12 Jan 2016 | Americas, Cuba, mobile, News and features

August 2015: opening of the Cuban Film Posters exhibition Soy Cuba as part of World Cinema Amsterdam. Credit: Shutterstock / Cloud Mine Amsterdam
“[T]he fault of many of our intellectuals and artists is to be found in their ‘original sin’: they are not authentically revolutionary.”
— Che Guevara, Man and Socialism in Cuba, 1965
Last year was a good one for Cuban artists. With renewed diplomatic relations with the US, a boom in Latin American art and Cuba’s exceptional artistic talent — fostered through institutions such as the Instituto Superior de Arte in Havana — works by prominent Cuban artists fetched top dollar at international auctions, and the Cuban film industry was firmly in the international spotlight.
While the end of the embargo brought with it hope for political liberalisation on the island, as with previous periods of promise in Cuban history cases of repression and censorship of dissident artists were rife in 2015.
So let’s begin again: Last year was a good one for Cuban artists who adhere to the country’s long-established revolutionary narrative and don’t embarrass the regime.
The fear of censorship for art that is critical of the government has been fostered through decades of laws and repression that limit freedom of expression. This can mean stigmatisation, the loss of employment and even imprisonment. Charges such as “social dangerousness” and insulting national symbols are so vague they make convictions very easy.
“Artists are among the most privileged people in Cuban society — they make money in hard currency, travel, have frequent interaction with foreigners and they don’t have boring jobs,” explains Coco Fusco, a Cuban-American artist, 2016 Index Freedom of Expression Awards nominee and author of Dangerous Moves: Performance and Politics in Cuba. “Artists function as a window display in Cuba; proof of the success of the system.”
But if an artist engages in political confrontations, they can draw unwanted attention, says Fusco.
One artist accused of doing just that is critically-acclaimed Cuban director and fellow nominee for this year’s Index Awards Juan Carlos Cremata. In 2015, he staged a production of Eugene Ionesco’s Exit the King, about an ageing ruler who refuses to give up power. The play lasted two performances before being shut down by the National Council of Theatre Arts and the Centre for Theatre in Havana.
“Exit the King was banned because according to the minister of culture and the secret police we were mocking Fidel Castro,” Cremata told Index on Censorship. “This wasn’t really true; what they fear is real revolutionary speech in theatre.”
When he spoke out against the move, Cuban authorities terminated his theatre contract, effectively dissolving his company, El Ingenio.
Cremata, whose career spans three decades, confesses the shutting down of Exit the King took him by surprise. “We are living in the 21st century, and according to the official propaganda, Cuba is changing and people can talk about anything,” he says. “This, as it turns out, is a big lie by people who are still dreaming of the revolution.”
“With their censorship, they show how stupid, retrograde and archaic their politics are,” he says.
As so much funding for artists comes from the state, non-conformist artists often find themselves in difficult financial situations. “I’ve had to reinvent my life,” Cremata says. “I’m trying to receive some help from friends who offer to work with me for free, but this will not be eternal, as they have families.”
Cremata himself has an adopted daughter and has her future to think about. “I truly believe life will change and better times will come with or without their approval, but it is very, very hard.”
Art has always been at the centre of Cuban culture, but under Fidel Castro it became a tool for spreading socialist ideas and censorship a tool for tackling dissent. Evidently, Cuba isn’t entirely post-Fidel, explains Fusco. “Fidel is still alive, his brother is in charge and his dynasty is firmly ensconced in the power, with sons, nieces and nephews in key positions,” she says. “Although I don’t think anyone over the age of 10 in Cuba believes the rhetoric anymore.”
Very few may believe the rhetoric, but going against it can still land you in prison, as was the case with Index Awards nominee Danilo Maldonado, the graffiti artist also known as El Sexto. Maldonado organised a performance called Animal Farm for Christmas 2014, where he intended to release two pigs with the names of Raúl and Fidel Castro painted on them. He was arrested on his way to carry out the performance and spent 10 months in prison without trial.
International human rights organisations condemned his imprisonment — during which he was on a month-long hunger strike — as an attack on freedom of expression.
The prospect for improving political freedoms doesn’t look good, and anyone who expected any different due to Cuba’s normalisation of relations with the US is naive, says Fusco.
