23 Apr 2018 | News, Turkey, Turkey Uncensored
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Academic Sharo Ibrahim Garip
Even before the attempted coup in July 2016, the situation for academics within Turkey was drastically changing.
Marking a turning point for the country’s political environment, the failed July 2016 coup was an attempt to oust president Recep Tayyip Erdogan.
In 2016 hundreds of academics were dismissed from their positions without notice, including sociologist Sharo Ibrahim Garip, who taught at Yuzuncu Yil University in the East Anatolian city of Van, Turkey.
A German national with Kurdish roots, Garip was dismissed from his position at the university in February 2016. Accused of spreading terrorist propaganda, he was arrested in January 2016 and placed under a two-year travel ban, after he signed a petition, along with 1,227 other academics, urging the Turkish government to end its crackdown on Kurdish communities in Turkey’s southeast.
The petition by Academics for Peace called for a peaceful situation to the conflict with the Kurdish Workers Party (PKK), a terrorist group seeking an independent Kurdish state within Turkey. Garip and the other academics denounced “war-like conditions” in the south-east and accused the government of an “extermination and expulsion policy” following the end of a ceasefire with the group and Turkish security forces in 2015. President Erdogan referred to them as “so-called intellectuals” and accused the signatories of “treason”.
Although there was no evidence Garip supported the group, he was still unable to leave the country or practice his profession, although his German citizenship prevented him from being detained pre-trial. Now working at the University of Essen-Duisburg, Garip spoke with Danyaal Yasin of Index on Censorship about his dismissal and the situation for academics following the coup.
Index: After you and hundreds of other academics were dismissed, what were your initial thoughts?
Sharo Ibrahim Garip: I was at the university. I received just a one-sentence decision from the university administration: “Mr Garip’s contract has been cancelled as the university no longer requires his services.” It was not surprising to me because I had already expected such an outcome. The history of the Turkish state is rife with instances of the elimination of political opposition, particularly critical thinkers such as academics and journalists. It was a planned action to eliminate critical thinkers from universities and the public sector. All those changes in the bureaucracy and public sector started before the military coup and continued following the civilian putsch. I could clearly observe the regime change in silence, but it was not possible to stop.
Index: Where were you when you found out? How did this affect you and your family?
Garip: I was detained on 15 January 2016 at the university in Van. I had to spend one night and one day in a jail cell of the special anti-terror unit of the police. I realised that I was a hostage from the beginning. I was threatened and humiliated during my interrogation. My family (who live mostly in Norway and Austria) was extremely concerned for my life. They still recall the events of the 1990s in Turkey, when many people were jailed/tortured or murdered, including the well-known cases of Hrant Dink and Tahir Elci, as well as many other intellectuals. The signatories have also been publicly exposed in the press and social media by government supporters and nationalists, leading to fears of reprisals from a mafia boss who declared that they will “spill the blood” of the signatories.
Index: What was the most difficult part?
Garip: I was removed from my academic position at Yuzuncu Yil (One Hundredth Year) University in Van in February 2016 because I had signed the petition by Academics for Peace, calling on the Turkish government to pursue a peaceful approach in its conflict with the Kurds, and in order to further punish me, the government forbade me to leave the country. I experienced a kind of structural violence, to live in Turkey without a job, health insurance, or a home. I shared a flat with friends for a while. I was trying to survive under very difficult conditions. I also experienced psychological violence. For example, all my phone calls were tapped and I was under regular surveillance. These had a very deep psychological effect on me. I didn’t want to meet with friends because I was constantly afraid of being attacked, imprisoned, killed, or tortured.
Under such circumstances is almost impossible to teach or produce any kind of academic work, write articles, do research, and so on.
It was painful to observe a country sink into political disaster again. Escalation of tensions, political collapse, and the war go back to the 90s, with civil war, political murders, missing people, bombing attacks on peaceful gatherings and meetings. It is also difficult to accept that at the moment approximately 70,000 students are in prison. One of my best students (who is only 22 years old) has been sentenced to 10 years in prison.
Index: Did you have to conceal your Kurdish heritage when studying or teaching?
Garip: No, I have never concealed my heritage. On the contrary, I disclosed my Kurdish heritage from the first day of teaching at the university in Van. Every day I talked to my students first in Kurdish and then continued in Turkish or sometimes in English. I arranged a Kurdish language course for sociology students as well. Kurds in Turkey have been assimilated for many years, a humiliating experience. Most Kurdish students have been psychologically damaged/traumatised by the violence perpetrated by the Turkish government. It was important to me to give my students a feeling of self-worth. This enabled me to establish a foundation of trust with my students, something not many other academics did.
Index: Why do you think academics are being brought to trial? What is the government’s goal?
Garip: It should be mentioned that Turkey has never, since its inception in 1921 until today, been a truly democratic country. Neither academic freedom nor freedom of speech has ever truly existed. The Turkish government has always thought of academics as well-paid public servants, a position which enjoys great privilege. Most Turkish academics have generally been loyal to the state and supported the official ideology. The petition for peace represented the first time that academics showed disloyalty to the state ideology, especially with regard to the Kurdish issue. For an authoritarian regime, such criticism was simply not acceptable. In this way, the government will punish academics. Turkey now appears to be inclined to go from an authoritarian regime to a totalitarian one. All undemocratic regimes try to maintain total control over society (the consolidation of institutional powers such as the NS regime). The masses must be repressed, and the media and intellectuals must be silenced and browbeaten. This is the goal of the government, which is why academics have been brought to trial. The academics have been punished in a number of different yet effective ways: dismissal, foreign travel bans, disciplinary processes.
Index: What has been the biggest change for academics in the country since the attempted coup?
Garip: The universities, schools, media, judiciary, and also parliament are now under the total control of the government. In particular, schools, the media, and universities have been shaped by a new ideology, which is both religious and nationalist. Many academics have been dismissed; more than 150,000 people in the public sector have lost their jobs. In the wake of the civilian putsch, 40,000 teachers, 8,247 academics, and 4,000 prosecutors and judges have been dismissed.
