13 Sep 2018 | Bahrain, Bahrain News, Middle East and North Africa, News
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
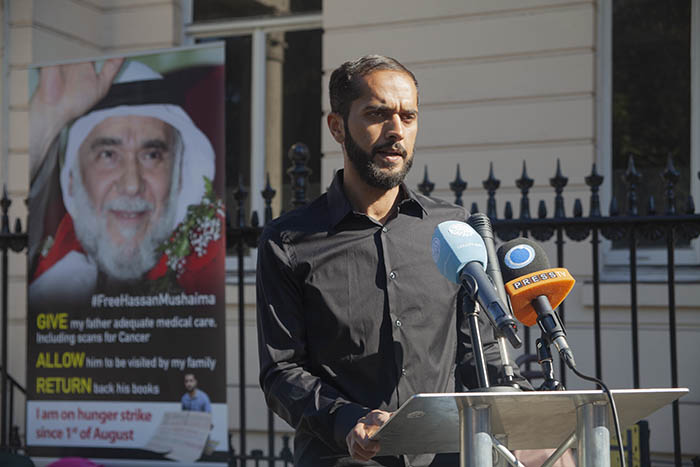

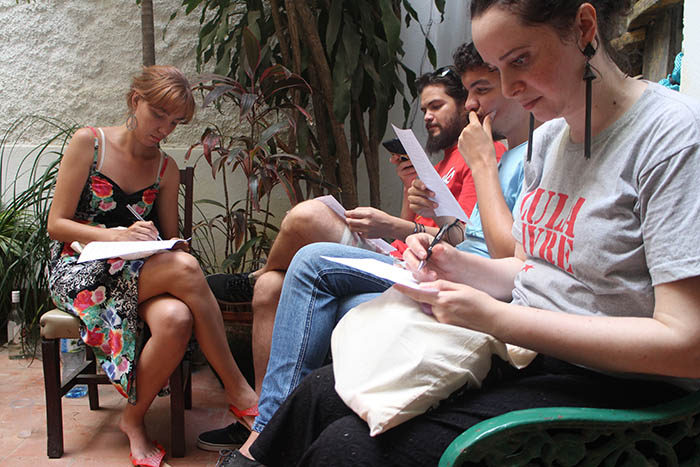
Ali Mushaima gives press conference in front of the Bahrain Embassy in London. (Credit: Gillian Trudeau)
At a press conference outside the Bahraini Embassy in London on 13 September, Bahraini human right activist Ali Mushaima vowed to continue fighting for his 70-year-old father Hassan Mushaima, who was imprisoned in 2011 as part of a crackdown on political activists in the country.
Mushaima said: “After 44 days many friends have argued for me to end my hunger strike. I even received a message from Nabeel Rajab in prison. But what affected me the most was my father telling me how scared he was that there I was hospitalised. I will not end my hunger strike but I will start a liquid diet that will include soups. My body needs to recover but if my father’s basic rights are not met, which is full medical care, family visits and access to books, I’m ready to resume my full hunger strike not because it’s easy and not because it is life-threatening, but because I will never stop fighting for my dad and for our cause.”
Human rights activist Zainab Al Khawaja, who has joined Mushaima’s demonstration after travelling from Denmark, was thanked for her solidarity. Khawaja’s activism has seen her arrested twice in Bahrain, once while pregnant and once with her infant son. Like Hassan Mushaima, Al Khawaja’s father, Abdulhadi Al Khawaja, faces possible life imprisonment.
Outside the Bahraini Embassy, Mushaima also expressed his gratitude towards MPs such as Caroline Lucas and Ian Blackford for raising his father’s case and shedding light on the suffering of political prisoners in Bahrain. His strike has garnered global recognition, going as far as being mentioned by the Human Rights Council in Geneva.
The British Government’s decision to support “false” statements made by the Bahraini Government was highlighted by Mushaima. He believes the UK has been part of the problem rather than the solution, alleging Britain has spent millions of pounds of taxpayers’ money to train Bahrain police violence and to teach them how to whitewash their crimes. Last month Mushaima asked for the Queen’s assistance, citing her friendship with the king of Bahrain as one of the many ways she could help influence the case.
Andrew Smith, who works for Campaign Against Arms Trade, was on hand to show his support. He said: “We want to express our support for Ali’s demands and solidarity with the stands that he has taken. This hunger strike should never have had to happen. The Bahraini regime should never be treating prisoners the way that they have treated Ali’s father. The UK Government should not be arming and supporting such a brutal, oppressive regime which has carried out atrocities against its people for years and has treated Ali’s father, and many other prisoners, absolutely appallingly.”
Background:
In response to Mushaima’s hunger strike, Hassan Mushaima received a cancer scan and has been given access to vital medication that was previously unavailable to him, but several issues remain:
In January 2018, Hassan Mushaima was told by a doctor at the Bahrain Defence Force Hospital that he urgently needs to see a diabetes specialist. He has not been granted access to a consultation yet by the authorities.
In October 2017, Hassan Mushaima’s books, personal notes, and writing materials were confiscated for no reason. They may have been destroyed.
Hassan Mushaima continues to be denied his right to family visitation without being subjected to humiliating measures, including being shackled. He last saw his family 18 months ago, in February 2017.
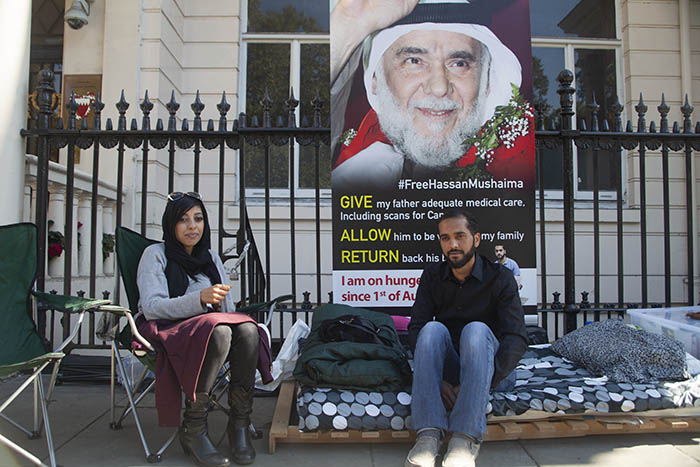

Bahraini human rights activists Zainab al-Khawaja and Ali Mushaima outside of the Bahrain Embassy in London. (Credit: Gillian Trudeau)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1537179808073-af3ba6e6-3e04-5″ taxonomies=”716″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
24 Aug 2018 | Europe and Central Asia, European Union, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News, Sweden
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

An image from the website of the right-wing populist Sweden Democrats, who changed their logo from a National Front-esque torch to a flower in an effort to clean up their image.
Sweden baked in record temperatures this summer, matched only by the increasingly heated political climate as it gears up for an unprecedentedly bitter and divisive general election. Front page stories about raging wildfires and drought have given a poll boost to the Swedish Green Party as climate change has leapt up the agenda. For populist media critics, however, the attention given to the fires is part of a conspiracy to keep the Greens in government and to give the governing left-wing bloc a victory in September’s vote.
Edward Riedl, a conservative member of parliament for the opposition Moderate Party accused major newspapers of “agenda setting” by giving such prominent coverage to the environment, with one if his party colleagues calling out newspapers for being pro-Green.
The far right meanwhile maintains a longstanding animosity with Sweden’s established print and public service media, which they accuse of being a cosy cartel.
Marie Grusell, a media researcher at Gothenburg University, has compared the attacks to the ongoing deligitimisation of the press in the USA by the White House.
“It is a tactic to undermine journalism. I think this is beneath contempt,” she said in an interview with the Swedish newspaper Aftonbladet.