“Washington is not promoting policy changes to improve human rights,” she says. “Washington is promoting policy changes to 1. develop better ways to exert political influence in Cuba; 2. to revise immigration policies and control the steep increase in Cuban illegal migration to the US; 3. to give US businesses and investment opportunity that they need (particularly agribusiness); 4. to avoid a tumultuous transition at the end of Raul Castro’s term in power that would produce more regional instability (i.e. the US does not want another Iraq, Libya or Syria).”
Even within Cuba there is an absence of discussion about civil liberties, strong voices of criticism of state controls and collective artist-based efforts to promote liberalisation.
“Artists are generally afraid to mingle with dissidents,” says Fusco. “There are a few bloggers who post stories about confrontations with police and political prisoners, a few older human rights activists who collect information about detentions and prison conditions, a handful of opposition groups who advocate for political reforms, but they have virtually no influence on the government.”
In the past, Cuban authorities used the US embargo as an excuse to justify restrictions on freedom of expression. Now that the excuses are running out, it is time for the Cuban government allow its dissidents the same freedoms as its conformists.
Ryan McChrystal is the assistant editor, online at Index on Censorship
11 Jan 2016 | Bulgaria, Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features
Journalists of the Bulgarian investigative news website Bivol.bg are facing an orchestrated smear campaign that’s unusual even for Bulgaria, the worst-ranking EU member in the 2015 Reporters Without Borders press freedom index.
The attacks can be linked to mainstream media outlets controlled by the Bulgarian media mogul and lawmaker Delyan Peevski, and seem to be a response to a number of investigations published recently by Bivol.bg, all involving Peevski in one way or another.
“Even if it is not like in the beginning, the smear campaign did not end,” Bivol’s editor-in-chief, Atanas Chobanov, told Index on Censorship in December 2015.
During the autumn, articles denigrating Chobanov and Assen Yordanov — Bivol’s founder, co-owner and director — began appearing in media outlets such as the Bulgarian weekly Politika, the Telegraph, Monitor and Trud dailies, as well as the news website Blitz, which are controlled either directly or through proxies by Delyan Peevski, an MP from the parliamentary group of the Turkish minority party, Movement for Rights and Freedoms (MRF).
According to a summary published by OCCRP, the articles allege that Yordanov uses Bivol.bg to publish fake stories to blackmail politicians and business people. The attack pieces allege that Bivol.bg publishes stories about environmental issues to serving the interests of fake eco-activists who pose as people concerned about the environment to extract cash from firms that want to build in the Bulgarian mountains and on the Black Sea coast.
There are allegations saying that Atanas Chobanov is a former Komsomol activist (the youth division of the Bulgarian Communist Party), aspired to a political career, and has links to a businessman whose media strongly oppose Peevski. Some articles insinuate that Chobanov works for foreign intelligence services; and that he lives a luxurious life in Paris where he milks the social welfare system. (The latter allegation is interesting because in 2013, it was Chobanov who uncovered that former planning and investment minister Ivan Danov was collecting €1,800 per month in unemployment benefits in France while working two jobs in Bulgaria.)
The pieces give a thoroughly negative depiction of Chobanov, saying that he is greedy, aggressive, mentally unstable, narcissistic, disliked and unwanted.
The campaign culminated on 10 October, when a crew of the Bulgarian TV Channel 3, a television where Peevski is a co-owner, showed up at the rented apartment in Paris where Chobanov and his family lives.
“I was at the Global Investigative Journalism Conference in Lillehammer, Norway,” Chobanov said, adding that the crew did not try to contact him by phone, e-mail or by any other means in advance. The journalist believes they must have known that he was away because he made a public announcement about his upcoming trip and he was tweeting from Lillehammer.
Although Bivol.bg was the target of similar articles in the past, the ongoing campaign started when the investigative news site published proof that Peevski is a shareholder at the Bulgarian cigarette maker Bulgartabac, a former state-owned company that underwent a controversial privatization process in 2011.
Then the journalists started publishing a story about the disappearance of €26 million ($28.3 million) from an EU food aid program for the poor, where the majority shareholders of Bulgaria’s First Investment Bank (FIB) were implicated. “After the Bulgarian bank crash, Peevski moved his assets, his credits and deposits to this bank, so this investigation also hurts Peevski’s interests,” Chobanov said.
Next, Bivol.bg broke “Yaneva Gate”, a series of stories based on leaked phone conversations between former Sofia City Court president Vladimira Yaneva and fellow judge Roumyana Chenalova over unlawful surveillance warrants that Yaneva had signed.
