, freedom of expression and access to information.
I believe that one of the greatest threats to freedom of expression is the flagrant violation of civil liberties under the banner of national security. The war on terror, underscored by Bush’s declaration “You’re either for us or against us”, has collapsed the middle ground, suppressing any struggles that challenge that statement. Freedom of expression has become a pretext for silencing those who have the least access to it; those who do not fall in line with the global order’s supposed defence of freedom against barbarism and obscurantism.
 Mark Crawford
Mark Crawford
I’m originally from Birmingham, and now a postgraduate student at University College London, specialising in Russian and post-Soviet politics. This has inevitably educated me on the pressures exerted upon freedom of expression in Russia, whose suffocated and disenfranchised opposition journalists I am currently investigating.
Hostility to free expression has become a staple of my university life. Rather than developing a coherent set of ideologies to challenge toxic values in the open, it has become mainstream for students of the most privileged universities in the world to veto them on behalf of everyone else, no-platforming and deriding free speech.
I am convinced that there is no point fighting for an egalitarian society if any monopolies over truth are permitted. Freedom of speech is, therefore, something I am keen to promote in whatever small way I can.
Madeleine Stone 
My home is in south-east London but I spend most of my time in York, studying for my bachelor’s degree in English and related literature. I am currently the co-chair of York PEN, the University of York’s branch of English PEN, and a founding member of the Antione Collective, a human rights-focused theatre company.
Studying literature from across the globe has introduced me to issues of freedom and censorship, and the devastating effects censorship can have on national progress. Freedom of expression on campuses is hugely important to me as a student and it is currently under threat. Well-meaning individuals are shutting down the open debate that is vital to academic institutions. The only way to fight harmful ideas is to engage them head-on and destroy them through academic debate, not to ban them.
Layli Foroudi 
I am a journalist and student currently studying for a MPhil in race, ethnicity and conflict at Trinity College Dublin. It was studying literary works from the Soviet period during my undergraduate degree in Russian and French at University College London that initially highlighted the issue of censorship for me. The quote I selected, “manuscripts don’t burn”, is from the book Master and Margarita by Russian author Mikhail Bulgakov. He wrote about the hardship that many writers faced as they had to adjust their own writing in accordance with the authority, as well as the fact that not all that is written can be taken to be true.
I think that these themes are very relevant today. Whether people are censored or self-censor out of fear of punishment or of being wrong, limiting freedom of expression results in loss of debate, of exchange and of creativity. Being denied freedom of expression is being denied the right to participation in society.
 Ian Morse
Ian Morse
I have been involved in journalism since I began studying at Lafayette College, Pennsylvania, USA, and have been engaged in press freedom and reporting in three countries since then. I studied in Turkey last spring, where I interviewed and wrote about journalists and press freedom. It motivated me to begin researching and writing on my own about these topics. Now, as I study for a semester in Cambridge in the UK, I continue to talk about and advocate for free speech and press.
I find it absolutely amazing the power words and information can have in a society. It becomes then extremely damaging to realise that some things cannot be published because they conflict with those in power. Free speech is now becoming a hot topic around the world, particularly among youth, and it makes it all the more important to be able to approach freedom of expression critically and objectively.









 Mariana Cunha e Melo
Mariana Cunha e Melo  Ephraim Kenyanito
Ephraim Kenyanito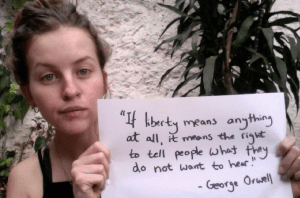
 Mark Crawford
Mark Crawford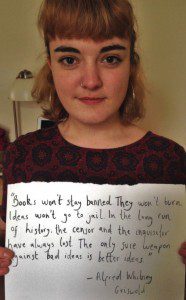

 Ian Morse
Ian Morse