This bizarre challenging of factual environmental journalism takes place against a backdrop of an increasingly contentious news landscape, in which the fragmentation and polarisation of the Swedish political system has made it increasingly difficult to maintain the balance of the media.
Over the past decade – and in common with other European countries – Sweden has seen the emergence of a powerful populist and anti-immigration party, the Sweden Democrats. The Sweden Democrats have deployed a familiar cocktail of anti-media conspiracism, welfare nationalism and climate scepticism, as well as anti-feminist and anti-Islamic rhetoric, to move from a fringe group to a major parliamentary force with ambitions to form a government. Although they have their roots in the 1990s white power movement, the Sweden Democrats have tried to soften their image by shunning some of their more extreme members and, in 2006, changed their logo from a torch — similar to that once used by the British far-right National Front — to a cartoonish anemone hepatica, a flower in the buttercup family.
Public trust in the Swedish media is still holding up but has diminished among those drifting towards the Sweden Democrats. This section of voters have become resistant to large sections of the established media and have instead turned to social network news groups and fringe sites which claim to expose what is really happening in Swedish society, as well as foreign news sites from the USA and Russia. In an attempt to increase the amount of freely available objective media outlets, the daily Dagens Nyheter recently removed its paywall for the duration of the election campaign, but as with other established media, it may be too late for readers who have already moved on.
Increased extremism
The dangerous situation is compounded by movements operating at the political fringes who have targeted journalists. The Nordic Resistance Movement (NMR), a neo-Nazi white power group, regularly marches in shows of force, intimidating journalists, minority groups and other members of the public. In May Swedish security services raided the home or prominent NMR member Peter Holm and found a suitcase they believed had been adapted for assassinations, along with a hard drive containing details on two journalists.
NMR activists also marched at this year’s Almedalen politics festival, a high point of the political calendar where journalists, civic and business groups and politicians get together to discuss contemporary issues. The investigative anti-fascist magazine EXPO uncovered instructions for NMR activists to attend speeches by politicians and others and to shout “traitor to the people” at politicians, and confront journalists in public. At the previous year’s event, the TV journalist Jan Scherman was called a “disgusting Jew” by an NMR member while filming.
Officially there is no link between the Sweden Democrats and groups like the NMR, but several SD politicians have voiced support for the organisation in the past and the increased support for SD in opinion polls has seemingly emboldened NMR activists to take more direct action on the streets according to data compiled by EXPO.
An uncertain future climate
A glimpse into what might happen should Sweden elect a government that includes the far right is provided by Denmark, where the hardline Danish People’s Party have cut state support to public broadcasting and consistently attacked its content as being leftist and unpatriotic. If a Sweden Democrat supported government becomes a reality, journalists could find themselves pressed by an increasingly powerful and emboldened populist movement that sees journalists as scapegoats for deeper seated problems, and where objective reporting of social challenges such as the environment and integration are dismissed as politically correct opinion rather than society-wide issues of critical importance.
It now falls to the press to fight its corner as a foundational part of the country’s democracy. Sweden, long considered a uniquely stable and tolerant democracy, is about to find out whether it really is safe from anti-democratic populism.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1535101855192-df766193-d628-5″ taxonomies=”9008, 507″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
8 Jun 2018 | Americas, Artistic Freedom, Awards, Cuba, Fellowship, Fellowship 2018, News
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Cuban artist Yasser Castellanos
Despite official efforts to stop it in its tracks, Cuba saw the successful completion of its first independent art biennial, organised without the support of the state, on 15 May. Artist Luis Manuel Otero Alcantara and curator Yanelys Nuñez Leyva, members of the Museum of Dissidence, winner of the 2018 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award for art, organised the ten-day #00Bienal de la Habana, which included over 170 artists, writers, musicians and theorists across nine different exhibitions in artists’ homes and studios around the country’s capital.
“Cuban culture is centralised culture and the government has absolute control,” Nuñez Leyva tells Index on Censorship. “The Ministry of Culture, together with all its branches such as the Union of Writers and Artists of Cuba and the National Council of Plastic Arts, are tentacles of the Ministry of the Interior, so all independent proposals, whether cultural, ecological or campaigns against gender violence, for example, are cursed with all the might of the government-controlled media.”
Even at schools pupils are served up propaganda intent on turning them against non-state-approved artists. Some art school students were shown a video portraying Otero Alcantara as a mercenary. “Such a campaign inevitably generates fear around independent projects which then suffer due to lack of both social and economic support,” Nuñez Leyva says.
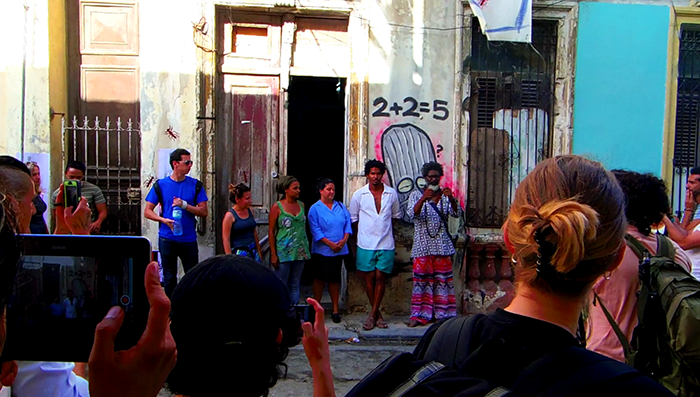
Economic support was one of the biggest obstacles for #00Bienal. “At the beginning, we thought that we would produce it with what we had at hand, but along the way we realised that we needed more,” Nuñez Leyva says. So a Gofundme campaign was set up, which raised $6,574. “But this wasn’t easy: the impact of the US blockade, our isolation from the world of networks and the impossibility of having credit cards made the process anguishing.”
Otero Alcantara was also imprisoned without cause on several occasions as part of the Cuban government’s campaign of harassment. Others who took part in #00Bienal, whether Cuban or foreign, received similar harassment. Many were even denied entry to the country, including the Cuban-American artist Coco Fusco.
When #00Biennial was announced in September 2017, the Cuban government immediately began to show its discontent through its cultural institutions. In an official declaration they branded the organisers as “unscrupulous people”. In response, #00Bienal’s first slogan was: “From the official to the unscrupulous.”
As culture is so tightly controlled in Cuba, only artists seen to be working in the interests of the regime can operate without restriction. Approved artists usually receive perks, something that gives them a higher status in society. Some artists risked all of this by taking part in #00Bienal. “The system used the worst blackmail against them because they gave the event a legitimacy that the government did not want,” Otero Alcantara says. “These artists were threatened by having their government accreditation taken away. Without this, they would find themselves without ‘official work’.”

Government agents stalked the exhibitions while the organisers were accused of being in league with Cuba’s enemies. How does one respond to such accusations? “We responded by making an event that is as honest as possible, with a wide range of manifestations and artistic expressions that reflected the reality of Cuban art,” Nuñez Leyva says. “We responded with a list of more than 170 participants, not only Cubans, but from Mexico, Spain, Germany, the United States, Romania, Angola, Colombia, Denmark, Ukraine, Brazil, Venezuela, among them high-profile artists that Cuban institutions admire and collaborated with.”
The authorities even tried to prohibit the public from attending, sometimes successfully. Flyers and stickers were also confiscated. “But none of these actions were ever going to stop the energy of the event,” Otero Alcantara says.
“Despite all this pressure, the event went ahead, demonstrating that there is a group of people who are very courageous and have a real commitment culture,” Nuñez Leyva says. #00Bienal helped revive “a spirit of alternative rebellion” through the involvement of “countless numbers of totally unknown artists” that the state would never endorse.
For Otero Alcantara, the event’s success lies in the cohesion it created between artists, scholars and art enthusiasts, something that is unprecedented in the world of Cuban art. “We built an inclusive space of free creation and true collaboration between the people involved, exhibited the work of artists who were never going to have space in an official Havana Biennial and set a precedent for future projects,” he says. “This is one more step towards eliminating a fear that exists throughout Cuba.”