At universities, cultural events and demonstrations are forbidden. Students are not allowed to choose topics for their master or doctoral studies. At the moment four academics are in prison and another 15 academics and I have been sentenced to one year and three months in prison. Academics in Turkey are trying to survive; many of them live in very poor conditions. They have come up with new ideas such as establishing houses of culture or academies on the street. It is important to mention that academics and intellectuals all over the world, including Judith Butler, Etienne Balibar, and many other prominent academics have supported academics in Turkey. The quality of education is declining rapidly because many well-educated professors and instructors are leaving Turkey.
Index: Was there backlash from other academics when the petition came out?
Garip: Yes, at first. After the petition for peace came out, a petition titled “We support our government against terrorism” was signed by 5,000 academics. Some colleagues at the university definitely distanced themselves from me. The reason for this was partly ideological and partly out of fear. However, some academics supported me, as did most of my students.
Index: Do you feel the current climate will ever improve within the country?
Garip: I don’t like to be completely pessimistic but it is very difficult to expect much change within a short period. Possibly the situation may improve over the long term. At the moment we are confronted with a regime change and a government acting in desperation. Turkish society is extremely polarised and the political climate embittered. Structures within the government have been almost completely stripped down. It will be not easy to shift society from an authoritarian structure to a democratic one. We cannot forget that half of Turkey wants a secular and democratic government.
Index: You are now based in Germany – how does it feel to teach again?
Garip: It is wonderful. Here I enjoy a climate of freedom with my students. As I stated above, I have academic freedom and freedom of speech here which I wish my Turkish friends also had. While I was in Van, Turkey I invited many professors from London, Canada, and Germany to give lectures to my students via Skype. I wish to thank them for their excellent contributions. If I have the opportunity I would like to teach my students in Van from Germany via Skype as well.
Index: How has your work changed since leaving Turkey?
Garip: To be honest it was not easy to settle down. I had to start from the bottom again. But thanks to the social government and constitutional democracy in Germany, I was fortunate to receive help from many of my friends. I received a scholarship first for three months from the University of Essen-Duisburg and now have a fellowship from the University of Cologne. I am currently working on a research project. I have finished a new article and can publish it without fear. In short, I enjoy academic freedom and freedom of speech again. I wish all my friends in Turkey could enjoy such freedoms as well.
Index: Do you think you will ever return to Turkey?
Garip: Yes, of course I will. Travelling is an essential human right. I will visit my friends there or attend conferences and work on research projects.
A previous version of this article incorrectly stated that “the intended coup was an attempt to protect the country’s democracy from president Recep Tayyip Erdogan”. This was updated on 24 April 2018[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1524653051961-3c4f18a5-613b-9″ taxonomies=”8607″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
19 Apr 2018 | Awards, News
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]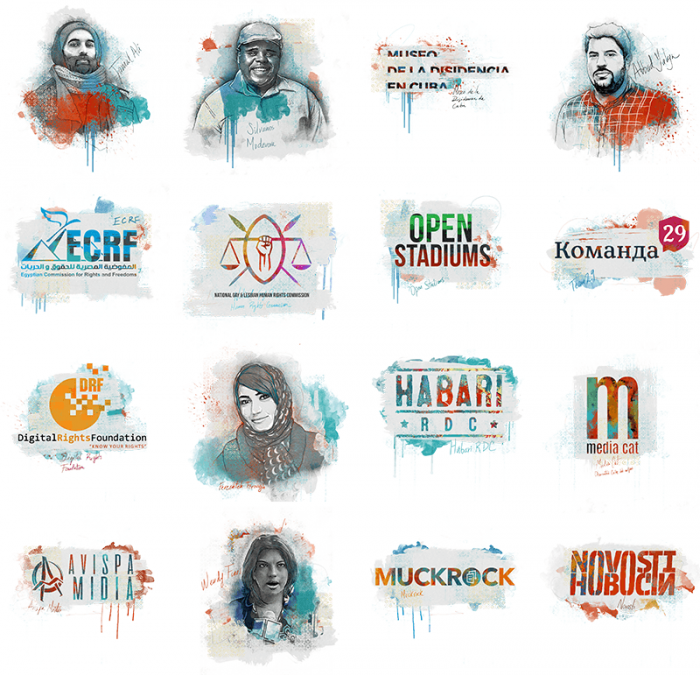
Each year, the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards gala honours courageous champions who fight for free speech around the world.
Drawn from more than 400 crowdsourced nominations, this year’s nominees include artists, journalists, campaigners and digital activists tackling censorship and fighting for freedom of expression. Many of the 16 shortlisted are regularly targeted by authorities or by criminal and extremist groups for their work: some face regular death threats, others criminal prosecution.
The gala takes place on Thursday 19 April in London and will be hosted by stand-up poet Kate Fox.
We will be live tweeting throughout the evening on @IndexCensorship. Get involved in the conversation using the hashtag #IndexAwards2018. Listen LIVE beginning at 7:30pm BST on Resonance FM
Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards nominees 2018
Arts

Jamal Ali, Azerbaijan
Jamal Ali is an exiled rap musician with a history of challenging Azerbaijan’s authoritarian regime. Ali was one of many who took to the streets in 2012 to protest spending around the country’s hosting of the Eurovision song contest. Detained and tortured for his role in the protests, he went into exile after his life was threatened. Ali has persisted in challenging the government by releasing music critical of the country’s dynastic leadership. Following the release of one song, Ali’s mother was arrested in a senseless display of aggression. In provoking such a harsh response with a single action, Ali has highlighted the repressive nature of the regime and its ruthless desire to silence all dissent.
Full profile
Silvanos Mudzvova, Zimbabwe
Playwright and activist Silvanos Mudzvova uses performance to protest against the repressive regime of recently toppled President Robert Mugabe and to agitate for greater democracy and rights for his country’s LGBT community. Mudzvova specialises in performing so-called “hit-and-run” actions in public places to grab the attention of politicians and defy censorship laws, which forbid public performances without police clearance. His activism has seen him be traumatically abducted: taken at gunpoint from his home he was viciously tortured with electric shocks. Nonetheless, Mudzvova has resolved to finish what he’s started and has been vociferous about the recent political change in Zimbabwe.