In those conversations, the judges mentioned Peevski by his first name, Delyan. “The Prosecutor General, one of the men of Peevski, is also involved,” Chobanov pointed out, adding that the story provoked an earthquake in Bulgarian politics, causing justice minister Hristo Ivanov to resign.
“It is a judicial battle now. We are turning to courts to stop the smear campaign, and we are also defending ourselves from legal complaints filed for the investigations we did in the past,” Chobanov said.
Reporters Without Borders expressed support and sympathy for Chobanov, condemning the smear campaign directed against him. “We can only condemn what are clearly attempts to intimidate Bivol’s journalists,” said Alexandra Geneste, the head of the Reporters Without Borders EU/Balkans desk. “Their investigative work is perfectly legitimate and we express our most sincere support and sympathy for them.”
The smear campaign orchestrated by the media outlets controlled by Peevski took an unexpected turn when they accused Xavier Lapeyre de Cabanes, the French Ambassador to Bulgaria with unacceptable meddling in Bulgaria’s affairs after he shared on Twitter a link to the press release by Reporters Without Borders with the comment: “Press freedom has no borders.”
The Bulgarian Association Network for Free Speech also issued a position saying that “the integrity of Bivol’s investigations and publications has not been and is not challenged in any way, despite repeated attempts to pressure our colleagues. (…) We have no reason to doubt the good faith of our colleagues, the journalist from Bivol (…).”
8 Jan 2016 | Belarus, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, News and features, Poland, Portugal, Serbia, Turkey
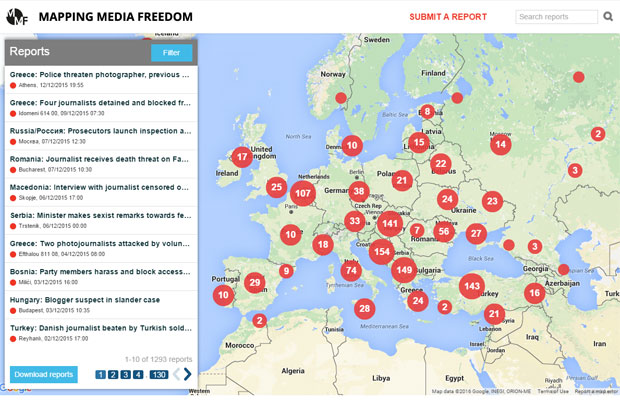
The attacks on the offices of satirical magazine Charlie Hebdo in Paris in January set the tone for conditions for media professionals in 2015. Throughout the year, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom correspondents verified a total of 745 violations of media freedom across Europe.
From the murders of journalists in Russia, Poland and Turkey to the growing threat posed by far-right extremists in Germany and government interference in Hungary — right down to the increasingly harsh legal measures imposed on reporters right across the continent — Mapping Media Freedom exposed many difficulties media workers face in simply doing their jobs.
“Last year was a tumultuous one for press freedom; from the attacks at Charlie Hebdo to the refugee crisis-related aggressions, Index observed many threats to the media across Europe,” said Hannah Machlin, Index on Censorship’s project officer for the Mapping Media Freedom project. “To highlight the important cases and trends of the year, we’ve asked our correspondents, who have been carefully monitoring the region, to discuss one violation each that stood out to them.”
