21 Dec 2018 | Croatia, Hungary, Macedonia, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, Montenegro, News and features, Poland, Serbia
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”104453″ img_size=”full” add_caption=”yes”][vc_column_text]Additional reporting by Ada Borowicz, Ilcho Cvetanoski, Lazara Marinković and Zoltán Sipos
Unpatriotic behaviour. Sedition. Being in the pay of shadowy external forces. Faking a neo-Nazi event. These are just a few of the charges that have recently been levelled against independent journalists by pro-government media outlets in several central and eastern European countries.
The opening volley in a sustained campaign of vilification directed at Serbia‘s independent media was fired by the state-owned weekly Ilustrovana Politika at the end of October, with an article that accused journalists who are critical of the government of being “traitors and collaborators with the enemies of Serbia”.
Two weeks later, Ilustrovana Politika followed up with another piece that accused the veteran journalist Ljiljana Smajlović – who has long been critical of the nationalistic legacy bequeathed on the country by its former leader Slobodan Milosević and co-founded the Commission Investigating the Murders of Journalists in Serbia – of complicity in the 1999 NATO bombing of Belgrade.
In mid-December, Ilustrovana Politika’s campaign of character assassination against Smajlović ratcheted up another level with a garish front page depicting her as a Madonna figure with two naked infants bearing the features of Veran Matić, the chairman of the commission, and US Ambassador to Serbia Kyle Scott.
Smajlović has no doubt over what lies behind this tidal wave of denigration, of which she has become the prime target.
History repeating itself?

Editor Slavko Ćuruvija was murdered in 1999.
The long-running trial of four ex-members of the Serbian intelligence service accused of the murder of Dnevni Telegraf editor Slavko Ćuruvija – shot dead in April 1999 a few days after the pro-government Politika Ekspres accused him of welcoming the NATO bombardment – is now in its final stages, and Smajlović is convinced that the current campaign against her is designed to influence the judges in the case.
“The attacks come from the same Milosevic-era editors who also targeted my colleague Ćuruvija as a traitor prior to his assassination,” she told Mapping Media Freedom. “What is also sinister is that they are published and printed by the same state-owned media company that targeted Slavko nearly twenty years ago.”
“The clear implication is that I am the same kind of traitor as he was. How will that affect the judges? Will they fear this is not a good time to hold state security chiefs to account?” she added.
While Smajlović admits that Ilustrovana Politika’s denunciation has made her feel insecure, she insists she is less concerned for her own safety than worried about the consequences for the outcome of the Ćuruvija trial. Quoting Marx’s dictum that “History repeats itself, first as tragedy and then as farce”, Smajlović said. “I hope this is the farce part.”
Laying the blame
In Serbia and other central and eastern European countries, the assignment of responsibility for historic causes of resentment and the potential of these to further divide a polarised public often form the background to attacks on independent journalists by their state-approved colleagues.
The thorny topic of Poland’s relations with Germany during the last century recently gave pro-government media in Poland a chance to accuse independent media of being insufficiently patriotic and even of falsifying facts.

Journalist Bartosz Wieliński was targeted by the head of TVP Info’s news site.
In November, after Bartosz Wieliński, a journalist with the independent daily Gazeta Wyborcza, gave a critical account of a speech made by the Polish ambassador to Berlin at a conference devoted to the centenary of Poland’s independence, the head of the state broadcaster’s news website, TVP Info, accused him of lying and of putting the interests of Germany before those of his own country.
Only a few days before this attack, two media outlets that support Poland’s ruling national-conservative Law and Justice (PiS) party accused the independent US-owned channel TVN of fabricating the evidence on which a report about the resurgence of neo-Nazism in Poland was based.
Since it came to power in 2015, PiS – which has been accused by its critics of tolerating organisations that espouse far-right ideologies – has put pressure on independent media outlets, many of which are foreign-owned, as part of its campaign to “re-polonise” the media, and now appears to be using the public broadcaster and other tame outlets as accessories in this drive.
Willing accomplices
In Hungary, where the government led by Viktor Orbán has succeeded in imposing tight control on all but a few determinedly independent media outlets, a number of loyal publications are available for the purposes of vilification.