Full profile
The Museum of Dissidence, Cuba
The Museum of Dissidence is a public art project and website celebrating dissent in Cuba. Set up in 2016 by acclaimed artist Luis Manuel Otero Alcántara and curator Yanelys Nuñez Leyva, their aim is to reclaim the word “dissident” and give it a positive meaning in Cuba. The museum organises radical public art projects and installations, concentrated in the poorer districts of Havana. Their fearlessness in opening dialogues and inhabiting public space has led to fierce repercussions: Nuñez was sacked from her job and Otero arrested and threatened with prison for being a “counter-revolutionary.” Despite this, they persist in challenging Cuba’s restrictions on expression.
Full profile
Abbad Yahya, Palestine
Abbad Yahya is a Palestinian author whose novel, Crime in Ramallah, was banned by the Palestinian Authority in 2017. The book tackles taboo issues such as homosexuality, fanaticism and religious extremism. It provoked a rapid official response and all copies of the book were seized. The public prosecutor issued a summons for questioning against Yahya while the distributor of the novel was arrested and interrogated. Yahya also received threats and copies of the book were burned. Despite this, he has spent the last year raising awareness of freedom of expression and the lives of young people in the West Bank and Gaza, particularly in relation to their sexuality.
Full profile
Campaigning

Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms, Egypt
The Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms is one of the few human rights organisations still operating in a country which has waged an orchestrated campaign against independent civil society groups. Egypt is becoming increasingly hostile to dissent, but ECRF continues to provide advocacy, legal support and campaign coordination, drawing attention to the many ongoing human rights abuses under the autocratic rule of President Abdel Fattah-el-Sisi. Their work has seen them subject to state harassment, their headquarters have been raided and staff members arrested. ECRF are committed to carrying on with their work regardless of the challenges.
Full profile
National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission, Kenya
The National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission is the only organisation in Kenya challenging and preventing LGBTI discrimination through the country’s courts. Even though homosexuality isn’t illegal in Kenya, homosexual acts are. Homophobia is commonplace and men who have sex with men can be punished by up to 14 years in prison, and while no specific laws relate to women, former Prime Minister Raila Odinga has said lesbians should also be imprisoned. NGLHRC has had an impact by successfully lobbying MPs to scrap a proposed anti-homosexuality bill and winning agreement from the Kenya Medical Association to stop forced anal examination of clients.
Full profile
Open Stadiums, Iran
The women behind Open Stadiums risk their lives to assert a woman’s right to attend public sporting events in Iran. The campaign challenges the country’s political and religious regime, and engages women in an issue many human rights activists have previously thought unimportant. Iranian women face many restrictions on using public space. Open Stadiums has generated broad support for their cause in and out of the country. As a result, MPs and people in power are beginning to talk about women’s rights to attend sporting events in a way that would have been taboo before.
Full profile
Team 29, Russia
Team 29 is an association of lawyers and journalists that defends those targeted by the state for exercising their right to freedom of speech in Russia. It is crucial work in a climate where hundreds of civil society organisations have been forced to close and where increasingly tight restrictions have been placed on public protest and political dissent since mass demonstrations rocked Russia in 2012. Team 29 conducts about 50 court cases annually, many involving accusations of high treason. Aside from litigation, they offer legal guides for activists and advice on what to do when summoned by state security for interrogation.
Full profile
Digital Activism

Digital Rights Foundation, Pakistan
In late 2016, the Digital Rights Foundation established a cyber-harassment helpline that supported more than a thousand women in its first year of operation alone. Women make up only about a quarter of the online population in Pakistan but routinely face intense bullying including the use of revenge porn, blackmail, and other kinds of harassment. Often afraid to report how badly they are treated, women react by withdrawing from online spaces. To counter this, DRF’s Cyber Harassment Helpline team includes a qualified psychologist, digital security expert, and trained lawyer, all of whom provide specialised assistance.
Full profile
Fereshteh Forough, Afghanistan
Fereshteh Forough is the founder and executive director of Code to Inspire, a coding school for girls in Afghanistan. Founded in 2015, this innovative project helps women and girls learn computer programming with the aim of tapping into commercial opportunities online and fostering economic independence in a country that remains a highly patriarchal and conservative society. Forough believes that with programming skills, an internet connection and using bitcoin for currency, Afghan women can not only create wealth but challenge gender roles and gain independence.
Full profile
Habari RDC, Congo
Launched in 2016, Habari RDC is a collective of more than 100 young Congolese bloggers and web activists, who use Facebook, Twitter and YouTube to give voice to the opinions of young people from all over the Democratic Republic of Congo. Their site posts stories and cartoons about politics, but it also covers football, the arts and subjects such as domestic violence, child exploitation, the female orgasm and sexual harassment at work. Habari RDC offers a distinctive collection of funny, angry and modern Congolese voices, who are demanding to be heard.
Full profile
Mèdia.cat, Spain
Mèdia.cat is a Catalan website devoted to highlighting media freedom violations and investigating under-reported stories. Unique in Spain, it was a particularly significant player in 2017 when the disputed independence referendum brought issues of censorship and the impartiality of news under the spotlight. The website provides an online platform that systematically catalogues censorship perpetrated in the region. Its map on censorship offers a way for journalists to report on abuses they have personally suffered.
Journalism

Avispa Midia, Mexico
Avispa Midia is an independent online magazine that prides itself on its use of multimedia techniques to bring alive the political, economic and social worlds of Mexico and Latin America. It specialises in investigations into organised crime and the paramilitaries behind mining mega-projects, hydroelectric dams and the wind and oil industry. Many of Avispa’s reports in the last 12 months have been focused on Mexico and Central America, where the media group has helped indigenous and marginalised communities report on their own stories through audio and video training.