According to the organisers, the terms “revolution” or “revolutionary” have been hijacked and distorted by the Cuban regime. Such deformation has taken root so deep in the imagination of the Cuban people that just by mentioning the word “dissidence” is enough to be shunned, they explain.
“The #00Bienal was a humanistic project that brought to the fore essential values for any society such as unity, solidarity and collaboration,” Nuñez Leyva says. “The event also favoured the less privileged and created beauty and dialogue in favour of a new Cuba.”
The organisers of #00Bienal are under no illusions that life for Cuba’a dissident artists will magically become any easier under Cuba’s new president, Miguel Díaz‑Canel, who took over from Raúl Castro in April 2018. “The Cuban regime is more than any Castro,” Nuñez Leyva says. “It is a system based on a group of families that live both inside and outside the island, who have control over everything, which ultimately contributes to their own wealth.” This corrupt system relies on the deception of a people who have been left without even the strength even to protect themselves against poverty, she adds. “This situation leaves us with little hope, but we have to keep working.”
Otero Alcantara and Nuñez Leyva’s now want to show that #00Bienal wasn’t just a one-off, but is a serious project with longevity. “We will see if it is possible in two years to achieve something similar,” Otero Alcantara says.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_media_grid grid_id=”vc_gid:1528443291288-dfd45bff-0a16-7″ include=”100716,100712,100711,100710,100713,100709,100708,100707,100706,100704,100715,100705″][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Artists, writers, musicians and theorists who took part in #00Bienal
Amaury Pacheco (Cuba), Iris Ruiz (Cuba), Coco Fusco (Cuba-USA), Tania Bruguera (Cuba), Reynier Leyva Novo (Cuba), Ernesto Oroza (Cuba), Gerardo Mosquera (Cuba), Katherine Bisquet (Cuba), Jose Ernesto Alonso, Yuri Obregón (Cuba), Alein Somonte (Cuba), Alejandro Barreras (Cuba), Anaeli Ibarra (Cuba), Alejandro Taquechel (Cuba), Ariel Maceo Tellez (Cuba), Aryam (Cuba), Aldeide Delgado (Cuba), Armando Cuspinera (Mexico), Antonio Mas (Spain), Alicia Torres (Spain), Ana Olema (Cuba), Alexis Ruiseco (Cuba-USA), Alexandru Raevschi (Germany), Andrés X (Cuba), Alain Aspiolea (Cuba), Alexandre Arrechea (Cuba), Antoni Muntadas (Spain), Biennial Project (USA), Boris González Arenas (Cuba), Colectivo Corason i uevo (Antonio A. Orta, Maykel Almenteros y Pedro Pablo Bacallao) (Cuba), Colectivo Guerrillas Girls, Celia y Yunior (Cuba), Colectivo 2.50 (Ana Gómez, Argelia Leodegarío, Marco Antonio Rodríguez, Itandehuitl Orta, Yuvia Pérez, Esmeralda Pérez) (Mexico), Carlos Manuel Álvarez (Cuba), Clara Astiasarán, Chu (Cuba), David de Omni, David León (Cuba), Danilo Maldonado (El Sexto), Diego Gil (Spain), Eliecer Jiménez Almeida (Cuba), Erish (Mexico), El Oficio (Cuba), Ernesto Hernandez Busto, Enfori García, Filipa César (Portugal), Fabián (2+2 =5) (Cuba), Francis Sánchez (Cuba), Francisco Méndez (Mexico), Francisco Masó (Cuba), Fabian Martínez, Filio Gálvez, Fredric Snitzer, Gabriel Coto (Cuba), Gerardo Stübing (España), Gean Moreno, Henri Eric Hernández (Cuba), Hamlet Lavastida (Cuba), Héctor Trujillo (Cuba), Hugo Patao, Italo Expósito (Cuba), Iván de la Nuez (Cuba), Jesús Hdez-Güero (Cuba), Jesús Benítez (Mexico), José Luis Marrero (Cuba), Josvan Gonzalez Agramonte (Cuba), Julián Yunda Yepes (Mexico), Jenifer Acuña (Cuba), Juan Melo (Colombia), Juan Carlos Alvarez Miranda (Cuba), Jean-Lorin Sterian (Romania), José Bedia (Cuba), Julio César Llopiz (Cuba), Javier Marimón, José Manuel Mesías (Cuba), Keyezua (Angola), Kevin Arrow, Lía Villares (Cuba), Luis Trápaga (Cuba), Luiso, Leandro Villanueva (Sam 33) (Cuba), Lester Dubé (Cuba), Lala Misosniky (Romania), La Alianza (Cuba), Liliam Dooley, Leandro Feal (Cuba), Lourdes Porrata, Miquel García (Spain), Marisol Maza (Mexico), Marcel Marquez (Cuba), Marianna Liosi (Germany), MO colectivo (Mariam Abrajim y Octavio Salazar) (Colombia), Magdiel Aspillaga, Mysora García, Nonardo Perea (Cuba), Natalia López (Colombia), Osmel Almaguer Delgado (Cuba), Osmany Carratalá (Cuba), Oscar Salamanca (Colombia), Orlando Hernández (Cuba), Pablo Pinto (Colombia), Polyanna Morgana (Brazil), Political Architecture: Critical Sustainability (PA:CS) (Denmark), Peter Menéndez, Rafael Carabano (Venezuela), Raúl Meriño (Cuba), Ras Yoe, Ricardo Figueredo, Rodolfo Peraza (Cuba), Rafael Domenech, Rirkrit Tiravanija, Svitlana Biedarieva (Ukraine), Soandry del Río (Cuba), Sandra Ceballos (Cuba), Santiago Alvarez Méndez (Colombia), Sandor (Cuba), Thiago Morandi (Brazil), Tomás Sánchez (Cuba), Tomas Vu, Tonel (Cuba), unx Pardo Ibarra (Colombia), Ulises Valdés (Mexico), Walfrido Valera (Cuba), Yaima Pardo (Cuba), Yasser Castellanos (Cuba), Yesica Suárez (Colombia), Yulier P. (Cuba), Yoenis Eloy Mayeta (Cuba), Yimi Konclase (Cuba), Yvelin Buenrostro (Mexico), Yucef Merhi (Venezuela), Yornel Martínez (Cuba), Yali Romagoza (Cuba), Yanier H. Palao (Cuba).[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1528443291296-0ad2c295-a239-7″ taxonomies=”104″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
16 Mar 2018
[vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” full_height=”yes” content_placement=”middle” css_animation=”fadeIn” css=”.vc_custom_1521806157541{margin-top: 0px !important;background-image: url(https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/MMF_2017_web-cover.jpg?id=98589) !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: contain !important;}”][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css_animation=”fadeIn” css=”.vc_custom_1521805928920{margin-top: 0px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
The case of Maltese journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia, who had for years worked to shine a light on corruption among politicians, businessmen and criminals in Malta, highlights the dire need for a free press. Between 2016 and 2017 Caruana Galizia linked the Maltese political elite to the Panama Papers, including the financial affairs of the prime minister, his wife and the leader of the country’s opposition party.
For her work, she paid with her life when a bomb exploded under her car on 16 October. She was not the only journalist to be murdered in Europe in 2017, nor were violations of media freedom confined to any one region.
Mapping Media Freedom has been recording threats to press freedom since 2014, highlighting the need for protection for journalists. The project monitors the media environment in 42 European and neighbouring countries. In 2017 1,089 reports of limitations to press freedom were verified by a network of correspondents, partners and other sources based in Europe, with a majority of violations coming from official or governmental bodies.