Belarus / 19 verified reports between May-Dec 2015
Journalist blocked from shooting entrance to polling station
“It demonstrates the Belarusian authorities’ attitude to media as well as ‘transparency’ of the presidential election – the most important event in the current year.” — Ольга К.-Сехович
Greece / 15 verified reports in 2015
Four journalists detained and blocked from covering refugee operation
“This is important because it is typical ‘attempt to limit press freedom’, as the Union wrote in a statement and it is not very hopeful for the future. The way refugees and migrants are treated is very sensitive and media should not be prevented from covering this issue.” — Christina Vasilaki
Hungary / 57 verified reports in 2015
Serbian camera crew beaten by border police
“These physical attacks, the harsh treatment and detention of journalists are striking because the Hungarian government usually uses ‘soft censorship’ to control media and journalists, they rarely use brute force.” — Zoltan Sipos
Italy / 72 verified reports in 2015
Italian journalists face up to eight years in prison for corruption investigation
“I chose it because this case is really serious: the journalists Emiliano Fittipaldi and Gianluigi Nuzzi are facing up to eight years in prison for publishing books on corruption in the Vatican. This case could have a chilling effect on press freedom. It is really important that journalists investigate and they must be free to do that.” — Rossella Ricchiuti
Lithuania / 9 verified reports in 2015
Journalist repeatedly harassed and pushed out of local area
“I chose it because I found it relevant to my personal experience and the fellow journalist has been the only one to have responded to my hundreds of e-mails — including requests to fellow Lithuanian journalists to share their personal experience on media freedom.” — Linas Jegelevicius
Macedonia / 27 verified reports in 2015
Journalist publicly assaults another journalist
“I have chosen this incident because it best describes the recent trend not only in Macedonia and my other three designated countries, Croatia, Bosnia and Montenegro, but also in the whole region. And that is polarization among journalists, more and more verbal and, like in this unique case, physical assaults among colleagues. It best describes the ongoing trend where journalists are not united in safeguarding public interest but are nothing more than a tool in the hands of political and financial elites. It describes the division between pro-opposition and pro-government journalists. It is a clear example of absolute deviation from the journalistic ethic.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Poland / 11 verified reports in 2015
Law on public service broadcasting removes independence guarantees
“The new media law, which was passed through Poland`s two-chamber parliament in the last week of December, constitutes a severe threat to pluralism of opinions in Poland, as it is aimed at streamlining public media along the lines of the PiS party that holds the overall majority. The law is currently only awaiting president Duda’s signature, who is a close PiS ally.” — Martha Otwinowski
Portugal / 9 verified reports in 2015
Two-thirds of newspaper employees will be laid off
“It’s a clear picture of the media in Portugal, which depends on investors who show no interest in a healthy, well-informed democracy, but rather in how owning a newspaper can help them achieve their goals — and when these are not met they don’t hesitate to jump boat, leaving hundreds unemployed.” — João de Almeida Dias
Russia / 37 verified reports between May-Dec 2015
Media freedom NGO recognised as foreign agent, faces closure
“The most important trend of the 2015 in Russia is the continuing pressure over the civil society. More than 100 Russian civil rights advocacy NGOs were recognized as organisations acting as foreign agents which leads to double control and reporting, to intimidation and insulting of activists, e.g., by the state-owned media. Many of them faced large fines and were forced to closure.” — Andrey Kalikh
Russia / 37 verified reports between May-Dec 2015
TV2 loses counter claim to renew broadcasting license Roskomnadzor
“It illustrates the crackdown on independent local media, which can not fight against the state officials even if they have support from the audience and professional community.” — Ekaterina Buchneva
Serbia / 41 verified reports in 2015
Investigative journalist severely beaten with metal bars
“It’s a disgrace and a flash-back to Serbia’s dark past that a journalist, who’s well known for investigating high-level corruption, get’s beaten up with metal bars late at night by ‘unknown men’.” — Mitra Nazar
Turkey / 97 verified reports in 2015
Police storm offices of Koza İpek, interrupting broadcast
“The raid on Bugün and Kanaltürk’s offices just days ahead of parliamentary elections was a drastic example — broadcasts were cut by police and around 100 journalists ended up losing their jobs over the next month — of how the current Turkish government tries to strong-arm media organisations.” — Catherine Stupp
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|
7 Jan 2016 | Campaigns, Europe and Central Asia, France, mobile, Statements

On the anniversary of the brutal attack on the offices of Charlie Hebdo we, the undersigned, reaffirm our commitment to the defence of the right to freedom of expression, even when that right is being used to express views that some may consider offensive.
The Charlie Hebdo attack, which left 11 dead and 12 wounded, was a horrific reminder of the violence to which journalists, artists and other critical voices are subjected in a global atmosphere marked by increasing intolerance of dissent. The killings inaugurated a year that has proved especially challenging for proponents of freedom of opinion.
Non-state actors perpetrated violence against their critics largely with impunity, including the brutal murders of four secular bloggers in Bangladesh by Islamist extremists, and the killing of an academic, M M Kalburgi, who wrote critically against Hindu fundamentalism in India.
Despite the turnout of world leaders on the streets of Paris in an unprecedented display of solidarity with free expression following the Charlie Hebdo murders, artists and writers faced intense repression from governments throughout the year. In Malaysia, cartoonist Zunar is facing a possible 43-year prison sentence for alleged ‘sedition’; in Iran, cartoonist Atena Fardaghani is serving a 12-year sentence for a political cartoon; and in Saudi Arabia, Palestinian poet Ashraf Fayadh was sentenced to death for the views he expressed in his poetry.