Wendy Funes, Honduras
Wendy Funes is an investigative journalist from Honduras who regularly risks her life for her right to report on what is happening in the country, an extremely harsh environment for reporters. Two journalists were murdered in 2017 and her father and friends are among those who have met violent deaths in the country – killings for which no one has ever been brought to justice. Funes meets these challenges with creativity and determination. For one article she had her own death certificate issued to highlight corruption. Funes also writes about violence against women, a huge problem in Honduras where one woman is killed every 16 hours.
MuckRock, United States
MuckRock is a non-profit news site used by journalists, activists and members of the public to request and share US government documents in pursuit of more transparency. MuckRock has shed light on government surveillance, censorship and police militarisation among other issues. MuckRock produces its own reporting, and helps others learn more about requesting information. Last year the site produced a Freedom of Information Act 4 Kidz lesson plan to help educators to start discussions about government transparency. Since then, they have expanded their reach to Canada. The organisation hopes to continue increasing their impact by putting transparency tools in the hands of journalists, researchers and ordinary citizens.
Novosti, Croatia
Novosti is a weekly Serbian-language magazine in Croatia. Although fully funded as a Serb minority publication by the Serbian National Council, it deals with a whole range of topics, not only those directly related to the minority status of Croatian Serbs. In the past year, the outlet’s journalists have faced attacks and death threats mainly from the ultra-conservative far-right. For its reporting, the staff of Novosti have been met with protest under the windows of the magazine’s offices shouting fascist slogans and anti-Serbian insults, and told they would end up killed like Charlie Hebdo journalists. Despite the pressure, the weekly persists in writing the truth and defending freedom of expression.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1524073803130-58a2be32-5f5a-7″ taxonomies=”8935″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
14 Feb 2018 | Awards, News, Press Releases

- Judges include Serpentine CEO Yana Peel; BBC journalist Razia Iqbal
- Sixteen courageous individuals and organisations who fight for freedom of expression in every part of the world
An exiled Azerbaijani rapper who uses his music to challenge his country’s dynastic leadership, a collective of Russian lawyers who seek to uphold the rule of law, an Afghan seeking to economically empower women through computer coding and a Honduran journalist who goes undercover to expose her country’s endemic corruption are among the courageous individuals and organisations shortlisted for the 2018 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellowships.
Drawn from more than 400 crowdsourced nominations, the shortlist celebrates artists, writers, journalists and campaigners overcoming censorship and fighting for freedom of expression against immense obstacles. Many of the 16 shortlisted nominees face regular death threats, others criminal prosecution or exile.
“Free speech is vital in creating a tolerant society. These nominees show us that even a small act can have a major impact. These groups and individuals have faced the harshest penalties for standing up for their beliefs. It’s an honour to recognise them,” said Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of campaigning nonprofit Index on Censorship.
Awards fellowships are offered in four categories: arts, campaigning, digital activism and journalism.
Nominees include rapper Jamal Ali who challenged the authoritarian Azerbaijan government in his music – and whose family was targeted as a result; Team 29, an association of lawyers and journalists that defends those targeted by the state for exercising their right to freedom of speech in Russia; Fereshteh Forough, founder and executive director of Code to Inspire, a coding school for girls in Afghanistan; Wendy Funes, an investigative journalist from Honduras who regularly risks her life for her right to report on what is happening in the country.
Other nominees include The Museum of Dissidence, a public art project and website celebrating dissent in Cuba; the National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission, a group proactively challenging LGBTI discrimination through the Kenya’s courts; Mèdia.cat, a Catalan website highlighting media freedom violations and investigating under-reported or censored stories; Novosti, a weekly Serbian-language magazine in Croatia that deals with a whole range of topics.
Judges for this year’s awards, now in its 18th year, are BBC reporter Razia Iqbal, CEO of the Serpentine Galleries Yana Peel, founder of Raspberry Pi CEO Eben Upton and Tim Moloney QC, deputy head of Doughty Street Chambers.
Iqbal says: “In my lifetime, there has never been a more critical time to fight for freedom of expression. Whether it is in countries where people are imprisoned or worse, killed, for saying things the state or others, don’t want to hear, it continues to be fought for and demanded. It is a privilege to be associated with the Index on Censorship judging panel.”
Winners, who will be announced at a gala ceremony in London on 19 April, become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given year-long support for their work, including training in areas such as advocacy and communications.
“This award feels like a lifeline. Most of our challenges remain the same, but this recognition and the fellowship has renewed and strengthened our resolve to continue reporting, especially on the bleakest of days. Most importantly, we no longer feel so alone,” 2017 Freedom of Expression Awards Journalism Fellow Zaheena Rasheed said.
This year, the Freedom of Expression Awards are being supported by sponsors including SAGE Publishing, Google, Private Internet Access, Edwardian Hotels, Vodafone, media partner VICE News, Doughty Street Chambers and Psiphon. Illustrations of the nominees were created by Sebastián Bravo Guerrero.
Notes for editors:
- Index on Censorship is a UK-based non-profit organisation that publishes work by censored writers and artists and campaigns against censorship worldwide.
- More detail about each of the nominees is included below.
- The winners will be announced at a ceremony in London on 19 April.
For more information, or to arrange interviews with any of those shortlisted, please contact Sean Gallagher on 0207 963 7262 or [email protected].
More biographical information and illustrations of the nominees are available at indexoncensorship.org/indexawards2018.
Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellowship nominees 2018
ARTS

Jamal Ali
Azerbaijan
Jamal Ali is an exiled rapper and rock musician with a history of challenging Azerbaijan’s authoritarian regime. Ali was one of many who took to the streets in 2012 to protest spending around the country’s hosting of the Eurovision song contest. Detained and tortured for his role in the protests, he went into exile after his life was threatened. Ali has persisted in releasing music critical of the country’s dynastic leadership. Following the release of one song, Ali’s mother was arrested in a senseless display of aggression. In provoking such a harsh response with a single action, Ali has highlighted the repressive nature of the regime and its ruthless desire to silence all dissent.