Six journalists were killed during 2017; 178 reports of assault or injury were made; 220 media workers were detained or arrested; 193 reports included criminal charges and lawsuits; there were 367 reports of intimidation, which includes psychological abuse, sexual harassment, trolling/cyberbullying and defamation; in 113 incidents media professionals had their property vandalised or confiscated; there were 178 instances of journalists or sources being blocked; and journalists’ work was altered or censored 68 times.
“While the number of incidents reported to Mapping Media Freedom decreased between 2016 and 2017, this should not be taken as an indication that the work environment for journalists has improved in the countries monitored by the platform,” Hannah Machlin, project manager of Mapping Media Freedom, said. “Media professionals still work under threat of death, assault, prison and harassment, while the law is being abused as a means to silence those who seek to tell the truth.”
ABOUT MAPPING MEDIA FREEDOM
Each report is fact-checked with local sources before becoming publicly available on Mapping Media Freedom. The number of reports per country relates to the number of incidents reported to the map. The data should not be taken as representing absolute numbers. For example, the number of reported incidents of censorship appears low given the number of other types of incidents reported on the map. This could be due to an increase in acts of intimidation and pressure that deter media workers from reporting such cases.
The platform – a joint undertaking with the European Federation of Journalists partially funded by the European Commission – covers 42 countries, including all EU member states, plus Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iceland, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro, Norway, Serbia, Turkey, along with Russia, Belarus and Ukraine (added in April 2015), and Azerbaijan (added in February 2016). The database uses Ushahidi, an open source software to map and categorise incidents.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row equal_height=”yes”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Deaths” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 Six journalists were killed as a result of their reporting in 2017.
Six journalists were killed as a result of their reporting in 2017.
Q1: In Russia on 9 March, two unknown individuals approached Nikolai Andrushchenko, an investigative journalist for the weekly newspaper Novyi Petersburg, near his home in St. Petersburg and demanded that he surrender documents and materials from his ongoing investigation into abuses of power by police officers. After the journalist refused, he was physically assaulted by the assailants, who were not apprehended. Andrushchenko refused to file a complaint with the police. A second assault took place a few days later, after which he was found unconscious near his apartment. The journalist never regained consciousness and, following brain surgery, died in hospital as a result of his injuries on 19 April.
On 16 March, in Ulan-Ude, Russia, Yevgeny Khamaganov, the editor-in-chief of Asia-Russia Daily and The Site of the Buryat People died in unexplained circumstances. The cause of death is unclear and no official response has been made. According to local media, Khamaganov was taken to hospital on 10 March because of his diabetes, fell into a coma and died several days later. Some reports cited speculation that he was instead hospitalised after being beaten by unknown assailants. Khamaganov was known for articles critical of the Russian federal government’s policies.
Q2: In Minusinsk, Russia, journalist Dmitri Popkov, editor-in-chief and founder of local newspaper Ton-M, was shot five times and killed on 24 May. His body was found in a sauna in his backyard. Prior to his death, Popkov had told RFE/RL that his newspaper became “an obstacle” for local officials who are now “threatening and intimidating journalists”.
Q3: On 10 August Swedish freelance journalist Kim Wall boarded an experimental submarine in Copenhagen, Denmark, to profile the vessel’s Danish inventor. The following morning, the submarine sank under suspicious circumstances. Peter Madsen, the inventor, told police he had set Wall ashore before the incident. However, between August and October, Wall’s dismembered remains were found washed ashore. Madsen has been charged with the journalist’s murder and with sexual assault.
On 22 September Syrian journalists Orouba Barakat and her daughter Halla Barakat were found dead in their apartment in Istanbul, Turkey. The exact date of the murders is unknown. Orouba Barakat, a journalist, filmmaker and activist, was outspokenly critical of the Syrian regime. Her daughter was a reporter for Alekhbarya TV, news editor for the Orient and a former editor at Turkish state channel TRT World. The pair had received threats from groups associated with the Syrian government. Police reports said they were strangled and then stabbed. The murders are still being investigated by police.
Q4: Maltese journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia was killed when the car she was driving exploded in Bidnija, near Mosta. Caruana Galizia had filed a police report 15 days earlier saying she was being threatened. The journalist had conducted a series of high-profile corruption investigations in Malta and was being sued in relation to her work.
One additional media worker was killed in 2017. On 29 April Saeed Karimian, an Iranian television executive, was shot and killed along with his partner in Istanbul, Turkey.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Physical assaults and injury” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 Mapping Media Freedom documented 175 verified incidents of assault and injury, 109 of which occurred in just five countries: Russia (47), Spain (19), Ukraine (18), Italy (15) and France (10).
Mapping Media Freedom documented 175 verified incidents of assault and injury, 109 of which occurred in just five countries: Russia (47), Spain (19), Ukraine (18), Italy (15) and France (10).
On 14 September Taras Khalyava, a local YouTube blogger, was assaulted by three unidentified people near his apartment in Dobropillye, Ukraine. The assailants knocked him to the ground, kicked him and beat him on the head with a steel rod. “I survived because I was wearing a bicycle helmet,” Khalyava told Novosti Donbassa. The blogger has said the attack was related to his work.
On 10 October, Drago Miljus, a Croatian journalist for the news website Index.hr, was pushed by a police officer, who then took his mobile phone and threw it into the sea. Another officer hit the journalist on the head, knocking him to the ground. The incident happened at a beach in Split, where Miljus was covering a story about a man who claimed to have a bomb.
On 23 October, a man broke into Echo Moskvy’s office in the centre of Moscow, Russia, and stabbed programme host Tatiana Felgengauer, who is also one of the editor-in-chief’s deputies, several times in the neck. Felgengauer was hospitalised in a critical condition and underwent several operations. The attacker was sent for psychiatric evaluation.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Arrests/Detainments” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 A total of 216 journalists were arrested or detained in 2017, including 21 in Azerbaijan. On 5 July Afgan Mukhtarli was kidnapped from Georgia, where he had lived in self-imposed exile for three years, and taken to Azerbaijan. While in prison, he suffered serious health problems and lost a significant amount of weight. In January 2018 he was sentenced to six years in prison by an Azerbaijani court.
A total of 216 journalists were arrested or detained in 2017, including 21 in Azerbaijan. On 5 July Afgan Mukhtarli was kidnapped from Georgia, where he had lived in self-imposed exile for three years, and taken to Azerbaijan. While in prison, he suffered serious health problems and lost a significant amount of weight. In January 2018 he was sentenced to six years in prison by an Azerbaijani court.
Mapping Media Freedom verified the arrest or detainment of 65 journalists in Russia throughout 2017. The majority of these took place during anti-corruption protests throughout the country organised by opposition figure Alexei Navalny in March and June.
By the close of 2017, 151 journalists were in prison in Turkey, making the country the largest jailer of journalists in the world. On 20 October police took five journalists working for the Kurdish Jin News and Mesopotamia agencies into custody: Jin News editor Sibel Yükler; Jin News reporters Duygu Erol and Habibe Eren; and Mezopotamya Agency reporters Diren Yurtsever and Selman Güzelyüz. Both agencies were launched in late September by staff from organisations shut down during Turkey’s state of emergency.
While only five media workers were arrested or detained in 2017 in the United Kingdom, one case stands out. On 7 December two Kurdish women and two 17-year-old boys were arrested at dawn by armed police in Alexandra Palace and in Crouch End, London. They were questioned about the sale and distribution of the Kurdish-language Yeni Ozgur Politika. All four were arrested on suspicion of funding terrorism, money laundering and fraud.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Criminal charges/civil lawsuits” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 There were 192 cases of criminal charges or civil litigation reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. In Italy, lawsuits demanding millions of euros in damages were filed throughout the year. In March Claudio Riva, former owner of the steelworks company Ilva, sued newspaper Gazzetta del Mezzogiorno for €2.2 million in damages, for publishing an article about pollution allegedly linked to the company’s operations in Taranto. Riva’s lawyers asked for €550,000 in compensation for each of the four damaged parties: Riva Forni Elettrici SPA, Claudio Riva, Fabio Arturo Riva and Nicola Riva. In October Il Locale News was sued for €1 million by Giancarlo Guarrera, an engineer and director of Airgest, the company that manages Trapani airport in Sicily. On 8 November 2016 Il Locale News featured an article on financial issues at Airgest.