2015 Freedom of Expression Journalism Award winner Tamás Bodoky, founder of Atlatszo.hu
In September, a whole raft of pro-government media outlets vied with each other to depict Tamás Bodoky, the editor-in-chief of the investigative journalism platform Átlátszó and winner of the 2015 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award for Journalism, as a “Soros hireling”. Bodoky became the target of a co-ordinated smear campaign after he posted on Facebook a picture of himself taken in Brussels with Dutch Green MEP Judith Sargentini, whose report on the Fidesz government’s infringement of core EU values had formed the basis for the European parliament’s censure motion against Hungary a few weeks earlier.
Another Hungarian journalist, András Dezső, who works for the independent news website Index.hu, also recently came under attack from pro-government media outlets after a Budapest court let him off with a reprimand over a case in which he was alleged to have made unauthorised use of personal information. In an article published before April’s general election, Dezső had cast doubt on the account of a woman who declared on Hungarian TV that she felt safer in Budapest than in Stockholm because of the lower level of immigration in Hungary. The airing of the interview by the public broadcaster was seen as providing support for Fidesz’s anti-immigration stance and aiding its election victory.
A criminal charge was issued against Dezső for “misuse of personal data”, and after he received what was described in the Hungarian media as “the mildest possible punishment”, two pro-government news websites, 888.hu and Origo.hu, accused him of deliberately propagating fake news and seeking to mislead his readers.
Why do they do it?
What motivates those journalists who smear their colleagues who seek to hold power to account?
There does not appear to be a simple answer to this question. While some may vilify fellow journalists to order purely for financial gain (or because of a desire for job security, government-sponsored media outlets generally being on a more secure financial footing than their independent counterparts), some appear to approach the task with at least a measure of conviction.
Ilcho Cvetanoski, who reports on Bosnia, Croatia, Macedonia and Montenegro for Mapping Media Freedom and has observed many smear campaigns over the years, believes that financial and ideological motivating factors are often inextricably intertwined. He points out that two decades on from the armed conflicts in the region, Balkans societies are still deeply divided along ideological and ethnic lines, and many people still find it extremely difficult to accept the right of others to see things differently. Cvetanoski notes that there are many “true believers” who are genuinely convinced that they have a duty to defend their country from the “other” – a group in which they tend to lump critical journalists along with mercenaries, spies and traitors.
Lazara Marinković, who covers Serbia for Mapping Media Freedom, believes that the main motivation there is a need to be on the winning side and to please those in power. “Often they actually enjoy doing it, either for ideological reasons or because they feel more powerful when they are on the side of the ruling party,” she told Mapping Media Freedom. Marinković noted that the majority of Serbian tabloids and TV stations that conduct smear campaigns against independent journalists are owned by businessmen who have close links to President Aleksandar Vučić’s national conservative Serbian Progressive Party (SNS). Vučić began his political career during the Milosević era, when he served as Minister of Information.
In Poland, the divisions in society and the consequent lack of tolerance in political culture have been blamed for the increasing polarisation of the media. Michal Głowacki, a professor of media studies at Warsaw University, told Mapping Media Freedom that journalists take their cue from politicians in failing to show respect for fellow journalists associated with the “other side”. “They even use the same language as politicians,” Głowacki notes.