Silvanos Mudzvova
Zimbabwe
Playwright and activist Silvanos Mudzvova uses performance to protest against the repressive regime of recently toppled President Robert Mugabe and to agitate for greater democracy and rights for his country’s LGBT community. Mudzvova specialises in performing so-called “hit-and-run” actions in public places to grab the attention of politicians and defy censorship laws, which forbid public performances without police clearance. His activism has seen him be traumatically abducted: taken at gunpoint from his home he was viciously tortured with electric shocks. Nonetheless, Mudzvova has resolved to finish what he’s started and has been vociferous about the recent political change in Zimbabwe.
The Museum of Dissidence
Cuba
The Museum of Dissidence is a public art project and website celebrating dissent in Cuba. Set up in 2016 by acclaimed artist Luis Manuel Otero Alcántara and curator Yanelys Nuñez Leyva, their aim is to reclaim the word “dissident” and give it a positive meaning in Cuba. The museum organises radical public art projects and installations, concentrated in the poorer districts of Havana. Their fearlessness in opening dialogues and inhabiting public space has led to fierce repercussions: Nuñez was sacked from her job and Otero arrested and threatened with prison for being a “counter-revolutionary.” Despite this, they persist in challenging Cuba’s restrictions on expression.
Abbad Yahya
Palestine
Abbad Yahya is a Palestinian author whose fourth novel, Crime in Ramallah, was banned by the Palestinian Authority in 2017. The book tackles taboo issues such as homosexuality, fanaticism and religious extremism. It provoked a rapid official response and all copies of the book were seized. The public prosecutor issued a summons for questioning against Yahya while the distributor of the novel was arrested and interrogated. Yahya also received threats on social media and copies of the book were burned. Despite this, he has spent the last year giving interviews to international and Arab press and raising awareness of freedom of expression and the lives of young people in the West Bank and Gaza, particularly in relation to their sexuality.
CAMPAIGNING

Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms
Egypt
The Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms or ECRF is one of the few human rights organisations still operating in a country which has waged an orchestrated campaign against independent civil society groups. Egypt is becoming increasingly hostile to dissent, but ECRF continues to provide advocacy, legal support and campaign coordination, drawing attention to the many ongoing human rights abuses under the autocratic rule of President Abdel Fattah-el-Sisi. Their work has seen them subject to state harassment, their headquarters have been raided and staff members arrested. ECRF are committed to carrying on with their work regardless of the challenges.
National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission
Kenya
The National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission is the only organisation in Kenya proactively challenging and preventing LGBTI discrimination through the country’s courts. Even though being homosexual isn’t illegal in Kenya, homosexual acts are. Homophobia is commonplace and men who have sex with men can be punished by up to 14 years in prison, and while no specific laws relate to women, former Prime Minister Raila Odinga has said lesbians should also be imprisoned. NGLHRC has had an impact by successfully lobbying MPs to scrap a proposed anti-homosexuality bill and winning agreement from the Kenya Medical Association to stop forced anal examination of clients “even in the guise of discovering crimes.”
Open Stadiums
Iran
The women behind Open Stadiums risk their lives to assert a woman’s right to attend public sporting events in Iran. The campaign that challenges the country’s political and religious regime, and engages women in an issue many human rights activists have previously thought unimportant. Iranian women face many restrictions on using public space. Open Stadiums has generated broad support for their cause in and out of the country. As a result, MPs and people in power are beginning to talk about women’s rights to attend sporting events in a way that would have been taboo before.
Team 29
Russia
Team 29 is an association of lawyers and journalists that defends those targeted by the state for exercising their right to freedom of speech in Russia. It is crucial work in a climate where hundreds of civil society organisations have been forced to close and where increasingly tight restrictions have been placed on public protest and political dissent since mass demonstrations rocked Russia in 2012. Team 29 conducts about 50 court cases annually, many involving accusations of high treason. Aside from litigation, they offer legal guides for activists, advice on what to do when state security comes for you and how to conduct yourself under interrogation.
DIGITAL ACTIVISM

Digital Rights Foundation
Pakistan
In late 2016, the Digital Rights Foundation established a cyber-harassment helpline that supported more than a thousand women in its first year of operation alone. Women make up only about a quarter of the online population in Pakistan but routinely face intense bullying including the use of revenge porn, blackmail, and other kinds of harassment. Often afraid to report how badly they are treated, women react by withdrawing from online spaces. To counter this, DRF’s Cyber Harassment Helpline team includes a qualified psychologist, digital security expert, and trained lawyer, all of whom provide specialised assistance.
Fereshteh Forough
Afghanistan
Fereshteh Forough is the founder and executive director of Code to Inspire, a coding school for girls in Afghanistan. Founded in 2015, this innovative project helps women and girls learn computer programming with the aim of tapping into commercial opportunities online and fostering economic independence in a country that remains a highly patriarchal and conservative society. Forough believes that with programming skills, an internet connection and using bitcoin for currency, Afghan women can not only create wealth but challenge gender roles and gain independence.
Habari RDC
Congo
Launched in 2016, Habari RDC is a collective of more than 100 young Congolese bloggers and web activists, who use Facebook, Twitter and YouTube to give voice to the opinions of young people from all over the Democratic Republic of Congo. Their site posts stories and cartoons about politics, but it also covers football, the arts and subjects such as domestic violence, child exploitation, the female orgasm and sexual harassment at work. Habari RDC offers a distinctive collection of funny, angry and modern Congolese voices, who are demanding to be heard.
Mèdia.cat
Spain
Mèdia.cat is a Catalan website devoted to highlighting media freedom violations and investigating under-reported or censored stories. Unique in Spain, it was a particularly significant player in 2017 when the heightened atmosphere in Catalonia over the disputed independence referendum brought issues of censorship and the impartiality of news under the spotlight. The website provides an online platform that catalogues systematically, publicly and in real time censorship perpetrated in the region. Its map on censorship offers a way for journalists to report on abuses they have personally suffered.