There were 192 cases of criminal charges or civil litigation reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. In Italy, lawsuits demanding millions of euros in damages were filed throughout the year. In March Claudio Riva, former owner of the steelworks company Ilva, sued newspaper Gazzetta del Mezzogiorno for €2.2 million in damages, for publishing an article about pollution allegedly linked to the company’s operations in Taranto. Riva’s lawyers asked for €550,000 in compensation for each of the four damaged parties: Riva Forni Elettrici SPA, Claudio Riva, Fabio Arturo Riva and Nicola Riva. In October Il Locale News was sued for €1 million by Giancarlo Guarrera, an engineer and director of Airgest, the company that manages Trapani airport in Sicily. On 8 November 2016 Il Locale News featured an article on financial issues at Airgest.
In Spain, wealthy businessman Alvaro de Marichalar filed legal action against freelance journalist Sabina Urraca in March, demanding she pay €30,000 in damages for an article she wrote after accompanying him on a trip. In July Hermann Tertsch, a columnist for daily newspaper ABC, was ordered by a court in Zamora to pay €12,000 to Javier Iglesias for “unlawfully offending the honour” of his father Manuel. Javier Iglesias is the father of Pablo Iglesias, the leader of the left-wing Podemos party, the third largest party in the Spanish parliament.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Legal measures” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 There were 112 legal measures taken against journalists in 2017. In the United Kingdom, the offshore company Appleby, which was at the heart of the Panama Papers scandal, launched breach of confidence proceedings against the Guardian and the BBC on 18 December, in an attempt to force them to disclose the documents used in the investigation. Appleby said the documents were stolen in a cyberattack and there was no public interest in the revealing of their contents.
There were 112 legal measures taken against journalists in 2017. In the United Kingdom, the offshore company Appleby, which was at the heart of the Panama Papers scandal, launched breach of confidence proceedings against the Guardian and the BBC on 18 December, in an attempt to force them to disclose the documents used in the investigation. Appleby said the documents were stolen in a cyberattack and there was no public interest in the revealing of their contents.
In February the UK government proposed extending jail time for journalists who have obtained leaked official documents to up to 14 years. The major overhaul of the Official Secrets Act – to be replaced by an updated Espionage Act – would give courts the power to increase jail terms against journalists receiving such material. Should the law get approval, documents containing “sensitive information” about the economy could fall foul of national security laws for the first time. Jodie Ginsberg, chief executive of Index on Censorship, said: “It is unthinkable that whistleblowers and those to whom they reveal their information should face jail for leaking and receiving information that is in the public interest.”
In November, after the US added several media outlets funded by the Russian state on a list of foreign agents, Russia adopted a new restrictive law against foreign media that allows such journalists and organisations to be recognised as foreign agents, which makes them subject to numerous additional checks and obliges them to mark their content as being produced by a foreign agent.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Job loss” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 There were 51 reports of job loss recorded on Mapping Media Freedom throughout 2017, more than half of which came from Russia (13), Poland (8) and Spain (5).
There were 51 reports of job loss recorded on Mapping Media Freedom throughout 2017, more than half of which came from Russia (13), Poland (8) and Spain (5).
In Poland, Michał Fabisiak, a journalist for the public media outlet Polskie Radio, was fired for refusing to reveal the source of information for an article about an alleged internal survey in the Law and Justice (PiS) party, measuring support for potential PiS candidates in municipal elections in 2018.
Eleven days later, Barbara Burdzy, a Polish journalist for the public media outlet TVP Info, was dismissed after she published an article stating that the intelligence service, under the minister of defence Antoni Macierewicz, lied when claiming that deputy minister Jacek Kotas was not involved in property restoration in Warsaw.
On 14 December a documentary critical of Togo’s president was removed from the website of the French cable television channel Canal Plus and two employees of the channel were subsequently dismissed. Faure Gnassingbé, the president of Togo, is a friend of Vincent Bolloré, French businessman and chairman of Canal Plus’ parent company Vivendi. The documentary, entitled Let Go of the Throne, focused on ongoing protests against the country’s president. In November it was aired on Canal Afrique, a decision attributed to an employee who was later fired. François Deplanck, head of channels and content at Canal Plus International was also dismissed.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Intimidation” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 Intimidation was widespread across Europe in 2017, with 275 incidents reported to the map. In the United Kingdom, the BBC’s political editor Laura Kuenssberg was assigned a security detail at the Labour party conference in late September following online threats and abuse. The journalist attracted anger from some Labour supporters for her coverage of the 2016 Labour leadership race and the party’s poor performance in local elections, while a petition for her to be fired received 35,000 signatures.
Intimidation was widespread across Europe in 2017, with 275 incidents reported to the map. In the United Kingdom, the BBC’s political editor Laura Kuenssberg was assigned a security detail at the Labour party conference in late September following online threats and abuse. The journalist attracted anger from some Labour supporters for her coverage of the 2016 Labour leadership race and the party’s poor performance in local elections, while a petition for her to be fired received 35,000 signatures.
Kuenssberg — the first woman to lead political coverage at the public broadcaster — also reported that she had bolstered her security during the general election in June 2017 after receiving threats over her coverage of Labour Party leader Jeremy Corbyn.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Attacks to property” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 There were 109 attacks on the property of journalists in 2017. On the morning of 26 November Yulia Zavialova, editor-in-chief of the Russian investigative website Bloknot Volgograd, known for its coverage of political and business corruption, asked her father to have the tires on her car checked. Thirty minutes later he rang her to say the brakes were completely out of service. Her brakes had been cut and her anti-lock braking system was damaged. Zavialova called the police but, according to the journalist, they did not properly investigate the scene, failing to take fingerprints or full details of the damage.
There were 109 attacks on the property of journalists in 2017. On the morning of 26 November Yulia Zavialova, editor-in-chief of the Russian investigative website Bloknot Volgograd, known for its coverage of political and business corruption, asked her father to have the tires on her car checked. Thirty minutes later he rang her to say the brakes were completely out of service. Her brakes had been cut and her anti-lock braking system was damaged. Zavialova called the police but, according to the journalist, they did not properly investigate the scene, failing to take fingerprints or full details of the damage.
Supporters of the Italian far-right party Forza Nuova attacked the offices of the left-wing newspaper La Repubblica in Rome on 6 December. The party declared “war” on L’Espresso Group, the newspaper’s publisher, through a Facebook post. During the protest, Forza Nuova supporters threw flares at La Repubblica’s office while carrying a banner reading “Boycott L’Espresso and La Repubblica”. Members of the group read a statement denouncing journalists employed there.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Blocked access” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 There were 169 confirmed cases of blocked access throughout Europe in 2017, in which journalists were expelled from a location or prevented from speaking to a source by way of obstruction. Many of these reports were connected to other violations, such as assault, damage to property and intimidation.
There were 169 confirmed cases of blocked access throughout Europe in 2017, in which journalists were expelled from a location or prevented from speaking to a source by way of obstruction. Many of these reports were connected to other violations, such as assault, damage to property and intimidation.