Perhaps the most far-reaching threats to freedom of expression in 2015 came from governments ostensibly motivated by security concerns. Following the attack on Charlie Hebdo, 11 interior ministers from European Union countries including France, Britain and Germany issued a statement in which they called on Internet service providers to identify and remove online content ‘that aims to incite hatred and terror.’ In July, the French Senate passed a controversial law giving sweeping new powers to the intelligence agencies to spy on citizens, which the UN Human Rights Committee categorised as “excessively broad”.
This kind of governmental response is chilling because a particularly insidious threat to our right to free expression is self-censorship. In order to fully exercise the right to freedom of expression, individuals must be able to communicate without fear of intrusion by the State. Under international law, the right to freedom of expression also protects speech that some may find shocking, offensive or disturbing. Importantly, the right to freedom of expression means that those who feel offended also have the right to challenge others through free debate and open discussion, or through peaceful protest.
On the anniversary of the Charlie Hebdo attacks, we, the undersigned, call on all Governments to:
- Uphold their international obligations to protect the rights of freedom of expression and information for all, and especially for journalists, writers, artists and human rights defenders to publish, write and speak freely;
- Promote a safe and enabling environment for those who exercise their right to freedom of expression, and ensure that journalists, artists and human rights defenders may perform their work without interference;
- Combat impunity for threats and violations aimed at journalists and others exercising their right to freedom of expression, and ensure impartial, timely and thorough investigations that bring the executors and masterminds behind such crimes to justice. Also ensure victims and their families have expedient access to appropriate remedies;
- Repeal legislation which restricts the right to legitimate freedom of expression, especially vague and overbroad national security, sedition, obscenity, blasphemy and criminal defamation laws, and other legislation used to imprison, harass and silence critical voices, including on social media and online;
- Ensure that respect for human rights is at the heart of communication surveillance policy. Laws and legal standards governing communication surveillance must therefore be updated, strengthened and brought under legislative and judicial control. Any interference can only be justified if it is clearly defined by law, pursues a legitimate aim and is strictly necessary to the aim pursued.
PEN International
ActiveWatch – Media Monitoring Agency
Adil Soz – International Foundation for Protection of Freedom of Speech
Africa Freedom of Information Centre
ARTICLE 19
Bahrain Center for Human Rights
Belarusian Association of Journalists
Brazilian Association for Investigative Journalism
Bytes for All
Cambodian Center for Human Rights
Canadian Journalists for Free Expression
Center for Independent Journalism – Romania
Center for Media Freedom and Responsibility
Comité por la Libre Expresión – C-Libre
Committee to Protect Journalists
Electronic Frontier Foundation
Foundation for Press Freedom – FLIP
Freedom Forum
Fundamedios – Andean Foundation for Media Observation and Study
Globe International Center
Independent Journalism Center – Moldova
Index on Censorship
Initiative for Freedom of Expression – Turkey
Institute for the Studies on Free Flow of Information
Instituto de Prensa y Libertad de Expresión – IPLEX
Instituto Prensa y Sociedad de Venezuela
International Federation of Journalists
International Federation of Library Associations and Institutions
International Press Institute
International Publishers Association
Journaliste en danger
Maharat Foundation
MARCH
Media, Entertainment and Arts Alliance
Media Foundation for West Africa
National Union of Somali Journalists
Observatorio Latinoamericano para la Libertad de Expresión – OLA
Pacific Islands News Association
Palestinian Center for Development and Media Freedoms – MADA
PEN American Center
PEN Canada
Reporters Without Borders
South East European Network for Professionalization of Media
Vigilance pour la Démocratie et l’État Civique
World Association of Community Radio Broadcasters – AMARC
PEN Mali
PEN Kenya
PEN Nigeria
PEN South Africa
PEN Eritrea in Exile
PEN Zambia
PEN Afrikaans
PEN Ethiopia
PEN Lebanon
Palestinian PEN
Turkish PEN
PEN Quebec
PEN Colombia
PEN Peru
PEN Bolivia
PEN San Miguel
PEN USA
English PEN
Icelandic PEN
PEN Norway
Portuguese PEN
PEN Bosnia
PEN Croatia
Danish PEN
PEN Netherlands
German PEN
Finnish PEN
Wales PEN Cymru
Slovenian PEN
PEN Suisse Romand
Flanders PEN
PEN Trieste
Russian PEN
PEN Japan