JOURNALISM

Avispa Midia
Mexico
Avispa Midia is an independent online magazine that prides itself on its daring use of multimedia techniques to bring alive the political, economic and social worlds of Mexico and Latin America. It specialises in investigations into organised criminal gangs and the paramilitaries behind mining mega-projects, hydroelectric dams and the wind and oil industry. Many of Avispa’s reports in the last 12 months have been focused on Mexico and Central America, where the media group has helped indigenous and marginalised communities report on their own stories by helping them learn to do audio and video editing. In the future, Avispa wants to create a multimedia journalism school to help indigenous and young people inform the world what is happening in their region, and break the stranglehold of the state and large corporations on the media.
Wendy Funes
Honduras
Wendy Funes is an investigative journalist from Honduras who regularly risks her life for her right to report on what is happening in the country, an extremely harsh environment for reporters. Two journalists were murdered in 2017 and her father and friends are among those who have met violent deaths in the country – killings for which no one has ever been brought to justice. Funes meets these challenges with creativity and determination. For one article she had her own death certificate issued to highlight corruption. Funes also writes about violence against women, a huge problem in Honduras where one woman is killed every 16 hours.
MuckRock
United States
MuckRock is a non-profit news site used by journalists, activists and members of the public to request and share US government documents in pursuit of more transparency. MuckRock has shed light on government surveillance, censorship and police militarisation among other issues. MuckRock produces its own reporting, and helps others learn more about requesting information. Last year the site produced a Freedom of Information Act 4 Kidz lesson plan to help educators to start discussions about government transparency. Since then, they have expanded their reach to Canada. The organisation hopes to continue increasing their impact by putting transparency tools in the hands of journalists, researchers and ordinary citizens.
Novosti
Croatia
Novosti is a weekly Serbian-language magazine in Croatia. Although fully funded as a Serb minority publication by the Serbian National Council, it deals with a whole range of topics, not only those directly related to the minority status of Croatian Serbs. In the past year, the outlet’s journalists have faced attacks and death threats mainly from the ultra-conservative far-right. For its reporting, the staff of Novosti have been met with protest under the windows of the magazine’s offices shouting fascist slogans and anti-Serbian insults, and told they would end up killed like Charlie Hebdo journalists. Despite the pressure, the weekly persists in writing the truth and defending freedom of expression.
20 Dec 2017 | Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]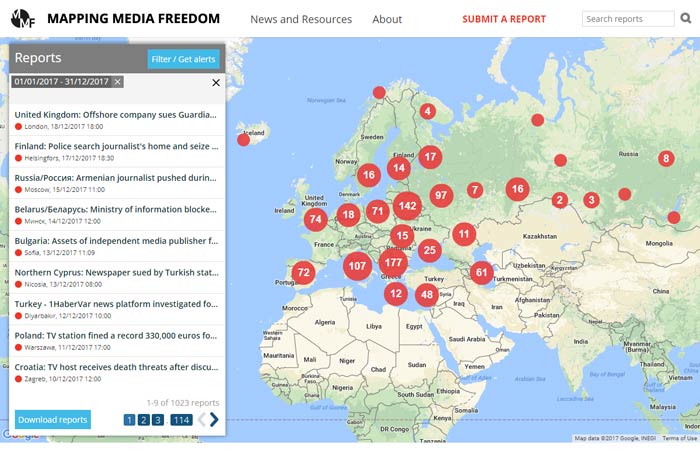 This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most.
This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most.
Russia / 197 verified reports in 2017
“In November Russia adopted a new restrictive law against foreign media. It allows recognising foreign media as foreign agents, which makes them subjects of numerous additional checks and obliges them to mark the content as produced by a foreign agent. The vague and ambiguous wording means it applies to many outlets – from established media to email newsletters. Which media will be recognised as foreign agents will be decided by Russian Ministry of justice. However, US media such as Voice of America or Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty have already received warnings about possible restrictions on their work in Russia.” — Ekaterina Buchneva
Turkey / 132 verified reports in 2017
“Although 155 journalists are currently imprisoned in Turkey — almost all of them on trumped-up charges — the trial of journalist Nedim Türfent, who reported on security operations in Turkey’s Kurdish regions, is by far the worst violation as open experiences of torture at the hands of police officers were recounted by at least a dozen people in the case. This violation shows that torture is making a comeback in Turkey.” — Barış Altıntaş
More on Nedim Türfent’s case.
Belarus / 92 verified reports in 2017
“The mass detention of journalists on Freedom Day in March was indicative of the Belarusian authorities’ campaign launched in 2017 on preventing journalists from performing their professional duties. The situation was provoked by mass protests across Belarus against introducing presidential decree on “social parasites”, which imposes a tax on the unemployed amid increasing economic crisis. The authorities have shown their real attitude to freedom of speech through real hunting on independent journalists and bloggers that are blocked from access to information, detained, jailed, and fined.” — Volha Siakovich
Spain / 66 verified reports in 2017
“The referendum on the independence of Catalonia, north-east of Spain, provoked an avalanche of incidents against reporters. On 1 October 2017, on the day of referendum considered illegal by the Spanish Constitutional Court, various journalists were assaulted during police intervention in polling stations. Spanish public television RTVE was biased in favour of Spanish unity while Catalan public television TV3 was biased in favour of the independence. In the aftermath of the referendum, many reporters on the ground suffered insults and assaults usually during street rallies. Unionist protesters used to insult and assault Catalan media. Catalunya Radio glass door was smashed and TV3 car window broken. Catalan protesters chanted “Spanish press manipulators” during Spanish televisions live coverage and Crònica Global website headquarters vandalised with spray paints and posters. The Catalan political question brought a wave of intimidation against journalists, never seen in such numbers and scale in recent years.” — Miho Dobrasin
Italy / 57 verified reports in 2017
“In 2017 Italian journalists experienced a high level of conflict with the judiciary. Journalists are constantly possible targets of law enforcement raids, also in breaching the privacy of journalists’ sources. In July, Il Fatto Quotidiano journalist Marco Lillo’s house was searched because he published a scoop concerning the investigation on people close to Matteo Renzi, prime minister at time time, for a case of corruption at the most important contracting authority in Italy: Consip. Last but not least, Il Sole 24 Ore journalist Nicola Borzi had seized his computer and archives by the law enforcement because he revealed a “secret of State”, without any formal charge against the journalist. These events show how hard is making scoops in Italy. Moreover, journalists are constantly targeted with lawsuits, frequently used as threats against freelancers. Nowadays the big unsolved issue for Italian journalism is at court.” — Lorenzo Bagnoli
France / 54 verified reports in 2017
“In February, presidential candidate Fillon smeared media outlets who covered alleged corruption case. This was an important moment in the treatment of the media in France. When accused of corruption, conservative presidential candidate François Fillon refused to step down and chose to attack the media and journalists. Journalists covering his campaign saw their working conditions deteriorate and had supporters insulting and attacking them.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Azerbaijan / 47 reports in 2017