Throughout Europe, journalists were blocked from attending events by political parties, including the Labour Party’s annual conference in Brighton, United Kingdom, in September. Sussex police refused to grant Huck Magazine news editor Michael Segalov the security clearance he needed to attend. The journalist had applied for press accreditation three months prior but was informed on 19 September that it had been denied by police on security grounds. “Rather than provide reasons and rationale for our journalistic freedom being curtailed, the police said they would not divulge why they made their call,” Segalov wrote. The journalist has never been arrested, charged or convicted of a crime. Michael Walker, a journalist working for the left-wing Novara Media, was also barred by police from entering the conference.
On 25 October three journalists working for Echo TV in Hungary were banned from entering the country’s parliament. The parliament press office said the journalists had broken official rules multiple times by filming in areas closed to the media.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”Work censored or altered” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
 In 2017 Mapping Media Freedom documented 81 cases in which journalists had their work censored or altered. On 15 October in the city of Uppsala, Sweden, local newspaper UNT and public broadcaster SVT identified what they saw as a concerted effort by press officers at the local council to control statements made by staff to journalists. Both complained that press officers were exerting pressure on staff to change statements that reflect badly on the council.
In 2017 Mapping Media Freedom documented 81 cases in which journalists had their work censored or altered. On 15 October in the city of Uppsala, Sweden, local newspaper UNT and public broadcaster SVT identified what they saw as a concerted effort by press officers at the local council to control statements made by staff to journalists. Both complained that press officers were exerting pressure on staff to change statements that reflect badly on the council.
On 4 November the Spanish newspaper El País removed a column from its website that questioned and criticised allegations of sexual harassment in the film industry against the likes of Kevin Spacey, Harvey Weinstein and Roman Polanski.
On 19 December the Malta Independent, a Maltese newspaper and publishing house, announced it would remove some online content relating to a whistleblower at Pilatus Bank due to the threat of a multi-million euro lawsuit from the bank. Pilatus Bank first threatened the independent publishing house in mid-October, with lawsuits in the USA and United Kingdom.
[/vc_column_text][vc_separator color=”black” style=”dashed”][vc_column_text]
CASE STUDIES
2018 WATCH LIST
Index on Censorship is especially disturbed by the five countries on the map with over 60 violations in 2017. These are:
Russia (197)
 During protests organised by Russian lawyer and activist Alexei Navalny in March and June, 1,000 people were arrested, including 19 journalists, in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Makhachkala, Petrozavodsk and Samara. At a rally in Moscow on 26 March, police detained RBC correspondent Timofey Dzyadko, Mediazona publisher Piotr Verzilov, Open Russia correspondent Sofiko Arifdzhanova, Public Television of Russia journalist Olga Orlova, Echo of Moscow journalist Alexandr Pluschev and Kommersant-FM reporter Pyotr Parkhomenko. At the same rally, Guardian correspondent Alec Luhn was detained after he took a photo of a protester being arrested. He spent more than five hours at a police station without an explanation of why he was detained. Luhn was eventually charged with participating in an unsanctioned rally, even though he showed officers his press accreditation. At least nine media workers were detained across Russia on 8 October during further protests organised by Navalny.
During protests organised by Russian lawyer and activist Alexei Navalny in March and June, 1,000 people were arrested, including 19 journalists, in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Makhachkala, Petrozavodsk and Samara. At a rally in Moscow on 26 March, police detained RBC correspondent Timofey Dzyadko, Mediazona publisher Piotr Verzilov, Open Russia correspondent Sofiko Arifdzhanova, Public Television of Russia journalist Olga Orlova, Echo of Moscow journalist Alexandr Pluschev and Kommersant-FM reporter Pyotr Parkhomenko. At the same rally, Guardian correspondent Alec Luhn was detained after he took a photo of a protester being arrested. He spent more than five hours at a police station without an explanation of why he was detained. Luhn was eventually charged with participating in an unsanctioned rally, even though he showed officers his press accreditation. At least nine media workers were detained across Russia on 8 October during further protests organised by Navalny.
On 20 December photographers Andrey Zolotov and Denis Bochkarev, along with Maria Alyokhina, a member of punk collective Pussy Riot, were detained during a protest at the entrance of the FSB, the Russian federal security service. All three were taken to the nearest police station, where Alyokhina and Bochkaryov spent the night ahead of an administrative hearing.
Often referred to as the only independent radio station in Russia, Echo Moskvy was subjected to significant pressure and harassment throughout 2017, with Mapping Media Freedom verifying 15 reports against the station including one radio host stabbed, two journalists fleeing the country after threats, several detained and an American company forced to withdraw funding from the station.
Turkey
 Although the number of violations reported to Mapping Media Freedom that took place in Turkey decreased between 2016 and 2017 — from 231 to 135 — the country remains the number one jailer of journalists in the world with 151 media workers behind bars by the end of 2017. In all, 65 journalists were jailed and sentenced on charges including the spreading of terrorist propaganda. At the trial of journalist Nedim Türfent, who reported on security operations in Turkey’s Kurdish majority provinces, at least a dozen people claimed they were tortured by police.
Although the number of violations reported to Mapping Media Freedom that took place in Turkey decreased between 2016 and 2017 — from 231 to 135 — the country remains the number one jailer of journalists in the world with 151 media workers behind bars by the end of 2017. In all, 65 journalists were jailed and sentenced on charges including the spreading of terrorist propaganda. At the trial of journalist Nedim Türfent, who reported on security operations in Turkey’s Kurdish majority provinces, at least a dozen people claimed they were tortured by police.
In November, Turkish journalists Ahmet Altan and Mehmet Altan’s defence attorneys were forced to leave the courtroom as their clients stood trial, accused of taking part in Turkey’s failed 2016 coup. Both brothers are prominent Turkish journalists, known for their critical reporting on president Erdogan’s regime. Without lawyers present, the court then ruled that the Altan brothers — along with four other journalists — would remain in pretrial detention. On 16 February 2018 they were sentenced to aggravated life sentences.
Belarus
 A total of 92 violations of media freedom were recorded in Belarus throughout 2017, including the detainment of 101 journalists. In all, 30 journalists received criminal charges. A wave of detentions occurred on the Belarusian holiday Freedom Day on 25 March, when 36 journalists were placed in custody. Olga Morva, Philip Warwick, Andrey Dubinin, Valery Shchukin, Katsiaryna Bakhvalava, Ihar Ilyash and Volha Davydava said they were beaten by police while under arrest. Warwick, from the United Kingdom, said he was denied the right to contact his embassy after being handcuffed and hit in the face; he spent over six hours at the police station. The apartment of journalist Maryna Kastylyanchanka, who works with human rights organisations, was searched. She was later jailed for 15 days for disobeying police and participating in the unsanctioned mass protests.
A total of 92 violations of media freedom were recorded in Belarus throughout 2017, including the detainment of 101 journalists. In all, 30 journalists received criminal charges. A wave of detentions occurred on the Belarusian holiday Freedom Day on 25 March, when 36 journalists were placed in custody. Olga Morva, Philip Warwick, Andrey Dubinin, Valery Shchukin, Katsiaryna Bakhvalava, Ihar Ilyash and Volha Davydava said they were beaten by police while under arrest. Warwick, from the United Kingdom, said he was denied the right to contact his embassy after being handcuffed and hit in the face; he spent over six hours at the police station. The apartment of journalist Maryna Kastylyanchanka, who works with human rights organisations, was searched. She was later jailed for 15 days for disobeying police and participating in the unsanctioned mass protests.
Throughout the year, 69 fines were administered to journalists for violating Article 22.9 of Belarus’ Code of Administrative Offences on the illegal production and/or distribution of media content.
Ukraine
 In all, 74 violations against the media in Ukraine were reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. One of the most worrying trends included the treatment of foreign journalists or journalists working for Russian companies. Sixteen journalists were expelled from, or not allowed to enter the country, including some who worked for Russian state media outlets. There were three cases involving the abuse of Interpol warrants to arrest or detain foreign journalists in Ukraine by their countries of origin as a means of silencing critical voices. These were: Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. Three journalists were arrested in territory controlled by self-proclaimed separatists in 2017, including Ukrainian blogger and writer Stanyslav Aseev, one of the few journalists contributing to western and independent media outlets in eastern Ukraine.