This is a view echoed by Hungarian journalist Anita Kőműves, a colleague of Bodoky’s at Átlátszó. Kőműves, however, insists that while journalists who work for independent media outlets strive to uphold the principles of journalistic ethics, the same cannot be said of those employed by pro-government outlets. “Some of those serving the government at propaganda outlets think that the two ‘sides’ of the Hungarian media are equally biased and that they are not acting any differently from their counterparts in the independent media sphere. However, this is not true: pro-government propaganda outlets do not adhere to even the basic rules of journalism,” she told Mapping Media Freedom.[/vc_column_text][vc_raw_html]JTNDaWZyYW1lJTIwd2lkdGglM0QlMjI3MDAlMjIlMjBoZWlnaHQlM0QlMjI0MDAlMjIlMjBzcmMlM0QlMjJodHRwcyUzQSUyRiUyRm1hcHBpbmdtZWRpYWZyZWVkb20udXNoYWhpZGkuaW8lMkZ2aWV3cyUyRm1hcCUyMiUyMGZyYW1lYm9yZGVyJTNEJTIyMCUyMiUyMGFsbG93ZnVsbHNjcmVlbiUzRSUzQyUyRmlmcmFtZSUzRQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1545385969139-cb42990e-b3e2-3″ taxonomies=”9044″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
2 May 2017 | Campaigns -- Featured, Macedonia, Statements
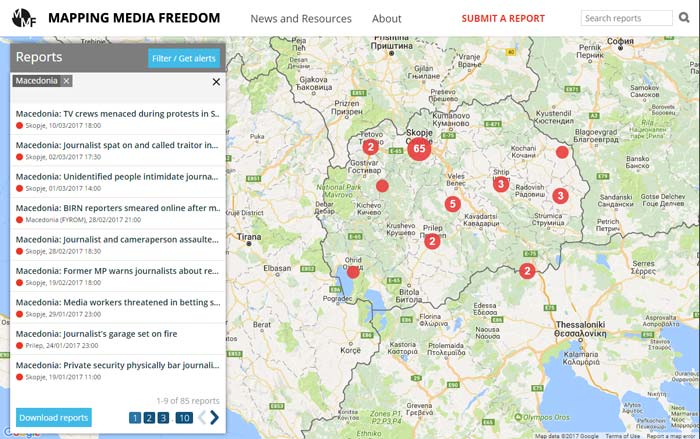
Index on Censorship signed a joint statement by issued after a ECPMF-EFJ-SEEMO-OBCT fact-finding mission to Macedonia, on 25th-28th April regarding rising violence against journalists in Macedonia:
We hereby express our deep concerns about the yesterday‘s violent attacks against journalists in the parliament of the Republic of Macedonia.
From the beginning of 2016 until yesterday at least 21 attacks against journalists in Macedonia have been registered by the Association of Journalists of Macedonia (ZNM), out of a total of several dozens within the last years. All this clearly demonstrates a rising trend in violence against journalists.
The state of media freedom in the country is very worrying. Attacks on journalists are a direct threat to democracy.
On invitation of ZNM and the Western Balkan´s Regional Platform for Advocating Media Freedom and Journalists Safety the European Centre for Press and Media Freedom (ECPMF) conducted a fact-finding mission to Skopje from 25 to 28 April 2017. The delegation, including the European Federation of Journalists (EFJ), South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO) and Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso Transeuropa (OBCT) examined the increased violence against journalists in Macedonia and listened to their experiences.
During the mission, the international delegation so far conducted a total of 13 interviews with 15 representatives of several media outlets, NGO´s, the Agency for Audio and Audiovisual Media Services and the Media Ethics Council. Additionally, the delegation met the Minister of the Interior, Mr Agim Nuhiu.
According to our findings among the main reasons for the increased violence are the following:
- The political climate, anti-media rhetoric and polarisation lead to a highly unsafe environment for journalists.
- There is no political will to ensure conditions for free and independent journalism. State institutions and political stakeholders undertake no responsibility for the protection of journalists.
- The criminal and civil justice systems do not deal effectively with threats and violence against journalists. No implementation of media protection laws and no prosecution of the perpetrators make journalists an easy target.
The signees of this statement condemn any aggression on journalists in Macedonia.
We want to strongly urge the political parties and all related bodies and authorities to prevent further attacks and ensure a safe environment for journalism and freedom of expression. We call on the judiciary and all responsible authorities to stop the ongoing impunity.
- Macedonian authorities must conduct swift and efficient investigations on any single case of attack on physical safety and integrity of journalists. Politicians should refrain from spreading hateful rhetoric that serves violence.
- International conventions protecting human rights and freedom of expression shall be respected.
- The coming ruling coalition and the opposition must comply with Macedonia’s commitment to protect journalism and to guarantee internet freedom. Macedonian authorities must implement without any delay the recommendations of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe on safety of journalists (Recommendation 2016-4) and on Internet freedom (Recommendation 2016-5), adopted on 13 April 2016. Following these standards, any kind of additional state regulation on media content is unacceptable.
- Macedonian authorities must consult for any coming reform in the media sector the legitimate national organisations promoting media freedom and independent journalism: the Council of Media Ethics of Macedonia (SEMM), the Association of Journalists (ZNM), the Trade Union of Journalists (SSNM).