“While there on-going violations of press freedom in Azerbaijan such as the jailing of journalists, office raids, bogus charges and other forms of persecution of journalists, I chose the blocking of opposition and independent news websites in March because it is a sign of further deterioration of media freedom in Azerbaijan. If before there were deliberate slowdowns or DDoS attacks, changes in legislation give full authority to the government institutions wanting to shut down or limit access to the flow of independent and alternative news.” — Arzu Geybullayeva
Croatia / 33 verified reports in 2017
“In September, around 20 members of the Autochthonous Croatian Party of Rights (A-HSP), a far-right political party, which is led by Drazen Keleminec, burned a copy of weekly newspaper Novosti, regional broadcaster N1 reported. This is another example where nationalistic and conservative narratives are endangering media freedom. In this particular case a right-wing political party is targeting the others, in this case the others is an ethnically and linguistically minority weekly, describing them as enemies of the state. The widespread narrative that has resulted in several severe media freedom infringements in this EU country.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Macedonia / 27 verified reports in 2017
“During the April’s storming of the Assembly building in the capital Skopje, 23 media workers were physically assaulted, threatened or barred from reporting at the scene. This case perfectly exemplifies what happens when political elites intentionally demonize and dehumanize media workers that are critically observing theirs work by describing them as traitors and foreign mercenaries. In the eyes of the common people, they instantly became a legitimate target. This is a widespread trend in Southeast Europe.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia and Herzegovina / 21 verified reports in 2017
“The case of Dragan Bursac is one of the many cases in Southeast Europe where journalists/media workers are threatened/attacked for challenging the mainstream nationalistic narrative. Namely, he was critical on the fact that a military leader, accused of committing war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY), is celebrated as a hero by the politicians and media.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Germany / 20 verified reports in 2017
“It is extremely concerning that journalists were assaulted and intimidated when reporting on protests in Hamburg. Journalists are there to do their job and it is important that they are able to tell the world what is happening at protests such as the ones in Hamburg.” – Joy Hyvarinen
Hungary / 20 verified reports in 2017
“There is an important change of tactics regarding censorship and defaming independent media in Hungary: instead of attacking the outlets critical to the government, the vast pro-government media started smearing individual journalists, trying to intimidate and discredit the few critical voices who are left in Hungary.” — Zoltan Sipos
Romania / 16 verified reports in 2017
“The national news agency AGERPRES might lose its independence after a draft law enabling the political majority to dismiss the director-general was passed by the chamber of deputies in Romania. If passed in the senate as well, such a provision would have the same impact as on the management of the Romanian Radio Broadcasting Corporation (SRR) and the Romanian National Television Corporation (SRTV): following each election, the SRR and SRTV administration boards can be dismissed before the end of their mandates to reflect the new political forces.” — Zoltan Sipos
United Kingdom / 17 verified reports in 2017
“In the United Kingdom, after the Grenfell tower fire, which claimed 71 deaths, Kensington and Chelsea council tried to ban journalists from attending their first council meeting. Five media organisations had to challenge this legally to gain access. This was a very important case illustrating how difficult it was to gain access and to expect accountability from the organisation which ran the council block.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Sweden / 15 verified reports in 2017
“The systematic campaign to smear and misrepresent journalists by Granskning Sverige was symptomatic of a wider attack on the legitimacy of liberal and left media by Sweden’s far-right movement, but the campaign detailed by the reporters at the Eskilstuna-kuriren newspaper was orchestrated and unlike anything seen before in the country.” — Dominic Hinde
Greece / 13 verified reports in 2017
“In February 2017, two journalists were harassed by far-right wing protesters, preventing refugee children from attending classes. This is very important, because it shows that although Greece’s economic and refugee crisis seem to have calmed down in the last year, the support for far-right wing organisations doesn’t show any sign of shrinking. This also concerns journalists in Greece, whose safety is in danger every day.” — Christina Vasilaki
The Netherlands / 12 verified reports in 2017
“The Netherlands is considered to be one of the countries where media freedom is widely protected. However, cases like the rape threats levelled at a journalist in May show that media workers are subjected to all sorts of threats. In this case it were rape threats by a popular right-wing weblog. This creates an atmosphere in which it’s conceived normal to use comments and social media to discredit and threaten a journalist. It also highlights the dangers and risks that female journalists face.” — Mitra Nazar
Bulgaria / 11 verified reports in 2017
“In November, it became known that members of an organised crime group from Vratsa planned to murder Zov News website publisher Georgi Ezekiev. The increase of violent incidents and serious threats towards journalists in 2017 is alarming in Bulgaria, a country that already has the worst press freedom status in the European Union.” — Zoltan Sipos
Serbia / 11 verified reports in 2017
“Serbia’s free media had a dark year with many incidents, threats and violence coming towards them. In May, journalists were assaulted during clashes at the presidential inauguration. This is just one of many cases, but it clearly demonstrates just how critical the state of the media is because they happened during the presidential inauguration. The assaults were committed by supporters of the government with a lot of police around. The impunity these assaulters meet is worrying for the lack of condemnation by authorities and the message they clearly want to send to critical journalists.” — Mitra Nazar
Malta / 8 verified reports in 2017
“The most worrying incident regards the murder of anti-corruption, investigative journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia. While this murder gripped the attention of international media and European authorities including the European Commission and Parliament, it is still shocking for every journalist that in a democratic, EU country, journalists’ lives could be in danger because they are doing their job, exposing high-level corruption in political, business and criminal elites.” — Christina Vasilaki
Kosovo / 6 verified reports in 2017|