In all, 74 violations against the media in Ukraine were reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. One of the most worrying trends included the treatment of foreign journalists or journalists working for Russian companies. Sixteen journalists were expelled from, or not allowed to enter the country, including some who worked for Russian state media outlets. There were three cases involving the abuse of Interpol warrants to arrest or detain foreign journalists in Ukraine by their countries of origin as a means of silencing critical voices. These were: Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. Three journalists were arrested in territory controlled by self-proclaimed separatists in 2017, including Ukrainian blogger and writer Stanyslav Aseev, one of the few journalists contributing to western and independent media outlets in eastern Ukraine.
Ukrainian president Petro Poroshenko signed a National Security and Defence Council decree in May that banned a number of Russian social media sites such as VKontakte and Odnoklassniki, along with the search engine Yandex and email service Mail.ru.
“The lack of safety for journalists in Ukraine, whether direct attacks or obstruction, remains a problem, and the level of response by the authorities is telling because too often the perpetrators go unpunished,” Vitalii Atanasov, Mapping Media Freedom correspondent for Ukraine, said. “The murder of prominent journalist Pavel Sheremet in July 2016 has not yet been properly investigated, while media workers continue to face pressure from the authorities, politicians and other influential actors. It is important to emphasise to that while the Mapping Media Freedom reflects the most disturbing and characteristic cases, it does not claim to be complete.”
Spain
 Between 2016 and 2017, media freedom violations in Spain increased from 56 to 66. Journalists experienced difficulties before, during and after the referendum on Catalan independence on 1 October. In July the daily newspaper La Vanguardia, based in Barcelona, refused to publish a column written by Gregorio Morán in which the journalist criticised the “corrupt” regional government of Catalonia. Morán also accused the Catalan media of receiving sums of public money, adding that it was therefore no surprise to see them supporting Catalan independence.
Between 2016 and 2017, media freedom violations in Spain increased from 56 to 66. Journalists experienced difficulties before, during and after the referendum on Catalan independence on 1 October. In July the daily newspaper La Vanguardia, based in Barcelona, refused to publish a column written by Gregorio Morán in which the journalist criticised the “corrupt” regional government of Catalonia. Morán also accused the Catalan media of receiving sums of public money, adding that it was therefore no surprise to see them supporting Catalan independence.
On the day of the referendum Mapping Media Freedom recorded five separate violations of media freedom. Journalists were among the many victims of violence by heavy-handed police deployed the Spanish government, who declared the referendum to be illegal. Xabi Barrena, a journalist for the newspaper El Periódico, was assaulted by Spanish national police while reporting on voters being evicted from a polling station in Barcelona. He was struck with a baton, knocked to the ground and kicked by police.
In the days following the referendum, media violations were widespread during the protests that swept parts of the country. On 2 October, for example, Ana Cuesta and José Yelámo, reporters for television La Sexta, were surrounded by protesters who chanted “Spanish press manipulators” and “assassins” during live coverage.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
TRENDS
Threats from the far-right
The far right has a record of violating freedom of the press throughout Europe, with 24 media violations across 13 countries involving far-right groups or activists in 2017.
Twelve attempts were made by the far-right to intimidate media workers. At the start of December, the Serbian journalist Marija Antic, a television host for the broadcaster N1, received death and rape threats on social media after interviewing a French-Serbian far-right activist. Antic had invited Arnaud Gouillon, who is known for his support for Serbs in Kosovo, to her talk show. During the interview, Antic asked him about his past involvement in the French far-right group Les Identitaires and about his connections with far-right Serbian groups after he attended some of their events. After the interview, Gouillon accused Antic of demonising him. Soon after, Antic received multiple threats on social media.
On six occasions, far-right groups attempted to defame journalists throughout Europe. This was the case on 15 March when Stina Blomgren, a Swedish journalist working for the state broadcaster SVT, was accused by the popular Swedish-Russian far-right blogger Egor Putilov of lying and creating fake reports about the risks Syrian migrants faced when trying to reach Sweden. Putilov claimed to have visited Egypt and uncovered inaccuracies in an article published by Blomgren in August.
In 2017 four reports made to Mapping Media Freedom involved violence from the far right and four involved attacks to property. These ranged from damages to camera equipment to an assault with a metal pipe.
Corruption
Corruption is a major issue in the EU and neighbouring countries, undermining democracy and putting people at risk. Journalists play a key role in uncovering and fighting corruption through their investigations and, as a result, put themselves in danger. In all, 67 cases of media workers facing difficulty in their reporting on corruption were recorded throughout 2017.
On 16 August, for instance, Parim Olluri, editor-in-chief of investigative website Insajderi, was physically assaulted by unknown individuals outside his home in Kosovo’s capital Pristina. Olluri believes the attack was linked to his work. A few days before the assault, Olluri had published an editorial about corruption allegations against former Kosovo Liberation Army commanders, after which he received a torrent of abuse and threats on social media.
On 16 October the Maltese journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia was murdered when the car she was driving exploded. On 11 March Silvio Debono, owner of real estate investment company DB Group, filed 19 libel cases against her. Caruana Galizia published a number of articles on her blog discussing a business deal between the developer and Malta’s government to take over a tract of public land on which he had planned to build a Hard Rock Hotel and two towers of flats for sale. Caruana Galizia also conducted an investigation allegedly linking prime minister Joseph Muscat and his wife to the Panama Papers scandal.
Harassment of female journalists
Mapping Media Freedom logged 10 cases where women journalists reported they suffered sexual harassment throughout 2017, from politicians, anonymous sources and fellow journalists alike. In February the Swedish newspaper journalist Evelyn Schreiber was subjected to persistent death threats and threats of sexual violence after questioning local police officer a Peter Springare’s assertion that immigrants were responsible for a spike in violent crime in Örebro, Sweden. Within 24 hours of her report, Schreiber received over 200 emails containing threats.
On 7 May Loes Reijmer, a journalist and columnist for the Dutch daily newspaper De Volkskrant, faced abuse after the popular right-wing blog GeenStijl published a photo of her with the text: “Would you do her?” Thousands of readers responded in the comments section, many containing sexual references and rape threats. Reijmer had published several articles critical of GeenStijl, which is owned by Telegraaf Media Group and is one of the top 10 most popular news sites in the Netherlands.
On 30 November, Dzenan Selimbegovic, a deputy secretary general of the presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, used offensive language to describe Sanele Prašović Gadžo, a journalist for the public broadcaster BHT, and Arijana Saračević-Helać, a journalist for the public broadcaster FTV, in a Facebook post. The comments followed a trailer aired on BHT for Gadžo’s interview with Saračević-Helać on her talk show.
Commercial interference
In 2017 Index on Censorship added the “commercial interference” category to Mapping Media Freedom to monitor actions that use money and/or financial pressure to influence editorial decisions of a media or news outlet. One of the most concerning issues highlighted was the lack of plurality in media ownership in Ireland and the impact this can have on the public’s right to information.
Broadcasting in the country is dominated by just two organisations, RTÉ and Communicorp. Semi-state RTÉ services are the most popular on television and radio, while businessman Denis O’Brien’s Communicorp owns the largest commercial news radio stations – Newstalk and Today FM, among others. There is currently a lack of imperative for reform on the issue of the concentration of media ownership by the Irish government, leaving journalists open to further pressure and self-censorship to suit commercial interests, according to the National Union of Journalists.
Across Europe commercial interference in the media is proving to be a growing problem. On 6 December in Nantes, France, for example, managers of McDonald’s restaurants were asked to remove a page from local newspaper Ouest France that contained an article about litigation between the fast food restaurant chain and two of its workers, who had campaigned for union representation.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Mapping Media Freedom’s annual report highlights issues affecting the state of press freedom throughout Europe in 2017. Index on Censorship urges that the following steps be taken.
-
All journalists, media workers and others arrested for exercising their right to freedom of expression must be immediately and unconditionally released. We make this plea directly to the Turkish government in particular, which has become the largest jailer of journalists not just among the countries monitored by Mapping Media Freedom, but the entire world.
-
Laws designed to impinge on the work of journalists must be reconsidered, whether amended or abolished. This includes defamation laws, hate speech laws and terror and security-related legislation. Lawmakers should also ensure that new or revised laws do not encroach on the work of journalists.
-
Governments must respect the right of journalists to protect confidential information and sources. This is vital, especially in cases involving whistleblowing in the public interest.
-
Harassment and crimes against journalists must be properly investigated and those responsible should be prosecuted to prevent the further proliferation of impunity.
-
Governments should do more to ensure the protection of media workers who are women.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row equal_height=”yes” css=”.vc_custom_1521129408155{background-color: #d5473c !important;}”][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_custom_heading text=”Protect media freedom”][vc_column_text]
We monitor threats to press freedom, produce an award-winning magazine and publish work by censored writers.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″ css=”.vc_custom_1521129253575{background-image: url(https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/MMF_2017_map-standalone.jpg?id=98665) !important;}”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][/vc_column][/vc_row]





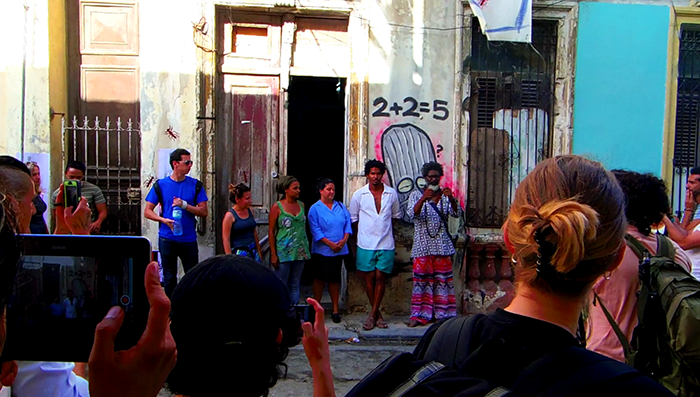


 Six journalists were killed as a result of their reporting in 2017.
Six journalists were killed as a result of their reporting in 2017.  Mapping Media Freedom documented 175 verified incidents of assault and injury, 109 of which occurred in just five countries: Russia (47), Spain (19), Ukraine (18), Italy (15) and France (10).
Mapping Media Freedom documented 175 verified incidents of assault and injury, 109 of which occurred in just five countries: Russia (47), Spain (19), Ukraine (18), Italy (15) and France (10).  A total of 216 journalists were arrested or detained in 2017, including 21 in Azerbaijan. On 5 July
A total of 216 journalists were arrested or detained in 2017, including 21 in Azerbaijan. On 5 July  There were 192 cases of criminal charges or civil litigation reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017.
There were 192 cases of criminal charges or civil litigation reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017.  There were 112 legal measures taken against journalists in 2017. In
There were 112 legal measures taken against journalists in 2017. In There were 51 reports of job loss recorded on Mapping Media Freedom throughout 2017, more than half of which came from Russia (13), Poland (8) and Spain (5).
There were 51 reports of job loss recorded on Mapping Media Freedom throughout 2017, more than half of which came from Russia (13), Poland (8) and Spain (5).  Intimidation was widespread across Europe in 2017, with 275 incidents reported to the map. In the United Kingdom, the
Intimidation was widespread across Europe in 2017, with 275 incidents reported to the map. In the United Kingdom, the  There were 109 attacks on the property of journalists in 2017. On the morning of 26 November Yulia Zavialova, editor-in-chief of the Russian investigative website Bloknot Volgograd, known for its coverage of political and business corruption, asked her father to have the tires on her car checked. Thirty minutes later he rang her to say the brakes were completely out of service.
There were 109 attacks on the property of journalists in 2017. On the morning of 26 November Yulia Zavialova, editor-in-chief of the Russian investigative website Bloknot Volgograd, known for its coverage of political and business corruption, asked her father to have the tires on her car checked. Thirty minutes later he rang her to say the brakes were completely out of service.  There were 169 confirmed cases of blocked access throughout Europe in 2017, in which journalists were expelled from a location or prevented from speaking to a source by way of obstruction. Many of these reports were connected to other violations, such as assault, damage to property and intimidation.
There were 169 confirmed cases of blocked access throughout Europe in 2017, in which journalists were expelled from a location or prevented from speaking to a source by way of obstruction. Many of these reports were connected to other violations, such as assault, damage to property and intimidation.  In 2017 Mapping Media Freedom documented 81 cases in which journalists had their work censored or altered. On 15 October in the city of Uppsala, Sweden, local newspaper UNT and public broadcaster SVT identified what they saw as a
In 2017 Mapping Media Freedom documented 81 cases in which journalists had their work censored or altered. On 15 October in the city of Uppsala, Sweden, local newspaper UNT and public broadcaster SVT identified what they saw as a  During protests organised by Russian lawyer and activist Alexei Navalny in March and June, 1,000 people were arrested, including 19 journalists, in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Makhachkala, Petrozavodsk and Samara.
During protests organised by Russian lawyer and activist Alexei Navalny in March and June, 1,000 people were arrested, including 19 journalists, in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Makhachkala, Petrozavodsk and Samara.  Although the number of violations reported to Mapping Media Freedom that took place in Turkey decreased between 2016 and 2017 — from 231 to 135 — the country remains the number one jailer of journalists in the world with 151 media workers behind bars by the end of 2017. In all, 65 journalists were jailed and sentenced on charges including the spreading of terrorist propaganda.
Although the number of violations reported to Mapping Media Freedom that took place in Turkey decreased between 2016 and 2017 — from 231 to 135 — the country remains the number one jailer of journalists in the world with 151 media workers behind bars by the end of 2017. In all, 65 journalists were jailed and sentenced on charges including the spreading of terrorist propaganda.  A total of 92 violations of media freedom were recorded in Belarus throughout 2017, including the detainment of 101 journalists. In all, 30 journalists received criminal charges.
A total of 92 violations of media freedom were recorded in Belarus throughout 2017, including the detainment of 101 journalists. In all, 30 journalists received criminal charges.  In all, 74 violations against the media in Ukraine were reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. One of the most worrying trends included the treatment of foreign journalists or journalists working for Russian companies. Sixteen journalists were expelled from, or not allowed to enter the country, including some who worked for Russian state media outlets. There were three cases involving the abuse of Interpol warrants to arrest or detain foreign journalists in Ukraine by their countries of origin as a means of silencing critical voices. These were:
In all, 74 violations against the media in Ukraine were reported to Mapping Media Freedom in 2017. One of the most worrying trends included the treatment of foreign journalists or journalists working for Russian companies. Sixteen journalists were expelled from, or not allowed to enter the country, including some who worked for Russian state media outlets. There were three cases involving the abuse of Interpol warrants to arrest or detain foreign journalists in Ukraine by their countries of origin as a means of silencing critical voices. These were:  Between 2016 and 2017, media freedom violations in Spain increased from 56 to 66. Journalists experienced difficulties before, during and after the referendum on Catalan independence on 1 October. In July the daily newspaper La Vanguardia, based in Barcelona,
Between 2016 and 2017, media freedom violations in Spain increased from 56 to 66. Journalists experienced difficulties before, during and after the referendum on Catalan independence on 1 October. In July the daily newspaper La Vanguardia, based in Barcelona,