We also call on all journalists to take their role as watchdogs seriously. We encourage them to report and file complaints if they are attacked, intimidated or harassed. They should stand in solidarity with their colleagues, cooperate and support each other.
We, as European media freedom and journalists organisations within the freedom of expression community, stand with our colleagues in Macedonia. We will further observe their situation and raise our voices to support them. There will be a full report on the fact-finding mission in May.
Skopje, 28 April 2017
Signing organisations:
- European Centre for Press and Media Freedom (ECPMF)
- European Federation of Journalists (EFJ)
- Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso Transeuropa (OBCT)
- South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO)
- Association of Journalists of Macedonia (ZNM)
- Western Balkan´s Regional Platform for Advocating Media Freedom and Journalists Safety
This statement is endorsed by the following organisations:
- Ethical Journalism Network
- Index on Censorship
- Journalismfund.eu
- Reporters Sans Frontières / Reporters Without Borders
- SCOOP Macedonia
29 Jul 2016 | Bosnia, Europe and Central Asia, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Poland, Turkey, United Kingdom
Click on the dots for more information on the incidents.
Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
Turkey: Warrants issued for arrest of 89 journalists
Turkish authorities have issued two lists of journalists to be arrested since the 15 July failed military coup attempt in the country. Firstly, on 25 July, authorities issued the names of 42 journalists as part of an inquiry into the coup attempt. Well-known commentator and former parliamentarian Nazli Ilicak was among those for whom a warrant was issued, as was Ercan Gun, the head of news department at Fox TV in Turkey.
Two days later, 27 July, authorities issued warrants for the detention of 47 former executives or senior journalists of the newspaper Zaman. The arrests were part of a large-scale crackdown on suspected supporters of US-based Muslim cleric Fethullah Gulen, accused by Ankara of masterminding the failed coup. The authorities shut down Zaman in March. At least one journalist, former Zaman columnist Şahin Alpay, was detained at his home early on Wednesday.
26 July, 2016 – Media Print Macedonia, the publisher of several daily and weekly newspapers, announced that it would dismiss 20 staff members, mostly experienced journalists and former editors from the daily Vest.
Layoffs are also to include employees from daily Utrinski Vesnik, Dnevnik, Makedonski Sport and weekly magazine Tea Moderna.
MPM stated layoffs were prompted by bad results and that the decision on who to dismiss would be based on the company’s internal procedures. Employees who lose heir jobs are to be compensated from one up to five average salaries, TV Nova reported.
24 July, 2016 – Emir Talirevic, a doctor who owns Moja Klinika, a private healthcare institution in Sarajevo, used Facebook to insult Selma Ucanbarlic, a journalist for the Centre for Investigative Journalism, following her articles about Moja Klinika, regional TV outlet N1 reported.
On 24 July Talirevic wrote on Facebook, among other things, that “judging by her psycho-physical attributes [the journalist] should never be allowed to do more complex work than grilling a barbecue”. He alleged hers were “imbecilic findings”, adding that “her work requires higher IQ than 65”.
In a second post, published on 27 July, Talirevic wrote that “as the toilet tank is taking away my associations on Selma and her CIN(ical) website I am thinking about the oldest profession in the world – prostitution”. He also wrote: “CIN is financed by gifts, like prostitutes”, and “after today’s article at least we know for whom Selma Ucanbarlic and her CIN colleagues are spreading their legs”.
22 July, 2016 – Masza Makarowa, a former journalist for the Russian language division of national broadcaster Polskie Radio, left the station due to a repressive climate and censorship, she claimed on her Facebook page.
An “atmosphere of scare tactics and paranoia” was prevalent at the broadcaster, Makarowa said. She also claimed that the station management instructed staff on which sources to consider for publication to Russian-speaking audiences, approving right-leaning, pro-governmental websites while explicitly prohibiting liberal sources like Gazeta Wyborcza for being opinionated. Certain updates, furthermore, were removed from the website.
22 June, 2016 – Jeff Howell, who had been writing a home maintenance advice column for The Telegraph for 17 years, was allegedly dismissed and removed from the Telegraph website after comments he made to his property section editor, Anna White.
According to Private Eye, the column, which was initially published both on the website and online, was removed from the website after he made a joke to property section editor White about correcting the Telegraph’s editing errors following a typo in January. Much of the column’s online archive was deleted following the incident.