“Kosovo’s media have been shaken up by two attacks on Insajderi investigative journalists. Insajderi is home to the best investigative journalists in the country, covering corruption and crime topics that nobody else dares to touch. Journalist Parim Olluri was beaten up outside his home in Pristina on 16 August. He needed medical assistance in a hospital. Nobody has been held responsible for the attack. Two months later, his colleague Vehbi Kajtazi was hit on the head in a cafe in downtown Pristina on 13 October. One person was arrested on the spot. We are talking about two violent incidents to Insajderi journalists within a period of three months. This shows that Kosovo’s journalists continue to face violence, even in very public places like cafe’s and neighbourhoods they live. For this reason there are just a few brave journalists who dare to touch sensitive topics, which is a worrying sign for the future of journalism and truth finding in the youngest country in Europe.” — Mitra Nazar
Montenegro / 6 verified reports in 2017
“Attack on journalist’s property is one of most common ways of intimidation. This is not only case for Montenegro, but also for all other countries in the region. What is striking is that intentional setting on fire of journalist’s vehicles is one of most common ways of limitation of media freedom in Montenegro. In recent years there have been several burnt vehicle in this small EU candidate country.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Portugal / 5 verified reports in 2017
“Similarly to what’s happening in other countries, Portugal has seen a rise of questioning towards journalism, those who work in the media industry and their work. Besides motivating a new and stimulating debate between journalists and their readers/viewers/listeners, this has also opened the gates to instances of abuse, cyberbullying and slander. The most significant example of that is that of Público’s journalist Margarida Gomes, whose work ethic was put in question by Facebook groups and public officials, who both used false information regarding her personal life to denigrate her work.” — João de Almeida Dias
Latvia / 3 verified reports in 2017
“In Latvia it was a quiet year for press freedom. However, the sudden and swift dismissal of Sigita Roķe, the head of public service Latvian Radio for alleged economic irregularities was seen as a pretext for dismissing her for efforts to disengage the radio from sponsorship agreements with the city of Ventspils, whose politically influential mayor has is on trial for money laundering and corruption. The dismissal raised questions about the political neutrality of Latvia’s media watchdog, the National Electronic Mass Media Council.” — Juris Kaza
Ireland / 3 verified reports in 2017
“Compared to the long list of countries in Europe where it is getting progressively dangerous for reporters to do their work, the situation in Ireland is relatively benign. There are renewed concerns over source protection, and the strict libel regime. However, the most serious concern is regarding media ownership. Index on Censorship published a detailed report on this in August 2017. One significant media takeover – Independent News and Media buying up Celtic Media – fell through after the Government ordered a statutory investigation following objections.” — Flor Mac Carthy
Estonia / 3 verified reports in 2017
“In March, journalists for Estonia’s largest daily in circulation Postimees, sent a letter to the owners and managers to complain about interference with editorial freedom. This event is a disturbing example of the interference attempts from media owners and advertisement department that had grown to the level that journalists of a daily, that prides itself with a long history and high-quality content, had to resort to an unprecedented united protest letter to fight it. Interference in journalistic decision making and content from outside or inside sources is in general the worrisome threat.” — Helle Tiikmaa
Belgium / 2 verified reports in 2017
“In Belgium, a journalist who had published a story on surveillance in Bruxelles’ metro was interrogated on her sources by the police, in clear breach of the principle of sources confidentiality. The case also reminds us of the risk for journalists covering surveillance.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Denmark / 2 verified reports in 2017
“The killing of Kim Wall by the inventor and entrepreneur Peter Madsen was a headline news event around the world. Stabbed to death and dumped at sea whilst interviewing Madsen on board his home-built submarine, her body was recovered after an extensive marine search. Although not typical of any wider trend, her murder was so brutal it raised significant questions about the safety and ethics of female freelancers working alone without support or safeguards.” — Dominic Hinde
Finland / 2 verified reports in 2017
“In March the Finnish government introduced restrictive changes to the functioning of the public broadcasting company Yle, which entailed putting the state-owned company more firmly under politicians’ decision-making power. The proposal was driven by the True Finns, a nationalist party that have repeatedly complained about Yle’s liberal views and non-sceptical approach to ‘multicultural Finland’. In the official briefing, stated the following: “The proposal is to strengthen the role of the Administrative Council so that they can decide on Yle’s journalistic strategy and regulate the permanent expert consultation process”. The council referred is mainly composed of politicians. — Katariina Salomäki
Iceland / 1 verified report in 2017
“Iceland has been rocked by political scandals and collapsing governments twice in the space of a year. In October it came to light that the prime minister had used financial confidentiality legislation to stop the investigative newspaper Stundin from publishing details of his offshore financial dealings in the run-up to the 2008 financial crash. Iceand’s main newspaper Morgunbladid is controlled by another former Prime Minister, also a member of the powerful Icelandic independence party, and Stundin has consistently sought to expose the Icelandic financial and political elite where other titles have remained silent.” — Dominic Hinde[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Mapping Media Freedom” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fmappingmediafreedom.org%2F%23%2F|||”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-times-circle” color=”black” background_style=”rounded” size=”xl” align=”right”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”3/4″][vc_column_text]
Since 24 May 2014, Mapping Media Freedom’s team of correspondents and partners have recorded and verified more than 3,700 violations against journalists and media outlets.
Index campaigns to protect journalists and media freedom. You can help us by submitting reports to Mapping Media Freedom.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Don’t lose your voice. Stay informed.” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship is a nonprofit that campaigns for and defends free expression worldwide. We publish work by censored writers and artists, promote debate, and monitor threats to free speech. We believe that everyone should be free to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution – no matter what their views.
Join our mailing list (or follow us on Twitter or Facebook) and we’ll send you our weekly newsletter about our activities defending free speech. We won’t share your personal information with anyone outside Index.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][gravityform id=”20″ title=”false” description=”false” ajax=”false”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row]