Howell’s page on the Telegraph website used to get up to 10,000 hits daily but the removal of most of his columns from the website “made it easy to justify his dismissal by saying he didn’t produce any online traffic”.
24 May 2016 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia, Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, France, Germany, Greece, Index Reports, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Poland, Serbia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine
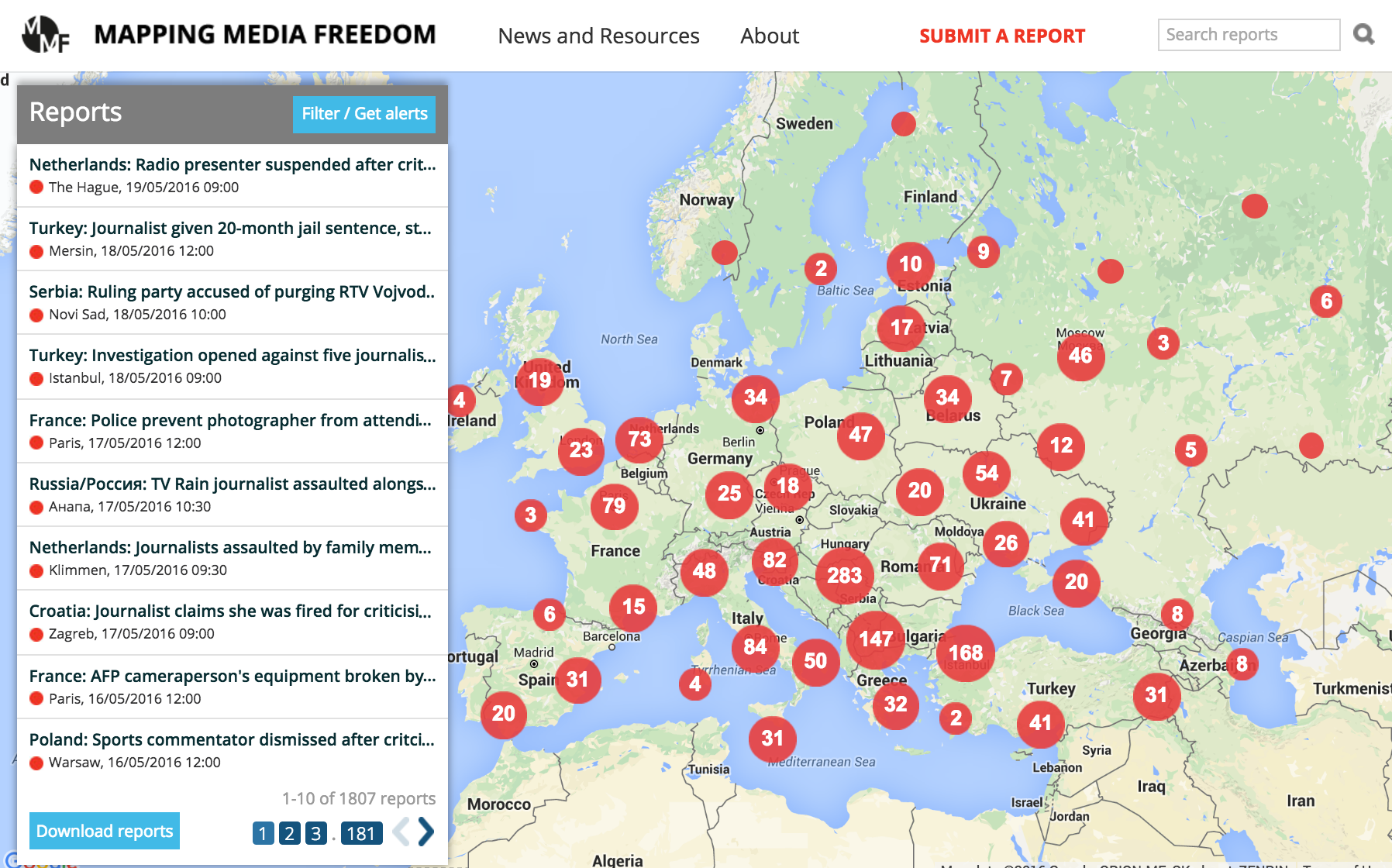
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar





